Plumbism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lead poisoning, also known as plumbism and saturnism, is a type of metal poisoning caused by
 Lead poisoning can cause a variety of
Lead poisoning can cause a variety of
 A pregnant woman who has elevated blood lead levels is at greater risk of a premature birth or with a low birth weight. Children are more at risk for lead poisoning because their smaller bodies are in a continuous state of growth and development. Young children are much more vulnerable to lead poisoning, as they absorb 4 to 5 times more lead than an adult from a given source. Furthermore, children, especially as they are learning to crawl and walk, are constantly on the floor and therefore more prone to ingesting and inhaling dust that is contaminated with lead.
The classic signs and symptoms in children are loss of appetite, abdominal pain, vomiting, weight loss, constipation, anemia, kidney failure, irritability, lethargy, learning disabilities, and behavioral problems. Slow development of normal childhood behaviors, such as talking and use of words, and permanent
A pregnant woman who has elevated blood lead levels is at greater risk of a premature birth or with a low birth weight. Children are more at risk for lead poisoning because their smaller bodies are in a continuous state of growth and development. Young children are much more vulnerable to lead poisoning, as they absorb 4 to 5 times more lead than an adult from a given source. Furthermore, children, especially as they are learning to crawl and walk, are constantly on the floor and therefore more prone to ingesting and inhaling dust that is contaminated with lead.
The classic signs and symptoms in children are loss of appetite, abdominal pain, vomiting, weight loss, constipation, anemia, kidney failure, irritability, lethargy, learning disabilities, and behavioral problems. Slow development of normal childhood behaviors, such as talking and use of words, and permanent
 Lead affects the
Lead affects the
 In adults, occupational exposure is the main cause of lead poisoning. People can be exposed when working in facilities that produce a variety of lead-containing products; these include radiation shields, ammunition, certain surgical equipment, developing dental X-ray films prior to digital X-rays (each film packet had a lead liner to prevent the radiation from going through), fetal monitors, plumbing, circuit boards, jet engines, and ceramic glazes. In addition, lead miners and smelters, plumbers and fitters, auto mechanics, glass manufacturers, construction workers, battery manufacturers and recyclers,
In adults, occupational exposure is the main cause of lead poisoning. People can be exposed when working in facilities that produce a variety of lead-containing products; these include radiation shields, ammunition, certain surgical equipment, developing dental X-ray films prior to digital X-rays (each film packet had a lead liner to prevent the radiation from going through), fetal monitors, plumbing, circuit boards, jet engines, and ceramic glazes. In addition, lead miners and smelters, plumbers and fitters, auto mechanics, glass manufacturers, construction workers, battery manufacturers and recyclers,
 Residual lead in soil contributes to lead exposure in urban areas. It has been thought that the more polluted an area is with various contaminants, the more likely it is to contain lead. However, this is not always the case, as there are several other reasons for lead contamination in soil.
Lead content in soil may be caused by broken-down lead paint, residues from lead-containing gasoline, used engine oil, tire weights, or pesticides used in the past, contaminated landfills, or from nearby industries such as foundries or smelters. For example, in the
Residual lead in soil contributes to lead exposure in urban areas. It has been thought that the more polluted an area is with various contaminants, the more likely it is to contain lead. However, this is not always the case, as there are several other reasons for lead contamination in soil.
Lead content in soil may be caused by broken-down lead paint, residues from lead-containing gasoline, used engine oil, tire weights, or pesticides used in the past, contaminated landfills, or from nearby industries such as foundries or smelters. For example, in the 
 To virtually eliminate the potential for lead contamination, some researchers have suggested the use of lead-free copper non-fragmenting bullets.
To virtually eliminate the potential for lead contamination, some researchers have suggested the use of lead-free copper non-fragmenting bullets.
 Exposure occurs through
Exposure occurs through
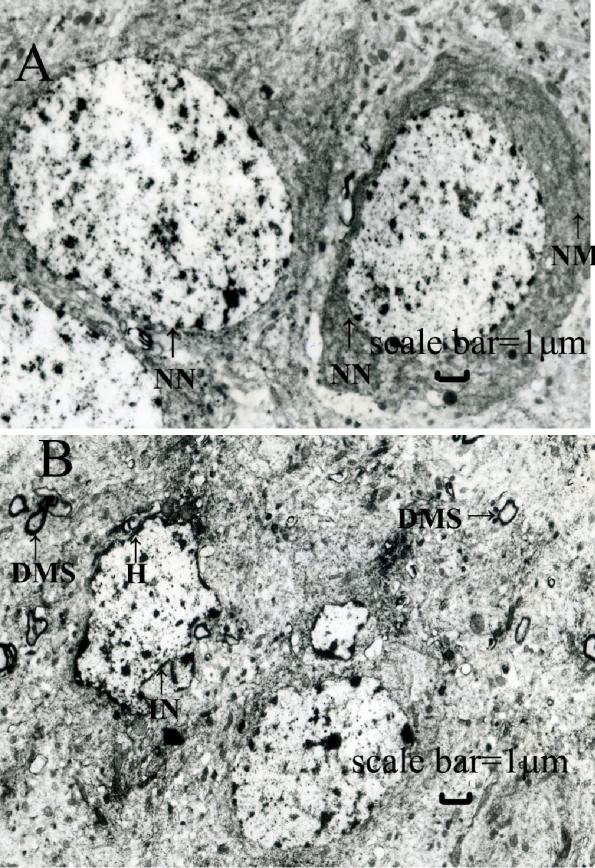 The brain is the organ most sensitive to lead exposure. Lead is able to pass through the endothelial cells at the
The brain is the organ most sensitive to lead exposure. Lead is able to pass through the endothelial cells at the
 Blood film examination may reveal basophilic stippling of red blood cells (dots in red blood cells visible through a microscope), as well as the changes normally associated with iron-deficiency anemia (microcytosis and hypochromic, hypochromasia). This may be known as sideroblastic anemia. However, basophilic stippling is also seen in unrelated conditions, such as megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 (colbalamin) and folate deficiencies.
Contrary to other sideroblastic anemia, there are no ring sideroblasts in a bone marrow smear.
Exposure to lead also can be evaluated by measuring zinc protoporphyrin, erythrocyte protoporphyrin (EP) in blood samples. EP is a part of red blood cells known to increase when the amount of lead in the blood is high, with a delay of a few weeks. Thus EP levels in conjunction with blood lead levels can suggest the time period of exposure; if blood lead levels are high but EP is still normal, this finding suggests exposure was recent. However, the EP level alone is not sensitive enough to identify elevated blood lead levels below about 35 μg/dL. Due to this higher threshold for detection and the fact that EP levels also increase in Iron deficiency (medicine), iron deficiency, use of this method for detecting lead exposure has decreased. Grant (2009) p. 784
Blood lead levels are an indicator mainly of recent or current lead exposure, not of total body burden. Lead in bones can be measured Invasiveness of surgical procedures, noninvasively by X-ray fluorescence; this may be the best measure of cumulative exposure and total body burden. However this method is not widely available and is mainly used for research rather than routine diagnosis. Another radiographic sign of elevated lead levels is the presence of radiodensity, radiodense lines called lead lines at the metaphysis in the long bones of growing children, especially around the knees. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 464 These lead lines, caused by increased calcification due to disrupted metabolism in the growing bones, become wider as the duration of lead exposure increases. X-rays may also reveal lead-containing foreign materials such as paint chips in the gastrointestinal tract.#CITEREFKatzung07, Kosnett (2007) p. 948
Fecal lead content that is measured over the course of a few days may also be an accurate way to estimate the overall amount of childhood lead intake. This form of measurement may serve as a useful way to see the extent of oral lead exposure from all the diet and environmental sources of lead.
Lead poisoning shares symptoms with other conditions and may be easily missed. Conditions that present similarly and must be ruled out in diagnosing lead poisoning include carpal tunnel syndrome, Guillain–Barré syndrome, renal colic, appendicitis, encephalitis in adults, and viral gastroenteritis in children. Other differential diagnosis, differential diagnoses in children include
Blood film examination may reveal basophilic stippling of red blood cells (dots in red blood cells visible through a microscope), as well as the changes normally associated with iron-deficiency anemia (microcytosis and hypochromic, hypochromasia). This may be known as sideroblastic anemia. However, basophilic stippling is also seen in unrelated conditions, such as megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 (colbalamin) and folate deficiencies.
Contrary to other sideroblastic anemia, there are no ring sideroblasts in a bone marrow smear.
Exposure to lead also can be evaluated by measuring zinc protoporphyrin, erythrocyte protoporphyrin (EP) in blood samples. EP is a part of red blood cells known to increase when the amount of lead in the blood is high, with a delay of a few weeks. Thus EP levels in conjunction with blood lead levels can suggest the time period of exposure; if blood lead levels are high but EP is still normal, this finding suggests exposure was recent. However, the EP level alone is not sensitive enough to identify elevated blood lead levels below about 35 μg/dL. Due to this higher threshold for detection and the fact that EP levels also increase in Iron deficiency (medicine), iron deficiency, use of this method for detecting lead exposure has decreased. Grant (2009) p. 784
Blood lead levels are an indicator mainly of recent or current lead exposure, not of total body burden. Lead in bones can be measured Invasiveness of surgical procedures, noninvasively by X-ray fluorescence; this may be the best measure of cumulative exposure and total body burden. However this method is not widely available and is mainly used for research rather than routine diagnosis. Another radiographic sign of elevated lead levels is the presence of radiodensity, radiodense lines called lead lines at the metaphysis in the long bones of growing children, especially around the knees. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 464 These lead lines, caused by increased calcification due to disrupted metabolism in the growing bones, become wider as the duration of lead exposure increases. X-rays may also reveal lead-containing foreign materials such as paint chips in the gastrointestinal tract.#CITEREFKatzung07, Kosnett (2007) p. 948
Fecal lead content that is measured over the course of a few days may also be an accurate way to estimate the overall amount of childhood lead intake. This form of measurement may serve as a useful way to see the extent of oral lead exposure from all the diet and environmental sources of lead.
Lead poisoning shares symptoms with other conditions and may be easily missed. Conditions that present similarly and must be ruled out in diagnosing lead poisoning include carpal tunnel syndrome, Guillain–Barré syndrome, renal colic, appendicitis, encephalitis in adults, and viral gastroenteritis in children. Other differential diagnosis, differential diagnoses in children include
 In most cases, lead poisoning is preventable by avoiding exposure to lead. Prevention strategies can be divided into individual (measures taken by a family), preventive medicine (identifying and intervening with high-risk individuals), and public health (reducing risk on a population level).
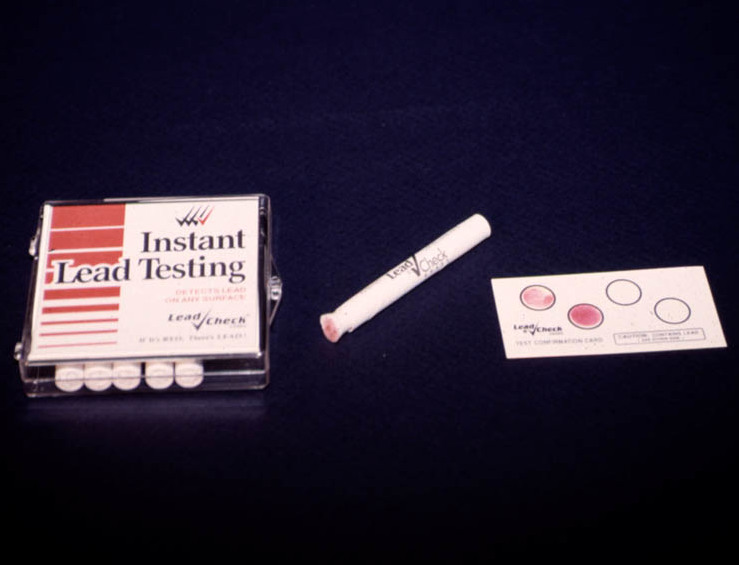
Recommended steps by individuals to reduce the blood lead levels of children include increasing their frequency of hand washing and their intake of calcium and iron, discouraging them from putting their hands to their mouths, vacuuming frequently, and eliminating the presence of lead-containing objects such as blinds and jewellery in the house. In houses with lead pipes or plumbing solder, these can be replaced. Less permanent but cheaper methods include running water in the morning to flush out the most contaminated water, or adjusting the water's chemistry to prevent corrosion of pipes. Lead testing kits are commercially available for detecting the presence of lead in the household. Salvato (2003) p.117 Testing kit accuracy depends on the user testing all layers of paint and the quality of the kit; the United States Environmental Protection Agency, US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) only approves kits with an accuracy rating of at least 95%. Professional lead testing companies caution that DIY test kits can create health risks for users that do not understand their limitations and liability issues for employers with regard to worker protection. As hot water is more likely than cold water to contain higher amounts of lead, use only cold water from the tap for drinking, cooking, and making baby formula. Since most of the lead in household water usually comes from plumbing in the house and not from the local water supply, using cold water can avoid lead exposure.National Environmental Public Health Tracking Network, 2010. Measures such as dust control and household education do not appear to be effective in changing children's blood levels.
Prevention measures also exist on national and municipal levels. Recommendations by health professionals for lowering childhood exposures include banning the use of lead where it is not essential and strengthening regulations that limit the amount of lead in soil, water, air, household dust, and products. Regulations exist to limit the amount of lead in paint; for example, a 1978 law in the US restricted the lead in paint for residences, furniture, and toys to 0.06% or less. In October 2008, the US EPA reduced the allowable lead level by a factor of ten to 0.15 micrograms per cubic meter of air, giving states five years to comply with the standards. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive limits amounts of lead and other toxic substances in electronics and electrical equipment. In some places, remediation programs exist to reduce the presence of lead when it is found to be high, for example in drinking water. As a more radical solution, entire towns located near former lead mines have been "closed" by the government, and the population resettled elsewhere, as was the case with Picher, Oklahoma, in 2009. Removing lead from airplane fuel would also be useful.
In most cases, lead poisoning is preventable by avoiding exposure to lead. Prevention strategies can be divided into individual (measures taken by a family), preventive medicine (identifying and intervening with high-risk individuals), and public health (reducing risk on a population level).
Recommended steps by individuals to reduce the blood lead levels of children include increasing their frequency of hand washing and their intake of calcium and iron, discouraging them from putting their hands to their mouths, vacuuming frequently, and eliminating the presence of lead-containing objects such as blinds and jewellery in the house. In houses with lead pipes or plumbing solder, these can be replaced. Less permanent but cheaper methods include running water in the morning to flush out the most contaminated water, or adjusting the water's chemistry to prevent corrosion of pipes. Lead testing kits are commercially available for detecting the presence of lead in the household. Salvato (2003) p.117 Testing kit accuracy depends on the user testing all layers of paint and the quality of the kit; the United States Environmental Protection Agency, US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) only approves kits with an accuracy rating of at least 95%. Professional lead testing companies caution that DIY test kits can create health risks for users that do not understand their limitations and liability issues for employers with regard to worker protection. As hot water is more likely than cold water to contain higher amounts of lead, use only cold water from the tap for drinking, cooking, and making baby formula. Since most of the lead in household water usually comes from plumbing in the house and not from the local water supply, using cold water can avoid lead exposure.National Environmental Public Health Tracking Network, 2010. Measures such as dust control and household education do not appear to be effective in changing children's blood levels.
Prevention measures also exist on national and municipal levels. Recommendations by health professionals for lowering childhood exposures include banning the use of lead where it is not essential and strengthening regulations that limit the amount of lead in soil, water, air, household dust, and products. Regulations exist to limit the amount of lead in paint; for example, a 1978 law in the US restricted the lead in paint for residences, furniture, and toys to 0.06% or less. In October 2008, the US EPA reduced the allowable lead level by a factor of ten to 0.15 micrograms per cubic meter of air, giving states five years to comply with the standards. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive limits amounts of lead and other toxic substances in electronics and electrical equipment. In some places, remediation programs exist to reduce the presence of lead when it is found to be high, for example in drinking water. As a more radical solution, entire towns located near former lead mines have been "closed" by the government, and the population resettled elsewhere, as was the case with Picher, Oklahoma, in 2009. Removing lead from airplane fuel would also be useful.
in ''Br Foreign Med Chir Rev.'' 1853 Jan; 11(21): 201–224. A chelating agent is a molecule with at least two negatively charged groups that allow it to form complexes with metal ions with multiple positive charges, such as lead. Trevor, Katzung, Masters (2007) p. 480 The chelate that is thus formed is nontoxic and can be excreted in the urine, initially at up to 50 times the normal rate. Kosnett (2005) p. 822 The chelating agents used for treatment of lead poisoning are edetate disodium calcium (Sodium calcium edetate, CaNa2EDTA), dimercaprol (BAL), which are injected, and Dimercaptosuccinic acid, succimer and d-penicillamine, which are administered orally. Menkes (2006) p.706
Chelation therapy is used in cases of acute lead poisoning, severe poisoning, and encephalopathy, and is considered for people with blood lead levels above 25 µg/dL. While the use of chelation for people with symptoms of lead poisoning is widely supported, use in asymptomatic people with high blood lead levels is more controversial. Chelation therapy is of limited value for cases of chronic exposure to low levels of lead. Chelation therapy is usually stopped when symptoms resolve or when blood lead levels return to premorbid levels. When lead exposure has taken place over a long period, blood lead levels may rise after chelation is stopped because lead is leached into blood from stores in the bone; thus repeated treatments are often necessary.
People receiving dimercaprol need to be assessed for peanut allergies since the commercial formulation contains peanut oil. Calcium EDTA is also effective if administered four hours after the administration of dimercaprol. Administering dimercaprol, DMSA (Succimer), or 2,3-Dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid, DMPS prior to calcium EDTA is necessary to prevent the redistribution of lead into the central nervous system. Dimercaprol used alone may also redistribute lead to the brain and testes. An adverse side effect of calcium EDTA is renal toxicity. Succimer (DMSA) is the preferred agent in mild to moderate lead poisoning cases. This may be the case in instances where children have a blood lead level >25μg/dL. The most reported adverse side effect for succimer is gastrointestinal disturbances. It is also important to note that chelation therapy only lowers blood lead levels and may not prevent the lead-induced cognitive problems associated with lower lead levels in tissue. This may be because of the inability of these agents to remove sufficient amounts of lead from tissue or inability to reverse preexisting damage.
Chelating agents can have adverse medical effect, adverse effects; for example, chelation therapy can lower the body's levels of necessary nutrients like zinc. Chelating agents taken orally can increase the body's absorption of lead through the intestine.
Chelation challenge, also known as provocation testing, is used to indicate an elevated and mobilizable body burden of heavy metals including lead. This testing involves collecting urine before and after administering a one-off dose of chelating agent to mobilize heavy metals into the urine. Then urine is analyzed by a laboratory for levels of heavy metals; from this analysis overall body burden is inferred. Chelation challenge mainly measures the burden of lead in soft tissues, though whether it accurately reflects long-term exposure or the amount of lead stored in bone remains controversial. Although the technique has been used to determine whether chelation therapy is indicated and to diagnose heavy metal exposure, some evidence does not support these uses as blood levels after chelation are not comparable to the reference range typically used to diagnose heavy metal poisoning. The single chelation dose could also redistribute the heavy metals to more sensitive areas such as central nervous system tissue.
A chelating agent is a molecule with at least two negatively charged groups that allow it to form complexes with metal ions with multiple positive charges, such as lead. Trevor, Katzung, Masters (2007) p. 480 The chelate that is thus formed is nontoxic and can be excreted in the urine, initially at up to 50 times the normal rate. Kosnett (2005) p. 822 The chelating agents used for treatment of lead poisoning are edetate disodium calcium (Sodium calcium edetate, CaNa2EDTA), dimercaprol (BAL), which are injected, and Dimercaptosuccinic acid, succimer and d-penicillamine, which are administered orally. Menkes (2006) p.706
Chelation therapy is used in cases of acute lead poisoning, severe poisoning, and encephalopathy, and is considered for people with blood lead levels above 25 µg/dL. While the use of chelation for people with symptoms of lead poisoning is widely supported, use in asymptomatic people with high blood lead levels is more controversial. Chelation therapy is of limited value for cases of chronic exposure to low levels of lead. Chelation therapy is usually stopped when symptoms resolve or when blood lead levels return to premorbid levels. When lead exposure has taken place over a long period, blood lead levels may rise after chelation is stopped because lead is leached into blood from stores in the bone; thus repeated treatments are often necessary.
People receiving dimercaprol need to be assessed for peanut allergies since the commercial formulation contains peanut oil. Calcium EDTA is also effective if administered four hours after the administration of dimercaprol. Administering dimercaprol, DMSA (Succimer), or 2,3-Dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid, DMPS prior to calcium EDTA is necessary to prevent the redistribution of lead into the central nervous system. Dimercaprol used alone may also redistribute lead to the brain and testes. An adverse side effect of calcium EDTA is renal toxicity. Succimer (DMSA) is the preferred agent in mild to moderate lead poisoning cases. This may be the case in instances where children have a blood lead level >25μg/dL. The most reported adverse side effect for succimer is gastrointestinal disturbances. It is also important to note that chelation therapy only lowers blood lead levels and may not prevent the lead-induced cognitive problems associated with lower lead levels in tissue. This may be because of the inability of these agents to remove sufficient amounts of lead from tissue or inability to reverse preexisting damage.
Chelating agents can have adverse medical effect, adverse effects; for example, chelation therapy can lower the body's levels of necessary nutrients like zinc. Chelating agents taken orally can increase the body's absorption of lead through the intestine.
Chelation challenge, also known as provocation testing, is used to indicate an elevated and mobilizable body burden of heavy metals including lead. This testing involves collecting urine before and after administering a one-off dose of chelating agent to mobilize heavy metals into the urine. Then urine is analyzed by a laboratory for levels of heavy metals; from this analysis overall body burden is inferred. Chelation challenge mainly measures the burden of lead in soft tissues, though whether it accurately reflects long-term exposure or the amount of lead stored in bone remains controversial. Although the technique has been used to determine whether chelation therapy is indicated and to diagnose heavy metal exposure, some evidence does not support these uses as blood levels after chelation are not comparable to the reference range typically used to diagnose heavy metal poisoning. The single chelation dose could also redistribute the heavy metals to more sensitive areas such as central nervous system tissue.
 Lead poisoning was among the first known and most widely studied work regarding environmental hazards. One of the first metals to be smelting, smelted and used, lead is thought to have been discovered and first mining, mined in Anatolia around 6500 BC. Its density, workability, and corrosion resistance were among the metal's attractions.
In the 2nd century BC the Greek botanist Nicander described the
Lead poisoning was among the first known and most widely studied work regarding environmental hazards. One of the first metals to be smelting, smelted and used, lead is thought to have been discovered and first mining, mined in Anatolia around 6500 BC. Its density, workability, and corrosion resistance were among the metal's attractions.
In the 2nd century BC the Greek botanist Nicander described the
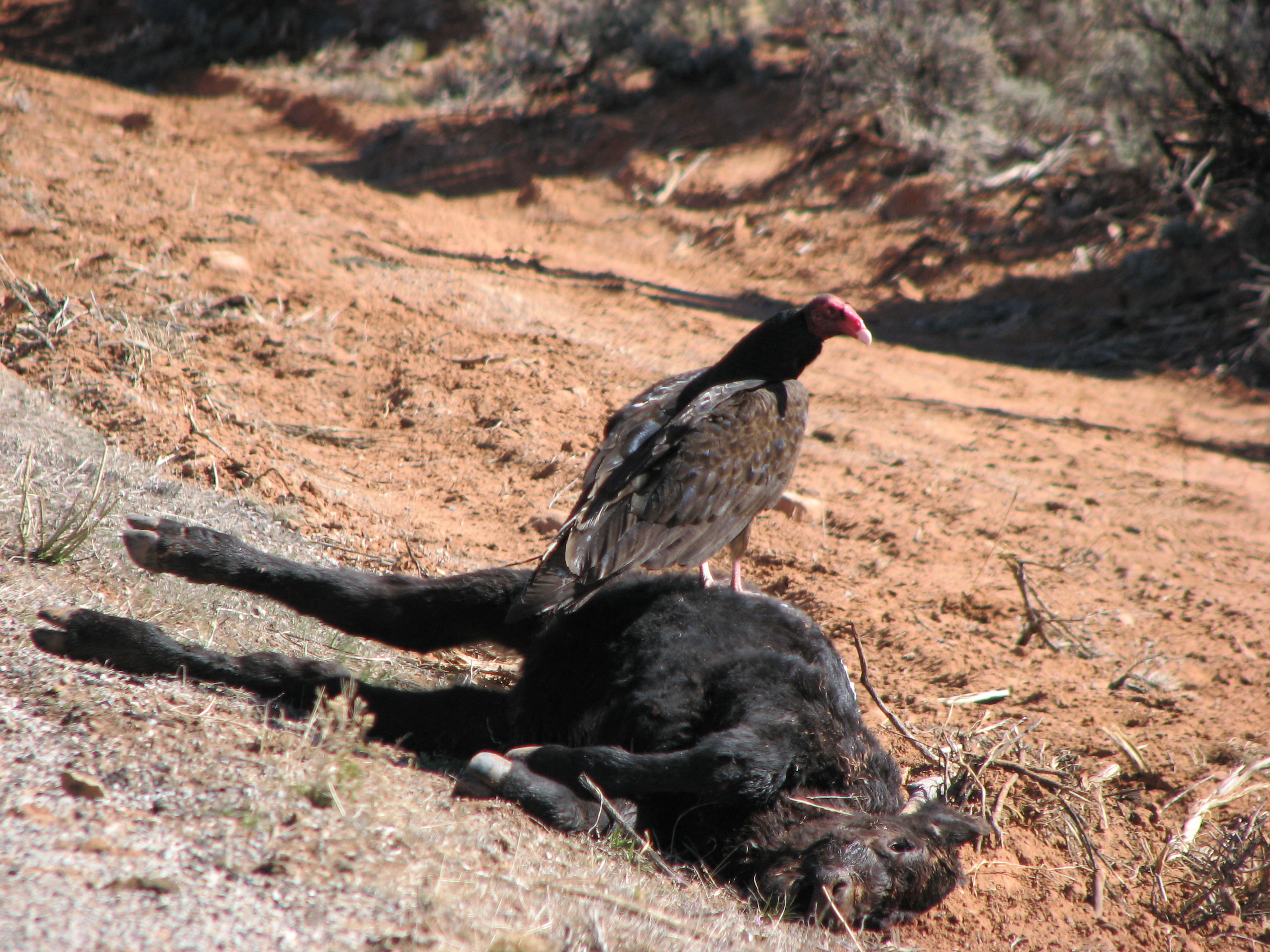 Lead, one of the leading causes of toxicity in waterfowl, has been known to cause die-offs of wild bird populations. When hunters use lead shot, waterfowl such as ducks can ingest the spent pellets later and be poisoned; predators that eat these birds are also at risk. Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s. By 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting was positively identified as the source of waterfowl deaths.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Lead shot has been banned for hunting waterfowl in several countries, including the US in 1991 and Canada in 1997. Other threats to wildlife include lead paint, sediment from lead mines and smelters, and lead weights from fishing lines. Lead in some fishing gear has been banned in several countries.
The Critically endangered species, critically endangered California condor has also been affected by lead poisoning. As scavengers, condors eat carcasses of game that have been shot but not retrieved, and with them the fragments from lead bullets; this increases their lead levels. Among condors around the Grand Canyon, lead poisoning due to eating lead shot is the most frequently diagnosed cause of death. In an effort to protect this species, in areas designated as the California condor's range the use of projectiles containing lead has been banned to hunt deer, feral pigs, elk, pronghorn antelope, coyotes, ground squirrels, and other non-game wildlife. Also, conservation programs exist which routinely capture condors, check their blood lead levels, and treat cases of poisoning.
Lead, one of the leading causes of toxicity in waterfowl, has been known to cause die-offs of wild bird populations. When hunters use lead shot, waterfowl such as ducks can ingest the spent pellets later and be poisoned; predators that eat these birds are also at risk. Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s. By 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting was positively identified as the source of waterfowl deaths.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Lead shot has been banned for hunting waterfowl in several countries, including the US in 1991 and Canada in 1997. Other threats to wildlife include lead paint, sediment from lead mines and smelters, and lead weights from fishing lines. Lead in some fishing gear has been banned in several countries.
The Critically endangered species, critically endangered California condor has also been affected by lead poisoning. As scavengers, condors eat carcasses of game that have been shot but not retrieved, and with them the fragments from lead bullets; this increases their lead levels. Among condors around the Grand Canyon, lead poisoning due to eating lead shot is the most frequently diagnosed cause of death. In an effort to protect this species, in areas designated as the California condor's range the use of projectiles containing lead has been banned to hunt deer, feral pigs, elk, pronghorn antelope, coyotes, ground squirrels, and other non-game wildlife. Also, conservation programs exist which routinely capture condors, check their blood lead levels, and treat cases of poisoning.
lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
in the body. The brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
, headaches, irritability, memory problems, infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st ...
, and tingling in the hands and feet. It causes almost 10% of intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
of otherwise unknown cause and can result in behavioral problems. Some of the effects are permanent. In severe cases, anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
, seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with los ...
, coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
, or death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
may occur.
Exposure to lead can occur by contaminated air, water, dust, food, or consumer products. Lead poisoning poses a significantly increased risk to children as they are far more likely to ingest lead indirectly by chewing on toys or other objects that are coated in lead paint
Lead paint or lead-based paint is paint containing lead. As pigment, lead(II) chromate (, "chrome yellow"), lead(II,IV) oxide, (, "red lead"), and lead(II) carbonate (, "white lead") are the most common forms.. Lead is added to paint to acce ...
. The amount of lead that can be absorbed by children is also higher than that of adults. Exposure at work is a common cause of lead poisoning in adults with certain occupations at particular risk. Diagnosis is typically by measurement of the blood lead level. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
(US) has set the upper limit for blood lead for adults at 10 µg/dl (10 µg/100 g) and for children at 3.5 µg/dl, previously before October 2021 5 µg/dl Elevated lead may also be detected by changes in red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s or dense lines in the bones of children as seen on X-ray
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ' ...
.
Lead poisoning is preventable. This includes individual efforts such as removing lead-containing items from the home, workplace efforts such as improved ventilation and monitoring, state and national policies that ban lead in products such as paint, gasoline, ammunition, wheel weights, and fishing weights, reduce allowable levels in water or soil, and provide for cleanup of contaminated soil. Workers' education could be helpful as well. The major treatments are removal of the source of lead and the use of medications that bind lead so it can be eliminated from the body, known as chelation therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the body. Chelation therapy has a long history of use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific medi ...
. Chelation therapy in children is recommended when blood levels are greater than 40–45 µg/dl. Medications used include dimercaprol, edetate calcium disodium, and succimer.
In 2016, lead is believed to have resulted in 540,000 deaths worldwide. It occurs most commonly in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agree ...
. There also are numerous cases in the developed world, with there being thousands of American communities with higher lead burdens than seen during the peak of the Flint water crisis. Those who are poor are at greater risk. Lead is believed to result in 0.6% of the world's disease burden
Disease burden is the impact of a health problem as measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Both ...
. According to a study, half of the US population has been exposed to substantially detrimental lead levels in early childhood – mainly from car exhaust whose lead pollution peaked in the 1970s and caused widespread loss in cognitive ability.
People have been mining and using lead for thousands of years. Descriptions of lead poisoning date to at least 2000 BC, while efforts to limit lead's use date back to at least the 16th century. Concerns for low levels of exposure began in the 1970s with there being no safe threshold for lead exposure.
Classification
Classically, "lead poisoning" or "lead intoxication" has been defined as exposure to high levels of lead typically associated with severe health effects. Grant (2009) p. 785 Poisoning is a pattern of symptoms that occur with toxic effects from mid to high levels of exposure; toxicity is a wider spectrum of effects, includingsubclinical
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
ones (those that do not cause symptoms). However, professionals often use "lead poisoning" and "lead toxicity" interchangeably, and official sources do not always restrict the use of "lead poisoning" to refer only to symptomatic effects of lead.
The amount of lead in the blood and tissues, as well as the time course of exposure, determine toxicity.
Lead poisoning may be acute (from intense exposure of short duration) or chronic (from repeat low-level exposure over a prolonged period), but the latter is much more common. Trevor, Katzung, Masters (2007) p. 479
Diagnosis and treatment of lead exposure are based on blood lead level (the amount of lead in the blood), measured in microgram
In the metric system, a microgram or microgramme is a unit of mass equal to one millionth () of a gram. The unit symbol is μg according to the International System of Units (SI); the recommended symbol in the United States and United Kingdom wh ...
s of lead per deciliter of blood (μg/dL). Urine lead levels may be used as well, though less commonly. In cases of chronic exposure, lead often sequesters in the highest concentrations first in the bones, then in the kidneys. If a provider is performing a provocative excretion test, or "chelation challenge", a measurement obtained from urine rather than blood is likely to provide a more accurate representation of total lead burden to a skilled interpreter.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
and the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
state that a blood lead level of 10 μg/dL or above is a cause for concern; however, lead may impair development and have harmful health effects even at lower levels, and there is no known safe exposure level. Authorities such as the American Academy of Pediatrics define lead poisoning as blood lead levels higher than 10 μg/dL.
Lead forms a variety of compounds and exists in the environment in various forms. Grant (2009) p. 761 Features of poisoning differ depending on whether the agent is an organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon- hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
(one that contains carbon), or an inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemis ...
one. Organic lead poisoning is now very rare, because countries across the world have phased out the use of organic lead compounds as gasoline additives, but such compounds are still used in industrial settings. Organic lead compounds, which cross the skin and respiratory tract easily, affect the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
predominantly.
Signs and symptoms
 Lead poisoning can cause a variety of
Lead poisoning can cause a variety of symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s and signs
Signs may refer to:
* ''Signs'' (2002 film), a 2002 film by M. Night Shyamalan
* ''Signs'' (TV series) (Polish: ''Znaki'') is a 2018 Polish-language television series
* ''Signs'' (journal), a journal of women's studies
*Signs (band), an American ...
which vary depending on the individual and the duration of lead exposure. Symptoms are nonspecific and may be subtle, and someone with elevated lead levels may have no symptoms. Symptoms usually develop over weeks to months as lead builds up in the body during a chronic exposure, but acute symptoms from brief, intense exposures also occur.
Symptoms from exposure to organic lead, which is probably more toxic than inorganic lead due to its lipid solubility, occur rapidly. Poisoning by organic lead compounds has symptoms predominantly in the central nervous system, such as insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy ...
, delirium
Delirium (also known as acute confusional state) is an organically caused decline from a previous baseline of mental function that develops over a short period of time, typically hours to days. Delirium is a syndrome encompassing disturbances ...
, cognitive deficit
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for ab ...
s, tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic, muscle contraction and relaxation involving oscillations or twitching movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the hands, arms, eyes, f ...
, hallucinations, and convulsions.
Symptoms may be different in adults and children; the main symptoms in adults are headache, abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, memory loss
Amnesia is a deficit in memory caused by brain damage or disease,Gazzaniga, M., Ivry, R., & Mangun, G. (2009) Cognitive Neuroscience: The biology of the mind. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. but it can also be caused temporarily by the use o ...
, kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
, male reproductive problems, and weakness, pain, or tingling in the extremities.
Early symptoms of lead poisoning in adults are commonly nonspecific and include depression, loss of appetite, intermittent abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and muscle pain
Myalgia (also called muscle pain and muscle ache in layman's terms) is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another li ...
. Other early signs in adults include malaise
As a medical term, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. The word has existed in French since at least the 12th century.
The term is often used ...
, fatigue, decreased libido
Libido (; colloquial: sex drive) is a person's overall sexual drive or desire for sexual activity. Libido is influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors. Biologically, the sex hormones and associated neurotransmitters that act ...
, and problems with sleep. An unusual taste in the mouth and personality changes are also early signs.
In adults, symptoms can occur at levels above 40 μg/dL, but are more likely to occur only above 50–60 μg/dL. Symptoms begin to appear in children generally at around 60 μg/dL. However, the lead levels at which symptoms appear vary widely depending on unknown characteristics of each individual. At blood lead levels between 25 and 60 μg/dL, neuropsychiatric effects such as delayed reaction time
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; sometimes referred to as "response time") is meas ...
s, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, as well as slowed motor nerve
A motor nerve is a nerve that transmits motor signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles of the body. This is different from the motor neuron, which includes a cell body and branching of dendrites, while the nerve is made up of ...
conduction and headache can occur. Kosnett (2006) p.240 Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
may appear at blood lead levels higher than 50 μg/dL. In adults, abdominal colic
Colic or cholic () is a form of pain that starts and stops abruptly. It occurs due to muscular contractions of a hollow tube (small and large intestine, gall bladder, ureter, etc.) in an attempt to relieve an obstruction by forcing content out. ...
, involving paroxysms of pain, may appear at blood lead levels greater than 80 μg/dL. Kosnett (2005) p. 825 Signs that occur in adults at blood lead levels exceeding 100 μg/dL include wrist drop and foot drop
Foot drop is a gait abnormality in which the dropping of the forefoot happens due to weakness, irritation or damage to the deep fibular nerve (deep peroneal), including the sciatic nerve, or paralysis of the muscles in the anterior portion of ...
, and signs of encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but ...
(a condition characterized by brain swelling
Cerebral edema is excess accumulation of fluid (edema) in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain. This typically causes impaired nerve function, increased pressure within the skull, and can eventually lead to direct compressio ...
), such as those that accompany increased pressure within the skull, delirium, coma, seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with los ...
, and headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a resul ...
. Henretig (2006) p. 1314 In children, signs of encephalopathy such as bizarre behavior, discoordination, and apathy occur at lead levels exceeding 70 μg/dL. For both adults and children, it is rare to be asymptomatic if blood lead levels exceed 100 μg/dL.
Acute poisoning
In acute poisoning, typical neurological signs are pain, muscle weakness,numbness and tingling
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
, and, rarely, symptoms associated with inflammation of the brain. Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are other acute symptoms. Lead's effects on the mouth include astringency
An astringent (sometimes called adstringent) is a chemical that shrinks or constricts body tissues. The word derives from the Latin ''adstringere'', which means "to bind fast". Calamine lotion, witch hazel, and yerba mansa, a Californian pl ...
and a metallic taste. Gastrointestinal problems, such as constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin ...
, poor appetite, or weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other con ...
, are common in acute poisoning. Absorption of large amounts of lead over a short time can cause shock (insufficient fluid in the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
) due to loss of water from the gastrointestinal tract. Hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo o ...
(the rupture of red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
) due to acute poisoning can cause anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
and hemoglobin in the urine. Damage to kidneys can cause changes in urination such as acquired fanconi syndrome and decreased urine output. People who survive acute poisoning often go on to display symptoms of chronic poisoning.
Chronic poisoning
Chronic poisoning usually presents with symptoms affecting multiple systems, but is associated with three main types of symptoms:gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
, neuromuscular, and neurological. Central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
and neuromuscular symptoms usually result from intense exposure, while gastrointestinal symptoms usually result from exposure over longer periods. Signs of chronic exposure include loss of short-term memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recit ...
or concentration, depression, nausea, abdominal pain, loss of coordination, and numbness and tingling in the extremities. Fatigue, problems with sleep, headaches, stupor, slurred speech, and anemia are also found in chronic lead poisoning. A "lead hue" of the skin with pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes on ...
and/or lividity
Livor mortis (Latin: ''līvor'' – "bluish color, bruise", ''mortis'' – "of death"), postmortem lividity (Latin: ''postmortem'' – "after death", ''lividity'' – "black and blue"), hypostasis (Greek: ὑπό, ''hypo'', meaning "under, bene ...
is another feature. A blue line along the gum with bluish black edging to the teeth, known as a Burton line, is another indication of chronic lead poisoning. Rambousek (2008) p.177 Children with chronic poisoning may refuse to play or may have hyperkinetic or aggressive behavior disorders. Visual disturbance may present with gradually progressing blurred vision as a result of central scotoma
A scotoma is an area of partial alteration in the field of vision consisting of a partially diminished or entirely degenerated visual acuity that is surrounded by a field of normal – or relatively well-preserved – vision.
Every normal ma ...
, caused by toxic optic neuritis
Optic neuritis describes any condition that causes inflammation of the optic nerve; it may be associated with demyelinating diseases, or infectious or inflammatory processes.
It is also known as optic papillitis (when the head of the optic nerv ...
.
Effects on children
intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
are both commonly seen. Although less common, it is possible for fingernails to develop leukonychia striata if exposed to abnormally high lead concentrations.
On July 30, 2020, a report by UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid t ...
and Pure Earth revealed that lead poisoning is affecting children on a "massive and previously unknown scale". According to the report, one in three children, up to 800 million globally, have blood lead levels at, or above, 5 micrograms per decilitre (µg/dL), the amount at which action is required.
By organ system
Lead affects every one of the body's organ systems, especially the nervous system, but also the bones and teeth, the kidneys, and thecardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
, and reproductive system
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are al ...
s. Hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken la ...
and tooth decay
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
have been linked to lead exposure, as have cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
. Intrauterine and neonatal lead exposure promote tooth decay. Aside from the developmental effects unique to young children, the health effects experienced by adults are similar to those in children, although the thresholds are generally higher.
Kidneys
Kidney damage occurs with exposure to high levels of lead, and evidence suggests that lower levels can damage kidneys as well. Grant (2009) p. 789 The toxic effect of lead causesnephropathy
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can b ...
and may cause Fanconi syndrome, in which the proximal tubular
The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. It can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal straig ...
function of the kidney is impaired. Rubin, Strayer (2008) p. 267 Long-term exposure at levels lower than those that cause lead nephropathy have also been reported as nephrotoxic Nephrotoxicity is toxicity in the kidneys. It is a poisonous effect of some substances, both toxic chemicals and medications, on kidney function. There are various forms, and some drugs may affect kidney function in more than one way. Nephrotoxin ...
in patients from developed countries that had chronic kidney disease or were at risk because of hypertension or diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
.
Lead poisoning inhibits excretion of the waste product urate
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown ...
and causes a predisposition for gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intens ...
, in which urate builds up. This condition is known as ''saturnine gout''.
Cardiovascular system
Evidence suggests lead exposure is associated withhigh blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
, and studies have also found connections between lead exposure and coronary heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
, heart rate variability
Heart rate variability (HRV) is the physiological phenomenon of variation in the time interval between heartbeats. It is measured by the variation in the beat-to-beat interval.
Other terms used include: "cycle length variability", "R–R variabi ...
, and death from stroke, but this evidence is more limited. People who have been exposed to higher concentrations of lead may be at a higher risk for cardiac autonomic dysfunction
Dysautonomia or autonomic dysfunction is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not work properly. This may affect the functioning of the heart, bladder, intestines, sweat glands, pupils, and blood vessels. Dysautonomia ha ...
on days when ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
and fine particles are higher.
Reproductive system
Lead affects both the male and female reproductive systems. In men, when blood lead levels exceed 40 μg/dL, sperm count is reduced and changes occur in volume of sperm, theirmotility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
, and their morphology. Grant (2009) p. 792
A pregnant woman's elevated blood lead level can lead to miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical ...
, prematurity, low birth weight
Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at its birth. The average birth weight in babies of European descent is , with the normative range between . On average, babies of South Asian and Chinese descent weigh about . As far as low birth weig ...
, and problems with development during childhood. Lead is able to pass through the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ (anatomy), organ that begins embryonic development, developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation (embryology), implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrien ...
and into breast milk, and blood lead levels in mothers and infants are usually similar. A fetus may be poisoned ''in utero'' if lead from the mother's bones is subsequently mobilized by the changes in metabolism due to pregnancy; increased calcium intake in pregnancy may help mitigate this phenomenon.
Nervous system
 Lead affects the
Lead affects the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain a ...
(especially motor nerve
A motor nerve is a nerve that transmits motor signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles of the body. This is different from the motor neuron, which includes a cell body and branching of dendrites, while the nerve is made up of ...
s) and the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
. Peripheral nervous system effects are more prominent in adults and central nervous system effects are more prominent in children. Lead causes the axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action ...
s of nerve cells to degenerate and lose their myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be l ...
coats.
Lead exposure in young children has been linked to learning disabilities
Learning disability, learning disorder, or learning difficulty (British English) is a condition in the brain that causes difficulties comprehending or processing information and can be caused by several different factors. Given the "difficult ...
, and children with blood lead concentrations greater than 10 μg/dL are in danger of developmental disabilities
Developmental disability is a diverse group of chronic conditions, comprising mental or physical impairments that arise before adulthood. Developmental disabilities cause individuals living with them many difficulties in certain areas of life, espe ...
. Increased blood lead level in children has been correlated with decreases in intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ...
, nonverbal reasoning, short-term memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recit ...
, attention, reading and arithmetic ability, fine motor skills, emotional regulation, and social engagement
Social engagement (also social involvement, social participation) refers to one's degree of participation in a community or society.
Definitions
Prohaska, Anderson and Binstock (2012) noted that the term social engagement is commonly used to r ...
.
The effect of lead on children's cognitive abilities takes place at very low levels. There is apparently no lower threshold to the dose-response relationship (unlike other heavy metals such as mercury). Reduced academic performance has been associated with lead exposure even at blood lead levels lower than 5 μg/dL. Casarett, Klaassen, Doull (2007) p. 944 Blood lead levels below 10 μg/dL have been reported to be associated with lower IQ and behavior problems such as aggression, in proportion with blood lead levels. Between the blood lead levels of 5 and 35 μg/dL, an IQ decrease of 2–4 points for each μg/dL increase is reported in children. However, studies that show associations between low-level lead exposure and health effects in children may be affected by confounding
In statistics, a confounder (also confounding variable, confounding factor, extraneous determinant or lurking variable) is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Con ...
and overestimate the effects of low-level lead exposure.
High blood lead levels in adults are also associated with decreases in cognitive performance and with psychiatric symptoms such as depression and anxiety. It was found in a large group of current and former inorganic lead workers in Korea that blood lead levels in the range of 20–50 μg/dL were correlated with neuro-cognitive defects. Increases in blood lead levels from about 50 to about 100 μg/dL in adults have been found to be associated with persistent, and possibly permanent, impairment of central nervous system function.
Lead exposure in children is also correlated with neuropsychiatric disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inap ...
and anti-social behaviour
Antisocial behavior is a behavior that is defined as the violation of the rights of others by committing crime, such as stealing and physical attack in addition to other behaviors such as lying and manipulation. It is considered to be disrupti ...
. Elevated lead levels in children are correlated with higher scores on aggression and delinquency measures. A correlation has also been found between prenatal and early childhood lead exposure and violent crime in adulthood. Countries with the highest air lead levels have also been found to have the highest murder rates, after adjusting for confounding factors. A May 2000 study by economic consultant Rick Nevin theorizes that lead exposure explains 65% to 90% of the variation in violent crime rates in the US. A 2007 paper by the same author claims to show a strong association between preschool blood lead and subsequent crime rate trends over several decades across nine countries. Lead exposure in childhood appears to increase school suspensions and juvenile detention among boys. It is believed that the U.S. ban on lead paint in buildings in the late 1970s, as well as the phaseout of leaded gasoline in the 1970s and 1980s, partially helped contribute to the decline of violent crime in the United States since the early 1990s.
Exposure routes
Lead is a common environmental pollutant. Causes of environmental contamination include industrial use of lead, such as found in facilities that process lead-acid batteries or produce lead wire or pipes, and metal recycling and foundries. Storage batteries and ammunition are made with the largest amounts of lead consumed in the economy each year, in the US as of 2013. Children living near facilities that process lead, such as lead smelters, have been found to have unusually high blood lead levels. In August 2009, parents rioted in China after lead poisoning was found in nearly 2000 children living near zinc and manganese smelters. Lead exposure can occur from contact with lead in air, household dust, soil, water, and commercial products.Leaded gasoline
Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula Pb( C2H5)4. It is a fuel additive, first being mixed with gasoline beginning in the 1920s as a patented octane rating booster that ...
has also been linked to increases in lead pollution. Some research has suggested a link between leaded gasoline and crime rates. Man made lead pollution has been elevated in the air for the past 2000 years. Lead pollution in the air is entirely due to human activity (mining and smelting, as well as in gasoline).
Occupational exposure
 In adults, occupational exposure is the main cause of lead poisoning. People can be exposed when working in facilities that produce a variety of lead-containing products; these include radiation shields, ammunition, certain surgical equipment, developing dental X-ray films prior to digital X-rays (each film packet had a lead liner to prevent the radiation from going through), fetal monitors, plumbing, circuit boards, jet engines, and ceramic glazes. In addition, lead miners and smelters, plumbers and fitters, auto mechanics, glass manufacturers, construction workers, battery manufacturers and recyclers,
In adults, occupational exposure is the main cause of lead poisoning. People can be exposed when working in facilities that produce a variety of lead-containing products; these include radiation shields, ammunition, certain surgical equipment, developing dental X-ray films prior to digital X-rays (each film packet had a lead liner to prevent the radiation from going through), fetal monitors, plumbing, circuit boards, jet engines, and ceramic glazes. In addition, lead miners and smelters, plumbers and fitters, auto mechanics, glass manufacturers, construction workers, battery manufacturers and recyclers, firing range
A shooting range, firing range, gun range or shooting ground is a specialized facility, venue or field designed specifically for firearm usage qualifications, training, practice or competitions. Some shooting ranges are operated by milita ...
workers, and plastic manufacturers are at risk for lead exposure. Other occupations that present lead exposure risks include welding, manufacture of rubber, printing, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
smelting, processing of ore, combustion of solid waste
Municipal solid waste (MSW), commonly known as trash or garbage in the United States and rubbish in Britain, is a waste type consisting of everyday items that are discarded by the public. "Garbage" can also refer specifically to food waste ...
, and production of paints and pigments. Dart, Hurlbut, Boyer-Hassen (2004) p. 1424 Lead exposure can also occur with intense use of gun ranges, regardless of whether these ranges are indoor or out. Parents who are exposed to lead in the workplace can bring lead dust home on clothes or skin and expose their children. Occupational exposure to lead increases the risk of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
, in particular: stroke, and high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
.
Food
Lead may be found in food when food is grown in soil that is high in lead, airborne lead contaminates the crops, animals eat lead in their diet, or lead enters the food either from what it was stored or cooked in. Ingestion of lead paint and batteries is also a route of exposure for livestock, which can subsequently affect humans. Milk produced by contaminated cattle can be diluted to a lower lead concentration and sold for consumption. In Bangladesh, lead compounds have been added toturmeric
Turmeric () is a flowering plant, ''Curcuma longa'' (), of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae, the rhizomes of which are used in cooking. The plant is a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast ...
to make it more yellow. This is believed to have started in the 1980s and continues . It is believed to be one of the main sources of high lead levels in the country. In Hong Kong the maximum allowed lead parts per million is 6 in solid foods and 1 in liquid foods.
Paint
Some lead compounds are colorful and are used widely in paints, Henretig (2006) p. 1310 and lead paint is a major route of lead exposure in children. A study conducted in 1998–2000 found that 38 million housing units in the US had lead-based paint, down from a 1990 estimate of 64 million. Deteriorating lead paint can produce dangerous lead levels in household dust and soil. Dart, Hurlbut, Boyer-Hassen (2004) p. 1423 Deteriorating lead paint and lead-containing household dust are the main causes of chronic lead poisoning. The lead breaks down into the dust and since children are more prone to crawling on the floor, it is easily ingested. Many young children display pica, eating things that are not food. Even a small amount of a lead-containing product such as a paint chip or a sip of glaze can contain tens or hundreds of milligrams of lead. Eating chips of lead paint presents a particular hazard to children, generally producing more severe poisoning than occurs from dust. Because removing lead paint from dwellings, e.g. by sanding or torching, creates lead-containing dust and fumes, it is generally safer to seal the lead paint under new paint (excepting moveable windows and doors, which create paint dust when operated). Alternatively, special precautions must be taken if the lead paint is to be removed. Salvato (2003) p. 116 Inoil painting
Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments with a medium of drying oil as the binder. It has been the most common technique for artistic painting on wood panel or canvas for several centuries, spreading from Europe to the rest ...
, it was once common for colours such as yellow or white to be made with lead carbonate. Lead white
White lead is the basic lead carbonate 2PbCO3·Pb(OH)2. It is a complex salt, containing both carbonate and hydroxide ions. White lead occurs naturally as a mineral, in which context it is known as hydrocerussite, a hydrate of cerussite. It wa ...
oil colour was the main white of oil painters until superseded by compounds containing zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
or titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ...
in the mid-20th century. It is speculated that the painter Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
and possibly Francisco Goya
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and e ...
and Vincent Van Gogh
Vincent Willem van Gogh (; 30 March 185329 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who posthumously became one of the most famous and influential figures in Western art history. In a decade, he created about 2,100 artworks, inc ...
had lead poisoning due to overexposure or carelessness when handling this colour.
Soil
 Residual lead in soil contributes to lead exposure in urban areas. It has been thought that the more polluted an area is with various contaminants, the more likely it is to contain lead. However, this is not always the case, as there are several other reasons for lead contamination in soil.
Lead content in soil may be caused by broken-down lead paint, residues from lead-containing gasoline, used engine oil, tire weights, or pesticides used in the past, contaminated landfills, or from nearby industries such as foundries or smelters. For example, in the
Residual lead in soil contributes to lead exposure in urban areas. It has been thought that the more polluted an area is with various contaminants, the more likely it is to contain lead. However, this is not always the case, as there are several other reasons for lead contamination in soil.
Lead content in soil may be caused by broken-down lead paint, residues from lead-containing gasoline, used engine oil, tire weights, or pesticides used in the past, contaminated landfills, or from nearby industries such as foundries or smelters. For example, in the Montevideo
Montevideo () is the capital and largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the city proper has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population) in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern ...
neighborhood of La Teja, former industrial sites became important sources of exposure in local communities in the early 2000s. Although leaded soil is less of a problem in countries that no longer have leaded gasoline
Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula Pb( C2H5)4. It is a fuel additive, first being mixed with gasoline beginning in the 1920s as a patented octane rating booster that ...
, it remains prevalent, raising concerns about the safety of urban agriculture
Urban agriculture, urban farming, or urban gardening is the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It encompasses a complex and diverse mix of food production activities, including fisheries and f ...
; eating food grown in contaminated soil can present a lead hazard. Yu (2005) p. 188 Interfacial solar evaporation has been recently studied as a technique for remediating lead-contaminated sites, which involves the evaporation of heavy metal ions from moist soil.

Water
Lead from the atmosphere or soil can end up in groundwater and surface water. Yu (2005) p. 187 It is also potentially indrinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ...
, e.g. from plumbing and fixtures that are either made of lead or have lead solder. Chisolm (2004) pp. 221–22 Menkes (2006) p. 703 Since acidic water breaks down lead in plumbing more readily, chemicals can be added to municipal water to increase the pH and thus reduce the corrosivity of the public water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. T ...
. Chloramines, which were adopted as a substitute for chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is ...
disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than s ...
s due to fewer health concerns, increase corrositivity. In the US, 14–20% of total lead exposure is attributed to drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ...
. In 2004, a team of seven reporters from ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large n ...
'' discovered high levels of lead in the drinking water in Washington, DC, and won an award for investigative reporting
Investigative journalism is a form of journalism in which reporters deeply investigate a single topic of interest, such as serious crimes, political corruption, or corporate wrongdoing. An investigative journalist may spend months or years res ...
for a series of articles about this contamination. In the water crisis in Flint, Michigan, a switch to a more corrosive municipal water source caused elevated lead levels in domestic tap water.
Like Flint MI and Washington DC, a similar situation affects the State of Wisconsin, where estimates call for replacement of up to 176,000 underground pipes made of lead known as lead service line
A lead service line (LSL, also known as lead service pipe, and lead connection pipe) is a pipe made of lead which is used in potable water distribution to connect a water main to a user's premises.
Lead exposure is a public health hazard as it cau ...
s. The city of Madison, Wisconsin
Madison is the county seat of Dane County, Wisconsin, Dane County and the capital city of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census the population was 269,840, making it the second-largest city in Wisconsin b ...
addressed the issue and replaced all of their lead service lines, but there are still others that have yet to follow suit. While there are chemical methods that could help reduce the amount of lead in the water distributed, a permanent fix would be to replace the pipes completely. While the state may replace the pipes below ground, it will be up to the homeowners to replace the pipes on their property, at an average cost of $3,000. Experts say that if the city were to replace their pipes and the citizens were to keep the old pipes located within their homes, there would be a potential for more lead to dissolve into their drinking water.
Collected rainwater from roof runoff used as potable water may contain lead, if there are lead contaminants on the roof or in the storage tank. The Australian Drinking Water Guidelines allow a maximum of 0.01 mg/L (10 ppb) lead in water.
Lead wheel weights have been found to accumulate on roads and interstates and erode in traffic entering the water runoff through drains. Leaded fishing weights accumulate in rivers, streams, ponds, and lakes.
Gasoline
Lead was first added to gasoline in 1923, as it helped keep car engines healthy. Automotive exhaust represented a major way for lead to be inhaled, invade the bloodstream and pass into the brain. The use of lead in gasoline peaked in the 1970s. By the next decade most high incomes countries prohibited the use of leaded petrol. As late as 2002, almost all low- and middle-income countries including some OECD members still used it. The UN Environment Programme (UNEP) thus launched a campaign in 2002 to eliminate its use, leading to Algeria being the last country to stop its use in July 2021.Lead-containing products
Lead can be found in products such as kohl, an ancient cosmetic from the Middle East, South Asia, and parts of Africa that has many other names; and from some toys. In 2007, millions of toys made in China were recalled from multiple countries owing to safety hazards including lead paint. Vinyl mini-blinds, found especially in older housing, may contain lead. Lead is commonly incorporated intoherbal remedies
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedie ...
such as Indian Ayurvedic
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population repor ...
preparations and remedies of Chinese origin. There are also risks of elevated blood lead levels caused by folk remedies like ''azarcon'' and ''greta'', which each contain about 95% lead.
Ingestion of metallic lead, such as small lead fishing lures, increases blood lead levels and can be fatal. Ingestion of lead-contaminated food is also a threat. Ceramic glaze often contains lead, and dishes that have been improperly fired can leach the metal into food, potentially causing severe poisoning. In some places, the solder in cans used for food contains lead. When manufacturing medical instruments and hardware, solder containing lead may be present. People who eat animals hunted with lead bullets may be at risk for lead exposure. Bullets lodged in the body rarely cause significant levels of lead, but bullets lodged in the joints are the exception, as they deteriorate and release lead into the body over time.
In May 2015, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
n food safety regulators in the state of Uttar Pradesh found that samples of Maggi 2 Minute Noodles contained lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
up to 17 times beyond permissible limits. On 3 June 2015, New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the NCT Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati B ...
Government banned the sale of Maggi noodles in New Delhi stores for 15 days because it was found to contain lead beyond the permissible limit. The Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
FDA on 4 June 2015 banned the noodles for 30 days after 27 out of 39 samples were detected with objectionable levels of metallic lead, among other things. Some of India's biggest retailers like Future Group, Big Bazaar, Easyday and Nilgiris have imposed a nationwide ban on Maggi noodles. Many other states too have banned Maggi noodles.
Bullets
Contact with ammunition is a source of lead exposure. As of 2013, lead-based ammunition production is the second largest annual use of lead in the US, accounting for over 84,800 metric tons consumed in 2013, second only to the manufacture of storage batteries. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) cannot regulate cartridges and shells, as a matter of law. Lead birdshot is banned in some areas, but this is primarily for the benefit of the birds and their predators, rather than humans. Contamination from heavily used gun ranges is of concern to those who live near by. Non-lead alternatives includecopper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
, steel, tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
-nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
-iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs ...
- tin, and polymer blends such as tungsten-polymer and copper-polymer.
Because game animals can be shot using lead bullets, the potential for lead ingestion from game meat consumption has been studied clinically and epidemiologically. In a recent study conducted by the CDC, a cohort from North Dakota was enrolled and asked to self-report historical consumption of game meat, and participation in other activities that could cause lead exposure. The study found that participants' age, sex, housing age, current hobbies with potential for lead exposure, and game consumption were all associated with blood lead level (PbB).
According to a study published in 2008, 1.1% of the 736 persons consuming wild game meat tested had PbB ≥5 μg/dl In November 2015 The US HHS/CDC/NIOSH designated 5 µg/dL (five micrograms per deciliter) of whole blood, in a venous blood sample, as the reference blood lead level for adults. An elevated BLL is defined as a BLL ≥5 µg/dL. This case definition is used by the ABLES program, the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE), and CDC's National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS). Previously (i.e. from 2009 until November 2015), the case definition for an elevated BLL was a BLL ≥10 µg/dL.
 To virtually eliminate the potential for lead contamination, some researchers have suggested the use of lead-free copper non-fragmenting bullets.
To virtually eliminate the potential for lead contamination, some researchers have suggested the use of lead-free copper non-fragmenting bullets.
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs ...
is an element used as a lead-replacement for shotgun pellets used in waterfowl hunting although shotshells made from bismuth are nearly ten times the cost of lead.
Opium
Lead contaminatedopium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
has been the source of poisoning in Iran and other Middle Eastern countries. This has also appeared in the illicit narcotic supply in North America, resulting in confirmed lead poisoning.
Pathophysiology
 Exposure occurs through
Exposure occurs through inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs.
Inhalation of air
Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions ...
, ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms ingest ...
or occasionally skin contact. Lead may be taken in through direct contact with mouth, nose, and eyes (mucous membranes), and through breaks in the skin. Tetraethyllead
Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula Pb( C2H5)4. It is a fuel additive, first being mixed with gasoline beginning in the 1920s as a patented octane rating booster that a ...
, which was a gasoline additive and is still used in aviation gasoline
Avgas (aviation gasoline, also known as aviation spirit in the UK) is an aviation fuel used in aircraft with spark-ignited internal combustion engines. ''Avgas'' is distinguished from conventional gasoline (petrol) used in motor vehicles, whi ...
, passes through the skin; and other forms of lead, including inorganic lead are also absorbed through skin. The main sources of absorption of inorganic lead are from ingestion and inhalation. Merrill, Morton, Soileau (2007) p. 860 In adults, about 35–40% of inhaled lead dust is deposited in the lungs, and about 95% of that goes into the bloodstream. Of ingested inorganic lead, about 15% is absorbed, but this percentage is higher in children, pregnant women, and people with deficiencies of calcium, zinc, or iron. Infants may absorb about 50% of ingested lead, but little is known about absorption rates in children. Grant (2009) p. 767
The main body tissues that store lead are the blood, soft tissues, and bone; the half-life of lead in these tissues is measured in weeks for blood, months for soft tissues, and years for bone. Lead in the bones, teeth, hair, and nails is bound tightly and not available to other tissues, and is generally thought not to be harmful. Rubin, Strayer (2008) p. 266 In adults, 94% of absorbed lead is deposited in the bones and teeth, but children only store 70% in this manner, a fact which may partially account for the more serious health effects on children. The half-life of lead in bone has been estimated as years to decades, and bone can introduce lead into the bloodstream long after the initial exposure is gone. The half-life of lead in the blood in men is about 40 days, but it may be longer in children and pregnant women, whose bones are undergoing remodeling, which allows the lead to be continuously re-introduced into the bloodstream. Also, if lead exposure takes place over years, clearance is much slower, partly due to the re-release of lead from bone. Many other tissues store lead, but those with the highest concentrations (other than blood, bone, and teeth) are the brain, spleen, kidneys, liver, and lungs. Dart, Hurlbut, Boyer-Hassen (2004) p. 1426
Lead is removed from the body very slowly, mainly through urine. Smaller amounts of lead are also eliminated through the feces, and very small amounts in hair, nails, and sweat.
Lead has no known physiologically relevant role in the body, and its harmful effects are myriad. Lead and other heavy metals create reactive radicals
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
which damage cell structures including DNA and cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ...
s. Lead also interferes with DNA transcription
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules calle ...
, enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s that help in the synthesis of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 ...
, and enzymes that maintain the integrity of the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ...
. Anemia may result when the cell membranes of red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s become more fragile as the result of damage to their membranes. Yu (2005) p.193 Lead interferes with metabolism of bones and teeth and alters the permeability of blood vessels and collagen synthesis. Lead may also be harmful to the developing immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
, causing production of excessive inflammatory proteins; this mechanism may mean that lead exposure is a risk factor for asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, c ...
in children. Casarett, Klaassen, Doull (2007) p. 946 Lead exposure has also been associated with a decrease in activity of immune cells such as polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lead also interferes with the normal metabolism of calcium in cells and causes it to build up within them.
Enzymes
The primary cause of lead's toxicity is its interference with a variety of enzymes because it binds to sulfhydryl groups found on many enzymes. Part of lead's toxicity results from its ability to mimic other metals that take part in biological processes, which act as cofactors in many enzymatic reactions, displacing them at the enzymes on which they act. Lead is able to bind to and interact with many of the sameenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s as these metals but, due to its differing chemistry, does not properly function as a cofactor, thus interfering with the enzyme's ability to catalyze its normal reaction or reactions. Among the essential metals with which lead interacts are calcium, iron, and zinc. Kosnett (2006) p.238
The lead ion has a lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC '' Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. L ...
in its electronic structure, which can result in a distortion in the coordination
Coordination may refer to:
* Coordination (linguistics), a compound grammatical construction
* Coordination complex, consisting of a central atom or ion and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions
* Coordination number or ligancy of a centr ...
of ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's ele ...
s, and in 2007 was hypothesized to be important in lead poisoning's effects on enzymes (see ).
One of the main causes for the pathology of lead is that it interferes with the activity of an essential enzyme called delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (porphobilinogen synthase, or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''ALAD'' gene. Porphobilinogen synthase (or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate de ...
, or ALAD (see image of the enzyme structure), which is important in the biosynthesis of heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.
In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consis ...
, the cofactor found in hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
. Lead also inhibits the enzyme ferrochelatase
Protoporphyrin ferrochelatase (EC 4.98.1.1, formerly EC 4.99.1.1, or ferrochelatase; systematic name protoheme ferro-lyase (protoporphyrin-forming)) is an enzyme encoded by the FECH gene in humans. Ferrochelatase catalyses the eighth and termin ...
, another enzyme involved in the formation of heme. Ferrochelatase catalyzes the joining of protoporphyrin and Fe2+ to form heme. Lead's interference with heme synthesis results in production of zinc protoporphyrin and the development of anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 462 Another effect of lead's interference with heme synthesis is the buildup of heme precursors, such as aminolevulinic acid
δ-Aminolevulinic acid (also dALA, δ-ALA, 5ALA or 5-aminolevulinic acid), an endogenous non-proteinogenic amino acid, is the first compound in the porphyrin synthesis pathway, the pathway that leads to heme in mammals, as well as chlorophyll in ...
, which may be directly or indirectly harmful to neurons. Elevation of aminolevulinic acid results in lead poisoning having symptoms similar to acute porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are ra ...
.
Neurons
 The brain is the organ most sensitive to lead exposure. Lead is able to pass through the endothelial cells at the
The brain is the organ most sensitive to lead exposure. Lead is able to pass through the endothelial cells at the blood brain barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
because it can substitute for calcium ions and be taken up by calcium-ATPase pumps. Lead poisoning interferes with the normal development of a child's brain and nervous system
In Biology, biology, the nervous system is the Complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its Behavior, actions and Sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its ...
; therefore children are at greater risk of lead neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifical ...
than adults are. In a child's developing brain, lead interferes with synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses fr ...
formation in the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
, neurochemical A neurochemical is a small organic molecule or peptide that participates in neural activity. The science of neurochemistry studies the functions of neurochemicals.
Prominent neurochemicals
Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators
* Glutamate is ...
development (including that of neurotransmitters), and organization of ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
s. It causes loss of neurons' myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be l ...
sheaths, reduces numbers of neurons, interferes with neurotransmission, and decreases neuronal growth.
Lead-ions (Pb), like magnesium-ions (Mg), block NMDA receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA rece ...
s. Therefore, an increase in Pb concentration will effectively inhibit ongoing long-term potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons ...
(LTP), and lead to an abnormal increase in long-term depression
In neurophysiology, long-term depression (LTD) is an activity-dependent reduction in the efficacy of neuronal synapses lasting hours or longer following a long patterned stimulus. LTD occurs in many areas of the CNS with varying mechanisms dependi ...
(LTD) on neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, electrically excitable cell (biology), cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous ...
s in the affected parts of Nervous system, the nervous system. These abnormalities lead to the indirect Downregulation and upregulation, downregulation of NMDA-receptors, effectively initiating a Positive feedback#In biology, positive feedback-loop for LTD. The targeting of NMDA receptors is thought to be one of the main causes for lead's neurotoxicity, toxicity to neurons.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes determining the clinical signs and the medical history, with inquiry into possible routes of exposure. Henretig (2006) p. 1316 medical toxicology, Clinical toxicologists, medical specialists in the area of poisoning, may be involved in diagnosis and treatment. The main tool in diagnosing and assessing the severity of lead poisoning is laboratory analysis of the blood lead level (BLL). Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 463 Blood film examination may reveal basophilic stippling of red blood cells (dots in red blood cells visible through a microscope), as well as the changes normally associated with iron-deficiency anemia (microcytosis and hypochromic, hypochromasia). This may be known as sideroblastic anemia. However, basophilic stippling is also seen in unrelated conditions, such as megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 (colbalamin) and folate deficiencies.
Contrary to other sideroblastic anemia, there are no ring sideroblasts in a bone marrow smear.
Exposure to lead also can be evaluated by measuring zinc protoporphyrin, erythrocyte protoporphyrin (EP) in blood samples. EP is a part of red blood cells known to increase when the amount of lead in the blood is high, with a delay of a few weeks. Thus EP levels in conjunction with blood lead levels can suggest the time period of exposure; if blood lead levels are high but EP is still normal, this finding suggests exposure was recent. However, the EP level alone is not sensitive enough to identify elevated blood lead levels below about 35 μg/dL. Due to this higher threshold for detection and the fact that EP levels also increase in Iron deficiency (medicine), iron deficiency, use of this method for detecting lead exposure has decreased. Grant (2009) p. 784
Blood lead levels are an indicator mainly of recent or current lead exposure, not of total body burden. Lead in bones can be measured Invasiveness of surgical procedures, noninvasively by X-ray fluorescence; this may be the best measure of cumulative exposure and total body burden. However this method is not widely available and is mainly used for research rather than routine diagnosis. Another radiographic sign of elevated lead levels is the presence of radiodensity, radiodense lines called lead lines at the metaphysis in the long bones of growing children, especially around the knees. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 464 These lead lines, caused by increased calcification due to disrupted metabolism in the growing bones, become wider as the duration of lead exposure increases. X-rays may also reveal lead-containing foreign materials such as paint chips in the gastrointestinal tract.#CITEREFKatzung07, Kosnett (2007) p. 948
Fecal lead content that is measured over the course of a few days may also be an accurate way to estimate the overall amount of childhood lead intake. This form of measurement may serve as a useful way to see the extent of oral lead exposure from all the diet and environmental sources of lead.
Lead poisoning shares symptoms with other conditions and may be easily missed. Conditions that present similarly and must be ruled out in diagnosing lead poisoning include carpal tunnel syndrome, Guillain–Barré syndrome, renal colic, appendicitis, encephalitis in adults, and viral gastroenteritis in children. Other differential diagnosis, differential diagnoses in children include
Blood film examination may reveal basophilic stippling of red blood cells (dots in red blood cells visible through a microscope), as well as the changes normally associated with iron-deficiency anemia (microcytosis and hypochromic, hypochromasia). This may be known as sideroblastic anemia. However, basophilic stippling is also seen in unrelated conditions, such as megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin B12 (colbalamin) and folate deficiencies.
Contrary to other sideroblastic anemia, there are no ring sideroblasts in a bone marrow smear.
Exposure to lead also can be evaluated by measuring zinc protoporphyrin, erythrocyte protoporphyrin (EP) in blood samples. EP is a part of red blood cells known to increase when the amount of lead in the blood is high, with a delay of a few weeks. Thus EP levels in conjunction with blood lead levels can suggest the time period of exposure; if blood lead levels are high but EP is still normal, this finding suggests exposure was recent. However, the EP level alone is not sensitive enough to identify elevated blood lead levels below about 35 μg/dL. Due to this higher threshold for detection and the fact that EP levels also increase in Iron deficiency (medicine), iron deficiency, use of this method for detecting lead exposure has decreased. Grant (2009) p. 784
Blood lead levels are an indicator mainly of recent or current lead exposure, not of total body burden. Lead in bones can be measured Invasiveness of surgical procedures, noninvasively by X-ray fluorescence; this may be the best measure of cumulative exposure and total body burden. However this method is not widely available and is mainly used for research rather than routine diagnosis. Another radiographic sign of elevated lead levels is the presence of radiodensity, radiodense lines called lead lines at the metaphysis in the long bones of growing children, especially around the knees. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 464 These lead lines, caused by increased calcification due to disrupted metabolism in the growing bones, become wider as the duration of lead exposure increases. X-rays may also reveal lead-containing foreign materials such as paint chips in the gastrointestinal tract.#CITEREFKatzung07, Kosnett (2007) p. 948
Fecal lead content that is measured over the course of a few days may also be an accurate way to estimate the overall amount of childhood lead intake. This form of measurement may serve as a useful way to see the extent of oral lead exposure from all the diet and environmental sources of lead.
Lead poisoning shares symptoms with other conditions and may be easily missed. Conditions that present similarly and must be ruled out in diagnosing lead poisoning include carpal tunnel syndrome, Guillain–Barré syndrome, renal colic, appendicitis, encephalitis in adults, and viral gastroenteritis in children. Other differential diagnosis, differential diagnoses in children include constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
, abdominal colic, iron deficiency, subdural hematoma, neoplasms of the central nervous system, emotional and behavior disorders, and intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
.
Reference levels
The current reference range for acceptable blood lead concentrations in healthy persons without excessive exposure to environmental sources of lead is less than 3.5 µg/dL for children. It was less than 25 µg/dL for adults. Previous to 2012 the value for children was 10 (µg/dl). Lead-exposed workers in the U.S. are required to be removed from work when their level is greater than 50 µg/dL if they do construction and otherwise greater than 60 µg/dL. In 2015, US HHS/CDC/NIOSH designated 5 µg/dL (five micrograms per deciliter) of whole blood, in a venous blood sample, as the reference blood lead level for adults. An elevated BLL is defined as a BLL ≥5 µg/dL. This case definition is used by the ABLES program, the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE), and CDC's National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS). Previously (i.e. from 2009 until November 2015), the case definition for an elevated BLL was a BLL ≥10 µg/dL. The U.S. national BLL geometric mean among adults was 1.2 μg/dL in 2009–2010. Blood lead concentrations in poisoning victims have ranged from 30 to 80 µg/dL in children exposed to lead paint in older houses, 77–104 µg/dL in persons working with pottery glazes, 90–137 µg/dL in individuals consuming contaminated herbal medicines, 109–139 µg/dL in indoor shooting range instructors and as high as 330 µg/dL in those drinking fruit juices from glazed earthenware containers.Prevention
 In most cases, lead poisoning is preventable by avoiding exposure to lead. Prevention strategies can be divided into individual (measures taken by a family), preventive medicine (identifying and intervening with high-risk individuals), and public health (reducing risk on a population level).
Recommended steps by individuals to reduce the blood lead levels of children include increasing their frequency of hand washing and their intake of calcium and iron, discouraging them from putting their hands to their mouths, vacuuming frequently, and eliminating the presence of lead-containing objects such as blinds and jewellery in the house. In houses with lead pipes or plumbing solder, these can be replaced. Less permanent but cheaper methods include running water in the morning to flush out the most contaminated water, or adjusting the water's chemistry to prevent corrosion of pipes. Lead testing kits are commercially available for detecting the presence of lead in the household. Salvato (2003) p.117 Testing kit accuracy depends on the user testing all layers of paint and the quality of the kit; the United States Environmental Protection Agency, US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) only approves kits with an accuracy rating of at least 95%. Professional lead testing companies caution that DIY test kits can create health risks for users that do not understand their limitations and liability issues for employers with regard to worker protection. As hot water is more likely than cold water to contain higher amounts of lead, use only cold water from the tap for drinking, cooking, and making baby formula. Since most of the lead in household water usually comes from plumbing in the house and not from the local water supply, using cold water can avoid lead exposure.National Environmental Public Health Tracking Network, 2010. Measures such as dust control and household education do not appear to be effective in changing children's blood levels.
Prevention measures also exist on national and municipal levels. Recommendations by health professionals for lowering childhood exposures include banning the use of lead where it is not essential and strengthening regulations that limit the amount of lead in soil, water, air, household dust, and products. Regulations exist to limit the amount of lead in paint; for example, a 1978 law in the US restricted the lead in paint for residences, furniture, and toys to 0.06% or less. In October 2008, the US EPA reduced the allowable lead level by a factor of ten to 0.15 micrograms per cubic meter of air, giving states five years to comply with the standards. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive limits amounts of lead and other toxic substances in electronics and electrical equipment. In some places, remediation programs exist to reduce the presence of lead when it is found to be high, for example in drinking water. As a more radical solution, entire towns located near former lead mines have been "closed" by the government, and the population resettled elsewhere, as was the case with Picher, Oklahoma, in 2009. Removing lead from airplane fuel would also be useful.
In most cases, lead poisoning is preventable by avoiding exposure to lead. Prevention strategies can be divided into individual (measures taken by a family), preventive medicine (identifying and intervening with high-risk individuals), and public health (reducing risk on a population level).
Recommended steps by individuals to reduce the blood lead levels of children include increasing their frequency of hand washing and their intake of calcium and iron, discouraging them from putting their hands to their mouths, vacuuming frequently, and eliminating the presence of lead-containing objects such as blinds and jewellery in the house. In houses with lead pipes or plumbing solder, these can be replaced. Less permanent but cheaper methods include running water in the morning to flush out the most contaminated water, or adjusting the water's chemistry to prevent corrosion of pipes. Lead testing kits are commercially available for detecting the presence of lead in the household. Salvato (2003) p.117 Testing kit accuracy depends on the user testing all layers of paint and the quality of the kit; the United States Environmental Protection Agency, US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) only approves kits with an accuracy rating of at least 95%. Professional lead testing companies caution that DIY test kits can create health risks for users that do not understand their limitations and liability issues for employers with regard to worker protection. As hot water is more likely than cold water to contain higher amounts of lead, use only cold water from the tap for drinking, cooking, and making baby formula. Since most of the lead in household water usually comes from plumbing in the house and not from the local water supply, using cold water can avoid lead exposure.National Environmental Public Health Tracking Network, 2010. Measures such as dust control and household education do not appear to be effective in changing children's blood levels.
Prevention measures also exist on national and municipal levels. Recommendations by health professionals for lowering childhood exposures include banning the use of lead where it is not essential and strengthening regulations that limit the amount of lead in soil, water, air, household dust, and products. Regulations exist to limit the amount of lead in paint; for example, a 1978 law in the US restricted the lead in paint for residences, furniture, and toys to 0.06% or less. In October 2008, the US EPA reduced the allowable lead level by a factor of ten to 0.15 micrograms per cubic meter of air, giving states five years to comply with the standards. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive limits amounts of lead and other toxic substances in electronics and electrical equipment. In some places, remediation programs exist to reduce the presence of lead when it is found to be high, for example in drinking water. As a more radical solution, entire towns located near former lead mines have been "closed" by the government, and the population resettled elsewhere, as was the case with Picher, Oklahoma, in 2009. Removing lead from airplane fuel would also be useful.
Screening
Screening may be an important method of prevention for those at high risk, such as those who live near lead-related industries. The USPSTF has stated that general screening of those without symptoms include children and pregnant women is of unclear benefit . The ACOG and APP, however, recommends asking about risk factors and testing those who have them.Education
The education of workers on lead, its danger and how its workplace exposure can be decreased, especially when initial blood lead level and urine lead level are high, could help reduce the risk of lead poisoning in the workplace.Treatment
The mainstays of treatment are removal from the source of lead and, for people who have significantly high blood lead levels or who have symptoms of poisoning,chelation therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the body. Chelation therapy has a long history of use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific medi ...
. Henretig (2006) p. 1321 Treatment of iron, Hypocalcaemia, calcium, and zinc deficiency, zinc deficiencies, which are associated with increased lead absorption, is another part of treatment for lead poisoning. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 465 When lead-containing materials are present in the gastrointestinal tract (as evidenced by abdominal X-rays), whole bowel irrigation, Cathartic (medicine), cathartics, endoscopy, or even surgical removal may be used to eliminate it from the gut and prevent further exposure.#CITEREFOlson07, Olson (2007) p. 1658 Lead-containing bullets and shrapnel may also present a threat of further exposure and may need to be surgically removed if they are in or near fluid-filled or Synovial membrane, synovial spaces. Kosnett (2006) p. 241 If lead encephalopathy is present, anticonvulsants may be given to control seizures, and treatments to control cerebral edema, swelling of the brain include corticosteroids and mannitol. Kosnett (2005) p. 832 Treatment of organic lead poisoning involves removing the lead compound from the skin, preventing further exposure, treating seizures, and possibly chelation therapy for people with high blood lead concentrations.#CITEREFKatzung07, Kosnett (2007) p. 949
Before the advent of organic chelating agents, salts of iodide were given orally, such as heavily popularized by Louis Melsens and many nineteenth and early twentieth century doctors."On the Employment of Iodide of Potassium as a Remedy for the Affections Caused by Lead and Mercury"in ''Br Foreign Med Chir Rev.'' 1853 Jan; 11(21): 201–224.
Epidemiology
Since lead has been used widely for centuries, the effects of exposure are worldwide. Environmental lead is ubiquitous, and everyone has some measurable blood lead level. Atmospheric lead pollution increased dramatically beginning in the 1950s as a result of the widespread use of leaded gasoline. Lead is one of the largest environmental medicine problems in terms of numbers of people exposed and the public health toll it takes. Lead exposure accounts for about 0.2% of all deaths and 0.6% of disability adjusted life years globally. Although regulation reducing lead in products has greatly reduced exposure in the developed world since the 1970s, lead is still allowed in products in many developing countries. Despite phase out in many parts of the Global North, Global South exposure has increased by nearly three times. In all countries that have banned leaded gasoline, average blood lead levels have fallen sharply. However, some developing countries still allow leaded gasoline, which is the primary source of lead exposure in most developing countries. Beyond exposure from gasoline, the frequent use of pesticides in developing countries adds a risk of lead exposure and subsequent poisoning. Poor children in developing countries are at especially high risk for lead poisoning. Of North American children, 7% have blood lead levels above 10 μg/dL, whereas among Central and South American children, the percentage is 33–34%. About one fifth of the world'sdisease burden
Disease burden is the impact of a health problem as measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Both ...
from lead poisoning occurs in the Western Pacific, and another fifth is in Southeast Asia.
In developed countries, people with low levels of education living in poorer areas are most at risk for elevated lead. In the US, the groups most at risk for lead exposure are the impoverished, city-dwellers, and immigrants. African-American children and those living in old housing have also been found to be at elevated risk for high blood lead levels in the US. Low-income people often live in old housing with lead paint, which may begin to peel, exposing residents to high levels of lead-containing dust.
Risk factors for elevated lead exposure include alcohol consumption and smoking (possibly because of contamination of tobacco leaves with lead-containing pesticides). Adults with certain risk factors might be more susceptible to toxicity; these include calcium and iron deficiencies, old age, disease of organs targeted by lead (e.g. the brain, the kidneys), and possibly genetic susceptibility.
Differences in vulnerability to lead-induced neurological damage between males and females have also been found, but some studies have found males to be at greater risk, while others have found females to be.
In adults, blood lead levels steadily increase with increasing age. In adults of all ages, men have higher blood lead levels than women do. Children are more sensitive to elevated blood lead levels than adults are. Children may also have a higher intake of lead than adults; they breathe faster and may be more likely to have contact with and ingest soil. Children of ages one to three tend to have the highest blood lead levels, possibly because at that age they begin to walk and explore their environment, and they use their mouths in their exploration. Blood levels usually peak at about 18–24 months old. In many countries including the US, household paint and dust are the major route of exposure in children.
Notable cases
Cases of mass lead poisoning can occur. 15,000 people are being relocated from Jiyuan in central Henan province to other locations after 1000 children living around China's largest smelter plant (owned and operated by Yuguang Gold and Lead) were found to have excess lead in their blood. The total cost of this project is estimated to around 1 billion yuan ($150 million). 70% of the cost will be paid by local government and the smelter company, while the rest will be paid by the residents themselves. The government has suspended production at 32 of 35 lead plants. The affected area includes people from 10 different villages. The Zamfara State lead poisoning epidemic occurred in Nigeria in 2010. As of 5 October 2010 at least 400 children have died from the effects of lead poisoning.Sex-specific susceptibility
Neuroanatomical pathology due to lead exposure is more pronounced in males, suggesting that lead-related toxicity has a disparate impact across sexes.Prognosis
Reversibility
Outcome is related to the extent and duration of lead exposure. Chisolm (2004) p. 223 Effects of lead on the physiology of the kidneys and blood are generally reversible; its effects on the central nervous system are not. While peripheral effects in adults often go away when lead exposure ceases, evidence suggests that most of lead's effects on a child's central nervous system are irreversible. Children with lead poisoning may thus have adverse health, cognitive, and behavioral effects that follow them into adulthood.Encephalopathy
Lead encephalopathy is a medical emergency and causes permanent brain damage in 70–80% of children affected by it, even those that receive the best treatment. The mortality rate for people who develop cerebral involvement is about 25%, and of those who survive who had lead encephalopathy symptoms by the time chelation therapy was begun, about 40% have permanent neurological problems such as cerebral palsy.#CITEREFBrunton07, Brunton (2007) p. 1131Long-term
Exposure to lead may also decrease lifespan and have health effects in the long term. Mortality rate, Death rates from a variety of causes have been found to be higher in people with elevated blood lead levels; these include cancer, stroke, and heart disease, and general death rates from all causes. Lead is considered a possible human carcinogen based on evidence from animal experimentation, animal studies. Merrill, Morton, Soileau (2007) p. 862 Evidence also suggests that age-related mental decline and psychiatric symptoms are correlated with lead exposure. Cumulative exposure over a prolonged period may have a more important effect on some aspects of health than recent exposure. Some health effects, such ashigh blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
, are only significant risks when lead exposure is prolonged (over about one year). Furthermore, the neurological effects of lead exposure have been shown to be exacerbated and long lasting in low income children in comparison to those of higher economic standing. This does not imply that being wealthy can prevent lead from causing long-term mental health issues.
Violence
Lead poisoning in children has been linked to changes in brain function that can result in low Intelligence quotient, IQ, and increased impulsivity and aggression. These traits of childhood lead exposure are associated with crimes of passion, such as aggravated assault in young adults. An increase in lead exposure in children was linked to an increase in aggravated assault rates 22 years later. For instance, the peak in leaded gasoline use in the late 1970s corresponds to a peak in aggravated assault rates in the late 1990s in urban areas across the United States.History
 Lead poisoning was among the first known and most widely studied work regarding environmental hazards. One of the first metals to be smelting, smelted and used, lead is thought to have been discovered and first mining, mined in Anatolia around 6500 BC. Its density, workability, and corrosion resistance were among the metal's attractions.
In the 2nd century BC the Greek botanist Nicander described the
Lead poisoning was among the first known and most widely studied work regarding environmental hazards. One of the first metals to be smelting, smelted and used, lead is thought to have been discovered and first mining, mined in Anatolia around 6500 BC. Its density, workability, and corrosion resistance were among the metal's attractions.
In the 2nd century BC the Greek botanist Nicander described the colic
Colic or cholic () is a form of pain that starts and stops abruptly. It occurs due to muscular contractions of a hollow tube (small and large intestine, gall bladder, ureter, etc.) in an attempt to relieve an obstruction by forcing content out. ...
and paralysis seen in lead-poisoned people. Pedanius Dioscorides, Dioscorides, a Greek physician who lived in the 1st century AD, wrote that lead makes the mind "give way".
Lead was used extensively in Roman aqueducts from about 500 BC to 300 AD. Julius Caesar's engineer, Vitruvius, reported, "water is much more wholesome from earthenware pipes than from lead pipes. For it seems to be made injurious by lead, because white lead is produced by it, and this is said to be harmful to the human body." Gout, prevalent in affluent Rome, is thought to be the result of lead, or leaded eating and drinking vessels. Sugar of lead (lead(II) acetate) was used to sweeten wine, and the gout that resulted from this was known as "saturnine" gout. It is even hypothesized that lead poisoning may have contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire, a hypothesis thoroughly disputed:
However, recent research supports the idea that the lead found in the water came from the supply pipes, rather than another source of contamination. It was not unknown for locals to punch holes in the pipes to draw water off, increasing the number of people exposed to the lead.
Romans also consumed lead through the consumption of defrutum, defrutum, carenum, and sapa, musts made by boiling down fruit in lead cookware. Defrutum and its relatives were used in ancient Roman cuisine and cosmetics, including as a food preservative. The use of leaden cookware, though popular, was not the general standard and copper cookware was used far more generally. There is also no indication how often sapa was added or in what quantity.
The consumption of sapa as having a role in the fall of the Roman Empire was used in a theory proposed by geochemist Jerome Nriagu to state that "lead poisoning contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire". In 1984, John Scarborough, a pharmacologist and classicist, criticized the conclusions drawn by Nriagu's book as "so full of false evidence, miscitations, typographical errors, and a blatant flippancy regarding primary sources that the reader cannot trust the basic arguments."
After Classical Antiquity, antiquity, mention of lead poisoning was absent from medical literature until the end of the Middle Ages. In 1656 the German physician Samuel Stockhausen recognized dust and fumes containing lead compounds as the cause of disease, called since ancient Roman times ''morbi metallici'', that were known to afflict miners, smelter workers, pottery, potters, and others whose work exposed them to the metal.
The painter Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
might have died of lead poisoning. Bones with high lead levels were recently found in a grave thought likely to be his. Paints used at the time contained high amounts of lead salts. Caravaggio is known to have exhibited violent behavior, a symptom commonly associated with lead poisoning.
In 17th-century Germany, the physician Eberhard Gockel discovered lead-contaminated wine to be the cause of an epidemic of colic
Colic or cholic () is a form of pain that starts and stops abruptly. It occurs due to muscular contractions of a hollow tube (small and large intestine, gall bladder, ureter, etc.) in an attempt to relieve an obstruction by forcing content out. ...
. He had noticed that monks who did not drink wine were healthy, while wine drinkers developed colic, and traced the cause to sugar of lead, made by simmering litharge with vinegar. As a result, Eberhard Ludwig, Duke of Württemberg issued an edict in 1696 banning the adulteration of wines with litharge.
In the 18th century lead poisoning was fairly frequent on account of the widespread drinking of rum, which was made in stills with a lead component (the "worm"). It was a significant cause of mortality amongst slaves and sailors in the colonial West Indies. Lead poisoning from rum was also noted in Boston, Massachusetts, Boston. Benjamin Franklin suspected lead to be a risk in 1786. Also in the 18th century, "Devonshire colic" was the name given to the symptoms experienced by people of Devon who drank cider made in fruit press, presses that were lined with lead. Lead was added to cheap wine illegally in the 18th and early 19th centuries as a sweetener. The composer Ludwig van Beethoven, Beethoven, a heavy wine drinker, had elevated lead levels (as later detected in his human hair, hair) possibly due to this; the cause of his death is controversial, but lead poisoning is a contender as a factor.
With the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century, lead poisoning became common in the work setting. The introduction of lead paint for residential use in the 19th century increased childhood exposure to lead; for millennia before this, most lead exposure had been occupational disease, occupational. William James Furnival (1853-1928), research ceramist of City & Guilds London Institute, appeared before Parliament in 1901 and presented a decade's evidence to convince the nation's leaders to remove lead completely from the British ceramic industry. His 852-page treatise, ''Leadless Decorative Tiles, Faience, and Mosaic'' of 1904 published that campaign and provided recipes to promote lead-free ceramics. At the request of the Illinois state government, Alice Hamilton (1869-1970) documented lead toxicity in Illinois industry and in 1911 presented results to the 23rd Annual Meeting of the American Economic Association. Dr. Hamilton was a founder of the field of occupational safety and health and published the first edition of her manual, ''Industrial Toxicology'' in 1934, yet in print in revised forms. An important step in the understanding of childhood lead poisoning occurred when toxicity in children from lead paint was recognized in Australia in 1897. France, Belgium, and Austria banned white lead interior paints in 1909; the League of Nations followed suit in 1922. However, in the United States, laws banning lead house paint were not passed until 1971,and it was phased out and not fully banned until 1978.
The 20th century saw an increase in worldwide lead exposure levels due to the increased widespread use of the metal. Grant (2009) p. 757 Beginning in the 1920s, Gasoline#Tetraethyl lead, lead was added to gasoline to improve its combustion; lead from this exhaust gas, exhaust persists today in soil and dust in buildings. Midcentury ceramicist Carol Janeway provides a case history of lead poisoning in an artist using lead glazes in decorating tiles in the 1940s; her monograph suggests that other artists' potential for lead poisoning be investigated, for example Vally Wieselthier and Dora Carrington. Blood lead levels worldwide have been declining sharply since the 1980s, when leaded gasoline began to be phased out. In those countries that have banned lead in solder for food and drink cans and have banned leaded gasoline additives, blood lead levels have fallen sharply since the mid-1980s. Mycyk, Hryhorczuk, Amitai (2005) p. 467
The levels found today in most people are orders of magnitude greater than those of pre-industrial society. Merrill, Morton, Soileau (2007) p. 861 Due to reductions of lead in products and the workplace, acute lead poisoning is rare in most countries today, but low-level lead exposure is still common. It was not until the second half of the 20th century that subclinical
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
lead exposure became understood to be a problem. During the end of the 20th century, the blood lead levels deemed acceptable steadily declined. Grant (2009) p. 758 Blood lead levels once considered safe are now considered hazardous, with no known safe threshold.
In the late 1950s through the 1970s Herbert Needleman and Clair Cameron Patterson did research trying to prove lead's toxicity to humans. In the 1980s Needleman was falsely accused of scientific misconduct by the lead industry associates.
In 2002 Tommy Thompson, secretary of Health and Human Services appointed at least two persons with Conflict of interest, conflicts of interest to the CDC's Lead Advisory Committee.
In 2014 a case by the state of California against a number of companies decided against Sherwin-Williams, NL Industries and ConAgra and ordered them to pay $1.15 billion. The disposition of ''The People v. ConAgra Grocery Products Company et al.'' in the California 6th Appellate District Court on 14 November 2017 is that:
On 6 December 2017, the petitions for rehearing from NL Industries, Inc., ConAgra Grocery Products Company and The Sherwin-Williams Company were denied.
Studies have found a weak link between lead from leaded gasoline and crime rates.
in the United States lead paint in rental housing remains a hazard to children. Both landlords and insurance companies have adopted strategies which limit the chance of recovery for damages due to lead poisoning: insurance companies by excluding coverage for lead poisoning from policies and landlords by crafting barriers to collection of any money damages compensating plaintiffs for damage.
Other species
Humans are not alone in suffering from lead's effects; plants and animals are also affected by lead toxicity to varying degrees depending on species. Animals experience many of the same effects of lead exposure as humans do, such as abdominal pain, peripheral neuropathy, and behavioral changes such as increased aggression. Much of what is known about human lead toxicity and its effects is derived from animal studies. Animals are used to test the effects of treatments, such as chelating agents, and to provide information on the pathophysiology of lead, such as how it is absorbed and distributed in the body. Grant (2009) pp. 768, 771, 774 Farm animals such as cows and horses as well as pet animals are also susceptible to the effects of lead toxicity. Sources of lead exposure in pets can be the same as those that present health threats to humans sharing the environment, such as paint and blinds, and there is sometimes lead in toys made for pets. Lead poisoning in a pet dog may indicate that children in the same household are at increased risk for elevated lead levels.Wildlife
 Lead, one of the leading causes of toxicity in waterfowl, has been known to cause die-offs of wild bird populations. When hunters use lead shot, waterfowl such as ducks can ingest the spent pellets later and be poisoned; predators that eat these birds are also at risk. Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s. By 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting was positively identified as the source of waterfowl deaths.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Lead shot has been banned for hunting waterfowl in several countries, including the US in 1991 and Canada in 1997. Other threats to wildlife include lead paint, sediment from lead mines and smelters, and lead weights from fishing lines. Lead in some fishing gear has been banned in several countries.
The Critically endangered species, critically endangered California condor has also been affected by lead poisoning. As scavengers, condors eat carcasses of game that have been shot but not retrieved, and with them the fragments from lead bullets; this increases their lead levels. Among condors around the Grand Canyon, lead poisoning due to eating lead shot is the most frequently diagnosed cause of death. In an effort to protect this species, in areas designated as the California condor's range the use of projectiles containing lead has been banned to hunt deer, feral pigs, elk, pronghorn antelope, coyotes, ground squirrels, and other non-game wildlife. Also, conservation programs exist which routinely capture condors, check their blood lead levels, and treat cases of poisoning.
Lead, one of the leading causes of toxicity in waterfowl, has been known to cause die-offs of wild bird populations. When hunters use lead shot, waterfowl such as ducks can ingest the spent pellets later and be poisoned; predators that eat these birds are also at risk. Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s. By 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting was positively identified as the source of waterfowl deaths.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Lead shot has been banned for hunting waterfowl in several countries, including the US in 1991 and Canada in 1997. Other threats to wildlife include lead paint, sediment from lead mines and smelters, and lead weights from fishing lines. Lead in some fishing gear has been banned in several countries.
The Critically endangered species, critically endangered California condor has also been affected by lead poisoning. As scavengers, condors eat carcasses of game that have been shot but not retrieved, and with them the fragments from lead bullets; this increases their lead levels. Among condors around the Grand Canyon, lead poisoning due to eating lead shot is the most frequently diagnosed cause of death. In an effort to protect this species, in areas designated as the California condor's range the use of projectiles containing lead has been banned to hunt deer, feral pigs, elk, pronghorn antelope, coyotes, ground squirrels, and other non-game wildlife. Also, conservation programs exist which routinely capture condors, check their blood lead levels, and treat cases of poisoning.
Notes
References * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Lead Poisoning Lead poisoning, Environmental impact by effect Occupational diseases Mass poisoning Disturbances of human pigmentation Intellectual disability Biology of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate