|
Ferrochelatase
Protoporphyrin ferrochelatase (EC 4.98.1.1, formerly EC 4.99.1.1, or ferrochelatase; systematic name protoheme ferro-lyase (protoporphyrin-forming)) is an enzyme encoded by the ''FECH'' gene in humans. Ferrochelatase catalyses the eighth and terminal step in the biosynthesis of heme, converting protoporphyrin IX into heme B. It catalyses the reaction: : Function Ferrochelatase catalyzes the insertion of ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX in the heme biosynthesis pathway to form heme B. The enzyme is localized to the matrix-facing side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Ferrochelatase is the best known member of a family of enzymes that add divalent metal cations to tetrapyrrole structures. For example, magnesium chelatase adds magnesium to protoporphyrin IX in the first step of bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis. Heme B is an essential cofactor in many proteins and enzymes. In particular, heme b plays a key role as the oxygen carrier in hemoglobin in red blood cells a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prosthetic group, component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 Vinyl group, vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. Heme plays a critical role in multiple different redox reactions in mammals, due to its ability to carry the oxygen molecule. Reactions include oxidative metabolism (cytochrome c oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase), xenobiotic detoxification via cytochrome P450 pathways (including Drug metabolism, metabolism of some drugs), gas sensing (Guanylate cyclase, guanyl cyclases, nitric oxide synthase), and microRNA processing (DGCR8). Heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protoporphyrin IX
Protoporphyrin IX is an organic compound, classified as a porphyrin, that plays an important role in living organisms as a precursor to other critical compounds like heme (hemoglobin) and chlorophyll. It is a deeply colored solid that is not soluble in water. The name is often abbreviated as PPIX. Protoporphyrin IX contains a porphine core, a tetrapyrrole macrocycle with a marked aromatic character. Protoporphyrin IX is essentially planar, except for the N-H bonds that are bent out of the plane of the rings, in opposite (trans) directions. Nomenclature The general term protoporphyrin refers to porphine derivatives that have the outer hydrogen atoms in the four pyrrole rings replaced by other functional groups. The prefix proto often means 'first' in science nomenclature (such as carbon protoxide), hence Hans Fischer is thought to have coined the name protoporphyrin as the first class of porphyrins. Fischer described iron-deprived heme becoming the "proto-" porphyrin, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heme Synthesis
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a ligand of various proteins, more notably as a component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. Heme plays a critical role in multiple different redox reactions in mammals, due to its ability to carry the oxygen molecule. Reactions include oxidative metabolism (cytochrome c oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase), xenobiotic detoxification via cytochrome P450 pathways (including metabolism of some drugs), gas sensing ( guanyl cyclases, nitric oxide synthase), and microRNA processing (DGCR8). Heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a tetrapyrrole acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands". The definition is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protoporphyrin IX With Letters
Protoporphyrin IX is an organic compound, classified as a porphyrin, that plays an important role in living organisms as a precursor to other critical compounds like heme (hemoglobin) and chlorophyll. It is a deeply colored solid that is not soluble in water. The name is often abbreviated as PPIX. Protoporphyrin IX contains a porphine core, a tetrapyrrole macrocycle with a marked aromatic character. Protoporphyrin IX is essentially planar, except for the N-H bonds that are bent out of the plane of the rings, in opposite (trans) directions. Nomenclature The general term protoporphyrin refers to porphine derivatives that have the outer hydrogen atoms in the four pyrrole rings replaced by other functional groups. The prefix proto often means 'first' in science nomenclature (such as carbon protoxide), hence Hans Fischer is thought to have coined the name protoporphyrin as the first class of porphyrins. Fischer described iron-deprived heme becoming the "proto-" porphyrin, particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ī²-sheets
The beta sheet (Ī²-sheet, also Ī²-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (Ī²-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A Ī²-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of Ī²-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies. History The first Ī²-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended Ī²-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose is released by the cell in the citric acid cycle, producing carbon dioxide and the energetic reducing agent, electron donors NADH and FADH. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules and O2 to ATP synthase, produce ATP, which is used throughout the cell whenever energy is needed. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from the electron donors to a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Target Peptide
A target peptide is a short (3-70 amino acids long) peptide chain that directs the transport of a protein to a specific region in the cell, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), chloroplast, apoplast, peroxisome and plasma membrane. Some target peptides are cleaved from the protein by signal peptidases after the proteins are transported. Types by protein destination Secretion Almost all proteins that are destined to the secretory pathway have a sequence consisting of 5-30 hydrophobic amino acids on the N-terminus, which is commonly referred to as the signal peptide, signal sequence or leader peptide. Signal peptides form alpha-helical structures. Proteins that contain such signals are destined for either extra-cellular secretion, the plasma membrane, the lumen or membrane of either the (ER), Golgi or endosomes. Certain membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which resembles a typical sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Post-translational Modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biology), translate mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then change to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signal transduction, signalling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C-terminus, C- or N-terminus, N- termini. They can expand the chemical set of the 22 proteinogenic amino acid, amino acids by changing an existing functional group or adding a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is highly effective for controlling the enzyme activity and is the most common change after translation. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ī±-helices
An alpha helix (or Ī±-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone NāH group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid that is four residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * PaulingāCoreyāBranson Ī±-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were dras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. LCysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Ancient Greek, Greek ĪŗĻĻĻĪ¹Ļ ''kĆ½stis'', "bladder". The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide bond, disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. When used as a food additive, cysteine has the E number E920. Cysteine is Genetic code, encoded by the codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
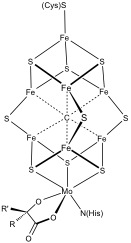
Ironāsulfur Protein
Ironāsulfur proteins are proteins characterized by the presence of ironāsulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states. Ironāsulfur clusters are found in a variety of metalloproteins, such as the ferredoxins, as well as NADH dehydrogenase, hydrogenases, coenzyme Q ā cytochrome c reductase, succinate ā coenzyme Q reductase and nitrogenase. Ironāsulfur clusters are best known for their role in the oxidation-reduction reactions of electron transport in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Both Complex I and Complex II of oxidative phosphorylation have multiple FeāS clusters. They have many other functions including catalysis as illustrated by aconitase, generation of radicals as illustrated by SAM-dependent enzymes, and as sulfur donors in the biosynthesis of lipoic acid and biotin. Additionally, some FeāS proteins regulate gene expression. FeāS proteins are vulnerable to attack by biogenic nitric oxide, formin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |