Platanaceae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Platanaceae, the plane family, is a 
Image:Platanus orientalis fruit body 01.jpg, Fruiting body of ''P. orientalis'' (Oriental plane).
Image:American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis) 2.jpg, Fruiting body of ''P. occidentalis'' (American sycamore) with some achenes removed
Image:Platanus nucula 01.JPG, An achene
Image:Fruit morphology fruit type - achene (from multiple fruit of achenes Platanus).svg, Cross section of an achene with the seed shown in brown
*
 The main use for a number of the species is to provide shade in pedestrian areas in temperate regions, particularly the London plane (''
The main use for a number of the species is to provide shade in pedestrian areas in temperate regions, particularly the London plane (''
AP-website
.
 The London plane or hybrid plane has long been considered a hybrid derived from the cross between ''P. occidentalis'' and ''P. orientalis'', despite this its origin is not clear. Some experts think it originated in London and others in Spain or even in natural or cultivated hybrid form (or not) in Turkey. The question has not been investigated with modern molecular methods. As a consequence, even its nomenclature is hotly debated, to the extent that until recently, some anglophone authors denied the priority of the name used by Otto von Münchhausen (following Maria da Luz de Oliveira Tavares Monteiro da Rocha Afonso, 1990, see References). The plant is not found in the wild, though it appears in a naturalised form along the banks of rivers and streams.
Hybrid ''
The London plane or hybrid plane has long been considered a hybrid derived from the cross between ''P. occidentalis'' and ''P. orientalis'', despite this its origin is not clear. Some experts think it originated in London and others in Spain or even in natural or cultivated hybrid form (or not) in Turkey. The question has not been investigated with modern molecular methods. As a consequence, even its nomenclature is hotly debated, to the extent that until recently, some anglophone authors denied the priority of the name used by Otto von Münchhausen (following Maria da Luz de Oliveira Tavares Monteiro da Rocha Afonso, 1990, see References). The plant is not found in the wild, though it appears in a naturalised form along the banks of rivers and streams.
Hybrid ''
Platanaceae
in L. Watson and M.J. Dallwitz (1992 onwards)
The families of flowering plants
.
''Flora of North America'': Platanaceae
''Flora of China'': Platanaceae
NCBI Taxonomy Browser
links at CSDL
Map, incomplete for Asia
Foliage of ''Platanus racemosa''
''Platanus wrightii''
Drawing of ''Platanus mexicana''
Female inflorescence of ''Platanus rzedowskii''
{{Authority control Eudicot families Extant Cretaceous first appearances
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
of flowering plants in the order Proteales
Proteales is an order of flowering plants consisting of three (or four) families. The Proteales have been recognized by almost all taxonomists.
The representatives of the Proteales can be very different from each other due to their very early d ...
. The family consists of only a single extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
genus ''Platanus
''Platanus'' ( ) is a genus consisting of a small number of tree species native to the Northern Hemisphere. They are the sole living members of the family Platanaceae.
All mature members of ''Platanus'' are tall, reaching in height. The type ...
'', with twelve known species. The plants are tall trees, native to temperate and subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The hybrid London plane
The London plane, or sometimes hybrid plane, ''Platanus'' × ''hispanica'', is a tree in the genus ''Platanus''. It is often known by the Synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'', a later name. It is a Hybrid (biology ...
is widely planted in cities worldwide.

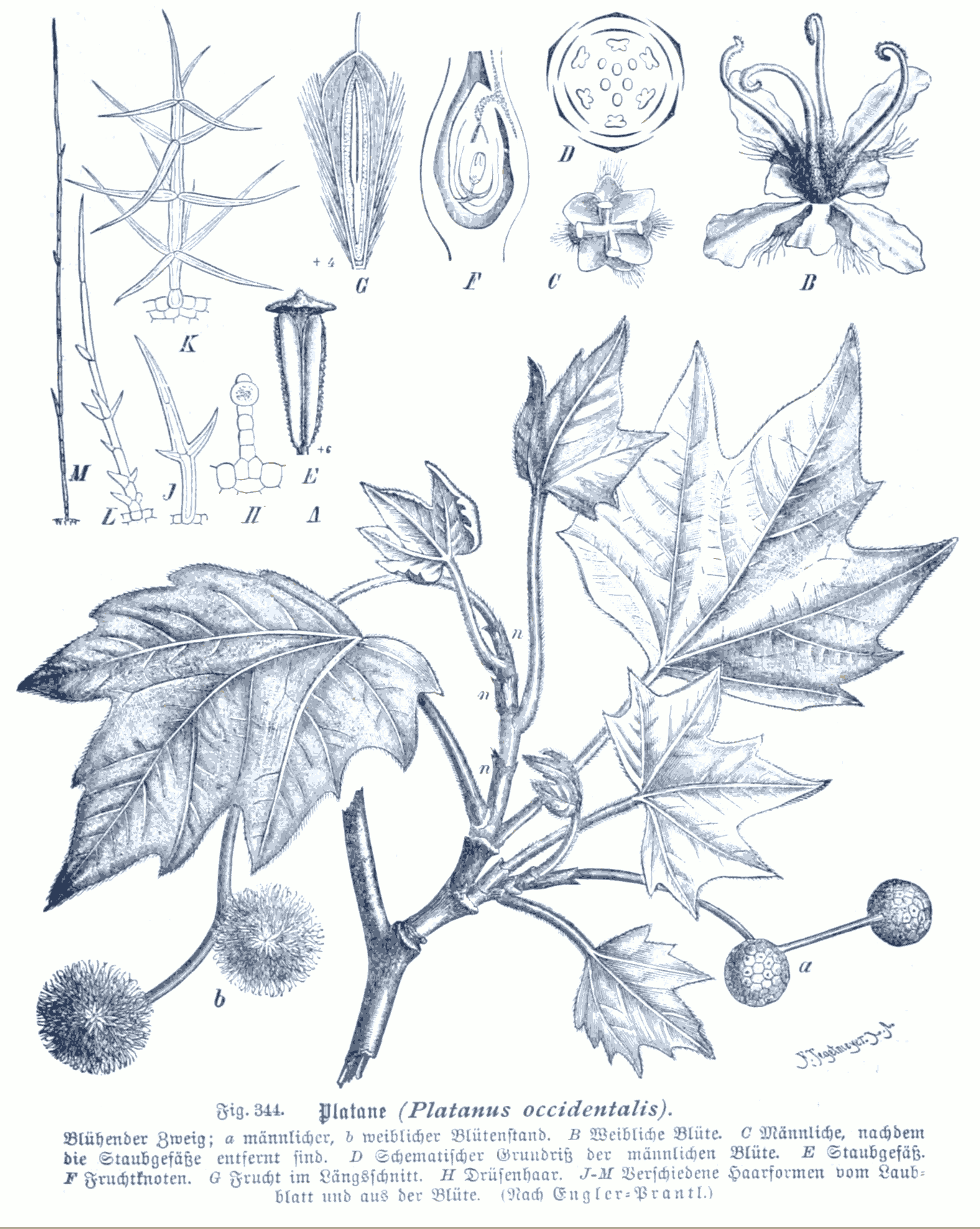
Description
* Large, sympodial, deciduoustree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
, speckled bark
Bark may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Arts and entertainment
* ''Bark'' (Jefferson Airplane album), ...
that sheds in large irregular sheets, leaving a smooth surface that is mottled and pale, persistent bark at the base of the trunk, indumentum with large glandular hairs, multicellular and uniserrate or short with uniserrate ramification (in candelabrum), in stellate fascicles; glandular hairs with unicellular, globular capitulum, cuticular waxes without crystalloids, with rods and plates
* Leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
generally with very variable shapes and nervation, simple, alternate, more or less distichous, isobilateral palmate with three to seven lobes (palmatifid to palmatisect) with whole edges or with glandular teeth (each one with a midvein that broadens towards the glandular apex, where it ends in an open hole), or penninerved and whole ('' Platanus kerrii''), this shape common in young, vernal leaves in other species, vernation
Vernation or leafing is the formation of new leaves or fronds. In plant anatomy, it is the arrangement of leaves in a bud.
In pine species, new leaves are short and encased in sheaths. Each leaf bundle consists of two to five needles. All the ...
folded, with the petiole usually sheathed, enclosing the axillary bud (bud is free in ''P. kerrii''), stipule
In botany, a stipule is an outgrowth typically borne on both sides (sometimes on just one side) of the base of a leafstalk (the petiole (botany), petiole). They are primarily found among dicots and rare among monocots. Stipules are considered part ...
s foliose, large, intrapetiolar, tubular, normally caduceus, in ''P. kerrii'' scarious, small, basally fused to the petiole, domatia
A domatium (plural: domatia, from the Latin "domus", meaning home) is a tiny chamber that houses arthropods, produced by a plant.
Ideally domatia differ from galls in that they are produced by the plant rather than being induced by their inhabi ...
present, stoma
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek language, Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exc ...
ta irregularly anomocytic
* Stem
Stem or STEM most commonly refers to:
* Plant stem, a structural axis of a vascular plant
* Stem group
* Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics
Stem or STEM can also refer to:
Language and writing
* Word stem, part of a word respon ...
s with aggregated rays in the xylem, with nodes septilacunar, cork cambium
Cork cambium (: cambia or cambiums) is a tissue found in many vascular plants as a part of the epidermis. It is one of the many layers of bark, between the cork and primary phloem. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for s ...
present and superficial, bud
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or Plant embryogenesis, embryonic Shoot (botany), shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a Plant stem, stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormancy, dormant conditi ...
s covered by single scale
* Plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s monoecious, the flowers of each sex in separate inflorescences
* Inflorescence
In botany, an inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a plant's Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a mai ...
s in large hanging peduncles, each one a unisexual, globular capitulum, pedunculate or seated, with numerous flowers, derived from the condensation of a panicle, with a circular bract
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale.
Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves in size, color, shape or texture. They also lo ...
at the base and bracteoles among the flowers
* Flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
s small, inconspicuous, hypogynous, regular unisexual, receptacle short, smooth, hypogynous disk absent, perianth
The perianth (perigonium, perigon or perigone in monocots) is the non-reproductive part of the flower. It is a structure that forms an envelope surrounding the sexual organs, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and the corolla (petals) or tepal ...
reduced, sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106
Etymology
The term ''sepalum'' ...
s number three to four, rarely eight, free or basally fused, shorter than the petals, triangular. Petal
Petals are modified leaves that form an inner whorl surrounding the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly coloured or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corol ...
s number three to four, rarely eight, truncated-spatulate or vestigial, scarious, frequently absent in the female flowers, male flowers with androecium haplostemonous, isostemonous, oppositisepal, with number three to four, rarely eight, stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
s, gynostemium short or vestigial, anther
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
s basifixed, not versatile, dithecous, tetrasporangiate, elongated, connectivum apically widened, peltate, dehiscence along longitudinal valves; pistillidium sometimes present, female flowers with superior gynoecium carpel
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more ...
s apocarpous in two or three whorl
A whorl ( or ) is an individual circle, oval, volution or equivalent in a whorled pattern, which consists of a spiral or multiple concentric objects (including circles, ovals and arcs).
In nature
File:Photograph and axial plane floral diagra ...
s, imperfectly closed apically, surrounded by large petals, linear stylodious, stigmas internal, decurrent in two ridges, more or less dry, two ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the sporangium, megasporangium), ...
s per carpel but one nearly always aborts, orthotropous, bitegmic, crassinucellated, pendulous, apical to marginal placentation
Placentation is the formation, type and structure, or modes of arrangement of the placenta. The function of placentation is to transfer nutrients, respiratory gases, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in some instances to re ...
, three or four staminode
In botany, a staminode is an often rudimentary, sterile or abortive stamen, which means that it does not produce pollen.Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; ''A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent''; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co ...
s 3-4, no nectaries
* Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
in an achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple fruit, simple dry fruits, dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and Dehi ...
, clavate, grouped in a globular capituliform infructescence
In botany, infructescence (fruiting head) is defined as the ensemble of fruits derived from the ovaries of an inflorescence. It usually retains the size and structure of the inflorescence.
In some cases, infructescences are similar in appearance ...
, each fruit surrounded by long hairs
Seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s are small with thin testa with little endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
, oily and proteinaceous, embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
thin and straight with two linear cotyledons, often uneven
* Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
in subprolate monads, 16-22 μm in length, tricolpate, sometimes sextarugate, tectate-columellate, reticulated surface, the base layer as thick as the tectum
* Chromosomal number: ''2n'' = 14, 16, 21, 42; ''x'' probably equal to 7 or 8
Ecology
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or bu ...
is anemophilous
Anemophily or wind pollination is a form of pollination whereby pollen is distributed by wind. Almost all gymnosperms are anemophilous, as are many plants in the order Poales, including grasses, sedges, and rushes. Other common anemophilous pla ...
; flowering begins at the start of spring when the new leaves are sprouting. The heads that sustain the fruit normally shed the year after they have matured, during the autumn. Dispersion of the individual fruiting bodies, with their thistledown, is anemochorous (they are sometimes dispersed by water as a secondary mechanism).
The plants grow in cool situations in temperate climates and are frequently found on the banks of rivers and streams. They are totally absent from dry or excessively cold areas.
Phytochemistry
They containcyanogenic glycosides
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. ...
derived from tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
, flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids ...
s belonging to the proanthocyanidins group (e.g. prodelphinidin
Prodelphinidin is a name for the polymeric tannins composed of gallocatechin. It yields delphinidin during depolymerisation under oxidative conditions.
Natural occurrences
Prodelphinidins are one of the two sorts of tannins in grape (the other ...
) and flavonol
Flavonols are a class of flavonoids that have the 3-hydroxyflavone backbone (IUPAC name: 3-hydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one). Their diversity stems from the different positions of the phenolic –OH groups. They are distinct from flavanols (with ...
s (kaempferol
Kaempferol (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a natural flavonol, a type of flavonoid, found in a variety of plants and plant-derived foods including kale, beans, tea, spinach, and broccoli. It is also found in propolis extracts. Kaempferol i ...
, quercetin
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor ...
, myricetin
Myricetin is a member of the flavonoid class of polyphenolic compounds, with antioxidant properties. Common dietary sources include vegetables (including tomatoes), fruits (including oranges), nuts, berries, tea, and red wine.
Myricetin is stru ...
), in addition to triterpenols (including betulinic acid
Betulinic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid which has antiretroviral, antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase. ...
). They lack ellagic acid
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.
Name
The name comes from the French term ''acide ellagique'', from the word ''galle'' spelled backward because it can be o ...
, saponin
Saponins (Latin ''sapon'', 'soap' + ''-in'', 'one of') are bitter-tasting, usually toxic plant-derived secondary metabolites. They are organic chemicals that become foamy when agitated in water and have high molecular weight. They are present ...
s, and sapogenin
Sapogenins are aglycones (non-saccharide moieties) of saponins, a large family of natural products. Sapogenins contain steroid or other triterpene frameworks as their key organic feature. For example, steroidal sapogenins such as tiggenin, neo ...
s.
Cultivation
 The main use for a number of the species is to provide shade in pedestrian areas in temperate regions, particularly the London plane (''
The main use for a number of the species is to provide shade in pedestrian areas in temperate regions, particularly the London plane (''Platanus × hispanica
The London plane, or sometimes hybrid plane, ''Platanus'' × ''hispanica'', is a tree in the genus ''Platanus''. It is often known by the synonym ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'', a later name. It is a hybrid of '' Platanus orientalis'' ...
''), which is widely distributed throughout Europe and North America. It is highly resistant, probably due to so-called hybrid vigour, although its use requires caution due to their allergy-producing thistledown. The parent species are also grown for the same effect, but with poorer results as they are less resistant to contamination, among other reasons. The wood is used in cabinetmaking, paneling, and other interior work, and is also prized for its long burn time.
Fossils
A large number of fossils of this family have been recorded from the LowerCretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
(98-113 million years ago, ''Platanocarpus''). The examples from that time had very small pollen (8-10 μm) and a developed perianth and they lacked hairs at the base of the nucule. It is thought to have had entomophilous pollination. During the mid Cretaceous, the fossilized forms with platanoid leaves became mixed with pinnate leaves (''Sapindopsis'') or pedatisect leaves (''Debeya'', ''Dewalquea''), and these forms lasted until the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
. The leaves with typical stipules belonging to the sub-genus ''Platanus'' are very common in Palaeocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palai ...
formations (60 M years ago). It is thought that the only modern genus, ''Platanus'', is a relict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.
Biology
A relict (or relic) is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas.
Geology and geomorphology
In geology, a r ...
that can be considered a living fossil
A living fossil is a Deprecation, deprecated term for an extant taxon that phenotypically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of or ...
. It must have been polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning ...
during its evolution judging by the size of its stomata.
Systematic position
TheAPG II system
The APG II system (Angiosperm Phylogeny Group II system) of plant classification is the second, now obsolete, version of a modern, mostly Molecular phylogenetics, molecular-based, list of systems of plant taxonomy, system of plant taxonomy that ...
(2003) allows the option of including it in the family Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family (biology), family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genus, genera with about 1,660 known species. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentr ...
, or treating it as distinct as a segregate family. In as far as APG II accepts the family, it is placed in the order Proteales
Proteales is an order of flowering plants consisting of three (or four) families. The Proteales have been recognized by almost all taxonomists.
The representatives of the Proteales can be very different from each other due to their very early d ...
, in the clade eudicots
The eudicots or eudicotyledons are flowering plants that have two seed leaves (cotyledons) upon germination. The term derives from ''dicotyledon'' (etymologically, ''eu'' = true; ''di'' = two; ''cotyledon'' = seed leaf). Historically, authors h ...
. This represents a slight change from the APG system
The APG system (Angiosperm Phylogeny Group system) of plant classification is the first version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy. Published in 1998 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, it was replaced by the improved ...
of 1998, which did accept this family. The Cronquist system
The Cronquist system is a list of systems of plant taxonomy, taxonomic classification system of angiosperms, flowering plants. It was developed by Arthur Cronquist in a series of monographs and texts, including ''The Evolution and Classification of ...
of 1981 recognized the family and placed it in order Hamamelidales, in subclass Hamamelidae in class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Dahlgren system and Thorne system (1992) also recognized this family and placed it in the order Hamamelidales in superorder Rosanae in subclass Magnoliidae ''sensu'' Dahlgren and Thorne (dicotyledons). The Engler system
One of the prime systems of plant taxonomy, the Engler system was devised by Adolf Engler (1844–1930), and is featured in two major taxonomic texts he authored or co-authored. His influence is reflected in the use of the terms "Engler School" and ...
, in its 1964 update, also recognized the family and placed it in the order Rosales
Rosales (, ) are an order of flowering plants. Peter F. Stevens (2001 onwards). "Rosales". At: Trees At: Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. At: Missouri Botanical Garden Website. (see ''External links'' below) Well-known members of Rosales include: ...
in subclass Archichlamydeae of class Dicotyledoneae. The Wettstein system
A list of systems of plant taxonomy, system of plant taxonomy, the Wettstein system recognised the following main groups, according to Richard Wettstein's ''Handbuch der Systematischen Botanik'' (1901–1924).
3rd edition (1924)
Outline
Syn ...
, last revised in 1935, also recognized the family and placed it in the order Hamamelidales in the Monochlamydeae in subclass Choripetalae of the class Dicotyledones. Based on molecular and morphological data the APW (Angiosperm Phylogeny Website) places the family in the order Proteales as a sister family to the Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family (biology), family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genus, genera with about 1,660 known species. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentr ...
, making them the Northern Hemisphere version of this family (cf.AP-website
.
Taxa included
:''Theoretical introduction toTaxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
''
The only extant genus, ''Platanus'' L., 1753, has the type species '' Platanus orientalis'' L., 1753. It is divided into two subgenera: the subgenus ''Castaneophyllum'' J.-F. Leroy, 1982, with elliptical, penninerved leaves with small scarious, stipules, that only includes '' Platanus kerrii'' Gagnep., 1939, an isolated relict species that represents the genus’ evolutionary basal branch and which is the sister group of the other species, which comprise the subgenus ''Platanus''.
Hybrids
 The London plane or hybrid plane has long been considered a hybrid derived from the cross between ''P. occidentalis'' and ''P. orientalis'', despite this its origin is not clear. Some experts think it originated in London and others in Spain or even in natural or cultivated hybrid form (or not) in Turkey. The question has not been investigated with modern molecular methods. As a consequence, even its nomenclature is hotly debated, to the extent that until recently, some anglophone authors denied the priority of the name used by Otto von Münchhausen (following Maria da Luz de Oliveira Tavares Monteiro da Rocha Afonso, 1990, see References). The plant is not found in the wild, though it appears in a naturalised form along the banks of rivers and streams.
Hybrid ''
The London plane or hybrid plane has long been considered a hybrid derived from the cross between ''P. occidentalis'' and ''P. orientalis'', despite this its origin is not clear. Some experts think it originated in London and others in Spain or even in natural or cultivated hybrid form (or not) in Turkey. The question has not been investigated with modern molecular methods. As a consequence, even its nomenclature is hotly debated, to the extent that until recently, some anglophone authors denied the priority of the name used by Otto von Münchhausen (following Maria da Luz de Oliveira Tavares Monteiro da Rocha Afonso, 1990, see References). The plant is not found in the wild, though it appears in a naturalised form along the banks of rivers and streams.
Hybrid ''Platanus × hispanica
The London plane, or sometimes hybrid plane, ''Platanus'' × ''hispanica'', is a tree in the genus ''Platanus''. It is often known by the synonym ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'', a later name. It is a hybrid of '' Platanus orientalis'' ...
'' Mill. ex Münchh., 1770 (= ''P. orientalis'' var. ''acerifolia'' Aiton, 1789; ''P. hybrida'' Brot., 1804; ''P. vulgaris'' Spach, 1841, ''nom. illeg.''; ''P. × acerifolia''.
Other names proposed for hybrids that are probably synonymous with the above, which is the only name in English, and which represent smaller minorities are:
* Hybrid ''Platanus'' × ''cantabrigensis'' A.Henry, 1919
* Hybrid ''Platanus'' × ''parviloba'' A.Henry, 1919
The references consulted do not agree as to whether the fruit is a nucule or achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple fruit, simple dry fruits, dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and Dehi ...
, the difference between the two ultimately depends on the size of the pericarp and the extent of its lignification. The fruit is dry, indehiscent, monocarpelar and monospermatic.
References
* * *External links
* *Platanaceae
in L. Watson and M.J. Dallwitz (1992 onwards)
The families of flowering plants
.
''Flora of North America'': Platanaceae
''Flora of China'': Platanaceae
NCBI Taxonomy Browser
links at CSDL
Map, incomplete for Asia
Foliage of ''Platanus racemosa''
''Platanus wrightii''
Drawing of ''Platanus mexicana''
Female inflorescence of ''Platanus rzedowskii''
{{Authority control Eudicot families Extant Cretaceous first appearances