Plant Nutrients In Soil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Seventeen elements or
 Plants obtain their carbon from atmospheric
Plants obtain their carbon from atmospheric
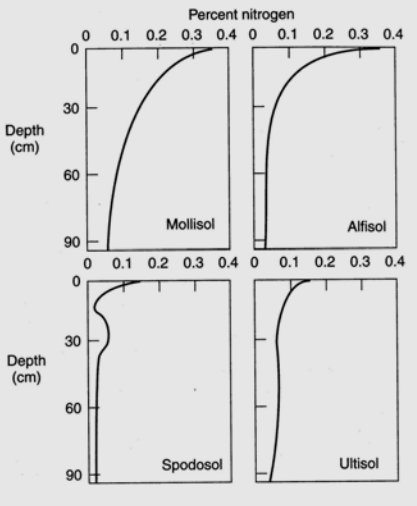 Nitrogen is the most critical element obtained by plants from the soil, to the exception of moist tropical forests where phosphorus is the limiting soil nutrient, and nitrogen deficiency often limits plant growth. Plants can use nitrogen as either the
Nitrogen is the most critical element obtained by plants from the soil, to the exception of moist tropical forests where phosphorus is the limiting soil nutrient, and nitrogen deficiency often limits plant growth. Plants can use nitrogen as either the
nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
are essential for plant growth and reproduction. They are carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
(C), hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
(H), oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
(O), nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
(N), phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
(P), potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
(K), sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
(S), calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
(Ca), magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
(Mg), iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
(Fe), boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
(B), manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
(Mn), copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
(Cu), zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
(Zn), molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
(Mo), nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
(Ni) and chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
(Cl). Nutrients required for plants to complete their life cycle are considered essential nutrients. Nutrients that enhance the growth of plants but are not necessary to complete the plant's life cycle are considered non-essential, although some of them, such as silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
(Si), have been shown to improve nutrient availability, hence the use of stinging nettle
''Urtica dioica'', often known as common nettle, burn nettle, stinging nettle (although not all plants of this species sting) or nettle leaf, or just a nettle or stinger, is a herbaceous perennial flowering plant in the family Urticaceae. Or ...
and horsetail (both silica-rich) macerations in Biodynamic agriculture
Biodynamic agriculture is a form of alternative agriculture based on pseudoscientific and esoteric concepts initially developed in 1924 by Rudolf Steiner (1861–1925). It was the first of the organic farming movements. It treats soil fertility, ...
. With the exception of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, which are supplied by carbon dioxide and water, and nitrogen, provided through nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
, the nutrients derive originally from the mineral component of the soil. The Law of the Minimum expresses that when the available form of a nutrient is not in enough proportion in the soil solution, then other nutrients cannot be taken up at an optimum rate by a plant. A particular nutrient ratio of the soil solution is thus mandatory for optimizing plant growth, a value which might differ from nutrient ratios calculated from plant composition.
Plant uptake of nutrients can only proceed when they are present in a plant-available form. In most situations, nutrients are absorbed in an ionic form by diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
or absorption of the soil water. Although minerals are the origin of most nutrients, and the bulk of most nutrient elements in the soil is held in crystalline form within primary and secondary minerals, they weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
too slowly to support rapid plant growth. For example, the application of finely ground minerals, feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagiocl ...
and apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of Hydroxide, OH−, Fluoride, F− and Chloride, Cl− ion, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of ...
, to soil seldom provides the necessary amounts of potassium and phosphorus at a rate sufficient for good plant growth, as most of the nutrients remain bound in the crystals of those minerals.
The nutrients adsorbed onto the surfaces of clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
colloids and soil organic matter
Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize. SOM provides numerou ...
provide a more accessible reservoir of many plant nutrients (e.g. K, Ca, Mg, P, Zn). As plants absorb the nutrients from the soil water, the soluble pool is replenished from the surface-bound pool. The decomposition of soil organic matter
Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize. SOM provides numerou ...
by microorganisms is another mechanism whereby the soluble pool of nutrients is replenished – this is important for the supply of plant-available N, S, P, and B from soil.
Gram for gram, the capacity of humus
In classical soil science, humus is the dark organic matter in soil that is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter. It is a kind of soil organic matter. It is rich in nutrients and retains moisture in the soil. Humus is the Lati ...
to hold nutrients and water is far greater than that of clay minerals, most of the soil cation exchange capacity arising from charged carboxylic
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e. ...
groups on organic matter. However, despite the great capacity of humus to retain water once water-soaked, its high hydrophobicity
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly intermolecular force, repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to b ...
decreases its wettability. All in all, small amounts of humus may remarkably increase the soil's capacity to promote plant growth.
Uptake processes
Nutrients in the soil are taken up by the plant through its roots, and in particular its root hairs. To be taken up by a plant, a nutrient element must be located near the root surface; however, the supply of nutrients in contact with the root is rapidly depleted within a distance of ca. 2 mm. There are three basic mechanisms whereby nutrient ions dissolved in the soil solution are brought into contact with plant roots: # Mass flow of water #Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
within water
# Interception by root growth
All three mechanisms operate simultaneously, but one mechanism or another may be most important for a particular nutrient. For example, in the case of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, which is generally plentiful in the soil solution, except when aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
over competes calcium on cation exchange sites in very acid soils (pH less than 4), mass flow alone can usually bring sufficient amounts to the root surface. However, in the case of phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, diffusion is needed to supplement mass flow. For the most part, nutrient ions must travel some distance in the soil solution to reach the root surface. This movement can take place by mass flow, as when dissolved nutrients are carried along with the soil water flowing toward a root that is actively drawing water from the soil. In this type of movement, the nutrient ions are somewhat analogous to leaves floating down a stream. In addition, nutrient ions continually move by diffusion from areas of greater concentration toward the nutrient-depleted areas of lower concentration around the root surface. That process is due to random motion, also called Brownian motion
Brownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas). The traditional mathematical formulation of Brownian motion is that of the Wiener process, which is often called Brownian motion, even in mathematical ...
, of molecules within a gradient of decreasing concentration. By this means, plants can continue to take up nutrients even at night, when water is only slowly absorbed into the roots as transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. It is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. Transpiration also cools plants, c ...
has almost stopped following stomatal closure. Finally, root interception comes into play as roots continually grow into new, undepleted soil. By this way roots are also able to absorb nanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science ...
such as nanoparticulate organic matter.
In the above table, phosphorus and potassium nutrients move more by diffusion than they do by mass flow in the soil water solution, as they are rapidly taken up by the roots creating a concentration of almost zero near the roots (the plants cannot transpire enough water to draw more of those nutrients near the roots). The very steep concentration gradient is of greater influence in the movement of those ions than is the movement of those by mass flow. The movement by mass flow requires the transpiration of water from the plant causing water and solution ions to also move toward the roots. Movement by root interception is slowest, being at the rate plants extend their roots.
Plants move ions out of their roots in an effort to move nutrients in from the soil, an exchange process which occurs in the root apoplast. Hydrogen H+ is exchanged for other cations, and carbonate (HCO3−) and hydroxide (OH−) anions are exchanged for nutrient anions. As plant roots remove nutrients from the soil water solution, they are replenished as other ions move off of clay and humus (by ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of ch ...
or desorption
Desorption is the physical process where Adsorption, adsorbed atoms or molecules are released from a surface into the surrounding vacuum or fluid. This occurs when a molecule gains enough energy to overcome the activation barrier and the binding e ...
), are added from the weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals (as well as wood and artificial materials) through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms. It occurs '' in situ'' (on-site, with little or no move ...
of soil minerals, and are released by the decomposition of soil organic matter. However, the rate at which plant roots remove nutrients may not cope with the rate at which they are replenished in the soil solution, stemming in nutrient limitation to plant growth. Plants derive a large proportion of their anion nutrients from decomposing organic matter, which typically holds about 95 percent of the soil nitrogen, 5 to 60 percent of the soil phosphorus and about 80 percent of the soil sulfur. Where crops are produced, the replenishment of nutrients in the soil must usually be augmented by the addition of fertilizer or organic matter.
Because nutrient uptake is an active metabolic process, conditions that inhibit root metabolism may also inhibit nutrient uptake. Examples of such conditions include waterlogging or soil compaction
In geotechnical engineering, soil compaction is the process in which stress applied to a soil causes densification as air is displaced from the pores between the soil grains. When stress is applied that causes densification due to water (or other ...
resulting in poor soil aeration, excessively high or low soil temperatures, and above-ground conditions that result in low translocation of sugars to plant roots.
Carbon
 Plants obtain their carbon from atmospheric
Plants obtain their carbon from atmospheric carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
through photosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
carboxylation, to which must be added the uptake of dissolved carbon from the soil solution and carbon transfer through mycorrhizal networks. About 45% of a plant's dry mass is carbon; plant residues typically have a carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N) of between 13:1 and 100:1. As the soil organic material is digested by micro-organisms and saprophagous soil fauna
Soil biology is the study of Soil microbiology, microbial and faunal activity and ecology in soil.
Soil life, soil biota, soil fauna, or edaphon is a collective term that encompasses all organisms that spend a significant portion of their biolo ...
, the C/N decreases as the carbonaceous material is metabolized and carbon dioxide (CO2) is released as a byproduct which then finds its way out of the soil and into the atmosphere. Nitrogen turnover (mostly involved in protein turnover
In cell biology, protein turnover refers to the replacement of older proteins as they are broken down within the cell. Different types of proteins have very different turnover rates.
A balance between protein synthesis and protein degradation ...
) is lesser than that of carbon (mostly involved in respiration) in the living, then dead matter of decomposers, which are always richer in nitrogen than plant litter, and so it builds up in the soil. Normal CO2 concentration in the atmosphere is 0.03%, this can be the factor limiting plant growth. In a field of maize on a still day during high light conditions in the growing season, the CO2 concentration drops very low, but under such conditions the crop could use up to 20 times the normal concentration. The respiration of CO2 by soil micro-organisms decomposing soil organic matter and the CO2 respired by roots contribute an important amount of CO2 to the photosynthesising plants, to which must be added the CO2 respired by aboveground plant tissues. Root-respired CO2 can be accumulated overnight within hollow stems of plants, to be further used for photosynthesis during the day. Within the soil, CO2 concentration is 10 to 100 times that of atmospheric levels but may rise to toxic levels if the soil porosity is low or if diffusion is impeded by flooding.
Nitrogen
 Nitrogen is the most critical element obtained by plants from the soil, to the exception of moist tropical forests where phosphorus is the limiting soil nutrient, and nitrogen deficiency often limits plant growth. Plants can use nitrogen as either the
Nitrogen is the most critical element obtained by plants from the soil, to the exception of moist tropical forests where phosphorus is the limiting soil nutrient, and nitrogen deficiency often limits plant growth. Plants can use nitrogen as either the ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
cation (NH4+) or the anion nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
(NO3−). Plants are commonly classified as ammonium or nitrate plants according to their preferential nitrogen nutrition. Usually, most of the nitrogen in soil is bound within organic compounds that make up the soil organic matter
Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize. SOM provides numerou ...
, and must be mineralized to the ammonium or nitrate form before it can be taken up by most plants. However, symbiosis with mycorrhizal fungi allow plants to get access to the organic nitrogen pool where and when mineral forms of nitrogen are poorly available. The total nitrogen content depends largely on the soil organic matter content, which in turn depends on texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Image texture, the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image
* Surface texture, the smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface c ...
, climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
, vegetation, topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
, age and soil management
Soil management is the application of operations, practices, and treatments to protect soil and enhance its performance (such as soil fertility or soil mechanics). It includes soil conservation, soil amendment, and optimal soil health. In agricult ...
. Soil nitrogen typically decreases by 0.2 to 0.3% for every temperature increase by 10 °C. Usually, grassland soils contain more soil nitrogen than forest soils, because of a higher turnover rate of grassland organic matter. Cultivation decreases soil nitrogen by exposing soil organic matter to decomposition by microorganisms, most losses being caused by denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
, and soils under no-tillage maintain more soil nitrogen than tilled soils.
Some micro-organisms are able to metabolise organic matter and release ammonium in a process called mineralisation. Others, called nitrifiers, take free ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
or nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name ...
as an intermediary step in the process of nitrification
''Nitrification'' is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrate via the intermediary nitrite. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. The process of complete nitrification may occur through separate organisms or ent ...
, and oxidise it to nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are capable of metabolising N2 into the form of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
or related nitrogenous compounds in a process called nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
. Both ammonium and nitrate can be immobilized by their incorporation into microbial living cells, where it is temporarily sequestered in the form of amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
and proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
. Nitrate may be lost from the soil to the atmosphere when bacteria metabolise it to the gases NH3, N2 and N2O, a process called denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
. Nitrogen may also be leached from the vadose zone
The vadose zone (from the Latin word for "shallow"), also termed the unsaturated zone, is the part of Earth between the land surface and the top of the phreatic zone, the position at which the groundwater (the water in the soil's pores) is at ...
if in the form of nitrate, acting as a pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effect, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like oi ...
if it reaches the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the phreatic zone or zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with groundwater, which may be fresh, saline, or brackish, depending on the loc ...
or flows over land, more especially in agricultural soils under high use of nutrient fertilizers. Ammonium may also be sequestered in 2:1 clay minerals
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates (e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4), sometimes with variable amounts of iron, magnesium, alkali metals, alkaline earths, and other cations found on or near some planetary surfaces.
Clay mineral ...
. A small amount of nitrogen is added to soil by rainfall
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. ...
, to the exception of wide areas of North America and West Europe where the excess use of nitrogen fertilizers and manure
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the fertility of soil by adding organic matter and nut ...
has caused atmospheric pollution by ammonia emission, stemming in soil acidification and eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
of soils and aquatic ecosystems.
Gains
In the process of mineralisation, microbes feed on organic matter, releasing ammonia (NH3), ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3−) and other nutrients. As long as the carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N) of fresh residues in the soil is above 30:1, nitrogen will be in short supply for the nitrogen-rich microbal biomass ( nitrogen deficiency), and other bacteria will uptake ammonium and to a lesser extent nitrate and incorporate them into their cells in the immobilization process. In that form the nitrogen is said to be ''immobilised''. Later, when such bacteria die, they too are ''mineralised'' and some of the nitrogen is released as ammonium and nitrate. Predation of bacteria by soil fauna, in particularprotozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
and nematodes
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (he ...
, play a decisive role in the return of immobilized nitrogen to mineral forms. If the C/N of fresh residues is less than 15, mineral nitrogen is freed to the soil and directly available to plants. Bacteria may on average add nitrogen per acre, and in an unfertilised field, this is the most important source of usable nitrogen. In a soil with 5% organic matter perhaps 2 to 5% of that is released to the soil by such decomposition. It occurs fastest in warm, moist, well aerated soil. The mineralisation of 3% of the organic material of a soil that is 4% organic matter overall, would release of nitrogen as ammonium per acre.
In nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
, rhizobium
''Rhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. ''Rhizobium'' species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of (primarily) legumes and other flowering plants.
The bacteria colonize plant ce ...
bacteria convert N2 to ammonia (NH3), which is rapidly converted to amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
, parts of which are used by the rhizobia for the synthesis of their own biomass proteins, while other parts are transported to the xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts o ...
of the host plant. Rhizobia
Rhizobia are diazotrophic bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside the root nodules of legumes (Fabaceae). To express genes for nitrogen fixation, rhizobia require a plant host; they cannot independently fix nitrogen. I ...
share a symbiotic relationship
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biolo ...
with host plants, since rhizobia supply the host with nitrogen and the host provides rhizobia with other nutrients and a safe environment. It is estimated that such symbiotic bacteria in the root nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known ...
s of legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s add 45 to 250 pounds of nitrogen per acre per year, which may be sufficient for the crop. Other, free-living nitrogen-fixing diazotroph
Diazotrophs are organisms capable of nitrogen fixation, i.e. converting the relatively inert diatomic nitrogen (N2) in Earth's atmosphere into bioavailable compound forms such as ammonia. Diazotrophs are typically microorganisms such as bacteria ...
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
live independently in the soil and release mineral forms of nitrogen when their dead bodies are converted by way of mineralization.
Some amount of atmospheric nitrogen is transformed by lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
s in gaseous nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
(NO) and nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, is an intermediate in the s ...
(NO2−). Nitrogen dioxide is soluble in water to form nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
(HNO3) dissociating in H+ and NO3−. Ammonia, NH3, previously emitted from the soil, may fall with precipitation as nitric acid at a rate of about five pounds nitrogen per acre per year.
Sequestration
When bacteria feed on soluble forms of nitrogen (ammonium and nitrate), they temporarily sequester that nitrogen in their bodies in a process called immobilization. At a later time when those bacteria die, their nitrogen may be released as ammonium by the process of mineralization, sped up by predatory fauna. Protein material is easily broken down, but the rate of its decomposition is slowed by its attachment to the crystalline structure of clay and when trapped between the clay layers or attached to rough clay surfaces. The layers are small enough that bacteria cannot enter. Some organisms exude extracellular enzymes that can act on the sequestered proteins. However, those enzymes too may be trapped on the clay crystals, resulting in a complex interaction between proteins, microbial enzymes and mineral surfaces. Ammonium fixation occurs mainly between the layers of 2:1 type clay minerals such as illite,vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently; commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the weathe ...
or montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite grou ...
, together with ions of similar ionic radius
Ionic radius, ''r''ion, is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, they are treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cati ...
and low hydration energy such as potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
, but a small proportion of ammonium is also fixed in the silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
fraction. Only a small fraction of soil nitrogen is held this way.
Losses
Usable nitrogen may be lost from soils when it is in the form ofnitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
, as it is easily leached, contrary to ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
which is easily fixed. Further losses of nitrogen occur by denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
, the process whereby soil bacteria convert nitrate (NO3−) to nitrogen gas, N2 or N2O. This occurs when poor soil aeration limits free oxygen, forcing bacteria to use the oxygen in nitrate for their respiratory process. Denitrification increases when oxidisable organic material is available, as in organic farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of ...
and when soils are warm and slightly acidic, as currently happens in tropical areas. Denitrification may vary throughout a soil as the aeration varies from place to place. Denitrification may cause the loss of 10 to 20 percent of the available nitrates within a day and when conditions are favourable to that process, losses of up to 60 percent of nitrate applied as fertiliser may occur.
Ammonia volatilisation occurs when ammonium reacts chemically with an alkaline soil
Alkali, or alkaline, soils are clay soils with high Soil pH, pH (greater than 8.5), a poor soil structure and a low infiltration capacity. Often they have a hard calcareous layer at 0.5 to 1 metre depth. Alkali soils owe their unfavorable ...
, converting NH4+ to NH3. The application of ammonium fertiliser to such a field can result in volatilisation losses of as much as 30 percent.
All kinds of nitrogen losses, whether by leaching or volatilization, are responsible for a large part of aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
pollution and air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
, with concomitant effects on soil acidification and eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
, a novel combination of environmental threats (acidity and excess nitrogen) to which extant organisms are badly adapted, causing severe biodiversity losses in natural ecosystems.
Phosphorus
After nitrogen, phosphorus is probably the element most likely to be deficient in soils, although it often turns to be the most deficient in tropical soils where the mineral pool is depleted under intense leaching and mineral weathering while, contrary to nitrogen, phosphorus reserves cannot be replenished from other sources. The soil mineralapatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of Hydroxide, OH−, Fluoride, F− and Chloride, Cl− ion, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of ...
is the most common mineral source of phosphorus, from which it can be extracted by microbial and root exudates, with an important contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The most common form of organic phosphate is phytate
Phytic acid is a six-fold dihydrogenphosphate ester of inositol (specifically, of the ''myo'' isomer), also called inositol hexaphosphate, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) or inositol polyphosphate. At physiological pH, the phosphates are partia ...
, the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues. While there is on average 1000 lb per acre (1120 kg per hectare) of phosphorus in the soil, it is generally in the form of orthophosphate
In chemistry, a phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners ...
with low solubility, except when linked to ammonium or calcium, hence the use of diammonium phosphate
Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4)) is one of a series of water- soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid.
Solid diammonium ph ...
or monocalcium phosphate
Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless so ...
as fertilizers. Total phosphorus is about 0.1 percent by weight of the soil, but only one percent of that is directly available to plants. Of the part available, more than half comes from the mineralisation of organic matter. Agricultural fields may need to be fertilised to make up for the phosphorus that has been removed in the crop.
When phosphorus does form solubilised ions of H2PO4−, if not taken up by plant roots these ions rapidly form insoluble calcium phosphates or hydrous oxides of iron and aluminum. Phosphorus is largely immobile in the soil and is not leached but actually builds up in the surface layer if not cropped. The application of soluble fertilisers to soils may result in zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
deficiencies as zinc phosphates form, but soil pH levels, partly depending on the form of phosphorus in the fertiliser, strongly interact with this effect, in some cases resulting in increased zinc availability. Lack of phosphorus may interfere with the normal opening of the plant leaf stomata
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange between the internal air spa ...
, decreased stomatal conductance resulting in decreased photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
and respiration rates while decreased transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. It is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. Transpiration also cools plants, c ...
increases plant temperature. Phosphorus is most available when soil pH is 6.5 in mineral soils and 5.5 in organic soils.
Potassium
The amount of potassium in a soil may be as much as 80,000 lb per acre-foot, of which only 150 lb is available for plant growth. Common mineral sources of potassium are the micabiotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron- endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more al ...
and potassium feldspar, KAlSi3O8. Rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or Substrate (biology), substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Pore space in soil, Soil pores in the rhizosphere can ...
bacteria, also called rhizobacteria, contribute through the production of organic acids to its solubilization. When solubilised, half will be held as exchangeable cations on clay while the other half is in the soil water solution. Potassium fixation often occurs when soils dry and the potassium is bonded between layers of 2:1 expansive clay
Expansive clay, also called expansive soil, is a clay soil prone to large volume changes (swelling and shrinking) directly related to changes in water content. Soils with a high content of expansive minerals can form deep cracks in drier seasons ...
minerals such as illite, vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently; commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the weathe ...
or montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite grou ...
. Under certain conditions, dependent on the soil texture, intensity of drying, and initial amount of exchangeable potassium, the fixed percentage may be as much as 90 percent within ten minutes. Potassium may be leached from soils low in clay.
Calcium
Calcium is one percent by weight of soils and is generally available but may be low as it is soluble and can be leached. It is thus low in sandy and heavily leached soil or strongly acidic mineral soils, resulting in excessive concentration of free hydrogen ions in the soil solution, and therefore these soils require liming. Calcium is supplied to the plant in the form of exchangeable ions and moderately soluble minerals. There are four forms of calcium in the soil. Soil calcium can be in insoluble forms such ascalcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
or dolomite, in the soil solution in the form of a divalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemica ...
cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
or retained in exchangeable form at the surface of mineral particles. Another form is when calcium complexes with organic matter, forming covalent bonds
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
between organic compounds
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
which contribute to structural stability. Calcium is more available on the soil colloids than is potassium because the common mineral calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
, CaCO3, is more soluble than potassium-bearing minerals such as feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagiocl ...
.
Calcium uptake by roots is essential for plant nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element i ...
, contrary to an old tenet that it was luxury consumption. Calcium is considered as an essential component of plant cell membranes, a counterion for inorganic and organic anions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
in the vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water ...
, and an intracellular messenger in the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
, playing a role in cellular ''learning'' and ''memory''.
Magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
is one of the dominant exchangeable cations in most soils (after calcium and potassium). Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
is an essential element for plants, microbes and animals, being involved in many catalytic reactions and in the synthesis of chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
. Primary minerals that weather to release magnesium include hornblende
Hornblende is a complex silicate minerals#Inosilicates, inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common ...
, biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron- endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more al ...
and vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently; commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the weathe ...
. Soil magnesium concentrations are generally sufficient for optimal plant growth, but highly weathered and sandy soils may be magnesium deficient due to leaching by heavy precipitation.
Sulfur
Most sulfur is made available to plants, like phosphorus, by its release from decomposing organic matter. Deficiencies may exist in some soils (especially sandy soils) and if cropped, sulfur needs to be added. The application of large quantities of nitrogen to fields that have marginal amounts of sulfur may cause sulfur deficiency by a ''dilution effect'' when stimulation of plant growth by nitrogen increases the plant demand for sulfur. A 15-ton crop of onions uses up to 19 lb of sulfur and 4 tons of alfalfa uses 15 lb per acre. Sulfur abundance varies with depth. In a sample of soils in Ohio, United States, the sulfur abundance varied with depths, 0–6 inches, 6–12 inches, 12–18 inches, 18–24 inches in the amounts: 1056, 830, 686, 528 lb per acre respectively.Micronutrients
Themicronutrients
Micronutrients are essential chemicals required by organisms in small quantities to perform various biogeochemical processes and regulate physiological functions of cells and organs. By enabling these processes, micronutrients support the heal ...
essential in plant life, in their order of importance, include iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
and molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
. The term refers to plants' needs, not to their abundance in soil. They are required in very small amounts but are essential to plant health in that most are required parts of enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
systems which are involved in plant metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. They are generally available in the mineral component of the soil, but the heavy application of phosphates can cause a deficiency in zinc and iron by the formation of insoluble zinc and iron phosphates. Iron deficiency, stemming in plant chlorosis
In botany, chlorosis is a condition in which leaves produce insufficient chlorophyll. As chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of leaves, chlorotic leaves are pale, yellow, or yellow-white. The affected plant has little or no ability to ...
and rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or Substrate (biology), substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Pore space in soil, Soil pores in the rhizosphere can ...
acidification, may also result from excessive amounts of heavy metals or calcium minerals (lime) in the soil. Excess amounts of soluble boron, molybdenum and chloride are toxic.
Non-essential nutrients
Nutrients which enhance the health but whose deficiency does not stop the life cycle of plants include:cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
, vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
. As their importance is evaluated they may be added to the list of essential plant nutrients, as is the case for silicon.
See also
* Alkali soil * Sodic soils * Cation-exchange capacity *Soil contamination
Soil contamination, soil pollution, or land pollution as a part of land degradation is caused by the presence of xenobiotic (human-made) chemicals or other alteration in the natural soil environment. It is typically caused by industrial activit ...
* Soil fertility
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality.
* Index of soil-related articles
References
Bibliography
* * * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** {{refend Soil Plant nutrition