Phyllolepids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phyllolepida ("leaf scales") is an extinct 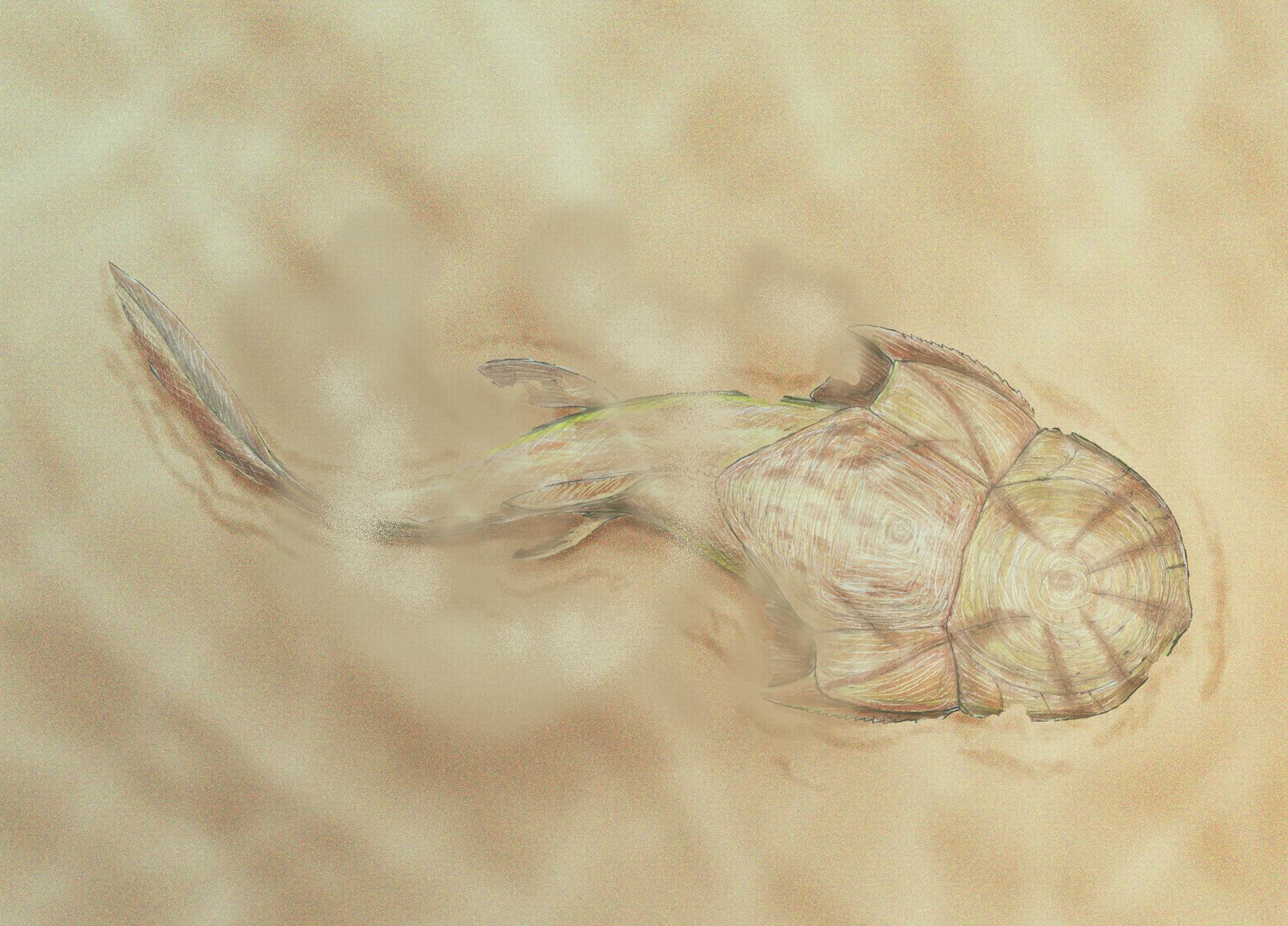 Despite having a relatively clear idea of the phyllolepids' lifestyle and anatomy, most fossils consist of fragments of their
Despite having a relatively clear idea of the phyllolepids' lifestyle and anatomy, most fossils consist of fragments of their
taxon
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular n ...
of flattened placoderms
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally ' plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were c ...
found throughout the world, with fossils being found in Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, w ...
strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum ( : strata) is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as e ...
. Like other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were bottom-dwelling predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
s that ambushed prey. Unlike other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were inhabitants of freshwater environments.
Unlike the Rhenanida
Rhenanida ("Rhine (fish)") is an order of scaly placoderms. Unlike most other placoderms, the rhenanids' armor was made up of a mosaic of unfused scales and tubercles. The patterns and components of this "mosaic" correspond to the plates of ar ...
, the armor of the phyllolepids were made of whole plates, rather than numerous tubercles and scales, and unlike the Petalichthyida, the components of the comparatively wide mouth are known. The phyllolepids are considered to have been blind, as the orbits for the eyes are extremely small, so much so as to suggest that the eyes were vestigial, and that they were placed on the sides of the head, as opposed to visually-oriented bottom-dwelling predators, like, say stargazers or flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the ray-finned demersal fish order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migratin ...
, which have the eyes placed high on top of the head.
 Despite having a relatively clear idea of the phyllolepids' lifestyle and anatomy, most fossils consist of fragments of their
Despite having a relatively clear idea of the phyllolepids' lifestyle and anatomy, most fossils consist of fragments of their thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
armor, and only two genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial ...
, ''Phyllolepis
''Phyllolepis'' (from the Greek roots for ‘leaf’ and ‘scale’)Murphy, Dennis C. 4..20.2016. “Phyllolepis rossimontia (placoderm).” ''Devonian'' Times. is the type genus of Phyllolepida, an extinct taxon of arthrodire placoderm fish ...
'' and '' Austrophyllolepis'' have been thoroughly studied. From the articulation of the thoracic and head plates, it has been suggested that they are either the sister group of order Arthrodira
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ec ...
, or are in fact, a group of highly derived arthrodires.
Taxonomy
The Phyllolepids are divided into twofamilies
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
, the more primitive Gavinaspididae, represented only by '' Gavinaspis'' of Early Devonian China, and Phyllolepididae, which contains all other genera. Barring the Chinese ''Gavinaspis'', the cosmopolitan '' Placolepis'' (fossils of which have been found in Australia, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
, and Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ...
), and the Euro-North American ''Phyllolepis
''Phyllolepis'' (from the Greek roots for ‘leaf’ and ‘scale’)Murphy, Dennis C. 4..20.2016. “Phyllolepis rossimontia (placoderm).” ''Devonian'' Times. is the type genus of Phyllolepida, an extinct taxon of arthrodire placoderm fish ...
'', the majority of genera are found in Early to Middle Devonian Australia. By the Famennian, only ''Phyllolepis'' survived, and became extinct at the close of the Devonian.
References
Long, John A. The Rise of Fishes: 500 Million Years of Evolution Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996. Prehistoric fish orders {{Placoderm-stub