Phuwiangvenator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Phuwiangvenator'' () is an extinct genus of
 The
The
 ;Legs
The leg bones share numerous marked similarities with other
;Legs
The leg bones share numerous marked similarities with other
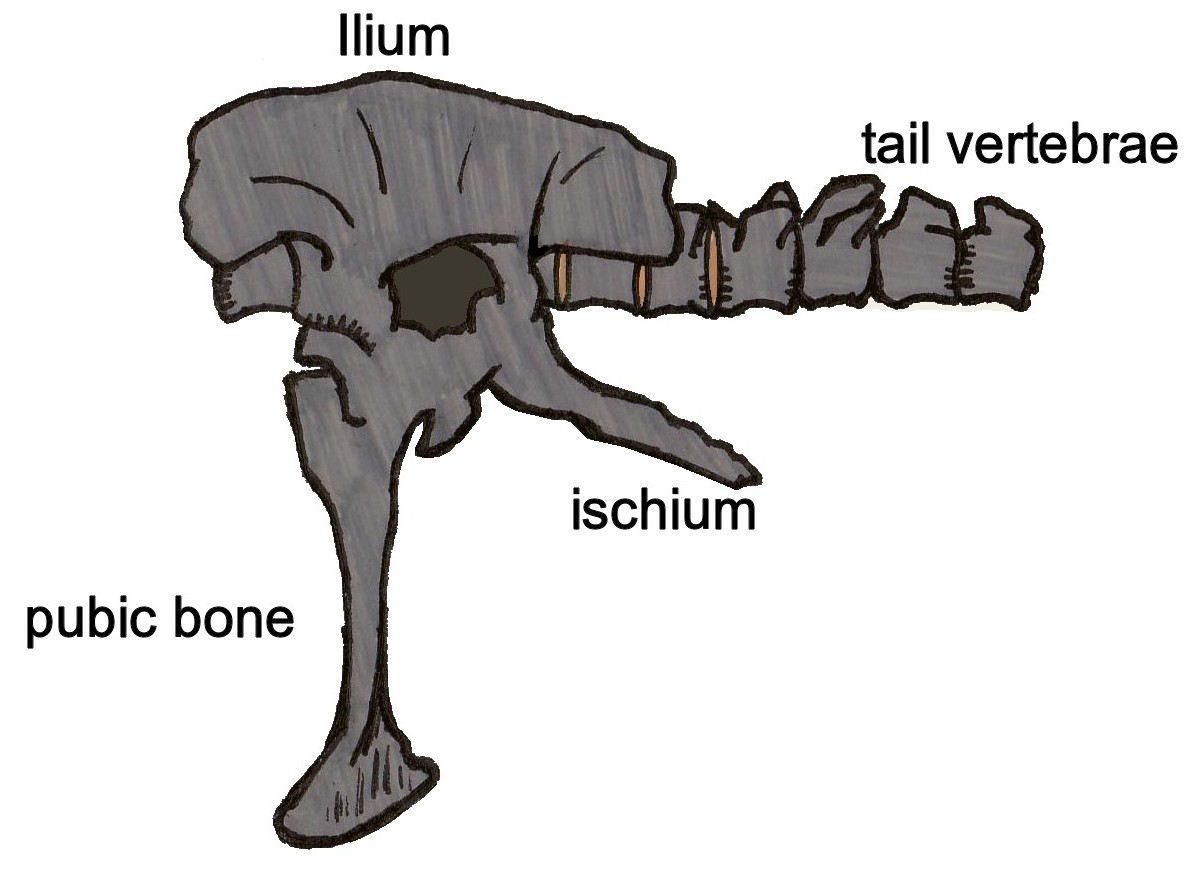 There are three mid-sized
There are three mid-sized
 One of the
One of the
 The
The
megaraptora
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Its derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their large hand claws and powerfully-built forelimbs, which are usually reduced in size in other large theropods. Although undoubt ...
n theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
that lived during the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
period in what is now Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. It contains only the type species, ''P. yaemniyomi''. The generic name of ''Phuwiangvenator'' comes from the Phu Wiang mountains, where the holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
was discovered, and the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word "''venator''" meaning hunter. The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
, "''yaemniyomi''", is in honor of Sudham Yaemniyom, who was a historical paleontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
from Thailand and the first person to discover fossils there.
Discovery
 The
The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
specimen of ''Phuwiangvenator'', designated SM-PW9B, is a partially-complete skeleton consisting of a dorsal vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae of intermediate size between the cervical and lumbar ve ...
, three sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
, a right metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate ...
, right manual phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digit (anatomy), digital bones in the hands and foot, feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the Thumb, thumbs and Hallux, big toes have two phalanges while the other Digit (anatomy), digits have three phalanges. ...
and unguals
An ungual (from Latin ''unguis'', i.e. ''nail'') is a highly modified distal toe bone which ends in a hoof, claw, or nail. Elephants and ungulates have ungual phalanx bones, phalanges, as did the sauropods and ceratopsia, horned dinosaurs. A claw i ...
, both tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
e, the left astragalocalcaneum, several left metatarsal
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are ...
s, and several right pedal phalanges and unguals. It was discovered in 1993 by a team led by Preecha Sainongkham in the Sao Khua Formation
The Sao Khua Formation () is a middle member of the Khorat Group. It consists of an alteration of pale red to yellowish-gray, fine to medium-grained sandstone and grayish-reddish brown siltstone and clay. Rare pale red to light gray conglomerates ...
of Khon Kaen province in Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. At the time of this discovery, Sainongkham was working at the Phu Wiang Dinosaur Museum
Phu Wiang Dinosaur Museum () is a geological museum mainly exhibiting fossils. It is under the administration of the Department of Mineral Resources, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, of the Royal Thai Government, and situated in th ...
. The specimen was transported to the Sirindhorn Museum
Sirindhorn Museum (aka Sirindhorn Dinosaur Museum) () is a geology museum in northeast Thailand. It is located at Non Buri, Sahatsakhan district, Kalasin province.
About
Dinosaur fossils were found by Phra Kru Vijitsahassakun, the abbot of Wa ...
in the town of Non Buri, which is near the locality where the fossils were discovered. The fossils were prepared and remained in the museum's collection until 2019
This was the year in which the first known human case of COVID-19 was documented, preceding COVID-19 pandemic, the pandemic which was declared by the World Health Organization the following year.
Up to that point, 2019 had been described as ...
when Adun Samathi, Phornphen Chanthasit, and P. Martin Sander published a formal description, which was accompanied by a description of the closely related taxon, ''Vayuraptor
''Vayuraptor'' (meaning "wind thief") is a genus of basal coelurosaurian (possibly megaraptoran) theropod dinosaur that lived in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The genus contains a single species, ''V. nongbual ...
''.
A few years after the description of the holotype, another specimen was discovered in the collections at the Sirindhorn Museum. This was described in 2022 by Adun Samathi (one of the original describers), Suravech Suteethorn, Nakorn Pradit, and Varavudh Suteethorn, the latter of whom was part of the original team which uncovered the holotype. They concluded, based on the reported type locality from which the specimen was retrieved as well as several characteristics of the bones themselves, that these bones likely belonged to the same individual animal as the holotype specimen. These additional elements were named as the topotype and were given the designation SM-PW9A. This specimen included both ends of the left fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. ...
, several of the left metatarsals, and the distal ends of the right metatarsals. One of the metatarsals was later discovered to contain a fracture, which was studied and published on in 2023.
The discovery of ''Phuwiangvenator'' in Thailand is used by its describers to suggest an Asian origin of megaraptora. They state that the existence of ''Vayuraptor'' in Thailand and ''Fukuiraptor
''Fukuiraptor'' ("thief of Fukui") is a genus of medium-sized megaraptoran theropod dinosaur of the Early Cretaceous epoch (either Barremian or Aptian) that lived in what is now Japan. ''Fukuiraptor'' is known from the Kitadani Formation and ...
'' in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
are also evidence of this.
Description
The authors of its original description estimate that ''Phuwiangvenator'' was probably about long in life. From what is known of the skeleton, it likely had proportions similar to the related taxon ''Australovenator
''Australovenator'' (meaning "southern hunter") is a genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation (dated to 95 million years ago) of Australia. Some specimens from the Albian-aged Eumeralla Forma ...
'', which is known from slightly more complete remains. The authors name two autapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to ...
for ''Phuwiangvenator''. The first of these are short furrows on the ventral side of the sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
on the front and rear ends. The other autapomorphy is a sloping rim of the fourth metatarsal
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are ...
which is angled away from the middle of the body at the dorsal end. This sloping fourth metatarsal is additionally unique in having the lowest corner relative to the third metatarsal of any known theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
.
;Vertebrae
''Phuwiangvenator'' is only known from four vertebrae, one from the dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
area and three from the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
. These vertebrae, as a whole, share numerous affinities with other large theropods
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
. The dorsal vertebra is hourglass-shaped when viewed from above (or below), which is similar to the vertebrae of ''Fukuiraptor
''Fukuiraptor'' ("thief of Fukui") is a genus of medium-sized megaraptoran theropod dinosaur of the Early Cretaceous epoch (either Barremian or Aptian) that lived in what is now Japan. ''Fukuiraptor'' is known from the Kitadani Formation and ...
'', ''Aerosteon
''Aerosteon'' is a genus of megaraptoran dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Argentina. Its remains were discovered in 1996 in the Anacleto Formation, which is from the late Campanian. The type and only known species is ''A. riocolorad ...
'', and numerous other avetheropods. In particular, the centrum of the only preserved dorsal vertebra does not have a pleurocoel
Skeletal pneumaticity is the presence of air spaces within bones. It is generally produced during development by excavation of bone by pneumatic diverticula (air sacs) from an air-filled space, such as the lungs or nasal cavity. Pneumatization is h ...
or any lateral ridges, which resembles the condition observed in ''Gualicho
''Gualicho'' (named in reference to the gualichu) is an enigmatic genus of theropod dinosaurs. The type species is ''Gualicho shinyae''. It lived in what is now northern Patagonia, on what was then a South American island continent split off fro ...
'', a theropod of controversial affinities. The three sacral vertebrae which are preserved are all fused and were damaged significantly during fossilization
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
. However, the centra are well-preserved enough to show one of the key autapomorphies of the genus, the saci (or furrows) on the anterior and posterior portion of the bone.
;Hands
Most of the preserved finger bones have deep and well-defined attachment sites for ligaments
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligam ...
, which resemble those found in the theropods ''Kileskus
''Kileskus'' (meaning ''lizard'' in the Khakas language) is a genus of tyrannosauroid dinosaur known from partial remains found in Middle Jurassic (Bathonian stage) Itat Formation of Sharypovsky District, Krasnoyarsk Krai (Russia). Fossils r ...
'' and ''Australovenator
''Australovenator'' (meaning "southern hunter") is a genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation (dated to 95 million years ago) of Australia. Some specimens from the Albian-aged Eumeralla Forma ...
''.
 ;Legs
The leg bones share numerous marked similarities with other
;Legs
The leg bones share numerous marked similarities with other megaraptorans
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Its Derived (phylogenetics), derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their large hand claws and powerfully-built forelimbs, which are usually reduced in size in other large the ...
. The tibia is more than twelve times longer than its mid-length anteroposterior width, which is a synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel Phenotypic trait, character or character state that has evolution, evolved from its ancestral form (or Plesiomorphy and symplesiomorphy, plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy sh ...
of megaraptorans and other coelurosaurs
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyran ...
. There are also several characteristics of the astragalus
Astragalus may refer to:
* ''Astragalus'' (plant), a large genus of herbs and small shrubs
*Astragalus (bone)
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known ...
and the metatarsals
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are nu ...
which resemble those of ''Australovenator
''Australovenator'' (meaning "southern hunter") is a genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation (dated to 95 million years ago) of Australia. Some specimens from the Albian-aged Eumeralla Forma ...
''. There is one major exception to the megaraptoran affinities of the holotype's leg bones; the anterolateral process of the lateral condyle is sharply curved downward, which is a condition seen in ''Neovenator
''Neovenator'' ( nˈiːə͡ʊvˌɛne͡ɪtə; "new hunter") is a genus of carcharodontosaurian theropod dinosaur. It is known primarily from several skeletons found in the Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian-Barremian) Wessex Formation on the south co ...
'' and numerous tyrannosaurids
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to fifteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera i ...
. This led the authors of the paper to suggest that this trait, and other characteristics of the leg bones may be more widespread among theropods than was previously thought. In their subsequent analysis of the topotype material, Samathi and colleagues draw comparisons between the metatarsal
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are ...
s of ''Phuwiangvenator'' with those of numerous theropods
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
including ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'', ''Concavenator
''Concavenator'' (meaning Cuenca hunter) is a genus of carcharodontosaurian dinosaur that lived in Spain during the Early Cretaceous epoch, about 125 million years ago. The genus contains a single species, ''Concavenator corcovatus'', named and ...
'', ''Neovenator
''Neovenator'' ( nˈiːə͡ʊvˌɛne͡ɪtə; "new hunter") is a genus of carcharodontosaurian theropod dinosaur. It is known primarily from several skeletons found in the Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian-Barremian) Wessex Formation on the south co ...
'', and ''Suchomimus
''Suchomimus'', from Ancient Greek ''σούχος'' (''soúkhos''), meaning "crocodile", and Latin ''mimus'', meaning "actor", is a genus of spinosaurid dinosaur that lived between 125 and 112 million years ago in what is now Niger, North A ...
''. They use this to suggest that the condition seen in the species represents the ancestral condition of all avetheropods, rather than the derived condition seen in megaraptorids.
Classification
Phylogeny
Samathi and colleagues performed aphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analysis in their description of ''Phuwiangvenator'' and ''Vayuraptor
''Vayuraptor'' (meaning "wind thief") is a genus of basal coelurosaurian (possibly megaraptoran) theropod dinosaur that lived in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The genus contains a single species, ''V. nongbual ...
'' based on the data set used by Apesteguía and colleagues in their 2016 description of ''Gualicho
''Gualicho'' (named in reference to the gualichu) is an enigmatic genus of theropod dinosaurs. The type species is ''Gualicho shinyae''. It lived in what is now northern Patagonia, on what was then a South American island continent split off fro ...
''. In their analysis, they added the two new taxa from their description as well as the contemporaneous theropod ''Siamotyrannus
''Siamotyrannus'' (meaning "Siamese tyrant") is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the early Cretaceous of Thailand.
Discovery and naming
In 1993, Somchai Traimwichanon found a partial skeleton of a large theropod at the Phu Wiang 9 site in Khon K ...
'' and removed the problematic ''Santanaraptor
''Santanaraptor'' (meaning " Santana Formation thief") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Early Cretaceous (late Aptian-early Albian), about 112 million years ago.
Discovery
The type species i ...
'' from their data set. They recovered ''Phuwiangvenator'' as a basal member of megaraptora
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Its derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their large hand claws and powerfully-built forelimbs, which are usually reduced in size in other large theropods. Although undoubt ...
with the following synapomorphies for the group: a ventral groove on the first manual phalanx, a transversely compressed first manual ungual, a prominence on the anterior surface of the distal end of the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
, a lateral extension of the astragalus, and a flattened sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
. Notably, they recovered ''Vayuraptor'' as a non-megaraptoran coelurosaur
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, ty ...
, which has not been recovered by subsequent analyses. The strict consensus tree from their analysis is shown below.
A more recent phylogenetic analysis to include ''Phuwiangvenator'' was the one which accompanied the description of ''Maip
''Maip'' is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, ''M. macrothorax'', known from an incomplete, disarticulated ...
'' in 2022
The year began with another wave in the COVID-19 pandemic, with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Omicron spreading rapidly and becoming the dominant variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide. Tracking a decrease in cases and deaths, 2022 saw ...
. The analysis of the authors, led by Alexis Aranciaga Rolando, included every taxon confidently assigned to megaraptora
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Its derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their large hand claws and powerfully-built forelimbs, which are usually reduced in size in other large theropods. Although undoubt ...
including an unnamed specimen from the Griman Creek Formation
The Griman Creek Formation is a geological formation in northern New South Wales and southern Queensland, Australia whose strata date back to the Albian-Cenomanian stages of the mid-Cretaceous. It is most notable being a major source of opal, ...
(called the "Lightning Claw" by some publications) and another unnamed specimen from the Bajo Barreal Formation
The Bajo Barreal Formation is a geological Formation (geology), formation in the Golfo San Jorge Basin of Chubut Province, Chubut and Santa Cruz Province, Argentina, Santa Cruz, Argentina whose strata date back to the Cenomanian, Middle Cenomanian ...
. Their analysis of Megaraptora differs from the initial only in the exact classification of ''Vayuraptor
''Vayuraptor'' (meaning "wind thief") is a genus of basal coelurosaurian (possibly megaraptoran) theropod dinosaur that lived in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The genus contains a single species, ''V. nongbual ...
'' and the inclusion of more taxa, which the authors state led to a more resolved tree consistent with previous analyses.
In 2024, Andrea Cau published a comprehensive analysis of theropod phylogeny using a novel analytical method to test the effects of ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the ovum, egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to t ...
on the phylogenetic position of various taxa. This was based on an earlier publication by Cau in which he hypothesized that the enigmatic European taxa ''Juratyrant
''Juratyrant'' (meaning "Jurassic tyrant") is a tyrannosauroid dinosaur genus from the late Jurassic period (early Tithonian age) of England. The genus contains a single species, ''Juratyrant langhami'', which was once classed as a species of '' ...
'', ''Scipionyx
''Scipionyx'' ( ) was a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Pietraroja Formation of Italy, around 113 mya (unit), million years ago.
There is only one fossil known of ''Scipionyx'', discovered in 1981 by an amateur paleontolog ...
'', and ''Sciurumimus
''Sciurumimus'' ("Squirrel-mimic," named for its tail's resemblance to that of the tree squirrel, ''Sciurus'') is an extinct genus of Tetanurae, tetanuran Theropoda, theropod from the Late Jurassic Torleite Formation of Germany. It is known from ...
'' (which are known to be juvenile specimens), may not be juvenile compsognathids, but rather juvenile megalosauroid
Megalosauroidea (meaning 'great/big lizard forms') is a Taxonomic rank, superfamily (or clade) of Tetanurae, tetanuran theropod dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period. The group is defined as ''Megalosaurus, M ...
s or allosauroid
Carnosauria is an extinct group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
While Carnosauria was historically considered largely synonymous with Allosauroidea, some recent studies have revived Carn ...
s. The 2024 analysis recovered a novel result, which placed ''Phuwiangvenator'' and the closely-related ''Vayuraptor
''Vayuraptor'' (meaning "wind thief") is a genus of basal coelurosaurian (possibly megaraptoran) theropod dinosaur that lived in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The genus contains a single species, ''V. nongbual ...
'' within the family Coeluridae
Coeluridae is a historically unnatural group of generally small, carnivorous dinosaurs from the late Jurassic Period. For many years, any small Jurassic or Cretaceous theropod that did not belong to one of the more specialized families recogniz ...
, which had previously been considered a wastebasket taxon
Wastebasket taxon (also called a wastebin taxon, dustbin taxon or catch-all taxon) is a term used by some taxonomists to refer to a taxon that has the purpose of classifying organisms that do not fit anywhere else. They are typically defined by e ...
. Cau also recovered a variety of disparate taxa to be a member of this clade including ''Shishugounykus
''Shishugounykus'' (meaning "Shishugou claw" after the Shishugou Formation where it was found) is a genus of basal alvarezsaurian dinosaur from the Shishugou Formation from Xinjiang in China. The type
Type may refer to:
Science and technolo ...
'', ''Fukuivenator
''Fukuivenator'' ("hunter of Fukui Prefecture") is an extinct genus of maniraptoran theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Japan.
Discovery and naming
The type species ''Fukuivenator paradoxus'' was named and described in 2016 by Yoi ...
'', and ''Migmanychion
''Migmanychion'' (meaning "claw mixture") is an extinct genus of maniraptoran theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Longjiang Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, ''M. laiyang'', known from an incomplete left forelimb ...
'', which had previously been recovered as maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Dromaeosauridae, Troodontidae, ...
ns. An abbreviated form of the relevant section of Cau's analysis is shown below.
Possible synonymity
theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
s which have been discovered so far in the Sao Khua Formation
The Sao Khua Formation () is a middle member of the Khorat Group. It consists of an alteration of pale red to yellowish-gray, fine to medium-grained sandstone and grayish-reddish brown siltstone and clay. Rare pale red to light gray conglomerates ...
, all of which are known from relatively incomplete remains. These are: ''Phuwiangvenator'', ''Vayuraptor
''Vayuraptor'' (meaning "wind thief") is a genus of basal coelurosaurian (possibly megaraptoran) theropod dinosaur that lived in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The genus contains a single species, ''V. nongbual ...
'', and ''Siamotyrannus
''Siamotyrannus'' (meaning "Siamese tyrant") is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the early Cretaceous of Thailand.
Discovery and naming
In 1993, Somchai Traimwichanon found a partial skeleton of a large theropod at the Phu Wiang 9 site in Khon K ...
''. The authors who described the former two were careful to draw numerous distinctions between all three taxa to ensure that they none of the three are junior synonyms of the others. The distinctions they draw between ''Phuwiangvenator'' and ''Siamotyrannus'' are as follows: the dorsal vertebra of the former is longer than it is tall, whereas in the latter they are much taller in relation to their length and the rims of the sacral centra
Centra is a convenience shop chain that operates throughout Ireland. The chain operates as a symbol group owned by Musgrave Group, the food wholesaler, meaning the individual shops are all owned by individual franchisees.
The chain has three ...
of ''Siamotyrannus'' are much more convex than in ''Phuwiangvenator''.
The distinctions between ''Phuwiangvenator'' and ''Vayuraptor'' which they outline are as follows: the cranioproximate process of the astragalus is much more pronounced in ''Vayuraptor'' and they note that ''Vayuraptor'' had two grooves on the body of the astragalus whereas ''Phuwiangvenator'' only had one. The final distinction between the two are the lack of an upward curving process of the lateral condyle in ''Vayuraptor'', which is one of the autapomorphies of ''Phuwiangvenator''. This last trait was also observed in all ontogenetic
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the stu ...
stages of ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'', which the authors state implies that the absence of this trait in ''Vayuraptor'' means that the distinction is probably not the result of ontogeny.
Paleobiology
Arm musculature
In 2023, Alexis M. Aranciaga Rolando and colleagues published an analysis of the inferred forelimb musculature ofmegaraptorans
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Its Derived (phylogenetics), derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their large hand claws and powerfully-built forelimbs, which are usually reduced in size in other large the ...
. Their reasoning for pursuing this analysis was the uniquely large forearms of megaraptorans that were not seen in any other group of large theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
s in the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
. The analysis focuses mostly on the derived members of megaraptoridae, but they comment on the muscular
MUSCULAR (DS-200B), located in the United Kingdom, is the name of a surveillance program jointly operated by Britain's Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) and the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) that was revealed by documents release ...
and tendinous attachment sites on the bones of ''Phuwiangvenator''. They outline several key differences between the manual phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digit (anatomy), digital bones in the hands and foot, feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the Thumb, thumbs and Hallux, big toes have two phalanges while the other Digit (anatomy), digits have three phalanges. ...
and unguals
An ungual (from Latin ''unguis'', i.e. ''nail'') is a highly modified distal toe bone which ends in a hoof, claw, or nail. Elephants and ungulates have ungual phalanx bones, phalanges, as did the sauropods and ceratopsia, horned dinosaurs. A claw i ...
of ''Phuwiangvenator'' and those of younger megaraptorans like ''Megaraptor
''Megaraptor'' () is a genus of large Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived during the Turonian and Coniacian ages of the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils have been discovered in the Patagonian Portezuelo Formation of Argentina, South America. Th ...
'', ''Maip
''Maip'' is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, ''M. macrothorax'', known from an incomplete, disarticulated ...
'', and ''Australovenator
''Australovenator'' (meaning "southern hunter") is a genus of megaraptoran theropod dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age Winton Formation (dated to 95 million years ago) of Australia. Some specimens from the Albian-aged Eumeralla Forma ...
''. These differences are concentrated in the first finger of the hand, which in derived megaraptorans hosts a single giant claw which is presumed to have served a purpose in hunting or feeding. The first claw of ''Phuwiangvenator'' lacks the well-developed furrows which are present on the proximal extension of the claw. In other species, these are thought to have been attachment sites for powerful muscles, enabling greater control and flexibility of the finger movements of these animals.
Pathology
 One of the
One of the metatarsals
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are nu ...
of the holotype of ''Phuwiangvenator'' was found to have signs of a greenstick fracture
A greenstick fracture is a partial bone break that typically occurs in children due to their more flexible and resilient bone composition. This fracture pattern is characterized by a break on one side of the bone while the other side remains inta ...
when analyzed by Samathi and colleagues in 2022. They inferred that this fracture is not taphonomic because of the texture of the bone, which is smooth on the medial side, but is very calloused on the lateral side. These are interpreted as signs of the fracture being healed, which implies that the animal survived this injury. The bone itself is also twisted, which would not be the normal condition because the second metatarsal would have been in the center of the foot in life. Samathi and colleagues compare this fracture to other known pathologies on theropod bones, including those seen in specimens ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'' and ''Yangchuanosaurus
''Yangchuanosaurus'' is an extinct genus of metriacanthosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in China from the Middle Jurassic to Late Jurassic periods (Bathonian to Tithonian stages), and was similar (although slightly larger) in size and appea ...
''. From these comparisons, they conclude that the injury was likely caused by an external blunt force. Other features of the bone determined by computer tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
led the authors to conclude that the animal was not yet fully grown when it died.
Samathi and colleagues suggest several possible causes of the fracture. They first suggest a blow from the tail club of an ankylosaur
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful l ...
, but they discard this hypothesis because no ankylosaur remains are known from the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
of Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. Possible competition or combat with another large theropod is also suggested, because there are several large theropods known from nearby localities, but they state that there is no direct evidence for this and it is impossible to determine without additional evidence. They conclude that the most likely explanation is that the animal hit its foot into a hard object such as a rock or possibly fell over to cause the type of incomplete fracture which is observed.
Evidence for severe pathologies being healed has been used by some authors to infer herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called '' herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' ...
ing behavior in extinct animals. There are known associations of large theropods (i.e. ''Albertosaurus
''Albertosaurus'' (; meaning "Alberta lizard") is a genus of large tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in northwestern North America during the early to middle Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period, about 71 million yea ...
'' and ''Mapusaurus
''Mapusaurus'' ( Earth lizard) is a genus of giant carcharodontosaurid carnosaurian dinosaur that lived in Argentina during the Turonian age of the Late Cretaceous.
Discovery
''Mapusaurus'' was excavated between 1997 and 2001, by the Argen ...
''), so the authors state that it is possible that ''Phuwiangvenator'' exhibited similar behaviors. However, they also suggest that the animal may have simply survived for a short time after the injury and lived with a limp.
Paleoecology
Diet
None of the skull of ''Phuwiangvenator'' has been preserved, but the animal is presumed to have beencarnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly mu ...
. However, it does not have the same specialized arm musculature to aid in feeding as other megaraptorans.
Paleoenvironment
Sao Khua Formation
The Sao Khua Formation () is a middle member of the Khorat Group. It consists of an alteration of pale red to yellowish-gray, fine to medium-grained sandstone and grayish-reddish brown siltstone and clay. Rare pale red to light gray conglomerates ...
has thus far only yielded continental fossils, with no evidence of marine fossils or marine sediments
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
. There have historically been reports of ichthyosaur
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fo ...
and plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an Order (biology), order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period (geology), Period, possibly in the Rhaetian st ...
teeth from the Sao Khua Formation, but these have now been identified as belonging to crocodyliformes
Crocodyliformes is a clade of crurotarsan archosaurs, the group often traditionally referred to as "crocodilians". They are the first members of Crocodylomorpha to possess many of the features that define later relatives. They are the only pseu ...
, which are mostly non-marine during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
. The sediments of the Sao Khua Formation are composed of red clay
Ultisol, commonly known as red clay soil, is one of twelve soil orders in the United States Department of Agriculture soil taxonomy. The word "Ultisol" is derived from "ultimate", because Ultisols were seen as the ultimate product of continuous ...
s, mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
s, sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
s, siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.
Although its permeabil ...
s, and conglomerate rocks, which indicate a fluvial
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ...
environment which also possessed lakes, floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
s, and braided channel
A braided river (also called braided channel or braided stream) consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called ''braid bars'' or, in British English usage, '' aits'' or ''eyots''.
Braided streams te ...
s.
Contemporary fauna
Of all theMesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
formations in northeastern Thailand, the Sao Khua has the most abundant and diverse fossils. In addition to ''Phuwiangvenator'' and ''Vayuraptor
''Vayuraptor'' (meaning "wind thief") is a genus of basal coelurosaurian (possibly megaraptoran) theropod dinosaur that lived in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The genus contains a single species, ''V. nongbual ...
'', the region was host to numerous other theropods including the spinosaurid
Spinosauridae (or spinosaurids) is a clade or Family (taxonomy), family of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs comprising ten to seventeen known genera. Spinosaurid fossils have been recovered worldwide, including Africa, Europe, South America, and Asia. ...
''Siamosaurus
''Siamosaurus'' (meaning "Siam lizard") is a potentially nomen dubium, dubious genus of Spinosauridae, spinosaurid dinosaur that lived in what is now known as China and Thailand during the Early Cretaceous Period (geologic time), period (Barr ...
'', the large theropod ''Siamotyrannus
''Siamotyrannus'' (meaning "Siamese tyrant") is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the early Cretaceous of Thailand.
Discovery and naming
In 1993, Somchai Traimwichanon found a partial skeleton of a large theropod at the Phu Wiang 9 site in Khon K ...
'', an unnamed spinosaurid, and an unnamed carcharodontosaurid
Carcharodontosauridae (carcharodontosaurids; from the Greek καρχαροδοντόσαυρος, ''carcharodontósauros'': "shark-toothed lizards") is a group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. In 1931, Ernst Stromer named Carcharodontosauridae ...
. The area was also home to numerous small theropods including the ornithomimosaur ''Kinnareemimus
''Kinnareemimus'' (, meaning "Kinnara#Thailand, Kinnaree mimic", after a figure from Thai folklore) is an extinct genus of ornithomimosaurian theropod dinosaur that was discovered in the Early Cretaceous Sao Khua Formation in what is now Thailand. ...
'' and an unnamed compsognathid. Numerous sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
s are also known from the area including ''Phuwiangosaurus
''Phuwiangosaurus'' (meaning "Phu Wiang lizard") is a genus of titanosaur dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Hauterivian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The type species, ''P. sirindhornae'', was described by Martin, Buffetaut, and ...
'' and several unnamed forms. However, there have yet to be any ornithischian
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek st ...
s discovered from the formation.
Freshwater life is abundant in the Sao Khua Formation. These include the neosuchian
Neosuchia is a clade within Mesoeucrocodylia that includes all modern extant crocodilians and their closest fossil relatives. It is defined as the most inclusive clade containing all crocodylomorphs more closely related to ''Crocodylus niloticus' ...
s '' Siamosuchus'', ''Sunosuchus
''Sunosuchus'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Fossils are known from China, Kyrgyzstan, and Thailand and are Jurassic in age, although some may be Early Cretaceous. Four species are currently assigned to the genus: the t ...
'', and ''Theriosuchus
''Theriosuchus'' is an extinct genus of atoposaurid neosuchian from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Europe (Hungary & southern England), Southeast Asia (Thailand) and western North America (Wyoming), with fragmentary records from Middle Jur ...
'', numerous species of turtles
Turtles are reptiles of the order Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtle ...
, amiiform fish, several hybodont
Hybodontiformes, commonly called hybodonts, are an extinct group of shark-like cartilaginous fish (chondrichthyans) which existed from the late Devonian to the Late Cretaceous. Hybodonts share a close common ancestry with modern sharks and rays ( ...
iform sharks, and freshwater bivalves
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consis ...
. There is also an indeterminate pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
known from the formation.
See also
*2019 in archosaur paleontology
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2019, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in 2019.
Ps ...
*Aptian extinction
The Aptian extinction was an extinction event of the early Cretaceous Period. It is dated to c. 116 or 117 million years ago, in the middle of the Aptian stage of the geological time scale, and has sometimes been termed the mid-Aptian extinction ev ...
* Khorat Group
*List of Asian dinosaurs
This is a list of dinosaurs whose remains have been recovered from Asia, excluding India, which was part of a separate landmass for much of the Mesozoic (See List of Indian and Madagascan Dinosaurs for a list of Dinosaurs from India). This list ...
*Paleontology in Thailand
Paleontology began as a subject of academic interest in Thailand in the early twentieth century, mainly conducted by foreign researchers working with the Royal Department of Mines and Geology, the precursor of the Department of Mineral Resources ( ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q63981558 Megaraptora Dinosaur genera Barremian dinosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2019 Dinosaurs of Thailand