grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=
la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the
Etymology
Apollo (Greco-Roman epithets
Apollo's chiefSun
*Aegletes ( ; Αἰγλήτης, ''Aiglētēs''), from , "light of the sun" *Helius ( ; , ''Wolf
*Lycegenes ( ; , ''Lukēgenēs''), literally "born of a wolf" or "born of Lycia" *Lycoctonus ( ; , ''Lykoktonos''), from , "wolf", and , "to kill"Origin and birth
Apollo's birthplace wasPlace of worship


Healing and disease
*Acesius ( ; , ''Akesios''), from , "healing". Acesius was the epithet of Apollo worshipped in Elis, where he had a temple in theFounder and protector
*Prophecy and truth
*Coelispex (Roman) ( ), from Latin ''coelum'', "sky", and ''specere'' "to look at" *Iatromantis ( ; , ''Iātromantis'',) from , "physician", and , "prophet", referring to his role as a god both of healing and of prophecy *Leschenorius ( ; , ''Leskhēnorios''), from , "converser" *Loxias ( ; , ''Loxias''), from , "to say", historically associated with , "ambiguous" *Manticus ( ; , ''Mantikos''), literally "prophetic" *Proopsios (), meaning "foreseer" or "first seen"Music and arts
*Musagetes ( ;Archery
*Aphetor ( ; , ''Aphētōr''), from , "to let loose" *Aphetorus ( ; , ''Aphētoros''), as the preceding *Arcitenens (Roman) ( ), literally "bow-carrying" *Argyrotoxus ( ; , ''Argyrotoxos''), literally "with silver bow" *Clytotoxus ( ; , ''Klytótoxos''), "he who is famous for his bow", the renowned archer. *Hecaërgus ( ; , ''Hekaergos''), literally "far-shooting" *Hecebolus ( ; , ''Hekēbolos''), "far-shooting" *Ismenius ( ; , ''Ismēnios''), literally "of Ismenus", after Ismenus, the son of Amphion and Niobe, whom he struck with an arrowAppearance
* Acersecomes (, ''Akersekómēs''), "he who has unshorn hair", the eternal ephebe. * Chrysocomes ( ; , ''Khrusokómēs''), literally "he who has golden hair."Amazons
*Other
*Patroos (Πατρώος, ancestral), there is the Temple of Apollo Patroos at the Ancient Agora of AthensCeltic epithets and cult titles
Apollo was worshipped throughout the Roman Empire. In the traditionallyOrigins
 The cult centers of Apollo in Greece,
The cult centers of Apollo in Greece, Healer and god-protector from evil
 In classical times, his major function in popular religion was to keep away evil, and he was therefore called "apotropaios" (, "averting evil") and "alexikakos" ( "keeping off ill"; from v. + n. ). Apollo also had many epithets relating to his function as a healer. Some commonly-used examples are "paion" ( literally "healer" or "helper") "epikourios" (, "succouring"), "oulios" (, "healer, baleful") and "loimios" (, "of the plague"). In later writers, the word, "paion", usually spelled "Paean", becomes a mere epithet of Apollo in his capacity as a god of healing.
Apollo in his aspect of "healer" has a connection to the primitive god Paean (), who did not have a cult of his own. Paean serves as the healer of the gods in the '' Iliad'', and seems to have originated in a pre-Greek religion. It is suggested, though unconfirmed, that he is connected to the Mycenaean figure ''pa-ja-wo-ne'' (Linear B: ). At Google Books. Paean was the personification of holy songs sung by "seer-doctors" (), which were supposed to cure disease.
Homer illustrated Paeon the god and the song both of apotropaic thanksgiving or triumph. Such songs were originally addressed to Apollo and afterwards to other gods: to
In classical times, his major function in popular religion was to keep away evil, and he was therefore called "apotropaios" (, "averting evil") and "alexikakos" ( "keeping off ill"; from v. + n. ). Apollo also had many epithets relating to his function as a healer. Some commonly-used examples are "paion" ( literally "healer" or "helper") "epikourios" (, "succouring"), "oulios" (, "healer, baleful") and "loimios" (, "of the plague"). In later writers, the word, "paion", usually spelled "Paean", becomes a mere epithet of Apollo in his capacity as a god of healing.
Apollo in his aspect of "healer" has a connection to the primitive god Paean (), who did not have a cult of his own. Paean serves as the healer of the gods in the '' Iliad'', and seems to have originated in a pre-Greek religion. It is suggested, though unconfirmed, that he is connected to the Mycenaean figure ''pa-ja-wo-ne'' (Linear B: ). At Google Books. Paean was the personification of holy songs sung by "seer-doctors" (), which were supposed to cure disease.
Homer illustrated Paeon the god and the song both of apotropaic thanksgiving or triumph. Such songs were originally addressed to Apollo and afterwards to other gods: to Dorian origin
The '' Homeric Hymn to Apollo'' depicts Apollo as an intruder from the north. The connection with the northern-dwelling Dorians and their initiation festival '' apellai'' is reinforced by the month ''Apellaios'' in northwest Greek calendars. The family-festival was dedicated to Apollo ( Doric Doric may refer to: * Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece ** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians * Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture * Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode * Doric dialect (Scotland) * Doric ...Minoan origin
 George Huxley regarded the identification of Apollo with the Minoan deity Paiawon, worshipped in Crete, to have originated at Delphi. In the ''Homeric Hymn'', Apollo appeared as a dolphin and carried Cretan priests to Delphi, where they evidently transferred their religious practices. ''Apollo Delphinios'' or ''Delphidios'' was a sea-god especially worshipped in Crete and in the islands. Apollo's sister Artemis, who was the Greek goddess of hunting, is identified with Britomartis (Diktynna), the Minoan "Mistress of the animals". In her earliest depictions she was accompanied by the "Master of the animals", a bow-wielding god of hunting whose name has been lost; aspects of this figure may have been absorbed into the more popular Apollo.Martin Nilsson (1967), Vol I, pp. 499–500
George Huxley regarded the identification of Apollo with the Minoan deity Paiawon, worshipped in Crete, to have originated at Delphi. In the ''Homeric Hymn'', Apollo appeared as a dolphin and carried Cretan priests to Delphi, where they evidently transferred their religious practices. ''Apollo Delphinios'' or ''Delphidios'' was a sea-god especially worshipped in Crete and in the islands. Apollo's sister Artemis, who was the Greek goddess of hunting, is identified with Britomartis (Diktynna), the Minoan "Mistress of the animals". In her earliest depictions she was accompanied by the "Master of the animals", a bow-wielding god of hunting whose name has been lost; aspects of this figure may have been absorbed into the more popular Apollo.Martin Nilsson (1967), Vol I, pp. 499–500
Anatolian origin
 A non-Greek origin of Apollo has long been assumed in scholarship. The name of Apollo's mother Leto has
A non-Greek origin of Apollo has long been assumed in scholarship. The name of Apollo's mother Leto has Proto-Indo-European
The Vedic Rudra has some similar functions with Apollo. The terrible god is called "the archer" and the bow is also an attribute of Shiva. Rudra could bring diseases with his arrows, but he was able to free people of them and his alternative Shiva is a healer physician god. However the Indo-European component of Apollo does not explain his strong relation with omens, exorcisms, and with the oracular cult.Oracular cult

 Unusually among the Olympic deities, Apollo had two cult sites that had widespread influence:
Unusually among the Olympic deities, Apollo had two cult sites that had widespread influence: Oracular shrines
 Apollo had a famous
Apollo had a famous Temples of Apollo
Many temples were dedicated to Apollo in Greece and the Greek colonies. They show the spread of the cult of Apollo and the evolution of the Greek architecture, which was mostly based on the rightness of form and on mathematical relations. Some of the earliest temples, especially in Crete, do not belong to any Greek order. It seems that the first peripteral temples were rectangular wooden structures. The different wooden elements were considered divine, and their forms were preserved in the marble or stone elements of the temples of Doric order. The Greeks used standard types because they believed that the world of objects was a series of typical forms which could be represented in several instances. The temples should be canonic, and the architects were trying to achieve this esthetic perfection. From the earliest times there were certain rules strictly observed in rectangular peripteral and prostyle buildings. The first buildings were built narrowly in order to hold the roof, and when the dimensions changed some mathematical relations became necessary in order to keep the original forms. This probably influenced the theory of numbers of Pythagoras, who believed that behind the appearance of things there was the permanent principle of mathematics.C. M. Bowra (1957). ''The Greek experience'', p. 166. The Doric order dominated during the 6th and the 5th century BC but there was a mathematical problem regarding the position of the triglyphs, which couldn't be solved without changing the original forms. The order was almost abandoned for theGreek temples
* Thebes, Greece: The oldest temple probably dedicated to ''Apollo Ismenius'' was built in the 9th century B.C. It seems that it was a curvilinear building. The * Corinth: A
* Corinth: A  *
*, World Heritage Site. containing a
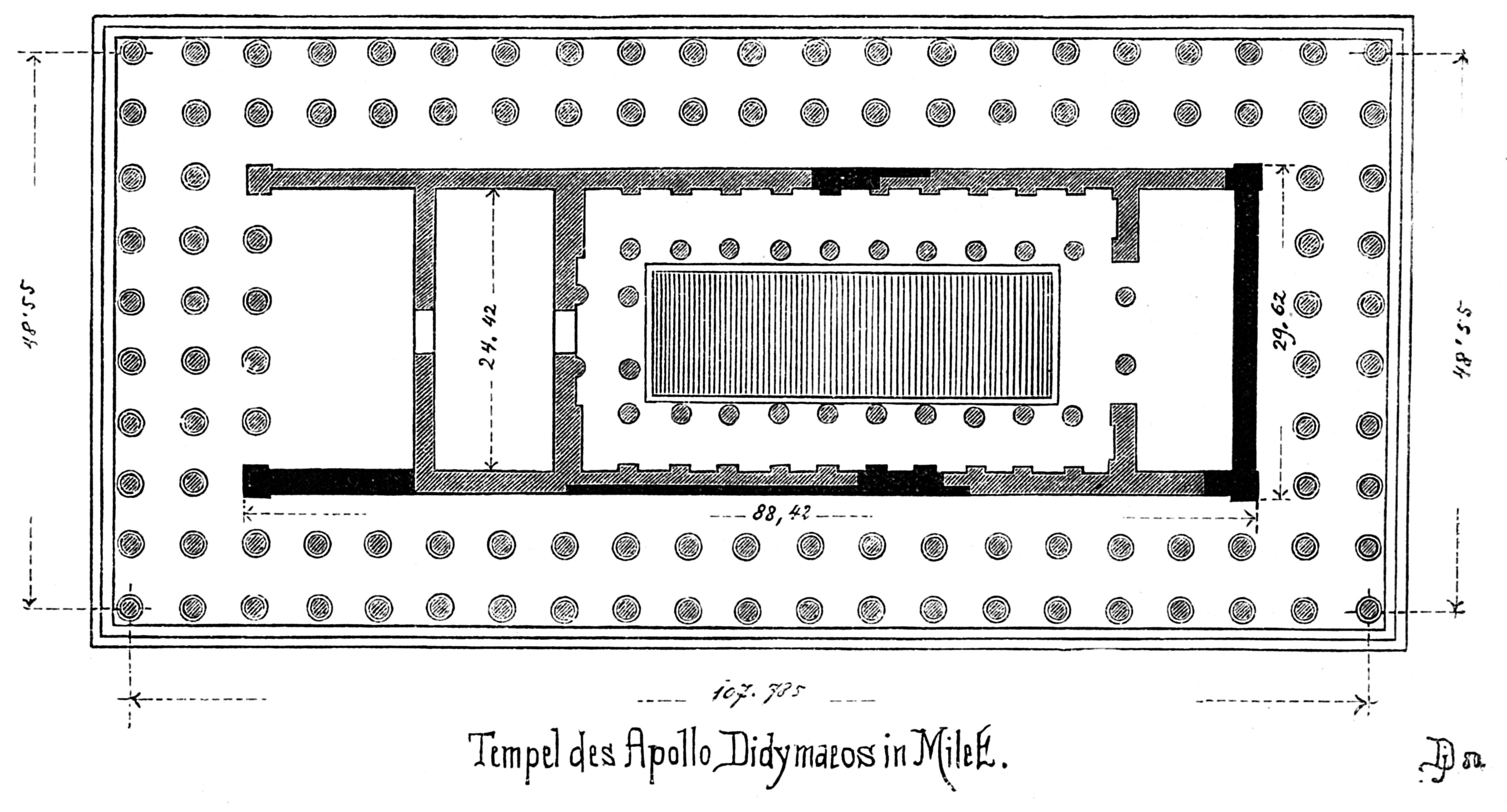 *
*Etruscan and Roman temples
* Veii (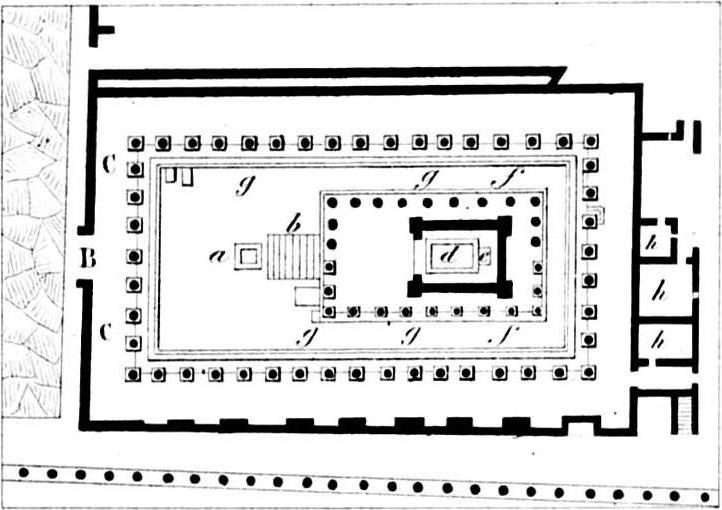 *
*Mythology
Apollo appears often in the myths, plays and hymns. As Zeus' favorite son, Apollo had direct access to the mind of Zeus and was willing to reveal this knowledge to humans. A divinity beyond human comprehension, he appears both as a beneficial and a wrathful god.Birth

 Apollo was the son of Zeus, the king of the gods, and Leto, his previous wife or one of his mistresses. Growing up, Apollo was nursed by the nymphs Korythalia and Aletheia, the personification of truth.
When Zeus' wife
Apollo was the son of Zeus, the king of the gods, and Leto, his previous wife or one of his mistresses. Growing up, Apollo was nursed by the nymphs Korythalia and Aletheia, the personification of truth.
When Zeus' wife Hyperborea
Hyperborea, the mystical land of eternal spring, venerated Apollo above all the gods. The Hyperboreans always sang and danced in his honor and hosted Pythian games. There, a vast forest of beautiful trees was called "the garden of Apollo". Apollo spent the winter months among the Hyperboreans. His absence from the world caused coldness and this was marked as his annual death. No prophecies were issued during this time.Joseph Eddy Fontenrose, ''Python: A Study of Delphic Myth and Its Origins'' He returned to the world during the beginning of the spring. The ''Theophania'' festival was held inChildhood and youth
As a child, Apollo is said to have built a foundation and an altar on Delos using the horns of the goats that his sister Artemis hunted. Since he learnt the art of building when young, he later came to be known asPython
Python, a chthonic serpent-dragon, was a child of Gaia and the guardian of the Delphic Oracle, whose death was foretold by Apollo when he was still in Leto's womb. Python was the nurse of the giant Typhon. In most of the traditions, Apollo was still a child when he killed Python. Python was sent by Hera to hunt the pregnant Leto to death, and had assaulted her. To avenge the trouble given to his mother, Apollo went in search of Python and killed it in the sacred cave at Delphi with the bow and arrows that he had received from Hephaestus. The Delphian nymphs who were present encouraged Apollo during the battle with the cry "Hie Paean". After Apollo was victorious, they also brought him gifts and gave the Corycian cave to him. According to Homer, Apollo had encountered and killed the Python when he was looking for a place to establish his shrine. According to another version, when Leto was in Delphi, Python had attacked her. Apollo defended his mother and killed Python. Euripides in his ''Iphigenia in Aulis'' gives an account of his fight with Python and the event's aftermath. A detailed account of Apollo's conflict with Gaia and Zeus' intervention on behalf of his young son is also given. Apollo also demanded that all other methods of divination be made inferior to his, a wish that Zeus granted him readily. Because of this, Athena, who had been practicing divination by throwing pebbles, cast her pebbles away in displeasure.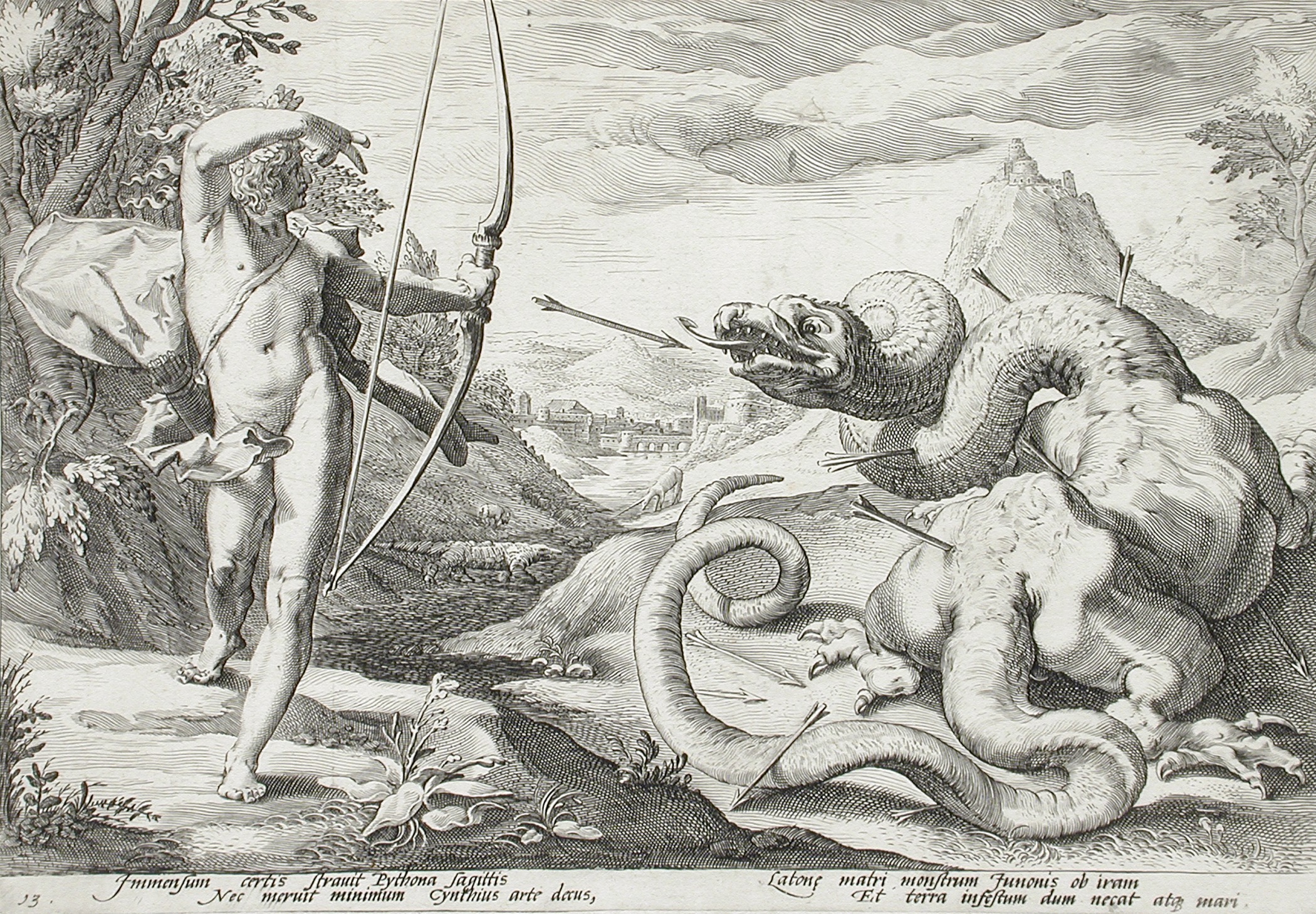 However, Apollo had committed a blood murder and had to be purified. Because Python was a child of Gaia, Gaia wanted Apollo to be banished to Tartarus as a punishment. Zeus didn't agree and instead exiled his son from Mount Olympus, Olympus, and instructed him to get purified. Apollo had to serve as a slave for nine years. After the servitude was over, as per his father's order, he travelled to the Vale of Tempe to bath in waters of Pineios (Thessaly), Peneus. There Zeus himself performed purificatory rites on Apollo. Purified, Apollo was escorted by his half sister Athena to Delphi where the oracular shrine was finally handed over to him by Gaia. According to a variation, Apollo had also travelled to Crete, where Carmanor (of Crete), Carmanor purified him. Apollo later established the Pythian games to appropriate Gaia. Henceforth, Apollo became the god who cleansed himself from the sin of murder and, made men aware of their guilt and purified them.
Soon after, Zeus instructed Apollo to go to Delphi and establish his law. But Apollo, disobeying his father, went to the land of Hyperborea and stayed there for a year. He returned only after the Delphians sang hymns to him and pleaded him to come back. Zeus, pleased with his son's integrity, gave Apollo the seat next to him on his right side. He also gave to Apollo various gifts, like a golden tripod, a golden bow and arrows, a golden chariot and the city of Delphi.
Soon after his return, Apollo needed to recruit people to Delphi. So, when he spotted a ship sailing from Crete, he sprang aboard in the form of a dolphin. The crew was awed into submission and followed a course that led the ship to Delphi. There Apollo revealed himself as a god. Initiating them to his service, he instructed them to keep righteousness in their hearts. The
However, Apollo had committed a blood murder and had to be purified. Because Python was a child of Gaia, Gaia wanted Apollo to be banished to Tartarus as a punishment. Zeus didn't agree and instead exiled his son from Mount Olympus, Olympus, and instructed him to get purified. Apollo had to serve as a slave for nine years. After the servitude was over, as per his father's order, he travelled to the Vale of Tempe to bath in waters of Pineios (Thessaly), Peneus. There Zeus himself performed purificatory rites on Apollo. Purified, Apollo was escorted by his half sister Athena to Delphi where the oracular shrine was finally handed over to him by Gaia. According to a variation, Apollo had also travelled to Crete, where Carmanor (of Crete), Carmanor purified him. Apollo later established the Pythian games to appropriate Gaia. Henceforth, Apollo became the god who cleansed himself from the sin of murder and, made men aware of their guilt and purified them.
Soon after, Zeus instructed Apollo to go to Delphi and establish his law. But Apollo, disobeying his father, went to the land of Hyperborea and stayed there for a year. He returned only after the Delphians sang hymns to him and pleaded him to come back. Zeus, pleased with his son's integrity, gave Apollo the seat next to him on his right side. He also gave to Apollo various gifts, like a golden tripod, a golden bow and arrows, a golden chariot and the city of Delphi.
Soon after his return, Apollo needed to recruit people to Delphi. So, when he spotted a ship sailing from Crete, he sprang aboard in the form of a dolphin. The crew was awed into submission and followed a course that led the ship to Delphi. There Apollo revealed himself as a god. Initiating them to his service, he instructed them to keep righteousness in their hearts. The Tityos
 Hera once again sent another giant, Tityos to rape Leto. This time Apollo shot him with his arrows and attacked him with his golden sword. According to other version, Artemis also aided him in protecting their mother by attacking Tityos with her arrows. After the battle Zeus finally relented his aid and hurled Tityos down to Tartarus. There, he was pegged to the rock floor, covering an area of , where a pair of vultures feasted daily on his liver.
Hera once again sent another giant, Tityos to rape Leto. This time Apollo shot him with his arrows and attacked him with his golden sword. According to other version, Artemis also aided him in protecting their mother by attacking Tityos with her arrows. After the battle Zeus finally relented his aid and hurled Tityos down to Tartarus. There, he was pegged to the rock floor, covering an area of , where a pair of vultures feasted daily on his liver.
Admetus
Admetus was the king of Pherae, who was known for his hospitality. When Apollo was exiled from Olympus for killing Python, he served as a herdsman under Admetus, who was then young and unmarried. Apollo is said to have shared a romantic relationship with Admetus during his stay.Callimachus, Hymn II to Apollo. After completing his years of servitude, Apollo went back to Olympus as a god. Because Admetus had treated Apollo well, the god conferred great benefits on him in return. Apollo's mere presence is said to have made the cattle give birth to twins. Apollo helped Admetus win the hand of Alcestis, the daughter of Pelias, King Pelias,Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Apollodorus1.9.15
Hyginus, ''Fabulae'
50-51
by taming a lion and a boar to draw Admetus' chariot. He was present during their wedding to give his blessings. When Admetus angered the goddess Artemis by forgetting to give her the due offerings, Apollo came to the rescue and calmed his sister. When Apollo learnt of Admetus' untimely death, he convinced or tricked the Moirai, Fates into letting Admetus live past his time. According to another version, or perhaps some years later, when Zeus struck down Apollo's son Asclepius with a lightning bolt for resurrecting the dead, Apollo in revenge killed the Cyclopes, who had fashioned the bolt for Zeus.Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Apollodorus
3.10.4
Apollo would have been banished to Tartarus for this, but his mother Leto intervened, and reminding Zeus of their old love, pleaded him not to kill their son. Zeus obliged and sentenced Apollo to one year of Penal labour, hard labor once again under Admetus. The love between Apollo and Admetus was a favored topic of Roman poets like Ovid and Maurus Servius Honoratus, Servius.
Niobe
The fate of Niobe was prophesied by Apollo while he was still in Leto's womb. Niobe was the queen of Thebes (Greece), Thebes and wife of Amphion. She displayed hubris when she boasted that she was superior to Leto because she had fourteen children (Niobids), seven male and seven female, while Leto had only two. She further mocked Apollo's effeminate appearance and Artemis' manly appearance. Leto, insulted by this, told her children to punish Niobe. Accordingly, Apollo killed Niobe's sons, and Artemis her daughters. According to some versions of the myth, among the Niobids, Chloris and her brother Amyclas were not killed because they prayed to Leto. Amphion, at the sight of his dead sons, either killed himself or was killed by Apollo after swearing revenge. A devastated Niobe fled to Spil Mount, Mount Sipylos in Asia Minor and turned into stone as she wept. Her tears formed the river Achelous. Zeus had turned all the people of Thebes to stone and so no one buried the Niobids until the ninth day after their death, when the gods themselves entombed them. When Chloris married and had children, Apollo granted her son Nestor (mythology), Nestor the years he had taken away from the Niobids. Hence, Nestor was able to live for 3 generations.Building the walls of Troy
 Once Apollo and Poseidon served under the Trojan king Laomedon in accordance to Zeus' words. Apollodorus states that the gods willingly went to the king disguised as humans in order to check his hubris. Apollo guarded the cattle of Laomedon in the valleys of mount Ida, while Poseidon built the walls of Troy. Other versions make both Apollo and Poseidon the builders of the wall. In Ovid's account, Apollo completes his task by playing his tunes on his lyre.
In Pindar's odes, the gods took a mortal named Aeacus as their assistant. When the work was completed, three snakes rushed against the wall, and though the two that attacked the sections of the wall built by the gods fell down dead, the third forced its way into the city through the portion of the wall built by Aeacus. Apollo immediately prophesied that Troy would fall at the hands of Aeacus's descendants, the Aeacidae (i.e. his son Telamon joined Heracles when he sieged the city during Laomedon's rule. Later, his great-grandson Neoptolemus was present in the wooden horse that lead to the downfall of Troy).
However, the king not only refused to give the gods the wages he had promised, but also threatened to bind their feet and hands, and sell them as slaves. Angered by the unpaid labour and the insults, Apollo infected the city with a pestilence and Posedion sent the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus. To deliver the city from it, Laomedon had to sacrifice his daughter Hesione (who would later be saved by Heracles).
During his stay in Troy, Apollo had a lover named Ourea, who was a nymph and daughter of Poseidon. Together they had a son named Ileus, whom Apollo loved dearly.Hesiod, ''Catalogues of Women'' Fragment 83
Once Apollo and Poseidon served under the Trojan king Laomedon in accordance to Zeus' words. Apollodorus states that the gods willingly went to the king disguised as humans in order to check his hubris. Apollo guarded the cattle of Laomedon in the valleys of mount Ida, while Poseidon built the walls of Troy. Other versions make both Apollo and Poseidon the builders of the wall. In Ovid's account, Apollo completes his task by playing his tunes on his lyre.
In Pindar's odes, the gods took a mortal named Aeacus as their assistant. When the work was completed, three snakes rushed against the wall, and though the two that attacked the sections of the wall built by the gods fell down dead, the third forced its way into the city through the portion of the wall built by Aeacus. Apollo immediately prophesied that Troy would fall at the hands of Aeacus's descendants, the Aeacidae (i.e. his son Telamon joined Heracles when he sieged the city during Laomedon's rule. Later, his great-grandson Neoptolemus was present in the wooden horse that lead to the downfall of Troy).
However, the king not only refused to give the gods the wages he had promised, but also threatened to bind their feet and hands, and sell them as slaves. Angered by the unpaid labour and the insults, Apollo infected the city with a pestilence and Posedion sent the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus. To deliver the city from it, Laomedon had to sacrifice his daughter Hesione (who would later be saved by Heracles).
During his stay in Troy, Apollo had a lover named Ourea, who was a nymph and daughter of Poseidon. Together they had a son named Ileus, whom Apollo loved dearly.Hesiod, ''Catalogues of Women'' Fragment 83
Trojan War
Apollo sided with the Trojans during the Trojan War waged by the Greeks against the Trojans. During the war, the Greek king Agamemnon captured Chryseis, the daughter of Apollo's priest Chryses, and refused to return her. Angered by this, Apollo shot arrows infected with the plague into the Greek encampment. He demanded that they return the girl, and the Achaeans (Greeks) complied, indirectly causing the ''Achilles and Patroclus#In the Iliad, anger of Achilles'', which is the theme of the '' Iliad''. Receiving the aegis from Zeus, Apollo entered the battlefield as per his father's command, causing great terror to the enemy with his war cry. He pushed the Greeks back and destroyed many of the soldiers. He is described as "the rouser of armies" because he rallied the Trojan army when they were falling apart. When Zeus allowed the other gods to get involved in the war, Apollo was provoked by Poseidon to a duel. However, Apollo declined to fight him, saying that he wouldn't fight his uncle for the sake of mortals. When the Greek hero Diomedes injured the Trojan hero Aeneas, Aphrodite tried to rescue him, but Diomedes injured her as well. Apollo then enveloped Aeneas in a cloud to protect him. He repelled the attacks Diomedes made on him and gave the hero a stern warning to abstain himself from attacking a god. Aeneas was then taken to Pergamos, a sacred spot in Troy, where he was healed. After the death of Sarpedon (Trojan War hero), Sarpedon, a son of Zeus, Apollo rescued the corpse from the battlefield as per his father's wish and cleaned it. He then gave it to Sleep (Hypnos) and Death (Thanatos). Apollo had also once convinced Athena to stop the war for that day, so that the warriors can relieve themselves for a while. The Trojan hero Hector (who, according to some, was the god's own son by Hecuba) was favored by Apollo. When he got severely injured, Apollo healed him and encouraged him to take up his arms. During a duel with Achilles, when Hector was about to lose, Apollo hid Hector in a cloud of mist to save him. When the Greek warrior Patroclus tried to get into the fort of Troy, he was stopped by Apollo. Encouraging Hector to attack Patroclus, Apollo stripped the armour of the Greek warrior and broke his weapons. Patroclus was eventually killed by Hector. At last, after Hector's fated death, Apollo protected his corpse from Achilles' attempt to mutilate it by creating a magical cloud over the corpse, shielding it from the rays of the Helios, sun.
Apollo held a grudge against Achilles throughout the war because Achilles had murdered his son Tenes before the war began and brutally assassinated his son Troilus in his own temple. Not only did Apollo save Hector from Achilles, he also tricked Achilles by disguising himself as a Trojan warrior and driving him away from the gates. He foiled Achilles' attempt to mutilate Hector's dead body.
Finally, Apollo caused Achilles' death by guiding an arrow shot by Paris (mythology), Paris into Achilles' heel. In some versions, Apollo himself killed Achilles by taking the disguise of Paris.
Apollo helped many Trojan warriors, including Agenor, Polydamas (mythology), Polydamas, Glaucus in the battlefield. Though he greatly favored the Trojans, Apollo was bound to follow the orders of Zeus and served his father loyally during the war.
The Trojan hero Hector (who, according to some, was the god's own son by Hecuba) was favored by Apollo. When he got severely injured, Apollo healed him and encouraged him to take up his arms. During a duel with Achilles, when Hector was about to lose, Apollo hid Hector in a cloud of mist to save him. When the Greek warrior Patroclus tried to get into the fort of Troy, he was stopped by Apollo. Encouraging Hector to attack Patroclus, Apollo stripped the armour of the Greek warrior and broke his weapons. Patroclus was eventually killed by Hector. At last, after Hector's fated death, Apollo protected his corpse from Achilles' attempt to mutilate it by creating a magical cloud over the corpse, shielding it from the rays of the Helios, sun.
Apollo held a grudge against Achilles throughout the war because Achilles had murdered his son Tenes before the war began and brutally assassinated his son Troilus in his own temple. Not only did Apollo save Hector from Achilles, he also tricked Achilles by disguising himself as a Trojan warrior and driving him away from the gates. He foiled Achilles' attempt to mutilate Hector's dead body.
Finally, Apollo caused Achilles' death by guiding an arrow shot by Paris (mythology), Paris into Achilles' heel. In some versions, Apollo himself killed Achilles by taking the disguise of Paris.
Apollo helped many Trojan warriors, including Agenor, Polydamas (mythology), Polydamas, Glaucus in the battlefield. Though he greatly favored the Trojans, Apollo was bound to follow the orders of Zeus and served his father loyally during the war.
Heracles
After Heracles (then named Alcides) was struck with madness and killed his family, he sought to purify himself and consulted the oracle of Apollo. Apollo, through the Pythia, commanded him to serve king Eurystheus for twelve years and complete the ten tasks the king would give him. Only then would Alcides be absolved of his sin. Apollo also renamed him as Heracles. To complete his third task, Heracles had to capture the Ceryneian Hind, a hind sacred to Artemis, and bring back it alive. After chasing the hind for one year, the animal eventually got tired, and when it tried crossing the river Ladon, Heracles captured it. While he was taking it back, he was confronted by Apollo and Artemis, who were angered at Heracles for this act. However, Heracles soothed the goddess and explained his situation to her. After much pleading, Artemis permitted him to take the hind and told him to return it later.
After he was freed from his servitude to Eurystheus, Heracles fell in conflict with Iphytus, a prince of Oechalia, and murdered him. Soon after, he contracted a terrible disease. He consulted the oracle of Apollo once again, in hope of ridding himself of the disease. The Pythia, however, denied to give any prophesy. In anger, Heracles snatched the sacred tripod and started walking away, intending to start his own oracle. However, Apollo did not tolerate this and stopped Heracles; a duel ensued between them. Artemis rushed to support Apollo, while Athena supported Heracles. Soon, Zeus threw his thunderbolt between the fighting brothers and separated them. He reprimanded Heracles for this act of violation and asked Apollo to give a solution to Heracles. Apollo then ordered the hero to serve under Omphale, queen of
To complete his third task, Heracles had to capture the Ceryneian Hind, a hind sacred to Artemis, and bring back it alive. After chasing the hind for one year, the animal eventually got tired, and when it tried crossing the river Ladon, Heracles captured it. While he was taking it back, he was confronted by Apollo and Artemis, who were angered at Heracles for this act. However, Heracles soothed the goddess and explained his situation to her. After much pleading, Artemis permitted him to take the hind and told him to return it later.
After he was freed from his servitude to Eurystheus, Heracles fell in conflict with Iphytus, a prince of Oechalia, and murdered him. Soon after, he contracted a terrible disease. He consulted the oracle of Apollo once again, in hope of ridding himself of the disease. The Pythia, however, denied to give any prophesy. In anger, Heracles snatched the sacred tripod and started walking away, intending to start his own oracle. However, Apollo did not tolerate this and stopped Heracles; a duel ensued between them. Artemis rushed to support Apollo, while Athena supported Heracles. Soon, Zeus threw his thunderbolt between the fighting brothers and separated them. He reprimanded Heracles for this act of violation and asked Apollo to give a solution to Heracles. Apollo then ordered the hero to serve under Omphale, queen of Periphas
Periphas was an Attican king and a priest of Apollo. He was noble, just and rich. He did all his duties justly. Because of this people were very fond of him and started honouring him to the same extent as Zeus. At one point, they worshipped Periphas in place of Zeus and set up shrines and temples for him. This annoyed Zeus, who decided to annihilate the entire family of Periphas. But because he was a just king and a good devotee, Apollo intervened and requested his father to spare Periphas. Zeus considered Apollo's words and agreed to let him live. But he metamorphosed Periphas into an eagle and made the eagle the king of birds. When Periphas' wife requested Zeus to let her stay with her husband, Zeus turned her into a vulture and fulfilled her wish.Plato's concept of soulmates
A long time ago, there were three kinds of human beings: male, descended from the sun; female, descended from the earth; and androgynous, descended from the moon. Each human being was completely round, with four arms and fours legs, two identical faces on opposite sides of a head with four ears, and all else to match. They were powerful and unruly. Aloadae, Otis and Aloadae, Ephialtes even dared to scale Mount Olympus. To check their insolence, Zeus devised a plan to humble them and improve their manners instead of completely destroying them. He cut them all in two and asked Apollo to make necessary repairs, giving humans the individual shape they still have now. Apollo turned their heads and necks around towards their wounds, he pulled together their skin at the abdomen, and sewed the skin together at the middle of it. This is what we call navel today. He smoothened the wrinkles and shaped the chest. But he made sure to leave a few wrinkles on the abdomen and around the navel so that they might be reminded of their punishment.Nurturer of the young
Apollo ''Kourotrophos'' is the god who nurtures and protects children and the young, especially boys. He oversees their education and their passage into adulthood. Education is said to have originated from Apollo and the Muses. Many myths have him train his children. It was a custom for boys to cut and dedicate their long hair to Apollo after reaching adulthood. Chiron, the abandoned centaur, was fostered by Apollo, who instructed him in medicine, prophecy, archery and more. Chiron would later become a great teacher himself. Asclepius in his childhood gained much knowledge pertaining to medicinal arts by his father. However, he was later entrusted to Chiron for further education. Anius, Apollo's son by Rhoeo, was abandoned by his mother soon after his birth. Apollo brought him up and educated him in mantic arts. Anius later became the priest of Apollo and the king of Delos. Iamus was the son of Apollo and Evadne. When Evadne went into labour, Apollo sent the Moirai to assist his lover. After the child was born, Apollo sent snakes to feed the child some honey. When Iamus reached the age of education, Apollo took him to Olympia and taught him many arts, including the ability to understand and explain the languages of birds. Idmon was educated by Apollo to be a seer. Even though he foresaw his death that would happen in his journey with the Argonauts, he embraced his destiny and died a brave death. To commemorate his son's bravery, Apollo commanded Boeotians to build a town around the tomb of the hero, and to honor him. Apollo adopted Carnus, the abandoned son of Zeus and Europa (consort of Zeus), Europa. He reared the child with the help of his mother Leto and educated him to be a seer. When his son Melaneus of Oechalia, Melaneus reached the age of marriage, Apollo asked the princess Stratonice (mythology), Stratonice to be his son's bride and carried her away from her home when she agreed. Apollo saved a shepherd boy (name unknown) from death in a large deep cave, by the means of vultures. To thank him, the shepherd built Apollo a temple under the name Vulturius.God of music
 Immediately after his birth, Apollo demanded a lyre and invented the paean, thus becoming the god of music. As the divine singer, he is the patron of poets, singers and musicians. The invention of string music is attributed to him. Plato said that the innate ability of humans to take delight in music, rhythm and harmony is the gift of Apollo and the Muses. According to Socrates, ancient Greeks believed that Apollo is the god who directs the harmony and makes all things move together, both for the gods and the humans. For this reason, he was called ''Homopolon'' before the ''Homo'' was replaced by ''A''. Apollo's harmonious music delivered people from their pain, and hence, like Dionysus, he is also called the liberator. The swans, which were considered to be the most musical among the birds, were believed to be the "singers of Apollo". They are Apollo's sacred birds and acted as his vehicle during his travel to Hyperborea. Claudius Aelianus, Aelian says that when the singers would sing hymns to Apollo, the swans would join the chant in unison.
Immediately after his birth, Apollo demanded a lyre and invented the paean, thus becoming the god of music. As the divine singer, he is the patron of poets, singers and musicians. The invention of string music is attributed to him. Plato said that the innate ability of humans to take delight in music, rhythm and harmony is the gift of Apollo and the Muses. According to Socrates, ancient Greeks believed that Apollo is the god who directs the harmony and makes all things move together, both for the gods and the humans. For this reason, he was called ''Homopolon'' before the ''Homo'' was replaced by ''A''. Apollo's harmonious music delivered people from their pain, and hence, like Dionysus, he is also called the liberator. The swans, which were considered to be the most musical among the birds, were believed to be the "singers of Apollo". They are Apollo's sacred birds and acted as his vehicle during his travel to Hyperborea. Claudius Aelianus, Aelian says that when the singers would sing hymns to Apollo, the swans would join the chant in unison.
 Among the Pythagoreanism, Pythagoreans, the study of mathematics and music were connected to the worship of Apollo, their principal deity. Their belief was that the music purifies the soul, just as medicine purifies the body. They also believed that music was delegated to the same mathematical laws of harmony as the mechanics of the cosmos, evolving into an idea known as the music of the spheres.
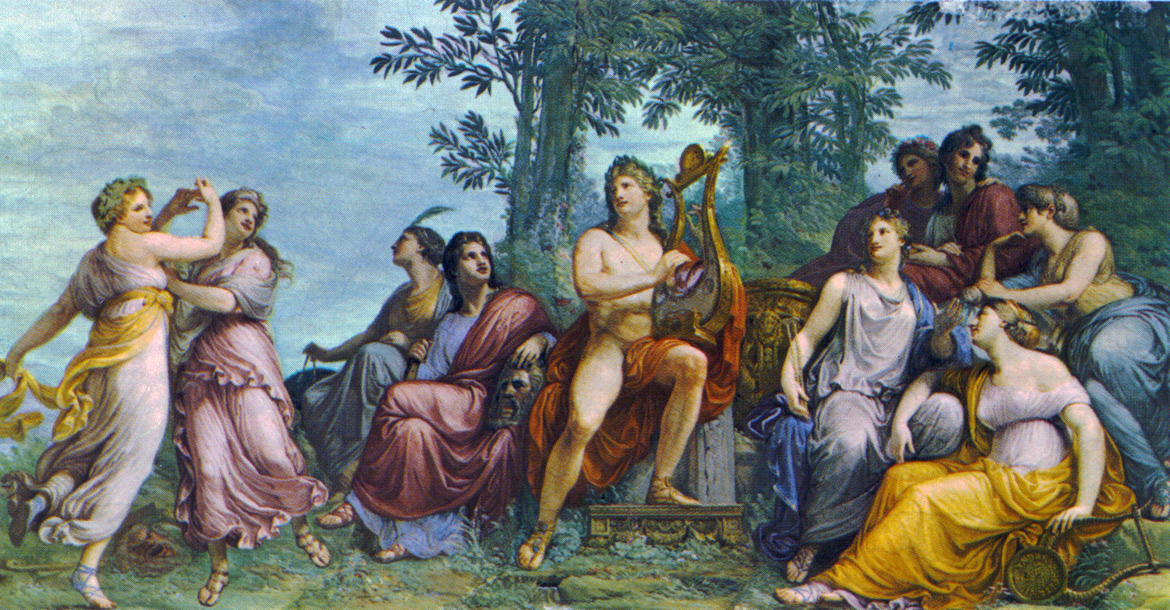
Apollo appears as the companion of the Muses, and as Musagetes ("leader of Muses") he leads them in dance. They spend their time on Parnassus, which is one of their sacred places. Apollo is also the lover of the Muses and by them he became the father of famous musicians like Orpheus and Linus of Thrace, Linus.
Apollo is often found delighting the immortal gods with his songs and music on the
Among the Pythagoreanism, Pythagoreans, the study of mathematics and music were connected to the worship of Apollo, their principal deity. Their belief was that the music purifies the soul, just as medicine purifies the body. They also believed that music was delegated to the same mathematical laws of harmony as the mechanics of the cosmos, evolving into an idea known as the music of the spheres.
Apollo appears as the companion of the Muses, and as Musagetes ("leader of Muses") he leads them in dance. They spend their time on Parnassus, which is one of their sacred places. Apollo is also the lover of the Muses and by them he became the father of famous musicians like Orpheus and Linus of Thrace, Linus.
Apollo is often found delighting the immortal gods with his songs and music on the Apollo's lyre
The invention of lyre is attributed either to Hermes or to Apollo himself. Distinctions have been made that Hermes invented lyre made of tortoise shell, whereas the lyre Apollo invented was a regular lyre. Myths tell that the infant Hermes stole a number of Apollo's cows and took them to a cave in the woods near Pylos, covering their tracks. In the cave, he found a tortoise and killed it, then removed the insides. He used one of the cow's intestines and the tortoise shell and made his Upon discovering the theft, Apollo confronted Hermes and asked him to return his cattle. When Hermes acted innocent, Apollo took the matter to Zeus. Zeus, having seen the events, sided with Apollo, and ordered Hermes to return the cattle. Hermes then began to play music on the lyre he had invented. Apollo fell in love with the instrument and offered to exchange the cattle for the lyre. Hence, Apollo then became the master of the lyre.
According to other versions, Apollo had invented the lyre himself, whose strings he tore in repenting of the excess punishment he had given to Marsyas. Hermes' lyre, therefore, would be a reinvention.
Upon discovering the theft, Apollo confronted Hermes and asked him to return his cattle. When Hermes acted innocent, Apollo took the matter to Zeus. Zeus, having seen the events, sided with Apollo, and ordered Hermes to return the cattle. Hermes then began to play music on the lyre he had invented. Apollo fell in love with the instrument and offered to exchange the cattle for the lyre. Hence, Apollo then became the master of the lyre.
According to other versions, Apollo had invented the lyre himself, whose strings he tore in repenting of the excess punishment he had given to Marsyas. Hermes' lyre, therefore, would be a reinvention.
Contest with Pan
 Once Pan (mythology), Pan had the audacity to compare his music with that of Apollo and to challenge the god of music to a contest. The mountain-god Tmolus (son of Ares), Tmolus was chosen to umpire. Pan blew on his pipes, and with his rustic melody gave great satisfaction to himself and his faithful follower, Midas, who happened to be present. Then, Apollo struck the strings of his lyre. It was so beautiful that Tmolus at once awarded the victory to Apollo, and everyone was pleased with the judgement. Only Midas dissented and questioned the justice of the award. Apollo did not want to suffer such a depraved pair of ears any longer, and caused them to become the ears of a donkey.
Once Pan (mythology), Pan had the audacity to compare his music with that of Apollo and to challenge the god of music to a contest. The mountain-god Tmolus (son of Ares), Tmolus was chosen to umpire. Pan blew on his pipes, and with his rustic melody gave great satisfaction to himself and his faithful follower, Midas, who happened to be present. Then, Apollo struck the strings of his lyre. It was so beautiful that Tmolus at once awarded the victory to Apollo, and everyone was pleased with the judgement. Only Midas dissented and questioned the justice of the award. Apollo did not want to suffer such a depraved pair of ears any longer, and caused them to become the ears of a donkey.
Contest with Marsyas
Marsyas was a satyr who was punished by Apollo for his hubris. He had found an aulos on the ground, tossed away after being invented by Athena because it made her cheeks puffy. Athena had also placed a curse upon the instrument, that whoever would pick it up would be severely punished. When Marsyas played the flute, everyone became frenzied with joy. This led Marsyas to think that he was better than Apollo, and he challenged the god to a musical contest. The contest was judged by the Muses, or the nymphs of Nysa (mythology), Nysa. Athena was also present to witness the contest. Marsyas taunted Apollo for "wearing his hair long, for having a fair face and smooth body, for his skill in so many arts".Apuleius, ''Florida'' 3.2 He also further said, The Muses and Athena sniggered at this comment. The contestants agreed to take turns displaying their skills and the rule was that the victor could "do whatever he wanted" to the loser. According to one account, after the first round, they both were deemed equal by the Nysiads. But in the next round, Apollo decided to play on his lyre and add his melodious voice to his performance. Marsyas argued against this, saying that Apollo would have an advantage and accused Apollo of cheating. But Apollo replied that since Marsyas played the flute, which needed air blown from the throat, it was similar to singing, and that either they both should get an equal chance to combine their skills or none of them should use their mouths at all. The nymphs decided that Apollo's argument was just. Apollo then played his lyre and sang at the same time, mesmerising the audience. Marsyas could not do this. Apollo was declared the winner and, angered with Marsyas' haughtiness and his accusations, decided to flay the satyr.Diodorus Siculus, Library of History 5. 75. 3
According to one account, after the first round, they both were deemed equal by the Nysiads. But in the next round, Apollo decided to play on his lyre and add his melodious voice to his performance. Marsyas argued against this, saying that Apollo would have an advantage and accused Apollo of cheating. But Apollo replied that since Marsyas played the flute, which needed air blown from the throat, it was similar to singing, and that either they both should get an equal chance to combine their skills or none of them should use their mouths at all. The nymphs decided that Apollo's argument was just. Apollo then played his lyre and sang at the same time, mesmerising the audience. Marsyas could not do this. Apollo was declared the winner and, angered with Marsyas' haughtiness and his accusations, decided to flay the satyr.Diodorus Siculus, Library of History 5. 75. 3
 According to another account, Marsyas played his flute out of tune at one point and accepted his defeat. Out of shame, he assigned to himself the punishment of being skinned for a wine sack. Another variation is that Apollo played his instrument upside down. Marsyas could not do this with his instrument. So the Muses who were the judges declared Apollo the winner. Apollo hung Marsyas from a tree to flay him.
Apollo flaying, flayed the limbs of Marsyas alive in a cave near Celaenae in Phrygia for his hubris to challenge a god. He then gave the rest of his body for proper burial and nailed Marsyas' flayed skin to a nearby pine-tree as a lesson to the others. Marsyas' blood turned into the river Marsyas. But Apollo soon repented and being distressed at what he had done, he tore the strings of his lyre and threw it away. The lyre was later discovered by the Muses and Apollo's sons Linus of Thrace, Linus and Orpheus. The Muses fixed the middle string, Linus the string struck with the forefinger, and Orpheus the lowest string and the one next to it. They took it back to Apollo, but the god, who had decided to stay away from music for a while, laid away both the lyre and the pipes at Delphi and joined Cybele in her wanderings to as far as Hyperborea.
According to another account, Marsyas played his flute out of tune at one point and accepted his defeat. Out of shame, he assigned to himself the punishment of being skinned for a wine sack. Another variation is that Apollo played his instrument upside down. Marsyas could not do this with his instrument. So the Muses who were the judges declared Apollo the winner. Apollo hung Marsyas from a tree to flay him.
Apollo flaying, flayed the limbs of Marsyas alive in a cave near Celaenae in Phrygia for his hubris to challenge a god. He then gave the rest of his body for proper burial and nailed Marsyas' flayed skin to a nearby pine-tree as a lesson to the others. Marsyas' blood turned into the river Marsyas. But Apollo soon repented and being distressed at what he had done, he tore the strings of his lyre and threw it away. The lyre was later discovered by the Muses and Apollo's sons Linus of Thrace, Linus and Orpheus. The Muses fixed the middle string, Linus the string struck with the forefinger, and Orpheus the lowest string and the one next to it. They took it back to Apollo, but the god, who had decided to stay away from music for a while, laid away both the lyre and the pipes at Delphi and joined Cybele in her wanderings to as far as Hyperborea.
Contest with Cinyras
Cinyras was a ruler of Cyprus, who was a friend of Agamemnon. Cinyras promised to assist Agamemnon in the Trojan war, but did not keep his promise. Agamemnon cursed Cinyras. He invoked Apollo and asked the god to avenge the broken promise. Apollo then had a
Patron of sailors
Apollo functions as the patron and protector of sailors, one of the duties he shares with Poseidon. In the myths, he is seen helping heroes who pray to him for safe journey. When Apollo spotted a ship of Cretan sailors that was caught in a storm, he quickly assumed the shape of a dolphin and guided their ship safely to Delphi. When the Argonauts faced a terrible storm, Jason prayed to his patron, Apollo, to help them. Apollo used his bow and golden arrow to shed light upon an island, where the Argonauts soon took shelter. This island was renamed "Anafi, Anaphe", which means "He revealed it". Apollo helped the Greek hero Diomedes, to escape from a great tempest during his journey homeward. As a token of gratitude, Diomedes built a temple in honor of Apollo under the epithet Epibaterius ("the embarker"). During the Trojan War, Odysseus came to the Trojan camp to return Chriseis, the daughter of Apollo's priest Chryses, and brought many offerings to Apollo. Pleased with this, Apollo sent gentle breezes that helped Odysseus return safely to the Greek camp. Arion was a poet who was kidnapped by some sailors for the rich prizes he possessed. Arion requested them to let him sing for the last time, to which the sailors consented. Arion began singing a song in praise of Apollo, seeking the god's help. Consequently, numerous dolphins surrounded the ship and when Arion jumped into the water, the dolphins carried him away safely.Wars
Titanomachy
OnceTrojan War
Apollo played a pivotal role in the entire Trojan War. He sided with the Trojans, and sent a terrible plague to the Greek camp, which indirectly led to the conflict between Achilles and Agamemnon. He killed the Greek heroes Patroclus, Achilles, and numerous Greek soldiers. He also helped many Trojan heroes, the most important one being Hector. After the end of the war, Apollo and Poseidon together cleaned the remains of the city and the camps.
Telegony war
A war broke out between the Brygoi and the Thesprotians, who had the support of Odysseus. The gods Athena and Ares came to the battlefield and took sides. Athena helped the hero Odysseus while Ares fought alongside of the Brygoi. When Odysseus lost, Athena and Ares came into a direct duel. To stop the battling gods and the terror created by their battle, Apollo intervened and stopped the duel between them.Indian war
When Zeus suggested thatTheban war
During the war between the sons of Oedipus, Apollo favored Amphiaraus, a seer and one of the leaders in the war. Though saddened that the seer was fated to be doomed in the war, Apollo made Amphiaraus' last hours glorious by "lighting his shield and his helm with starry gleam". When Hypseus tried to kill the hero by a spear, Apollo directed the spear towards the charioteer of Amphiaraus instead. Then Apollo himself replaced the charioteer and took the reins in his hands. He deflected many spears and arrows away them. He also killed many of the enemy warriors like Melaneus (mythology), Melaneus, Antiphus, Aetion, Polites and Lampus. At last when the moment of departure came, Apollo expressed his grief with tears in his eyes and bid farewell to Amphiaraus, who was soon engulfed by the Earth.Slaying of giants
Apollo killed the giants Python and Tityos, who had assaulted his mother Leto.Gigantomachy
During the gigantomachy, Apollo and Heracles blinded the giant Ephialtes (disambiguation), Ephialtes by shooting him in his eyes, Apollo shooting his left and Heracles his right. He also killed Porphyrion, the king of giants, using his bow and arrows.Aloadae
The Aloadae, namely Otis and Ephialtes, were twin giants who decided to wage war upon the gods. They attempted to storm Mt. Olympus by piling up mountains, and threatened to fill the sea with mountains and inundate dry land. They even dared to seek the hand of Hera and Artemis in marriage. Angered by this, Apollo killed them by shooting them with arrows. According to another tale, Apollo killed them by sending a deer between them; as they tried to kill it with their javelins, they accidentally stabbed each other and died.Phorbas
Phorbas was a savage giant king of Phlegyas (Boeotia), Phlegyas who was described as having swine like features. He wished to plunder Delphi for its wealth. He seized the roads to Delphi and started harassing the pilgrims. He captured the old people and children and sent them to his army to hold them for ransom. And he challenged the young and sturdy men to a match of boxing, only to cut their heads off when they would get defeated by him. He hung the chopped off heads to an oak tree. Finally, Apollo came to put an end to this cruelty. He entered a boxing contest with Phorbas and killed him with a single blow.Other stories
 In the first Olympic games, Apollo defeated Ares and became the victor in wrestling. He outran Hermes in the race and won first place.
Apollo divides months into summer and winter. He rides on the back of a swan to the land of the Hyperboreans during the winter months, and the absence of warmth in winters is due to his departure. During his absence, Delphi was under the care of
In the first Olympic games, Apollo defeated Ares and became the victor in wrestling. He outran Hermes in the race and won first place.
Apollo divides months into summer and winter. He rides on the back of a swan to the land of the Hyperboreans during the winter months, and the absence of warmth in winters is due to his departure. During his absence, Delphi was under the care of Molpadia and Parthenos
Molpadia and Parthenos were the sisters of Rhoeo, a former lover of Apollo. One day, they were put in charge of watching their father's ancestral wine jar but they fell asleep while performing this duty. While they were asleep, the wine jar was broken by the swines their family kept. When the sisters woke up and saw what had happened, they threw themselves off a cliff in fear of their father's wrath. Apollo, who was passing by, caught them and carried them to two different cities in Chersonesus, Molpadia to Castabus and Parthenos to Bubastus. He turned them into goddesses and they both received divine honors. Molpadia's name was changed to Hemithea (mythology), Hemithea upon her deification.Prometheus
Prometheus was the titan who was punished by Zeus for stealing fire. He was bound to a rock, where each day an eagle was sent to eat Prometheus' liver, which would then grow back overnight to be eaten again the next day. Seeing his plight, Apollo pleaded Zeus to release the kind Titan, while Artemis and Leto stood behind him with tears in their eyes. Zeus, moved by Apollo's words and the tears of the goddesses, finally sent Heracles to free Prometheus.
The rock of Leukas
Leukatas was believed to be a white colored rock jutting out from the island of Lefkada, Leukas into the sea. It was present in the sanctuary of Apollo Leukates. A leap from this rock was believed to have put an end to the longings of love.Strabo, ''Geographica, Geography''10.2.8
Once, Aphrodite fell deeply in love with Adonis, a young man of great beauty who was later accidentally killed by a boar. Heartbroken, Aphrodite wandered looking for the rock of Leukas. When she reached the sanctuary of Apollo in Argos, she confided in him her love and sorrow. Apollo then brought her to the rock of Leukas and asked her to throw herself from the top of the rock. She did so and was freed from her love. When she sought for the reason behind this, Apollo told her that Zeus, before taking another lover, would sit on this rock to free himself from his love to Hera.Ptolemy Hephaestion, ''New History Book'' 7 Another tale relates that a man named Nireus, who fell in love with the cult statue of Athena, came to the rock and jumped in order relieve himself. After jumping, he fell into the net of a fisherman in which, when he was pulled out, he found a box filled with gold. He fought with the fisherman and took the gold, but Apollo appeared to him in the night in a dream and warned him not to appropriate gold which belonged to others. It was an ancestral custom among the Leukadians to fling a criminal from this rock every year at the sacrifice performed in honor of Apollo for the sake of averting evil. However, a number of men would be stationed all around below rock to catch the criminal and take him out of the borders in order to exile him from the island. This was the same rock from which, according to a legend, Sappho took her suicidal leap.

Female lovers
Love affairs ascribed to Apollo are a late development in Greek mythology. Their vivid anecdotal qualities have made some of them favorites of painters since the Renaissance, the result being that they stand out more prominently in the modern imagination. Daphne was a nymph who scorned Apollo's advances and ran away from him. When Apollo chased her in order to persuade her, she changed herself into a laurel tree. According to other versions, she cried for help during the chase, and Gaia helped her by taking her in and placing a laurel tree in her place. According to Roman poet Ovid, the chase was brought about by Cupid, who hit Apollo with golden arrow of love and Daphne with leaden arrow of hatred. The myth explains the origin of the Bay Laurel, laurel and connection of Apollo with the laurel and its leaves, which his priestess employed at
Daphne was a nymph who scorned Apollo's advances and ran away from him. When Apollo chased her in order to persuade her, she changed herself into a laurel tree. According to other versions, she cried for help during the chase, and Gaia helped her by taking her in and placing a laurel tree in her place. According to Roman poet Ovid, the chase was brought about by Cupid, who hit Apollo with golden arrow of love and Daphne with leaden arrow of hatred. The myth explains the origin of the Bay Laurel, laurel and connection of Apollo with the laurel and its leaves, which his priestess employed at  Apollo is said to have been the lover of all nine Muses, and not being able to choose one of them, decided to remain unwed. He fathered the Corybantes by the Muse Thalia (Muse), Thalia, Orpheus by Calliope, Linus (Thracian), Linus of Thrace by Calliope or Urania and Hymenaios (Hymen) by one of the Muses.
In the Great Eoiae that is attributed to Hesoid, Scylla is the daughter of Apollo and Hecate.
Cyrene (mythology), Cyrene was a Thessalian princess whom Apollo loved. In her honor, he built the city Cyrene and made her its ruler. She was later granted longevity by Apollo who turned her into a nymph. The couple had two sons, Aristaeus, and Idmon.
Evadne was a nymph daughter of Poseidon and a lover of Apollo. She bore him a son, Iamos. During the time of the childbirth, Apollo sent Eileithyia, the goddess of childbirth to assist her.
Rhoeo, a princess of the island of Naxos was loved by Apollo. Out of affection for her, Apollo turned her sisters into goddesses. On the island Delos she bore Apollo a son named Anius. Not wanting to have the child, she entrusted the infant to Apollo and left. Apollo raised and educated the child on his own.
Ourea, a daughter of Poseidon, fell in love with Apollo when he and Poseidon were serving the Trojan king Laomedon. They both united on the day the walls of Troy were built. She bore to Apollo a son, whom Apollo named Ileus, after the city of his birth, Ilion ( Troy). Ileus was very dear to Apollo.
Thero (mythology), Thero, daughter of Phylas, a maiden as beautiful as the moonbeams, was loved by the radiant Apollo, and she loved him in return. By their union, she became mother of Chaeron, who was famed as "the tamer of horses". He later built the city Chaeronea.
Hyrie or Thyrie was the mother of Cycnus (son of Apollo), Cycnus. Apollo turned both the mother and son into swans when they jumped into a lake and tried to kill themselves.
Hecuba was the wife of King Priam of Troy, and Apollo had a son with her named Troilus. An
Apollo is said to have been the lover of all nine Muses, and not being able to choose one of them, decided to remain unwed. He fathered the Corybantes by the Muse Thalia (Muse), Thalia, Orpheus by Calliope, Linus (Thracian), Linus of Thrace by Calliope or Urania and Hymenaios (Hymen) by one of the Muses.
In the Great Eoiae that is attributed to Hesoid, Scylla is the daughter of Apollo and Hecate.
Cyrene (mythology), Cyrene was a Thessalian princess whom Apollo loved. In her honor, he built the city Cyrene and made her its ruler. She was later granted longevity by Apollo who turned her into a nymph. The couple had two sons, Aristaeus, and Idmon.
Evadne was a nymph daughter of Poseidon and a lover of Apollo. She bore him a son, Iamos. During the time of the childbirth, Apollo sent Eileithyia, the goddess of childbirth to assist her.
Rhoeo, a princess of the island of Naxos was loved by Apollo. Out of affection for her, Apollo turned her sisters into goddesses. On the island Delos she bore Apollo a son named Anius. Not wanting to have the child, she entrusted the infant to Apollo and left. Apollo raised and educated the child on his own.
Ourea, a daughter of Poseidon, fell in love with Apollo when he and Poseidon were serving the Trojan king Laomedon. They both united on the day the walls of Troy were built. She bore to Apollo a son, whom Apollo named Ileus, after the city of his birth, Ilion ( Troy). Ileus was very dear to Apollo.
Thero (mythology), Thero, daughter of Phylas, a maiden as beautiful as the moonbeams, was loved by the radiant Apollo, and she loved him in return. By their union, she became mother of Chaeron, who was famed as "the tamer of horses". He later built the city Chaeronea.
Hyrie or Thyrie was the mother of Cycnus (son of Apollo), Cycnus. Apollo turned both the mother and son into swans when they jumped into a lake and tried to kill themselves.
Hecuba was the wife of King Priam of Troy, and Apollo had a son with her named Troilus. An Male lovers

 Hyacinth (mythology), Hyacinth (or Hyacinthus), a beautiful and athletic Spartan prince, was one of Apollo's favourite lovers. The pair was practicing throwing the Discus throw, discus when a discus thrown by Apollo was blown off course by the jealous Zephyrus and struck Hyacinthus in the head, killing him instantly. Apollo is said to be filled with grief. Out of Hyacinthus' blood, Apollo created a hyacinth (plant), flower named after him as a memorial to his death, and his tears stained the flower petals with the interjection , meaning ''alas''. He was later resurrected and taken to heaven. The festival Hyacinthia was a national celebration of Sparta, which commemorated the death and rebirth of Hyacinthus.
Another male lover was Cyparissus, a descendant of Heracles. Apollo gave him a tame deer as a companion but Cyparissus accidentally killed it with a Pilum, javelin as it lay asleep in the undergrowth. Cyparissus was so saddened by its death that he asked Apollo to let his tears fall forever. Apollo granted the request by turning him into the Cupressaceae, Cypress named after him, which was said to be a sad tree because the sap forms droplets like tears on the trunk.
Hyacinth (mythology), Hyacinth (or Hyacinthus), a beautiful and athletic Spartan prince, was one of Apollo's favourite lovers. The pair was practicing throwing the Discus throw, discus when a discus thrown by Apollo was blown off course by the jealous Zephyrus and struck Hyacinthus in the head, killing him instantly. Apollo is said to be filled with grief. Out of Hyacinthus' blood, Apollo created a hyacinth (plant), flower named after him as a memorial to his death, and his tears stained the flower petals with the interjection , meaning ''alas''. He was later resurrected and taken to heaven. The festival Hyacinthia was a national celebration of Sparta, which commemorated the death and rebirth of Hyacinthus.
Another male lover was Cyparissus, a descendant of Heracles. Apollo gave him a tame deer as a companion but Cyparissus accidentally killed it with a Pilum, javelin as it lay asleep in the undergrowth. Cyparissus was so saddened by its death that he asked Apollo to let his tears fall forever. Apollo granted the request by turning him into the Cupressaceae, Cypress named after him, which was said to be a sad tree because the sap forms droplets like tears on the trunk.
 Admetus, the king of Pherae, was also Apollo's lover.Plutarch, ''Life of Numa''
Admetus, the king of Pherae, was also Apollo's lover.Plutarch, ''Life of Numa''4.5
During his exile, which lasted either for one year or nine years, Apollo served Admetus as a herdsman. The romantic nature of their relationship was first described by Callimachus of Alexandria, who wrote that Apollo was "fired with love" for Admetus. Plutarch lists Admetus as one of Apollo's lovers and says that Apollo served Admetus because he doted upon him. Latin poet Ovid in his Ars Amatoria said that even though he was a god, Apollo forsook his pride and stayed in as a servant for the sake of Admetus. Tibullus describes Apollo's love to the king as ''servitium amoris'' (slavery of love) and asserts that Apollo became his servant not by force but by choice. He would also make cheese and serve it to Admetus. His domestic actions caused embarrassment to his family.
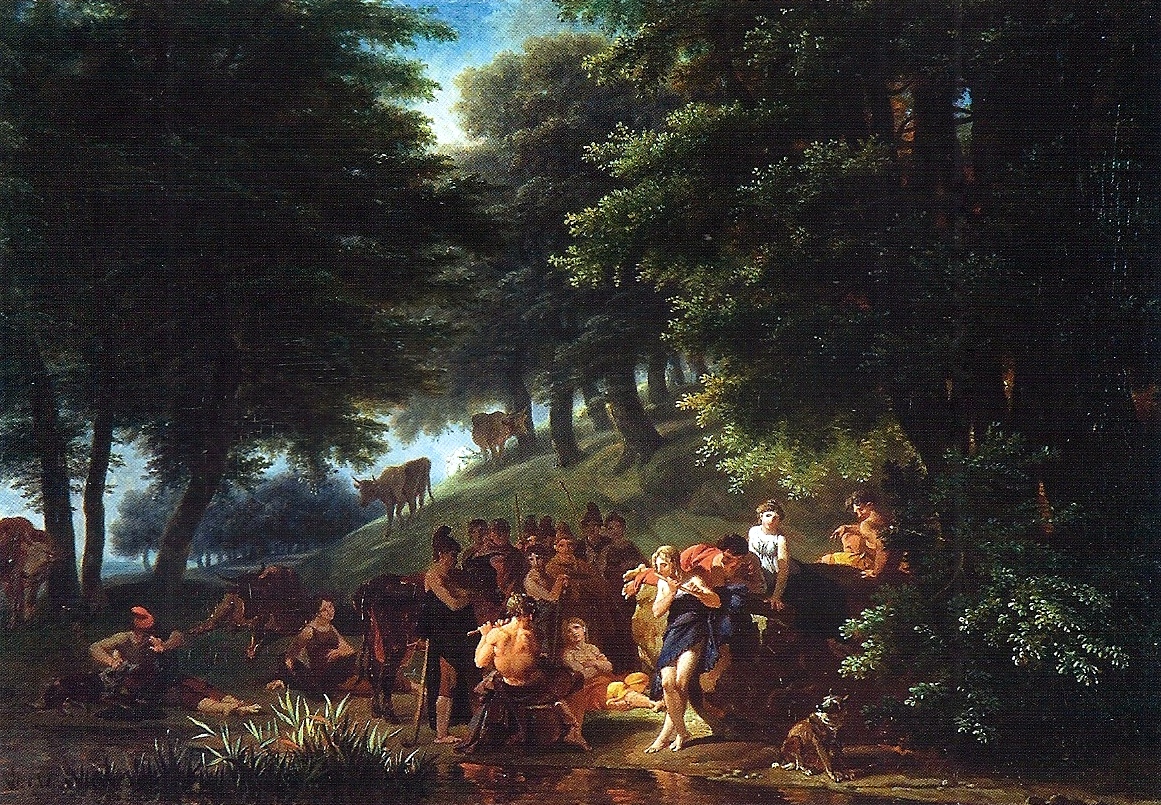 When Admetus wanted to marry princess Alcestis, Apollo provided a chariot pulled by a lion and a boar he had tamed. This satisfied Alcestis' father and he let Admetus marry his daughter. Further, Apollo saved the king from Artemis' wrath and also convinced the Moirai to postpone Admetus' death once.
When Admetus wanted to marry princess Alcestis, Apollo provided a chariot pulled by a lion and a boar he had tamed. This satisfied Alcestis' father and he let Admetus marry his daughter. Further, Apollo saved the king from Artemis' wrath and also convinced the Moirai to postpone Admetus' death once.
23
[= Hesiod, ''Megalai Ehoiai'' fr. 16]; Smith 1873
s.v. Hymen
Grimal, s.v. Hymenaeus. *Iapis, to whom Apollo taught the art of healing *Phorbas of Thessaly, Phorbas, the dragon slayer (probably the son of Triopas)Plutarch, ''Numa'
4.5
cf. Hyginus, ''De Astronomica''
2.14
Children
Apollo sired many children, from mortal women and nymphs as well as the goddesses. His children grew up to be physicians, musicians, poets, seers or archers. Many of his sons founded new cities and became kings. They were all usually very beautiful. Asclepius is the most famous son of Apollo. His skills as a physician surpassed that of Apollo's. Zeus killed him for bringing back the dead, but upon Apollo's request, he was resurrected as a god. Aristaeus was placed under the care of Chiron after his birth. He became the god of beekeeping, cheese making, animal husbandry and more. He was ultimately given immortality for the benefits he bestowed upon the humanity. The Corybantes were spear-clashing, dancing demigods. The sons of Apollo who participated in the Trojan War include the Trojan princes Hector and Troilus, as well as Tenes, the king of Tenedos, all three of whom were killed by Achilles over the course of the war. Apollo's children who became musicians and bards include Orpheus, Linus of Thrace, Linus, Ialemus, Hymen (god), Hymenaeus, Philammon, Eumolpus and Eleuther. Apollo fathered 3 daughters, Apollonis, Borysthenis and Cephisso, who formed a group of minor Muses, the "Musa Apollonides". They were nicknamed Nete, Mese and Hypate after the highest, middle and lowest strings of his lyre. Phemonoe was a seer and a poetess who was the inventor of Hexameter. Apis (Greek mythology), Apis, Idmon, Iamus, Tenerus (son of Apollo), Tenerus, Mopsus, Themisto (disambiguation), Galeus, Telmessus and others were gifted seers. Anius, Pythaeus and Ismenus lived as high priests. Most of them were trained by Apollo himself. Arabius (mythology), Arabus, Delphos (mythology), Delphos, Dryops (mythology), Dryops, Miletos, Tenes, Epidaurus (mythology), Epidaurus, Ceos, Lycorus, Lycoras, Syrus, Pisus, Marathus, Megarus, Patarus,Failed love attempts
Marpessa (daughter of Evenus), Marpessa was kidnapped by Idas but was loved by Apollo as well. Zeus made her choose between them, and she chose Idas on the grounds that Apollo, being immortal, would tire of her when she grew old. Sinope (mythology), Sinope, a nymph, was approached by the amorous Apollo. She made him promise that he would grant to her whatever she would ask for, and then cleverly asked him to let her stay a virgin. Apollo kept his promise and went back. Bolina was admired by Apollo but she refused him and jumped into the sea. To avoid her death, Apollo turned her into a nymph, saving her life. Castalia was a nymph whom Apollo loved. She fled from him and dove into the castalian Spring, spring at Delphi, at the base of Mt. Parnassos, which was then named after her. Water from this spring was sacred; it was used to clean the Delphian temples and inspire the priestesses. Cassandra, was a daughter of Hecuba and Priam. Apollo wished to court her. Cassandra promised to return his love on one condition - he should give her the power to see the future. Apollo fulfilled her wish, but she went back on her word and rejected him soon after. Angered that she broke her promise, Apollo cursed her that even though she would see the future, no one would ever believe her prophecies. Hestia, the goddess of the hearth, rejected both Apollo's and Poseidon's marriage proposals and swore that she would always stay unmarried.Female counterparts

Artemis
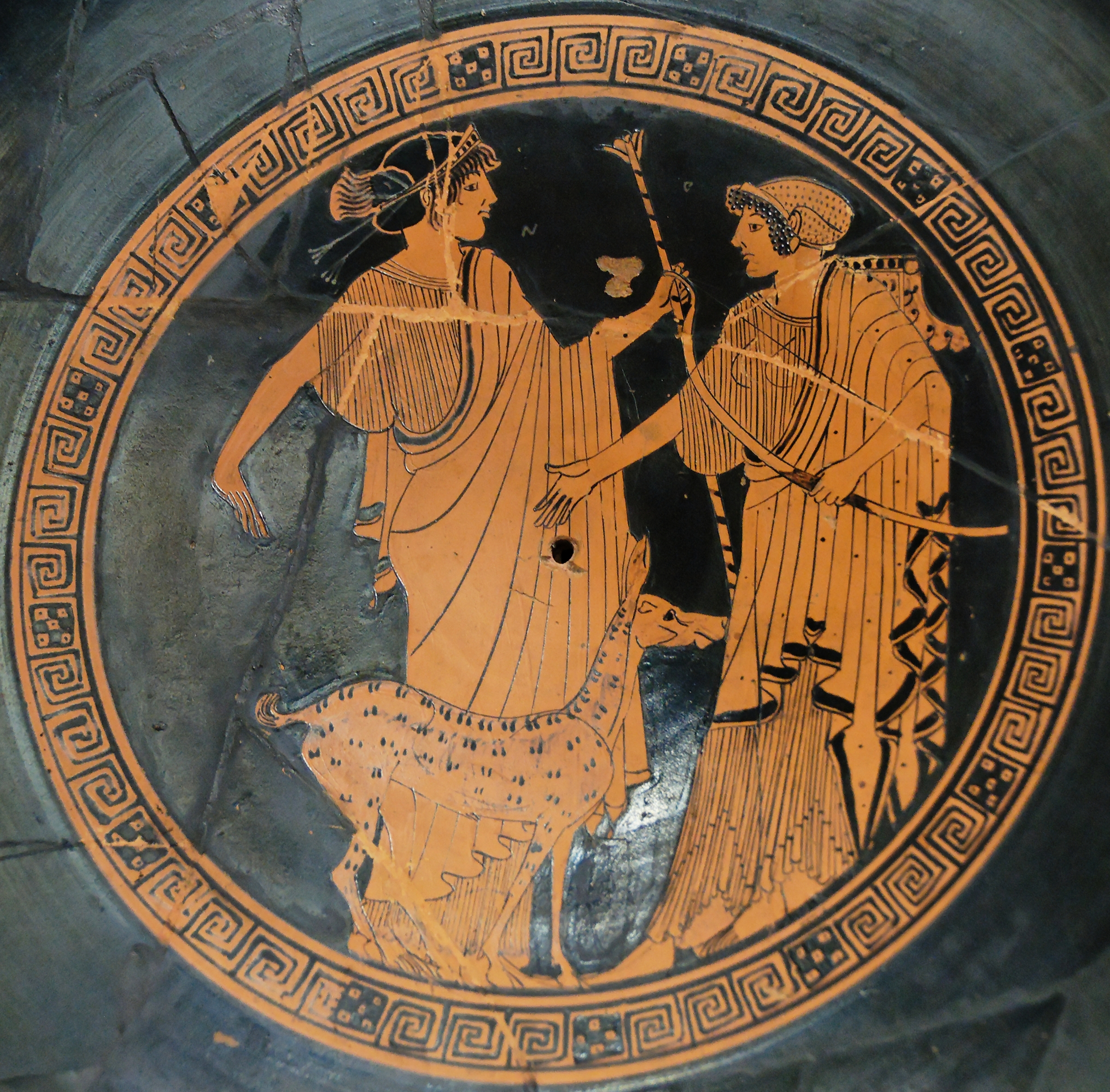 Artemis as the sister of Apollo, is ''thea apollousa'', that is, she as a female divinity represented the same idea that Apollo did as a male divinity. In the pre-Hellenic period, their relationship was described as the one between husband and wife, and there seems to have been a tradition which actually described Artemis as the wife of Apollo. However, this relationship was never sexual but spiritual, which is why they both are seen being unmarried in the Hellenic period.
Artemis, like her brother, is armed with a bow and arrows. She is the cause of sudden deaths of women. She also is the protector of the young, especially girls. Though she has nothing to do with oracles, music or poetry, she sometimes led the female chorus on Olympus while Apollo sang. The laurel (''daphne'') was sacred to both. ''Artemis Daphnaia'' had her temple among the Lacedemonians, at a place called Hypsoi.
''Apollo Daphnephoros'' had a temple in Eretria, a "place where the citizens are to take the oaths". In later times when Apollo was regarded as identical with the sun or
Artemis as the sister of Apollo, is ''thea apollousa'', that is, she as a female divinity represented the same idea that Apollo did as a male divinity. In the pre-Hellenic period, their relationship was described as the one between husband and wife, and there seems to have been a tradition which actually described Artemis as the wife of Apollo. However, this relationship was never sexual but spiritual, which is why they both are seen being unmarried in the Hellenic period.
Artemis, like her brother, is armed with a bow and arrows. She is the cause of sudden deaths of women. She also is the protector of the young, especially girls. Though she has nothing to do with oracles, music or poetry, she sometimes led the female chorus on Olympus while Apollo sang. The laurel (''daphne'') was sacred to both. ''Artemis Daphnaia'' had her temple among the Lacedemonians, at a place called Hypsoi.
''Apollo Daphnephoros'' had a temple in Eretria, a "place where the citizens are to take the oaths". In later times when Apollo was regarded as identical with the sun or Hecate
 Hecate, the goddess of witchcraft and magic, is the chthonic counterpart of Apollo. They both are cousins, since their mothers - Leto and Asteria - are sisters. One of Apollo's epithets, ''Hecatos'', is the masculine form of Hecate, and both the names mean "working from afar". While Apollo presided over the prophetic powers and magic of light and heaven, Hecate presided over the prophetic powers and magic of night and chthonian darkness. If Hecate is the "gate-keeper", Apollo ''Agyieus'' is the "door-keeper". Hecate is the goddess of crossroads and Apollo is the god and protector of streets.Carol M. Mooney, B.A., ''Hekate : Her Role And Character In Greek Literature From Before The Fifth Century B.C.''
The oldest evidence found for Hecate's worship is at Apollo's temple in Miletos. There, Hecate was taken to be Apollo's sister counterpart in the absence of Artemis. Hecate's lunar nature makes her the goddess of the waning moon and contrasts and complements, at the same time, Apollo's solar nature.
Hecate, the goddess of witchcraft and magic, is the chthonic counterpart of Apollo. They both are cousins, since their mothers - Leto and Asteria - are sisters. One of Apollo's epithets, ''Hecatos'', is the masculine form of Hecate, and both the names mean "working from afar". While Apollo presided over the prophetic powers and magic of light and heaven, Hecate presided over the prophetic powers and magic of night and chthonian darkness. If Hecate is the "gate-keeper", Apollo ''Agyieus'' is the "door-keeper". Hecate is the goddess of crossroads and Apollo is the god and protector of streets.Carol M. Mooney, B.A., ''Hekate : Her Role And Character In Greek Literature From Before The Fifth Century B.C.''
The oldest evidence found for Hecate's worship is at Apollo's temple in Miletos. There, Hecate was taken to be Apollo's sister counterpart in the absence of Artemis. Hecate's lunar nature makes her the goddess of the waning moon and contrasts and complements, at the same time, Apollo's solar nature.
Athena
As a deity of knowledge and great power, Apollo was seen being the male counterpart of Athena. Being Zeus' favorite children, they were given more powers and duties. Apollo and Athena often took up the role as protectors of cities, and were patrons of some of the important cities. Athena was the principle goddess of Athens, Apollo was the principle god of Sparta. As patrons of arts, Apollo and Athena were companions of the Muses, the former a much more frequent companion than the latter. Apollo was sometimes called the son of Athena and Hephaestus. In the Trojan war, as Zeus' executive, Apollo is seen holding the aegis like Athena usually does. Apollo's decisions were usually approved by his sister Athena, and they both worked to establish the law and order set forth by Zeus.Apollo in the ''Oresteia''
In Aeschylus' ''Oresteia'' trilogy, Clytemnestra kills her husband, King Agamemnon because he had sacrificed their daughter Iphigenia to proceed forward with the Trojan war. Apollo gives an order through the Oracle at Delphi that Agamemnon's son, Orestes, is to kill Clytemnestra and Aegisthus, her lover. Orestes and Pylades carry out the revenge, and consequently Orestes is pursued by the Erinyes or Furies (female personifications of revenge, vengeance). Apollo and the Furies argue about whether the matricide was justified; Apollo holds that the bond of marriage is sacred and Orestes was avenging his father, whereas the Erinyes say that the bond of blood between mother and son is more meaningful than the bond of marriage. They invade his temple, and he drives them away. He says that the matter should be brought before Athena. Apollo promises to protect Orestes, as Orestes has become Apollo's Supplication, supplicant. Apollo advocates Orestes at the trial, and ultimately Athena rules in favor of Apollo.Roman Apollo
The Roman worship of Apollo was adopted from the Greeks. As a quintessentially List of Greek mythological figures, Greek god, Apollo had no direct Roman equivalent, although later Roman poets often referred to him as Phoebus. There was a tradition that the Delphic oracle was consulted as early as the period of the Roman Kingdom, kings of Rome during the reign of Tarquinius Superbus. On the occasion of a pestilence in the 430s BCE, Apollo's Temple of Apollo Sosianus, first temple at Rome was established in the Flaminian fields, replacing an older cult site there known as the "Apollinare". During the Second Punic War in 212 BCE, the ''Ludi Apollinares'' ("Apollonian Games") were instituted in his honor, on the instructions of a prophecy attributed to one Marcius. In the time of Augustus, who considered himself under the special protection of Apollo and was even said to be his son, his worship developed and he became one of the chief gods of Rome. After the battle of Actium, which was fought near a sanctuary of Apollo, Augustus enlarged Apollo's temple, dedicated a portion of the spoils to him, and instituted quinquennial games in his honour. He also erected Temple of Apollo (Palatine), a new temple to the god on the Palatine Hill, Palatine hill. Sacrifices and prayers on the Palatine to Apollo and Diana (mythology), Diana formed the culmination of the Secular Games, held in 17 BCE to celebrate the dawn of a new era.Festivals
The chief Apollonian festival was the Pythian Games held every four years at Delphi and was one of the four great Panhellenic Games. Also of major importance was the Delia (festival), Delia held every four years on Delos. Athenian annual festivals included the Boedromia, Metageitnia, Pyanepsia, and Thargelia. Spartan annual festivals were the Carneia and the Hyacinthia. Thebes, Greece, Thebes every nine years held theAttributes and symbols
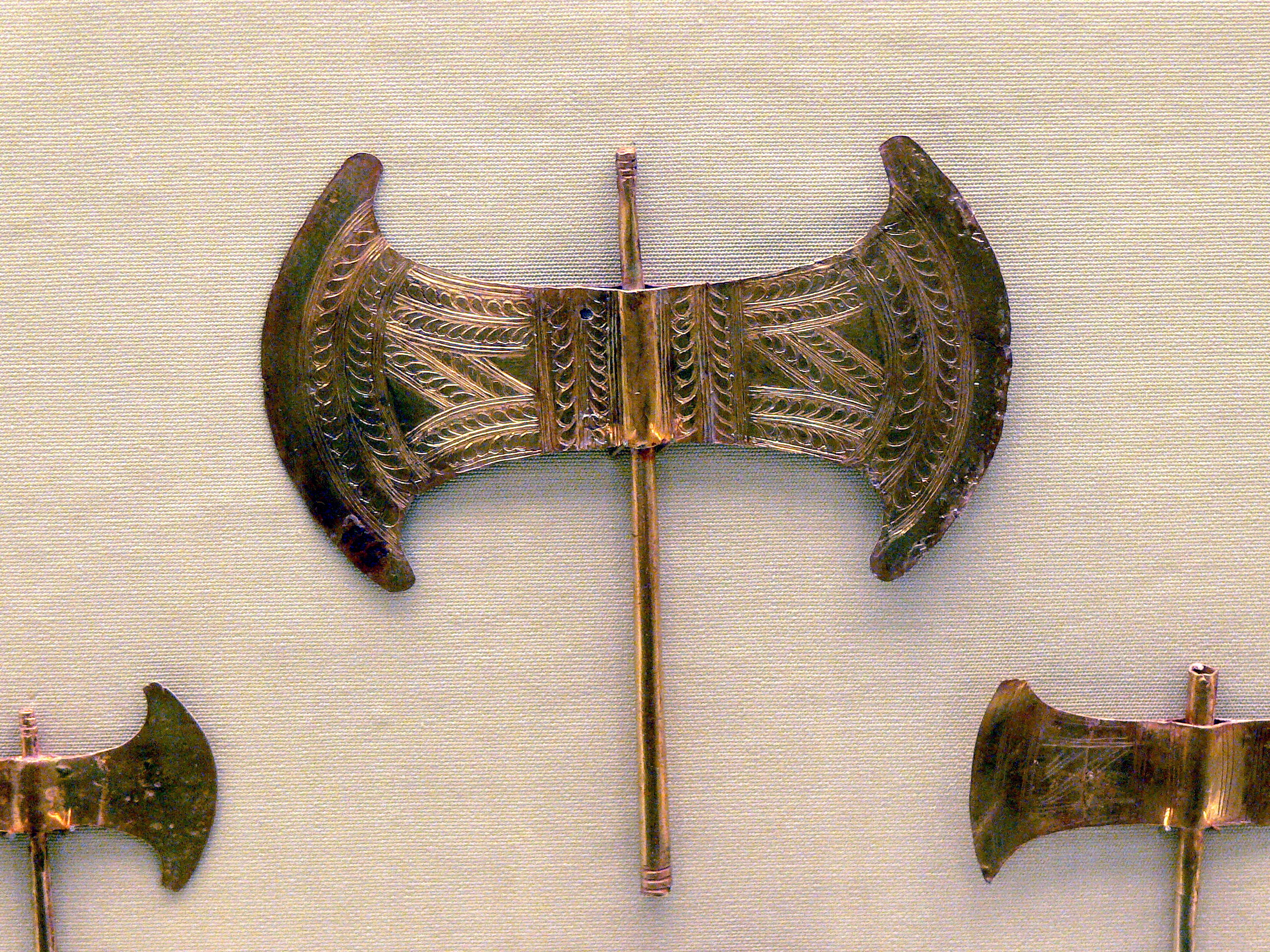
Apollo's most common attributes were the bow and arrow. Other attributes of his included the kithara (an advanced version of the common The palm tree was also sacred to Apollo because he had been born under one in
The palm tree was also sacred to Apollo because he had been born under one in /ref> In many myths Apollo is transformed into a hawk. In addition, Claudius Aelianus wrote that in Egyptians, Ancient Egypt people believed that hawks were sacred to the god and that according to the ministers of Apollo in Egypt there were certain men called "hawk-keepers" (ἱερακοβοσκοί) who fed and tended the hawks belonging to the god. Eusebius wrote that the second appearance of the moon is held sacred in the city of Apollo in Egypt and that the city's symbol is a man with a hawklike face (Horus). Claudius Aelianus wrote that Egyptians called Apollo Horus in their own language.Aelian, ''Characteristics of Animals'', 10.14
/ref>
 As god of colonization, Apollo gave oracular guidance on colonies, especially during the height of colonization, 750–550 BCE. According to Greek tradition, he helped Crete, Cretan or Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadian colonists found the city of Troy. However, this story may reflect a cultural influence which had the reverse direction: Hittite Cuneiform script, cuneiform texts mention an Asia Minor god called ''Appaliunas'' or ''Apalunas'' in connection with the city of Wilusa attested in Hittite inscriptions, which is now generally regarded as being identical with the Greek Troy, Ilion by most scholars. In this interpretation, Apollo's title of ''Lykegenes'' can simply be read as "born in Lycia", which effectively severs the god's supposed link with wolves (possibly a folk etymology).
In literary contexts, Apollo represents harmony, order, and reason—characteristics contrasted with those of
As god of colonization, Apollo gave oracular guidance on colonies, especially during the height of colonization, 750–550 BCE. According to Greek tradition, he helped Crete, Cretan or Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadian colonists found the city of Troy. However, this story may reflect a cultural influence which had the reverse direction: Hittite Cuneiform script, cuneiform texts mention an Asia Minor god called ''Appaliunas'' or ''Apalunas'' in connection with the city of Wilusa attested in Hittite inscriptions, which is now generally regarded as being identical with the Greek Troy, Ilion by most scholars. In this interpretation, Apollo's title of ''Lykegenes'' can simply be read as "born in Lycia", which effectively severs the god's supposed link with wolves (possibly a folk etymology).
In literary contexts, Apollo represents harmony, order, and reason—characteristics contrasted with those of Apollo in the arts
Apollo is a common theme in Greek and Roman art and also in the art of the Renaissance. The earliest Greek word for a statue is "delight" (, ''agalma''), and the sculptors tried to create forms which would inspire such guiding vision. Greek art puts into Apollo the highest degree of power and beauty that can be imagined. The sculptors derived this from observations on human beings, but they also embodied in concrete form, issues beyond the reach of ordinary thought. The naked bodies of the statues are associated with the cult of the body that was essentially a religious activity. The muscular frames and limbs combined with slim waists indicate the Greek desire for health, and the physical capacity which was necessary in the hard Greek environment. The statues of Apollo embody beauty, balance and inspire awe before the beauty of the world.Archaic sculpture
Numerous free-standing statues of male youths fromClassical sculpture

 The famous Apollo of Mantua and its variants are early forms of the Apollo Citharoedus statue type, in which the god holds the cithara, a sophisticated seven-stringed variant of the lyre, in his left arm. While none of the Greek originals have survived, several Roman copies from approximately the late 1st or early 2nd century exist.
Other notable forms are the Apollo Citharoedus and the Apollo Barberini.
The famous Apollo of Mantua and its variants are early forms of the Apollo Citharoedus statue type, in which the god holds the cithara, a sophisticated seven-stringed variant of the lyre, in his left arm. While none of the Greek originals have survived, several Roman copies from approximately the late 1st or early 2nd century exist.
Other notable forms are the Apollo Citharoedus and the Apollo Barberini.
Hellenistic Greece-Rome
Apollo as a handsome beardless young man, is often depicted with a cithara (as Apollo Citharoedus) or bow in his hand, or reclining on a tree (the Apollo Lykeios and Apollo Sauroctonos types). The Apollo Belvedere is a marble sculpture that was rediscovered in the late 15th century; for centuries it epitomized the ideals of Classical Antiquity for Europeans, from the Renaissance through the 19th century. The marble is a Hellenistic Greece, Hellenistic or Roman copy of a bronze original by the Greek sculptor Leochares, made between 350 and 325 BCE. The life-size so-called "Adonis" found in 1780 on the site of a ''Roman villa, villa suburbana'' near the Via Labicana in the Roman suburb of Centocelle is identified as an Apollo by modern scholars. In the late 2nd century CE floor mosaic from El Djem, Roman ''Thysdrus'', he is identifiable as Helios, Apollo Helios by his effulgent Halo (religious iconography), halo, though now even a god's divine nudity, nakedness is concealed by his cloak, a mark of increasing conventions of modesty in the later Roman Empire, Empire. Another haloed Apollo in mosaic, from Hadrumentum, is in the museum at Sousse. The conventions of this representation, head tilted, lips slightly parted, large-eyed, curling Hairstyle, hair cut in locks grazing the neck, were developed in the 3rd century BCE to depict Alexander the Great. Some time after this mosaic was executed, the earliest depictions of Christ would also be beardless and haloed.Modern reception
Apollo often appears in Modernity, modern and Greek mythology in popular culture, popular culture due to his status as the god of music, dance and poetry.Postclassical art and literature
Dance and music
Apollo has featured in dance and music in modern culture. Percy Bysshe Shelley composed a "Hymn of Apollo" (1820), and the god's instruction of the Muses formed the subject of Igor Stravinsky's ''Apollon musagète'' (1927–1928). In 1978, the Canadian band Rush (band), Rush released Hemispheres (Rush album), an album with songs Cygnus X-1 Book II, "Apollo: Bringer of Wisdom"/"Dionysus: Bringer of Love".Books
Apollo been portrayed in modern literature, such as when Charles Handy, in ''Gods of Management'' (1978) uses Greek gods as a metaphor to portray various types of organizational culture. Apollo represents a 'role' culture where order, reason, and bureaucracy prevail. In 2016, author Rick Riordan published the first book in the Trials of Apollo series, publishing four other books in the series in 2017, 2018, 2019 and 2020.
Film
Apollo has been depicted in modern films—for instance, by Keith David in the 1997 animated feature film ''Hercules (1997 film), Hercules,'' by Luke Evans in the 2010 action film Clash of the Titans (2010 film), ''Clash of the Titans'', and by Dimitri Lekkos in the 2010 film ''Percy Jackson & the Olympians: The Lightning Thief''.Video games
Apollo has appeared in many modern video games. Apollo appears as a minor character in Santa Monica Studio's 2010 Action-adventure game, action-adventure game ''God of War III'' with his bow being used by Pirithous, Peirithous. He also appears in the 2014 Hi-Rez Studios Multiplayer online battle arena, Multiplayer Online Battle Arena game ''Smite (video game), Smite'' as a playable character.Psychology and philosophy
In philosophical discussion of the arts, a distinction is sometimes made between the Apollonian and Dionysian impulses, where the former is concerned with imposing intellectual order and the latter with chaotic creativity. Friedrich Nietzsche argued that a fusion of the two was most desirable. Psychologist Carl Jung's Apollo archetype represents what he saw as the disposition in people to over-intellectualise and maintain emotional distance.Shinoda-Bolen, J., ''Gods in Everyman: A New Psychology of Men's Lives and Loves'' p.130-160 (1989)Spaceflight
In spaceflight, the 1960s and 1970s NASA program for orbiting and landing astronauts on the Moon was named after Apollo program, Apollo, by NASA manager Abe Silverstein:Genealogy
See also
*Darrhon *Dryad *Epirus *Family tree of the Greek gods *Phoebus (disambiguation) *Sibylline oracles *Tegyra *Temple of Apollo (disambiguation)Notes
References
Sources
Primary sources
* Claudius Aelianus, Aelian, ''On Animals'', Volume II: Books 6–11. Translated by A. F. Scholfield. Loeb Classical Library 447. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1958. * Aeschylus, ''Oresteia, The Eumenides'' in ''Aeschylus, with an English translation by Herbert Weir Smyth, Ph. D. in two volumes'', Vol 2, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1926Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Antoninus Liberalis, ''The Metamorphoses of Antoninus Liberalis'' translated by Francis Celoria (Routledge 1992)
Online version at the Topos Text Project.
* Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Apollodorus, ''Apollodorus, The Library, with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes.'' Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Apollonius of Rhodes, ''Apollonius Rhodius: the Argonautica'', translated by Robert Cooper Seaton, W. Heinemann, 1912
Internet Archive
* Callimachus, ''Callimachus and Lycophron with an English Translation by A. W. Mair; Aratus, with an English Translation by G. R. Mair'', London: W. Heinemann, New York: G. P. Putnam 1921
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cicero, Cicero, Marcus Tullius, ''De Natura Deorum'' in ''Cicero in Twenty-eight Volumes, XIX De Natura Deorum; Academica'', with an English translation by H. Rackham, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press; London: William Heinemann, Ltd, 1967
Internet Archive
* Diodorus Siculus, ''Library of History, Volume III: Books 4.59-8'', translated by Charles Henry Oldfather, C. H. Oldfather, Loeb Classical Library No. 340. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1939.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Herodotus, ''Herodotus, with an English translation by A. D. Godley.'' Cambridge. Harvard University Press. 1920
Online version available at The Perseus Digital Library
* Hesiod, ''Theogony'', in ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White'', Cambridge, MA., Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* ''Homeric Hymn 3 to Apollo'' in ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White'', Cambridge, MA., Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* ''Homeric Hymns, Homeric Hymn'' 4 ''to Hermes'', in ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White'', Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Homer, ''The Iliad with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, PhD in two volumes''. Cambridge, MA., Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1924
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Homer; ''The Odyssey with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, PH.D. in two volumes''. Cambridge, MA., Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1919
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Gaius Julius Hyginus, Hyginus, Gaius Julius, ''De Astronomica'', in ''The Myths of Hyginus'', edited and translated by Mary A. Grant, Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1960
Online version at ToposText
* Gaius Julius Hyginus, Hyginus, Gaius Julius, ''Fabulae'', in ''The Myths of Hyginus'', edited and translated by Mary A. Grant, Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1960
Online version at ToposText
* Livy, ''The History of Rome, Books I and II With An English Translation''. Cambridge. Cambridge, Mass., Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1919. * Nonnus, ''Dionysiaca''; translated by W. H. D. Rouse, Rouse, W H D, I Books I-XV. Loeb Classical Library No. 344, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1940
Internet Archive
* Nonnus, ''Dionysiaca''; translated by W. H. D. Rouse, Rouse, W H D, II Books XVI-XXXV. Loeb Classical Library No. 345, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1940
Internet Archive
* Statius, ''Thebaid (Latin poem), ''Thebaid''''. Translated by Mozley, J H. Loeb Classical Library Volumes. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1928. * Strabo, ''Geographica, The Geography of Strabo.'' Edition by H.L. Jones. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press; London: William Heinemann, Ltd. 1924
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library.
* Sophocles, ''Oedipus Rex'' * Palaephatus, ''On Unbelievable Tales'' 46. Hyacinthus (330 BCE) * Ovid, ''Metamorphoses'', Brookes More, Boston, Cornhill Publishing Co. 1922
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
10. 162–219 (1–8 CE) * Pausanias, ''Pausanias Description of Greece with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes.'' Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Philostratus the Elder, ''Imagines (work by Philostratus), Imagines'', in ''Philostratus the Elder, Imagines. Philostratus the Younger, Imagines. Callistratus, Descriptions.'' Translated by Arthur Fairbanks. Loeb Classical Library No. 256. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1931.
Online version at Harvard University Press
Internet Archive 1926 edition
i.24 Hyacinthus (170–245 CE) * Philostratus the Younger, ''Imagines (work by Philostratus), Imagines'', in ''Philostratus the Elder, Imagines. Philostratus the Younger, Imagines. Callistratus, Descriptions.'' Translated by Arthur Fairbanks. Loeb Classical Library No. 256. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1931.
Online version at Harvard University Press
14. Hyacinthus (170–245 CE) * Pindar, ''Odes'', Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1990
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Plutarch. ''Lives, Volume I: Theseus and Romulus. Lycurgus and Numa. Solon and Publicola.'' Translated by Bernadotte Perrin. Loeb Classical Library No. 46. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1914.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Pseudo-Plutarch, ''De fluviis'', in ''Plutarch's morals, Volume V'', edited and translated by William Watson Goodwin, Boston: Little, Brown & Co., 1874
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Lucian, ''Dialogues of the Dead. Dialogues of the Sea-Gods. Dialogues of the Gods. Dialogues of the Courtesans'', translated by M. D. MacLeod, Loeb Classical Library No. 431, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1961.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* First Vatican Mythographer, 197. Thamyris et Musae * John Tzetzes, Tzetzes, John, ''Chiliades'', editor Gottlieb Kiessling, F.C.G. Vogel, 1826
Google Books
(English translation: Book I by Ana Untila; Books II–IV, by Gary Berkowitz; Books V–VI by Konstantino Ramiotis; Books VII–VIII by Vasiliki Dogani; Books IX–X by Jonathan Alexander; Books XII–XIII by Nikolaos Giallousis
Internet Archive
. * Gaius Valerius Flaccus (poet), Valerius Flaccus, ''Argonautica'', translated by J. H. Mozley, Loeb Classical Library No. 286. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1928.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Virgil, Vergil, ''Aeneid.'' Theodore C. Williams. trans. Boston. Houghton Mifflin Co. 1910
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library.
Secondary sources
* Apostolos Athanassakis, Athanassakis, Apostolos N., and Benjamin M. Wolkow, ''The Orphic Hymns'', Johns Hopkins University Press; owlerirst Printing edition (May 29, 2013).Google Books
* M. Bieber, 1964. ''Alexander the Great in Greek and Roman Art''. Chicago. * Hugh Bowden, 2005. ''Classical Athens and the Delphic Oracle: Divination and Democracy''. Cambridge University Press. * Walter Burkert, 1985.
Greek Religion
' (Harvard University Press) III.2.5 ''passim'' * * Joseph Fontenrose, Fontenrose, Joseph Eddy, ''Python: A Study of Delphic Myth and Its Origins'', University of California Press, 1959. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * * Miranda J. Green, 1997. ''Dictionary of Celtic Myth and Legend'', Thames and Hudson. * Grimal, Pierre, ''The Dictionary of Classical Mythology'', Wiley-Blackwell, 1996. . * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
* Karl Kerenyi, 1953. ''Apollon: Studien über Antiken Religion und Humanität'' revised edition. * Károly Kerényi, Kerényi, Karl 1951, ''The Gods of the Greeks'', Thames and Hudson, London. * Mertens, Dieter; Schutzenberger, Margareta. ''Città e monumenti dei Greci d'Occidente: dalla colonizzazione alla crisi di fine V secolo a.C.''. Roma L'Erma di Bretschneider, 2006. . * Martin Nilsson, 1955. ''Die Geschichte der Griechische Religion'', vol. I. C.H. Beck. * Parada, Carlos, ''Genealogical Guide to Greek Mythology'', Jonsered, Paul Åströms Förlag, 1993. . * Pauly–Wissowa, ''Realencyclopädie der klassischen Altertumswissenschaft'': II, "Apollon". The best repertory of cult sites (Burkert). * Harry Thurston Peck, Peck, Harry Thurston, ''Harpers Dictionary of Classical Antiquities'', New York. Harper and Brothers. 1898
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Pfeiff, K.A., 1943. ''Apollon: Wandlung seines Bildes in der griechischen Kunst''. Traces the changing iconography of Apollo. * D.S.Robertson (1945) ''A handbook of Greek and Roman Architecture'' Cambridge University Press * William Smith (lexicographer), Smith, William; ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', London (1873)
"Apollo"
* * William Smith (lexicographer), Smith, William, ''A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities''. William Smith, LLD. William Wayte. G. E. Marindin. Albemarle Street, London. John Murray. 1890
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Spivey Nigel (1997) ''Greek art'' Phaedon Press Ltd.
External links
at the Greek Mythology Link, by Carlos Parada
The Warburg Institute Iconographic Database: ca 1650 images of Apollo
{{Authority control Apollo, Greek gods Roman gods Beauty gods Health gods Knowledge gods Light gods Maintenance deities Music and singing gods Oracular gods Solar gods Plague gods Dragonslayers Mythological Greek archers Mythological rapists Homosexuality and bisexuality deities Divine twins Deities in the Iliad Metamorphoses characters Musicians in Greek mythology Characters in Greek mythology LGBT themes in Greek mythology Children of Zeus Characters in the Odyssey Characters in the Argonautica Characters in Roman mythology Childhood gods Mythological Greek physicians Arts gods Dii Consentes Medicine deities Mercurian deities Twelve Olympians Dance gods Kourotrophoi Shapeshifters in Greek mythology Prophecy