Paramecium Primaurelia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Paramecium'' ( , , plural "paramecia" only when used as a


 ''Paramecium'' were among the first ciliates to be observed by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were most likely known to the Dutch pioneer of
''Paramecium'' were among the first ciliates to be observed by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were most likely known to the Dutch pioneer of
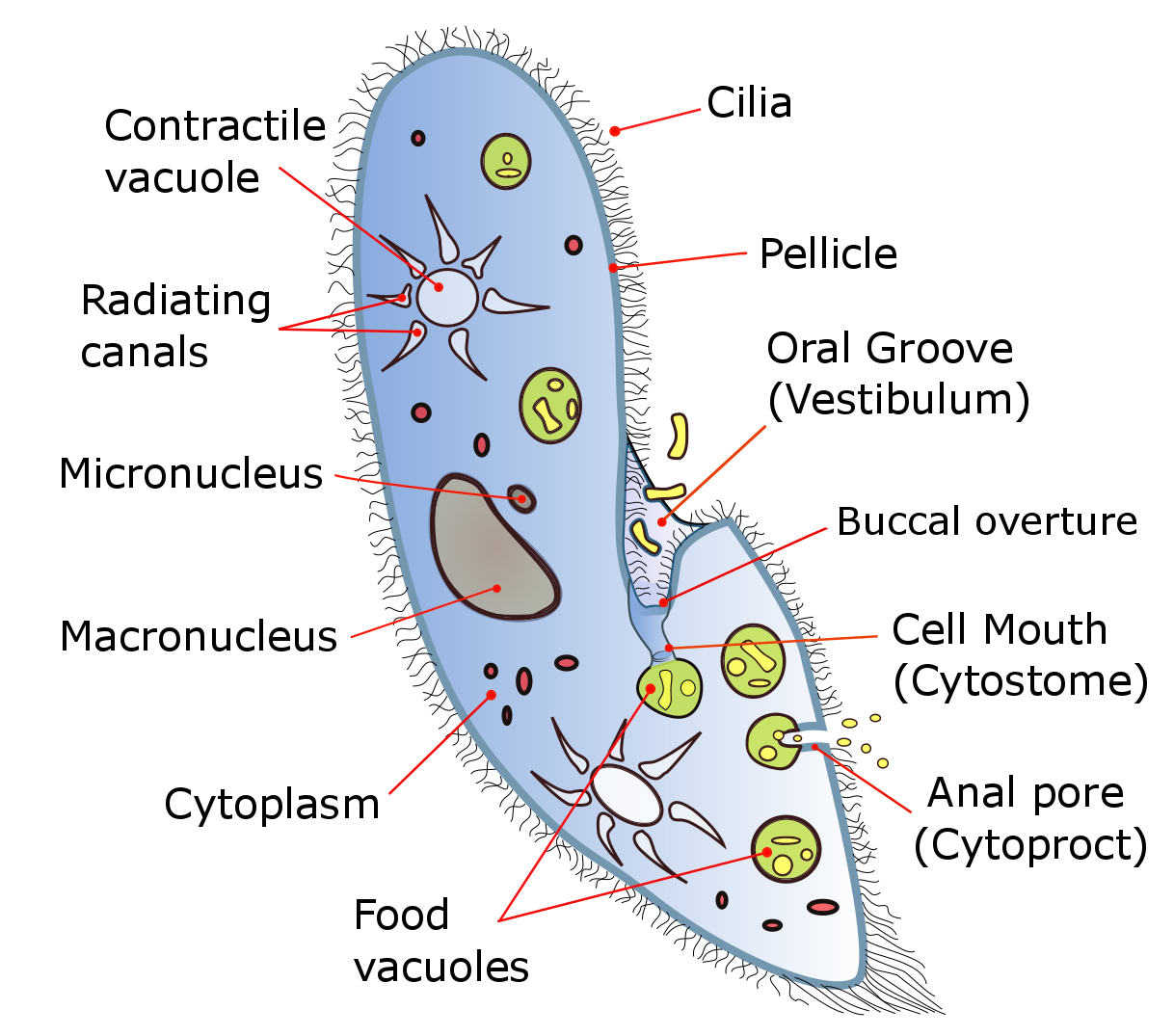 Species of ''Paramecium'' range in size from 0.06 mm to 0.3 mm in length. Cells are typically ovoid, elongate, or foot- or cigar-shaped.
The body of the cell is enclosed by a stiff but elastic structure called the pellicle. The pellicle consists of an outer
Species of ''Paramecium'' range in size from 0.06 mm to 0.3 mm in length. Cells are typically ovoid, elongate, or foot- or cigar-shaped.
The body of the cell is enclosed by a stiff but elastic structure called the pellicle. The pellicle consists of an outer
 In ''
In ''
File:Paramecium bursaria.ogv, ''Paramecium bursaria'', a species with symbiotic algae
File:Paramecium putrinum.ogv, ''Paramecium putrinum''
File:Paramecium Dividing.ogv, ''Paramecium'' binary fission
File:Conjugation in Paramecium.webm, ''Paramecium in conjugation''
File:Инфузория туфелька 7.webm, ''Paramecium caudatum''
vernacular name
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken form of language, particularly when perceived as having lower social status or less prestige than standard language, which is more codified, institutionally promoted, literary, or formal. More n ...
) is a genus of eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
, unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
s, widespread in freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
, brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
, and marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, they have been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological process
Biological processes are those processes that are necessary for an organism to live and that shape its capacities for interacting with its environment. Biological processes are made of many chemical reactions or other events that are involved in ...
es. ''Paramecium'' species are commonly studied as model organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Mo ...
s of the ciliate group and have been characterized as the "white rat
The fancy rat (''Rattus norvegicus domestica'') is the domesticated form of ''Rattus norvegicus'', the brown rat, and the most common species of rat kept as a pet. The name ''fancy rat'' derives from the use of the adjective ''fancy'' for a ...
s" of the phylum Ciliophora
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different ...
.
Historical background


 ''Paramecium'' were among the first ciliates to be observed by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were most likely known to the Dutch pioneer of
''Paramecium'' were among the first ciliates to be observed by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were most likely known to the Dutch pioneer of protozoology
Protistology is a scientific discipline devoted to the study of protists, a highly diverse group of eukaryotic organisms. All eukaryotes apart from animals, plants and fungi are considered protists. Its field of study therefore overlaps with the ...
, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch art, science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " ...
, and were clearly described by his contemporary Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
in a letter from 1678. The earliest known illustration of a ''Paramecium'' species was published anonymously in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the second journ ...
in 1703.
In 1718, the French mathematics teacher and microscopist Louis Joblot Louis Joblot (9 August 1645 – 27 April 1723) was a French naturalist. He was born in Bar-le-Duc and died, aged 57, in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest cit ...
published a description and illustration of a microscopic (fish), which he discovered in an infusion
Infusion is the process of extracting chemical compounds or flavors from plant material in a solvent such as water, oil or alcohol, by allowing the material to remain suspended in the solvent over time (a process often called steeping). An inf ...
of oak bark in water. Joblot gave this creature the name , or "slipper", and the phrase "slipper animalcule" remained in use as a colloquial epithet for ''Paramecium'', throughout the 18th and 19th centuries.
The name "''Paramecium''" – constructed from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
(''paramēkēs'', "oblong") – was coined in 1752 by the English microscopist John Hill, who applied the name generally to "Animalcules
Animalcule (; ) is an archaic term for microscopic organisms that included bacteria, protozoans, and very small animals. The word was invented by 17th-century Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek to refer to the microorganisms he observed i ...
which have no visible limbs or tails, and are of an irregularly oblong figure." In 1773, O. F. Müller, the first researcher to place the genus within the Linnaean system of taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
, adopted the name ''Paramecium'' but changed the spelling to ''Paramæcium.'' In 1783, Johann Hermann
Johann, or Jean-Frederic, Hermann, or Herrmann, (31 December 1738 in Barr, Alsace – 4 October 1800 in Strasbourg) was a French physician and naturalist
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi ...
changed the spelling once more, to ''Paramœcium''. C. G. Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German naturalist, zoologist, botanist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. He is considered to be one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. ...
, in a major study of the infusoria
Infusoria is a word used to describe various freshwater microorganisms, including ciliates, copepods, Euglena, euglenoids, planktonic crustaceans, protozoa, unicellular algae and small invertebrates. Some authors (e.g., Otto Bütschli, Bütschli) ...
published in 1838, restored Hill's original spelling for the name, and most researchers have followed his lead.
Description
 Species of ''Paramecium'' range in size from 0.06 mm to 0.3 mm in length. Cells are typically ovoid, elongate, or foot- or cigar-shaped.
The body of the cell is enclosed by a stiff but elastic structure called the pellicle. The pellicle consists of an outer
Species of ''Paramecium'' range in size from 0.06 mm to 0.3 mm in length. Cells are typically ovoid, elongate, or foot- or cigar-shaped.
The body of the cell is enclosed by a stiff but elastic structure called the pellicle. The pellicle consists of an outer cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
(plasma membrane), a layer of flattened membrane-bound sacs called ''alveoli'', and an inner membrane called the ''epiplasm''. The pellicle is not smooth, but textured with hexagonal or rectangular depressions. Each of these polygons is perforated by a central aperture through which a single cilium projects. Between the alveolar sacs of the pellicle, most species of ''Paramecium'' have closely spaced spindle-shaped trichocyst
A trichocyst is an organelle found in certain ciliates and dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered pr ...
s, explosive organelles that discharge thin, non-toxic filaments, often used for defensive purposes.
Typically, an anal pore (cytoproct) is located on the ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
surface, in the posterior half of the cell. In all species, there is a deep oral groove running from the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
of the cell to its midpoint. This is lined with inconspicuous cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
which beat continuously, drawing food into the cell. ''Paramecium'' are primarily heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
ic, feeding on bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and other small organisms. A few species are mixotroph
A mixotroph is an organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than ...
s, deriving some nutrients from endosymbiotic algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
(chlorella
''Chlorella'' is a genus of about thirteen species of single- celled or colonial green algae of the division Chlorophyta. The cells are spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are without flagella. Their chloroplasts contain t ...
) carried in the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
of the cell.
Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration ...
is carried out by contractile vacuole
A contractile vacuole (CV) is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists, including unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole.
Overview
The contrac ...
s, which actively expel water from the cell to compensate for fluid absorbed by osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of ...
from its surroundings. The number of contractile vacuoles varies depending on the species.
Movement
A ''Paramecium'' propels itself by whip-like movements of the cilia, which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body. The beat of each cilium has two phases: a fast "effective stroke," during which the cilium is relatively stiff, followed by a slow "recovery stroke," during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter-clockwise fashion. The densely arrayed cilia move in a coordinated fashion, with waves of activity moving across the "ciliary carpet," creating an effect sometimes likened to that of the wind blowing across a field of grain. The ''Paramecium'' spirals through the water as it progresses. When it happens to encounter an obstacle, the "effective stroke" of its cilia is reversed and the organism swims backward for a brief time, before resuming its forward progress. This is called theavoidance reaction
Avoidance reaction is a term used in the description of the movement of paramecium. This helps the cell avoid obstacles and causes other objects to bounce off of the cell's outer membrane. The paramecium does this by reversing the direction in w ...
. If it runs into the solid object again, it repeats this process, until it can get past the object.
It has been calculated that a ''Paramecium'' expends more than half of its energy in propelling itself through the water. This ciliary method of locomotion has been found to be less than 1% efficient. This low percentage is nevertheless close to the maximum theoretical efficiency that can be achieved by an organism equipped with cilia as short as those of the members of ''Paramecium.''
Gathering food
''Paramecium'' feed on microorganisms such as bacteria, algae, andyeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
s. To gather food, the ''Paramecium'' makes movements with cilia to sweep prey organisms, along with some water, through the oral groove (vestibulum, or vestibule), and into the cell. The food passes from the cilia-lined oral groove into a narrower structure known as the buccal cavity (gullet). From there, food particles pass through a small opening called the cytostome
A cytostome (from ''cyto-'', cell and ''stome-'', mouth) or cell mouth is a part of a cell specialized for phagocytosis, usually in the form of a microtubule-supported funnel or groove. Food is directed into the cytostome, and sealed into vacu ...
, or cell mouth, and move into the interior of the cell. As food enters the cell, it is gathered into food vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water ...
s, which are periodically closed off and released into the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
, where they begin circulating through the cell body by the streaming movement of the cell contents, a process called cyclosis or cytoplasmic streaming
Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the flow of the cytoplasm inside the cell, driven by forces from the cytoskeleton. It is likely that its function is, at least in part, to speed up the transport of mole ...
. As a food vacuole moves along, enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s from the cytoplasm enter it, to digest the contents. As enzymatic digestion proceeds, the vacuole contents become more acidic. Within five minutes of a vacuole's formation, the pH of its contents drops from 7 to 3. As digested nutrients pass into the cytoplasm, the vacuole shrinks. When the fully digested vacuole reaches the anal pore, it ruptures, expelling its waste contents outside the cell.
Symbiosis
Some species of ''Paramecium'' form mutualistic relationships with other organisms. '' Paramecium bursaria'' and ''Paramecium chlorelligerum'' harbour endosymbiotic green algae, from which they derive nutrients and a degree of protection from predators such as '' Didinium nasutum''. Numerous bacterial endosymbionts have been identified in species of ''Paramecium''. Some intracellular bacteria, known askappa particle
Kappa (; uppercase Κ, lowercase κ or cursive ; , ''káppa'') is the tenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless velar plosive sound in Ancient and Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals, has a value of 20. It was d ...
s, give ''Paramecium'' the ability to kill other strains of ''Paramecium'' that lack kappa particles.
Genome
Thegenome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
of the species '' Paramecium tetraurelia'' has been sequenced, providing evidence for three whole-genome duplications
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one from ...
.
In some ciliates, like ''Stylonychia
''Stylonychia'' is a genus of ciliates, in the subclass Hypotrichia. Species of ''Stylonychia'' are very common in fresh water and soil, and may be found on filamentous algae, surface films, and among particles of sediment. Like other Hypotrichs, ...
'' and ''Paramecium'', only UGA is decoded as a stop codon
In molecular biology, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the additio ...
, while UAG and UAA are reassigned as sense codons (that is, codons that code for standard amino acids), coding for the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
.
Learning
The question of whether ''Paramecium'' exhibit learning has been the object of a great deal of experimentation, yielding equivocal results. However, a study published in 2006 seems to show that ''Paramecium caudatum
''Paramecium caudatum'' is a species of unicellular protist in the phylum Ciliophora. They can reach 0.33 mm in length and are covered with minute hair-like organelles called cilia. The cilia are used in locomotion and feeding. The species i ...
'' may be trained, through the application of a 6.5 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, Voltage#Galvani potential vs. electrochemical potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units, International System of Uni ...
electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
, to discriminate between brightness levels. This experiment has been cited as a possible instance of cell memory, or epigenetic learning in organisms with no nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
.
Reproduction and sexual phenomena
Reproduction
Like all ciliates, ''Paramecium'' have a dual nuclear apparatus, consisting of apolyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning ...
macronucleus
A macronucleus (formerly also meganucleus) is the larger type of nucleus in ciliates. Macronuclei are polyploid and undergo direct division without mitosis. It controls the non-reproductive cell functions, such as metabolism
Metabolism (, ...
, and one or more diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
micronuclei
A micronucleus is a small cell nucleus, nucleus that forms whenever a chromosome or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during cell division. It usually is a sign of genotoxic events and chromosomal inst ...
. The macronucleus controls non-reproductive cell functions, expressing the gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s needed for daily functioning. The micronucleus is the generative, or germline
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes ( eggs and sperm), which can come together to form a zygote. They dif ...
nucleus, containing the genetic material that is passed along from one generation to the next.
''Paramecium'' reproduction is asexual
Asexual or Asexuals may refer to:
*Asexual reproduction
**Asexual reproduction in starfish
*Asexuality, the lack of sexual attraction to anyone or lack of interest in or desire for sexual activity.
**Gray asexuality, the spectrum between asexualit ...
, by binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
, which has been characterized as "the sole mode of reproduction in ciliates" (conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
*Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change o ...
being a sexual phenomenon, not directly resulting in increase of numbers). During fission, the macronucleus splits by a type of amitosis
Amitosis, also known as karyostenosis, direct cell division, or binary fission, is a form of asexual cell division primarily observed in bacteria and other prokaryotes. This process is distinct from other cell division mechanisms such as mitosis ...
, and the micronuclei undergo mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
. The cell then divides transversally, and each new cell obtains a copy of the micronucleus and the macronucleus.
Fission may occur spontaneously, in the course of the vegetative cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
. Under certain conditions, it may be preceded by self-fertilization (autogamy
Autogamy or self-fertilization refers to the Cell fusion, fusion of two gametes that come from one individual. Autogamy is predominantly observed in the form of self-pollination, a Reproduction, reproductive mechanism employed by many flowering pl ...
), or it may immediately follow conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
*Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change o ...
, in which ''Paramecium'' of compatible mating types fuse temporarily and exchange genetic material.
Conjugation
In ciliates such as ''Paramecium'', conjugation is a sexual phenomenon that results ingenetic recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryot ...
and nuclear reorganization within the cell. During conjugation, two ''Paramecium'' of a compatible mating type come together and form a bridge between their cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
s. Their respective micronuclei undergo meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
, and haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
micronuclei are exchanged over the bridge. Following conjugation, the cells separate. The old macronuclei are destroyed, and both post-conjugants form new macronuclei, by amplification of DNA in their micronuclei. Conjugation is followed by one or more "exconjugant divisions."
;Stages of conjugationParamecium caudatum
''Paramecium caudatum'' is a species of unicellular protist in the phylum Ciliophora. They can reach 0.33 mm in length and are covered with minute hair-like organelles called cilia. The cilia are used in locomotion and feeding. The species i ...
'', the stages of conjugation are as follows (see diagram at right):
# Compatible mating strains meet and partly fuse
# The micronuclei undergo meiosis, producing four haploid micronuclei per cell.
# Three of these micronuclei disintegrate. The fourth undergoes mitosis.
# The two cells exchange a micronucleus.
# The cells then separate.
# The micronuclei in each cell fuse, forming a diploid micronucleus.
# Mitosis occurs three times, giving rise to eight micronuclei.
# Four of the new micronuclei transform into macronuclei, and the old macronucleus disintegrates.
# Binary fission occurs twice, yielding four identical daughter cells.
Aging
In the asexual fission phase of growth, during which cell divisions occur by mitosis rather than meiosis, clonal aging occurs leading to a gradual loss of vitality. In some species, such as the well studied ''Paramecium tetraurelia'', the asexual line of clonally aging ''Paramecium'' loses vitality and expires after about 200 fissions if the cells fail to undergo autogamy or conjugation. The basis for clonal aging was clarified by transplantation experiments of Aufderheide in 1986. When macronuclei of clonally young ''Paramecium'' were injected into ''Paramecium'' of standard clonal age, the lifespan (clonal fissions) of the recipient was prolonged. In contrast, transfer ofcytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
from clonally young ''Paramecium'' did not prolong the lifespan of the recipient. These experiments indicated that the macronucleus, rather than the cytoplasm, is responsible for clonal aging. Other experiments by Smith-Sonneborn, Holmes and Holmes, and Gilley and Blackburn demonstrated that, during clonal aging, DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified ...
increases dramatically. Thus, DNA damage in the macronucleus appears to be the cause of aging in ''P. tetraurelia''. In this single-celled protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
, aging appears to proceed as it does in multicellular eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s, as described in DNA damage theory of aging
The DNA damage theory of aging proposes that aging is a consequence of unrepaired accumulation of DNA damage (naturally occurring), naturally occurring DNA damage. Damage in this context is a DNA alteration that has an abnormal structure. Although ...
.
Meiosis and rejuvenation
When clonally aged ''P. tetraurelia'' are stimulated to undergo meiosis in association with either conjugation orautomixis
Automixis is the fusion of (typically haploid) nuclei or gametes derived from the same individual. The term covers several reproductive mechanisms, some of which are parthenogenetic.
Diploidy might be restored by the doubling of the chromosomes ...
, the genetic descendants are rejuvenated, and are able to have many more mitotic binary fission divisions. During conjugation or automixis
Automixis is the fusion of (typically haploid) nuclei or gametes derived from the same individual. The term covers several reproductive mechanisms, some of which are parthenogenetic.
Diploidy might be restored by the doubling of the chromosomes ...
, the micronuclei of the cell(s) undergo meiosis, the old macronucleus disintegrates, and a new macronucleus is formed by replication of the micronuclear DNA that had recently undergone meiosis. There is apparently little, if any, DNA damage in the new macronucleus. These findings further support the idea that clonal aging is due, in large part, to a progressive accumulation of DNA damage; and that rejuvenation is due to the repair of this damage in the micronucleus during meiosis. Meiosis appears to be an adaptation for DNA repair and rejuvenation in ''P. tetraurelia''. In ''P. tetraurelia'', CtlP protein is a key factor needed for the completion of meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
during sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
and recovery of viable sexual progeny. The CtlP and Mre11 nuclease complex are essential for accurate processing and repair of double-strand breaks during homologous recombination.
The adaptive benefit of meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
and self-fertilization
Autogamy or self-fertilization refers to the Cell fusion, fusion of two gametes that come from one individual. Autogamy is predominantly observed in the form of self-pollination, a Reproduction, reproductive mechanism employed by many flowering pl ...
in response to starvation appears to be independent of the generation of any new genetic variation in ''P. tetraurelia''. This observation suggests that the underlying molecular mechanism of meiosis provides a fitness advantage regardless of any concomitant effect of sex on genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
.
Video gallery
List of species
''Paramecium aurelia
''Paramecium aurelia'' are unicellular organisms belonging to the genus ''Paramecium'' of the phylum Ciliophora. They are covered in cilia which help in movement and feeding.''Paramecium'' can reproduce sexually, asexually, or by the process ...
'' species complex:
*'' Paramecium primaurelia''
*'' Paramecium biaurelia''
*'' Paramecium triaurelia''
*'' Paramecium tetraurelia''
*'' Paramecium pentaurelia''
*'' Paramecium sexaurelia''
*'' Paramecium septaurelia''
*'' Paramecium octaurelia''
*'' Paramecium novaurelia''
*''Paramecium decaurelia
''Paramecium'' ( , , plural "paramecia" only when used as a vernacular name) is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagnant basins and ponds ...
''
*'' Paramecium undecaurelia''
*'' Paramecium dodecaurelia''
*'' Paramecium tredecaurelia''
*'' Paramecium quadecaurelia''
*'' Paramecium sonneborni''
Other species:
*'' Paramecium buetschlii''
*'' Paramecium bursaria''
*'' Paramecium calkinsi''
*''Paramecium caudatum
''Paramecium caudatum'' is a species of unicellular protist in the phylum Ciliophora. They can reach 0.33 mm in length and are covered with minute hair-like organelles called cilia. The cilia are used in locomotion and feeding. The species i ...
''
*'' Paramecium chlorelligerum''
*'' Paramecium duboscqui''
*'' Paramecium grohmannae''
*'' Paramecium jenningsi''
*'' Paramecium multimicronucleatum''
*'' Paramecium nephridiatum''
*'' Paramecium polycaryum''
*'' Paramecium putrinum''
*'' Paramecium schewiakoffi''
*'' Paramecium woodruffi''
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Oligohymenophorea Ciliate species Ciliate genera Articles containing video clips Taxa named by Otto Friedrich Müller