Paper Chemical on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Paper chemicals designate a group of 
 To enhance the paper's strength,
To enhance the paper's strength,


List of chemicals used in pulp and paper making
{{Authority control Papermaking Chemical processes Cellulose Pulp and paper industry
chemicals
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating/reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception dictated by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, and ...
, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water. The chemicals can be defined on basis of their usage in the process.
Chemical usage is not only for imparting properties to paper but to handle the water cycles in the process, conditioning of fabrics, cleaning of equipment and several other applications.

Chemicals used in paper manufacturing
Pulping
Chemical pulping involves dissolving lignin in order to extract the cellulose from the wood fiber. The different processes of chemical pulping include theKraft process
The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibres, the main component of paper. The kraft process involves treatment of wood chip ...
, which uses caustic soda and sodium sulfide and is the most common; alternatively, the use of sulfurous acid is known as the sulfite process
The sulfite process produces wood pulp that is almost pure cellulose fibers by treating wood chips with solutions of sulfite and bisulfite ions. These chemicals cleave the bonds between the cellulose and lignin components of the lignocellulose. A ...
, the neutral sulfite semichemical is treated as a third process separate from sulfite, and soda pulping
Soda pulping is a chemical process for making wood pulp with sodium hydroxide as the cooking chemical. In the ''Soda-AQ'' process, anthraquinone (AQ) may be used as a pulping additive to decrease the carbohydrate degradation. The soda process gives ...
which is the least ecologically hazardous utilizing sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
or anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic organic compound with formula . Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein th ...
.
Caustic soda is added to increase the pH in the pulping
Pulp is a fibrous lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemicals or plant-based additives, pul ...
process of fibers. The higher pH of the paper-fiber solution causes the fibers to smoothen and swell, which is important for the grinding process of the fibers.
Bleaching
In the production of white paper, the wood pulp is bleached to remove any color from the trace amounts of lignin that was not extracted in the chemical pulping process. There are three predominant methods of bleaching: * Elemental chlorine bleaching useschlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
and hypochlorite.
* Elemental chlorine-free bleaching is more environmentally friendly since it eliminates the use of hypochlorite and replaces chlorine with chlorine dioxide
Chlorine dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula ClO2 that exists as yellowish-green gas above 11 °C, a reddish-brown liquid between 11 °C and −59 °C, and as bright orange crystals below −59 °C. It is usually ...
or sodium chlorate.
* Totally chlorine-free bleaching utilizes oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
. This is the most environmentally friendly process since it eliminates all chlorinated pollutants.
Sizing
Most paper types must have some water-resistance to maintain a specific writing quality and printability. Until 1980, the typical manner of adding this resistance was by using arosin
Rosin (), also known as colophony or Greek pitch (), is a resinous material obtained from pine trees and other plants, mostly conifers. The primary components of rosin are diterpenoids, i.e., C20 carboxylic acids. Rosin consists mainly of r ...
in combination with alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium ...
. When the paper industry started using chalk instead of china clay
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedron, tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen ...
as filler, the paper chemistry had to switch to a neutral process. At several places AKD ( alkyl ketene dimer) and ASA ( alkenyl succinic anhydride) are used. Latest development is to use surface size, which is applied using a size press. The advantage of surface sizing is that it does not interfere with the backend water chemistry.
Strengthening
Wet-strength
Wet-strength additives ensure that paper retains its strength when it gets wet. This is especially important intissue paper
Tissue paper, or simply tissue, is a lightweight paper or light crêpe paper. Tissue can be made from recycled pulp (paper), paper pulp on a paper machine.
Tissue paper is very versatile, and different kinds are made to best serve these purposes ...
. Chemicals typically used for this purpose include epichlorohydrin, melamine
Melamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H6N6. This white solid is a trimer (chemistry), trimer of cyanamide, with a 1,3,5-Triazine, 1,3,5-triazine skeleton. Like cyanamide, it contains 66% nitrogen by mass, and its derivatives ha ...
, urea formaldehyde and polyimine
Polyimines are classified as polymer materials that contain imine groups, which are characterised by a double bond between a carbon and nitrogen atom. The term polyimine can also be found occasionally in covalent organic frameworks (COFs). In (ol ...
s. These substances polymerize in the paper and result in the construction of a strengthening network.
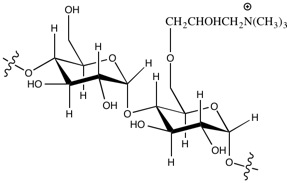
 To enhance the paper's strength,
To enhance the paper's strength, cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
ic starch is added to wet pulp in the manufacturing process. Starch has a similar chemical structure as the cellulose fibre of the pulp, and the surface of both the starch and fibre are negatively charged. By adding cationic (positive charged) starch, the fibre can bind with the starch and thus also increase the interconnections between the fibres. The positively charged portion of the starch is usually formed by quaternary ammonium cation
In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively-charged polyatomic ions of the structure , where R is an alkyl group, an aryl group or organyl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, ...
s. Quaternary salts that are used include 2.3-epoxy propyl trimethyl ammoniumchloride (EPTAC, also known as or Glytac Quab, GMAC™) and (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) trimethyl ammonium chloride (CHPTAC, also known as Quat 188, Quab 188, Reagens™).
Dry-strength
Dry-strength additives, or dry-strengthening agents, are chemicals that improve paper strength normal conditions. These improve the paper's compression strength, bursting strength, tensile breaking strength, and delamination resistance. Typical chemicals used include cationicstarch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
and polyacrylamide (PAM) derivatives. These substances work by binding fibers, often under the aid of aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
ions in paper sheet.
Binders
Binders promote the binding of pigment particles between themselves and the coating layer of the paper. Binders are spherical particles less than 1 μm in diameter. Common binders are styrene maleic anhydride copolymer or styrene-acrylate copolymer. The surface chemical composition is differentiated by theadsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a ...
of acrylic acid
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has ...
or an anionic surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent",
coined in ...
, both of which are used for stabilization of the dispersion in water. Co-binders, or thickeners, are generally water-soluble polymers that influence the paper's color viscosity, water retention, sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption ...
, and gloss. Some common examples are carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), cationic and anionic hydroxyethyl cellulose (EHEC), modified starch
Modified starch, also called starch derivative (chemistry), derivatives, is prepared by physical change, physically, enzymatically, or chemically treating native starch to change its properties. Modified starches are used in practically all starc ...
, and dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced fro ...
.
Styrene butadiene latex, Styrene acrylic, dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced fro ...
, oxidized starch are used in coatings to bind the filler to the paper. Co-binders are natural products such as starch and CMC ( Carboxymethyl cellulose), that are used along with the synthetic binders, like styrene acrylic or styrene butadiene. Co-binders are used to reduce the cost of the synthetic binder and improve the water retention and rheology
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid (liquid or gas) state but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applie ...
of the coating.


Fillers
Mineral fillers are used to lower the consumption of more expensive binder material or to improve some properties of the paper.China clay
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedron, tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen ...
, calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index Internationa ...
, and talc
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, with the chemical formula . Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant ...
are common mineral fillers used in paper production.
Retention
A Retention agent is added to bindfillers
In animal feed, a filler is an ingredient added to provide dietary fiber, bulk or some other non-nutritive purpose. Products like corn fiber (corncobs), fruit fibers (pulp), rice bran, and whole grains are possible fillers.
Purpose
As source ...
to the paper. Fillers, such as calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
, usually have a weak surface charge. The retention agent is a polymer with high cationic, positively charged groups. An additional feature of a retention agent is to accelerate the dewatering in the wire section of the paper machine. Polyethyleneimine
Polyethylenimine (PEI) or polyaziridine is a polymer with repeating units composed of the amine group and two carbon aliphatic ''CHCH'' spacers. Linear polyethyleneimines contain all secondary amines, in contrast to branched PEIs which contain ...
and polyacrylamide are examples of chemicals used in this process.
Coating
Pigments

Pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s that absorb in the yellow and red part of the visible spectrum can be added. As the dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
absorbs light, the brightness of the paper will decrease, unlike the effect of an optical-brightening agent. To increase whiteness, a combination of pigments and an optical-brightening agent are often used. The most commonly used pigments are blue and violet dyes.
Optical-brightening agent
Optical brightener is used to make paper appear whiter. Optical-brightening agents usefluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
to absorb invisible radiation from the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
part of the light spectrum and re-emit the radiation as light in the visible blue range. The optical-brightening agent thus generates blue light that is added to the reflected light. The additional blue light offsets the yellowish tinge that would otherwise exist in the reflected light characteristics. It thus increases the brightness of the material (when the illumination includes ultraviolet radiation).
See also
*Deinking
Deinking is the industrial process of removing printing ink from paperfibers of recycled paper to make deinked pulp.
The key in the deinking process is the ability to detach ink from the fibers. This is achieved by a combination of mechanical a ...
recycled paper
* Surface chemistry of paper
* Organosolv (pulping technique)
* Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (also PFAS, PFASs, and informally referred to as "forever chemicals") are a group of synthetic organofluorine chemical compounds that have multiple fluorine atoms attached to an alkyl chain; there are 7 milli ...
References
External links
List of chemicals used in pulp and paper making
{{Authority control Papermaking Chemical processes Cellulose Pulp and paper industry