Palpi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward
 Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the
Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the
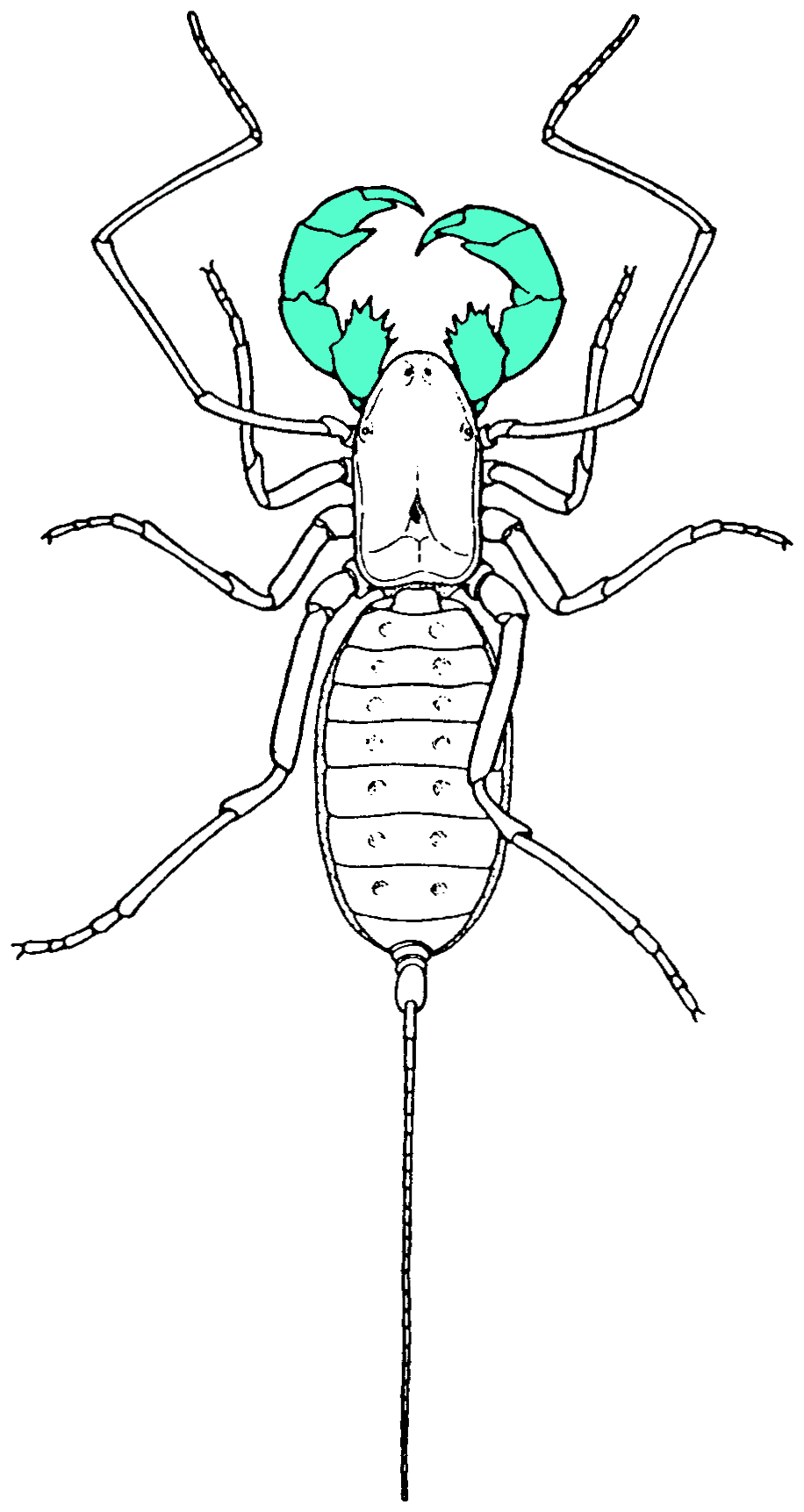
 Pedipalps of
Pedipalps of
Fig 6 – SEM of tibio-cymbial joint on the male palp of ''S. stridulans''
/ref> The embolus is a narrow whip-like or leaf-like extension of the palpal bulb.
 Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s among chelicerates
The subphylum Chelicerata (from Neo-Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. Chelicerates include the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, tic ...
– a group of arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s including spider
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and ran ...
s, scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward cur ...
s, horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only surviving xiphosurans. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or even crustaceans; they are chelicerates, more closely related to arachnids like spiders, ticks, and scor ...
s, and sea spider
Sea spiders are marine arthropods of the class (biology), class Pycnogonida, hence they are also called pycnogonids (; named after ''Pycnogonum'', the type genus; with the suffix '). The class includes the only now-living order (biology), order P ...
s. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated ...
("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs.
Overview
 Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the
Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the trochanter
A trochanter is a tubercle of the femur near its joint with the hip bone. In humans and most mammals, the trochanters serve as important muscle attachment sites. Humans have two, sometimes three, trochanters.
Etymology
The anatomical term ' ...
, the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
, the short patella
The patella (: patellae or patellas), also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in m ...
, the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillar ...
or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element cap ...
. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spider
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and ran ...
s, or chelate
Chelation () is a type of bonding of ions and their molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These l ...
weapons (pincers) of great size, as in scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward cur ...
s. The pedipalps of Solifugae
Solifugae is an Order (biology), order of Arachnid, arachnids known variously as solifuges, sun spiders, camel spiders, and wind scorpions. The order includes more than 1,000 described species in about 147 genus, genera. Despite the common names, ...
are covered in seta
In biology, setae (; seta ; ) are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Depending partly on their form and function, protostome setae may be called macrotrichia, chaetae, ...
e, but have not been studied in detail.
Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only reasonable alternative to this view is to assume that xiphosura
Xiphosura (; , in reference to its sword-like telson) is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are more commonly known as horseshoe crabs (a name applied more specifically to the only extant family, Horseshoe crab, Limulidae). They fir ...
ns reflect the morphology of the primitive arachnid pedipalp and to conclude that this appendage is primitively chelate. Pedipalps are traditionally thought to be homologous with mandibles
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
in crustaceans
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of Arthropod, arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquat ...
and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s, although more recent studies (e.g. using Hox genes
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox genes, are a group of related genes that specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the c ...
) suggest they are probably homologous with the crustacean second antennae.
Chelate pedipalps
Chelate or sub-chelate (pincer-like) pedipalps are found in several arachnid groups (Ricinulei
Ricinulei is a small order of arachnids. Like most arachnids, they are predatory; eating small arthropods. They occur today in west-central Africa ('' Ricinoides'') and the Americas ('' Cryptocellus'' and '' Pseudocellus'') from Brazil to southern ...
, Uropygi
Uropygi is an arachnid order comprising invertebrates commonly known as whip scorpions or vinegaroons (also spelled vinegarroons and vinegarones). They are often called uropygids. The name "whip scorpion" refers to their resemblance to scorpion ...
, scorpions and pseudoscorpion
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.
Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans bec ...
s) but the chelae in most of these groups may not be homologous with those found in Xiphosura
Xiphosura (; , in reference to its sword-like telson) is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are more commonly known as horseshoe crabs (a name applied more specifically to the only extant family, Horseshoe crab, Limulidae). They fir ...
. The pedipalps are distinctly raptorial
In biology (specifically the anatomy of arthropods), the term ''raptorial'' implies much the same as ''predatory'' but most often refers to modifications of an arthropod leg, arthropod's foreleg that make it function for the grasping of prey whi ...
(i.e., modified for seizing prey) in the Amblypygi
Amblypygi is an order of arachnids also known as whip-spiders or tailless whip-scorpions, not to be confused with whip-scorpions or vinegaroons that belong to the related order Thelyphonida. The name "amblypygid" means "blunt tail", a referen ...
, Uropygi, Schizomida
Schizomida, also known as sprickets or short-tailed whip-scorpions, is an order of arachnids, generally less than in length. The order is not yet widely studied. E. O. Wilson has identified schizomids as among the "groups of organisms that des ...
, and some Opiliones
The Opiliones (formerly Phalangida) are an Order (biology), order of arachnids,
Common name, colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs (see below). , over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered w ...
belonging to the laniatorid group.
Spider pedipalps
 Pedipalps of
Pedipalps of spider
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and ran ...
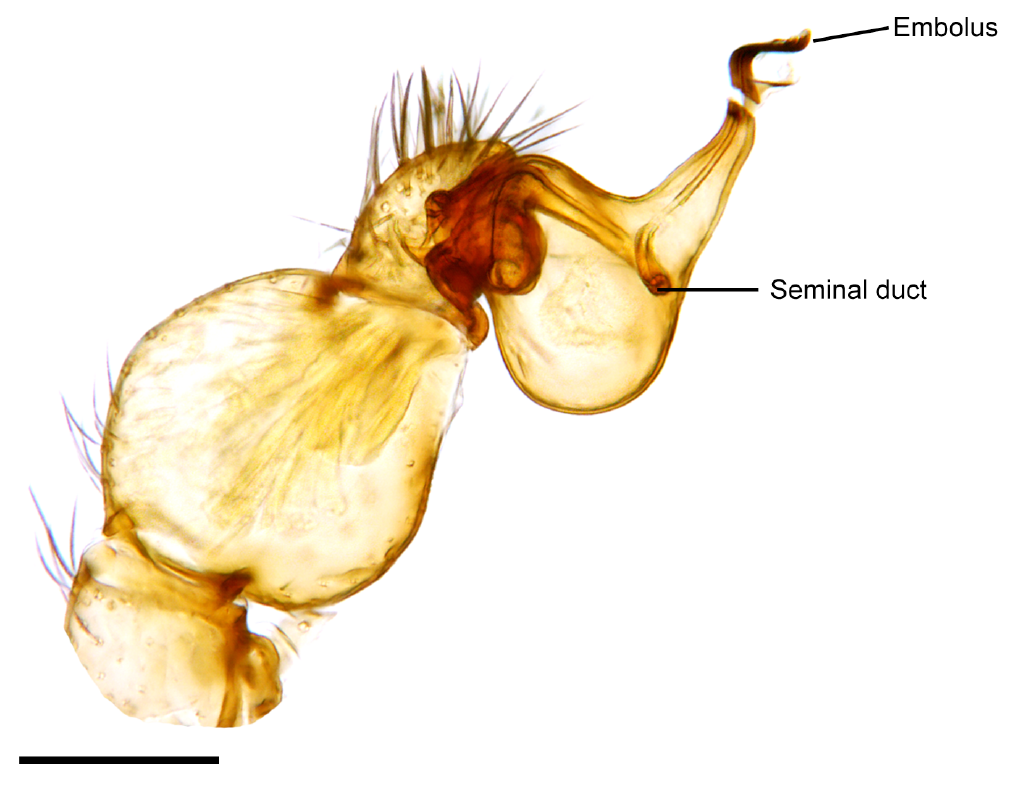
s have the same segmentation as the legs, but the tarsus is undivided, and the pretarsus has no lateral claws. Pedipalps contain sensitive chemical detectors and function as taste and smell organs, supplementing those on the legs. In sexually-mature male spiders, the final segment of the pedipalp, the tarsus, develops a complicated structure (sometimes called the palpal bulb
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often descr ...
or palpal organ) that is used to transfer sperm to the female seminal receptacles during mating. The details of this structure vary considerably between different groups of spiders and are useful for identifying species. The pedipalps are also used by male spiders in courtship displays, contributing to vibratory patterns in web-shaking, acoustic signals, or visual displays.
The cymbium is a spoon-shaped structure located at the end of the spider pedipalp that supports the palpal organ. The cymbium may also be used as a stridulatory organ in spider courtship. SeFig 6 – SEM of tibio-cymbial joint on the male palp of ''S. stridulans''
/ref> The embolus is a narrow whip-like or leaf-like extension of the palpal bulb.
References
Further reading
* * *External links
* * — Several close-up photos of a tarantula creating a sperm web * Phrynus longipes#Pedipalps {{Spider nav Arachnid anatomy Sex organs Spider anatomy