|
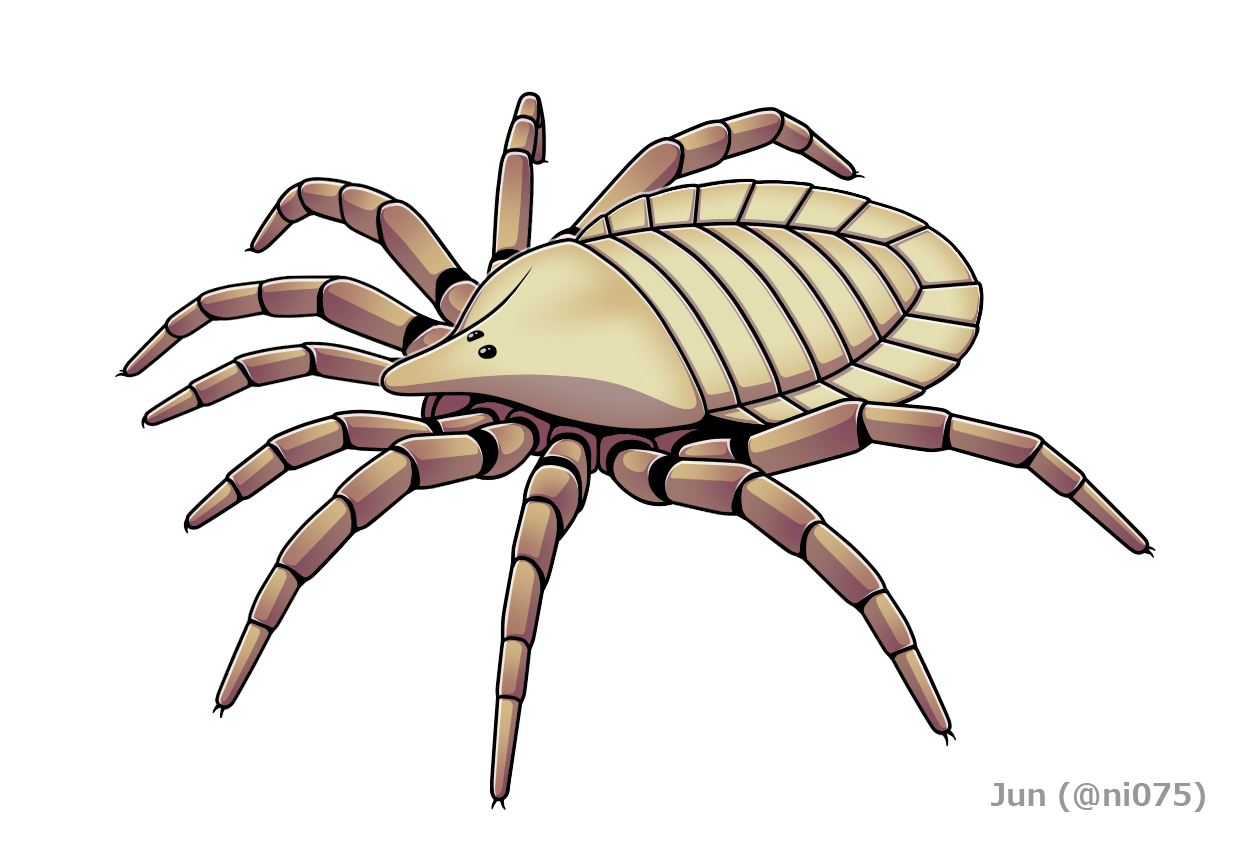
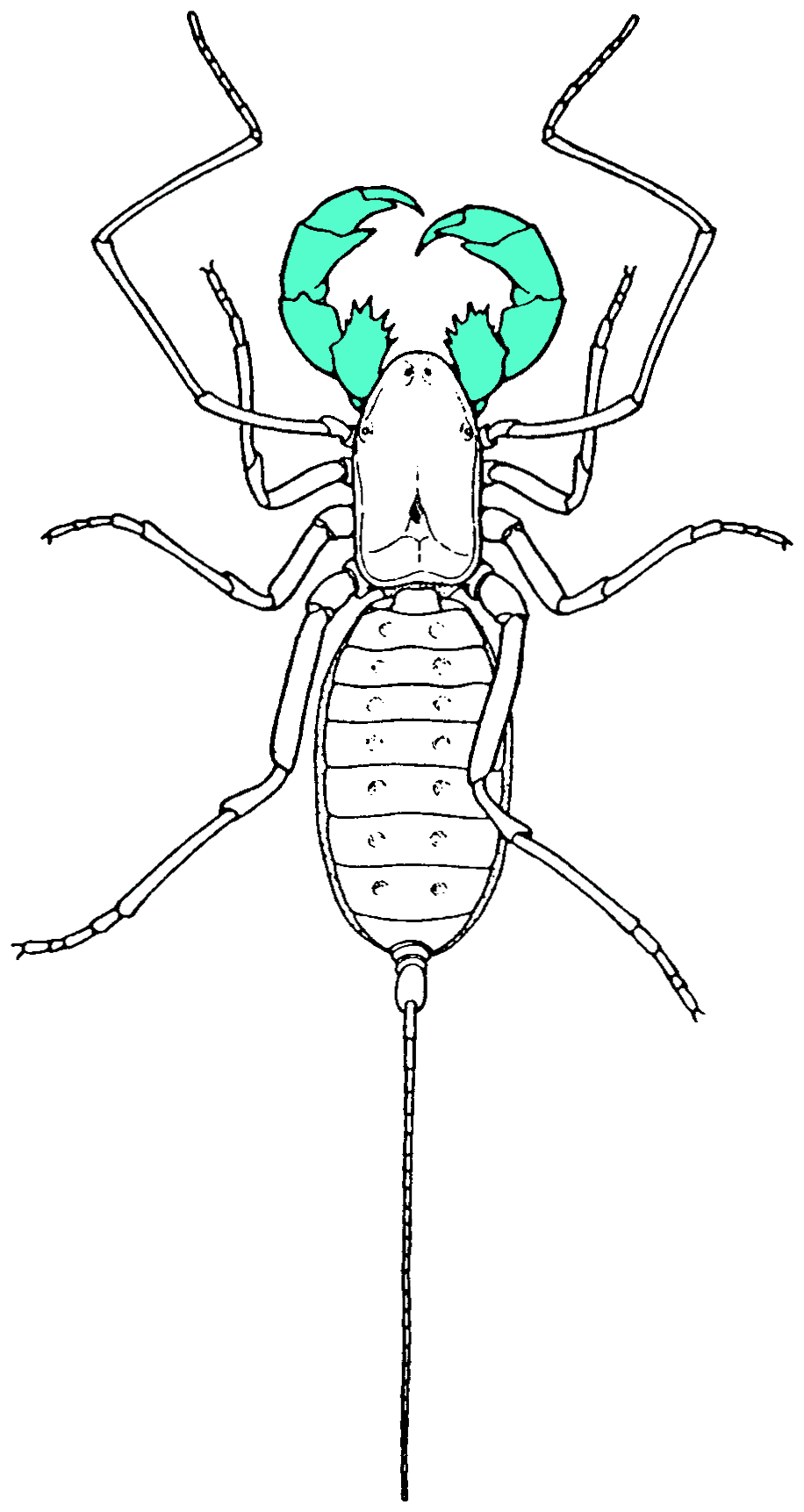
Schizomida
Schizomida, also known as sprickets or short-tailed whip-scorpions, is an order of arachnids, generally less than in length. The order is not yet widely studied. E. O. Wilson has identified schizomids as among the "groups of organisms that desperately need experts to work on them." Taxonomy Schizomids are grouped into three families: * Calcitronidae † (fossil; dubious) * Hubbardiidae * Protoschizomidae (2 genera, 15 species) **'' Agastoschizomus'' ** '' Protoschizomus'' About 300 species of schizomids have been described worldwide, most belonging to the Hubbardiidae family. A systematic review including a full catalogue may be found in Reddell & Cokendolpher (1995). The Schizomida is sister to the order Uropygi, the two clades together forming the Thelyphonida (in the broad sense of the name). Based on molecular clock dates, both orders likely originated in the late Carboniferous somewhere in the tropics of Pangea, and the Schizomida underwent substantial diversificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uropygi
Uropygi is an arachnid order comprising invertebrates commonly known as whip scorpions or vinegaroons (also spelled vinegarroons and vinegarones). They are often called uropygids. The name "whip scorpion" refers to their resemblance to scorpion, true scorpions and possession of a whiplike tail, and "vinegaroon" refers to their ability when attacked to discharge an offensive, vinegar-smelling liquid, which contains acetic acid. The order may also be called Thelyphonida. Both names, Uropygi and Thelyphonida, may be used either in a narrow sense for the order of whip scorpions, or in a broad sense which includes the order Schizomida. Taxonomy Carl Linnaeus first described a whip scorpion in 1758, although he did not distinguish it from what are now regarded as different kinds of arachnid, calling it ''Phalangium caudatum''. ''Phalangium'' is now used as a name for a genus of harvestmen (Opiliones). In 1802, Pierre André Latreille was the first to use a genus name solely for whip s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Uropygi, vinegaroons. Adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs attached to the cephalothorax. In some species the frontmost pair of legs has converted to a sensory function, while in others, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 110,000 named species, of which 51,000 are species of spiders. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapulmonata
Tetrapulmonata is a Taxonomic rank, non-ranked Order (biology), supra-ordinal clade of arachnids. It is composed of the Extant taxon, extant orders Uropygi (whip scorpions), Schizomida (short-tailed whip scorpions), Amblypygi (tail-less whip scorpions) and Spider, Araneae (spiders). It is the only supra-ordinal group of arachnids that is Resampling (statistics), strongly supported in molecular phylogenetic Research, studies. Two extinct orders are also placed in this clade, Haptopoda and Uraraneida. In 2016, a newly described fossil arachnid, ''Idmonarachne'', was also included in the Tetrapulmonata; it has not been assigned to an order. Etymology It receives its International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, name from the presence of paired book lungs occupying the second and third opisthosomal segments, although the posterior pair is absent in Schizomida and most Araneomorphae, araneomorph spiders. Previous synonym (taxonomy), synonyms of this lineage are rejected; "Caulogastra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitronidae
The family Calcitronidae is an extinct group of arachnids. Its two monotypic genera are only known from Pliocene deposits of calcite in Arizona. The family has been placed in the order Schizomida Schizomida, also known as sprickets or short-tailed whip-scorpions, is an order of arachnids, generally less than in length. The order is not yet widely studied. E. O. Wilson has identified schizomids as among the "groups of organisms that des ..., but a review of the order concluded that "the fossil taxa ... are so poorly known that final placement must await further study and possibly new material", and they are not listed in the order in a 2016 catalog of fossil arachnids. References † Cenozoic arachnids † Pliocene arthropods Pliocene animals of North America Neogene arthropods of North America Prehistoric arthropod families {{paleo-arachnid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubbardiidae
Hubbardiidae is a family (biology), family of arachnids, superficially resembling spiders. It is the larger of the two extant families of the Order (biology), order, Schizomida, and is divided into two subfamily, subfamilies. The family is based on the description published by Orator F. Cook in 1899. The American Arachnological Society assigns the common name hubbardiid shorttailed whipscorpion to members of this family. Genera , the ''World Schizomida Catalog'' accepted the following seventy-six genera: *''Adisomus'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 2000 *''Afrozomus'' Reddell & Cokendolpher, 1995 *''Ambulantactus'' Monjaraz-Ruedas, Prendini & Francke, 2019 *''Anepsiozomus'' Harvey, 2001 *''Antillostenochrus'' Armas & Teruel, 2002 *''Apozomus'' Harvey, 1992 *''Artacarus'' Cook, 1899 *''Attenuizomus'' Harvey, 2000 *''Baalrog'' Monjaraz-Ruedas, Prendini & Francke, 2019 *''Bamazomus'' Harvey, 1992 *''Belicenochrus'' Armas & Víquez, 2010 *''Brignolizomus'' Harvey, 2000 *''Bucinozomus'' Arma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agastoschizomus
''Agastoschizomus'' is a genus of protoschizomid short-tailed whipscorpions, first described by Jon Mark Rowland in 1971. Species , the World Schizomida Catalog accepts the following eight species: * '' Agastoschizomus huitzmolotitlensis'' Rowland, 1975 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus juxtlahuacensis'' Moreno & Francke, 2009 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus lucifer'' Rowland, 1971 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus patei'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus stygius'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus tamaulipensis'' Monjaraz-Ruedas, Francke & Cokendolpher, 2016 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus tenebris'' Monjaraz-Ruedas, Francke & Cokendolpher, 2016 – Mexico * '' Agastoschizomus texanus'' Monjaraz-Ruedas, Francke & Cokendolpher, 2016 – US (Texas) References Schizomida genera {{Arachnid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoschizomus
''Protoschizomus'' is a genus of protoschizomid short-tailed whipscorpions, first described by Jon Mark Rowland in 1975. Species , the World Schizomida Catalog accepts the following eight species: * '' Protoschizomus franckei'' Monjaraz-Ruedas, 2013 – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus gertschi'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus occidentalis'' Rowland, 1975 – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus pachypalpus'' (Rowland, 1973) – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus purificacion'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus rowlandi'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus sprousei'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico * '' Protoschizomus treacyae'' Cokendolpher & Reddell, 1992 – Mexico References Schizomida genera {{Arachnid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Lungs
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas-exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open, ventral-abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and connects with its surroundings through a small opening for the purpose of respiration. Structure and function Book lungs are not related to the lungs of modern land-dwelling vertebrates. Their name instead describes their structure and purpose as a case of convergent evolution. Stacks of alternating air pockets and tissue filled with hemolymph give them an appearance similar to a "folded" book. Their number varies from just one pair in most spiders to four pairs in scorpions. The unfolded "pages" (plates) of the book lung are filled with hemolymph. The folds maximize the surface exposed to air, and thereby maximize the amount of gas exchanged with the environment. In most species, no motion of the plates is needed to facilitate this kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Amber
Burmese amber, also known as Burmite or Kachin amber, is amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar. The amber is dated to around 100 million years ago, during the latest Albian to earliest Cenomanian ages of the mid-Cretaceous period. The amber is of significant palaeontological interest due to the diversity of flora and fauna contained as inclusions, particularly arthropods including insects and arachnids but also birds, lizards, snakes, frogs and fragmentary dinosaur remains. The amber has been known and commercially exploited since the first century AD, and has been known to science since the mid-nineteenth century. Research on the deposit has attracted controversy due to the potential role of the amber trade in funding internal conflict in Myanmar and hazardous working conditions in the mines where it is collected. Geological context, depositional environment and age The amber is found in the Hukawng Basin, a large Cretaceous-Cenozoic sedimentary basin within north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metapeltidium
Peltidium is a prodorsal shield found in animals of the subphylum Chelicerata, in the phylum Arthropoda. In some groups (Schizomida, Palpigradi, Solpugida and Opiliones The Opiliones (formerly Phalangida) are an Order (biology), order of arachnids, Common name, colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs (see below). , over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered w ...), the peltidium, also known as the schizopeltid, can be subdivided into the propeltidium, a carapace-like shield that covers the proterosoma, which comprises the fused acron (protocerebral region) and first four segments, and two free segments, the mesopeltidium and metapeltidium (Online Dictionary of Invertebrate Zoology). External links Online Dictionary of Invertebrate Zoology References {{reflist Chelicerate anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward appendages among Chelicerata, chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the Arthropod leg#Trochanter, trochanter, the Arthropod leg#Femur, femur, the short Glossary_of_spider_terms#patella, patella, the Glossary_of_spider_terms#tibia, tibia, and the Arthropod_leg#Tarsus, tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called Glossary_of_spider_terms#maxilla , maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior arthropod leg, legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |