Paleochristian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the historical era of the Christian religion up to the
 Christianity originated as a minor sect within
Christianity originated as a minor sect within
 Christianity centers on the
Christianity centers on the 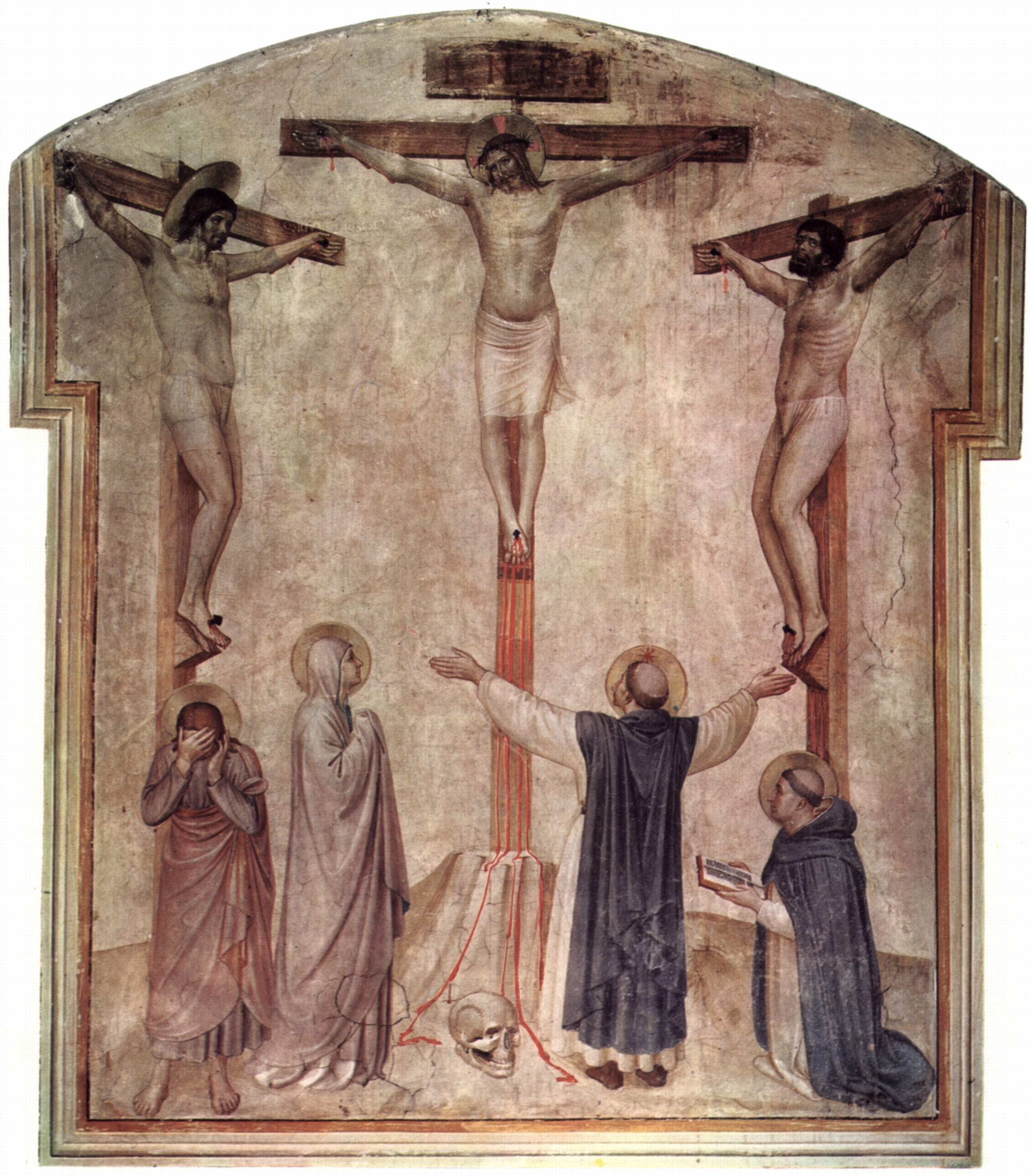 After three years of ministry, Jesus was crucified as a messianic pretender and insurgent. Paul, writing around 20 years after Jesus' death, provides the earliest account of the
After three years of ministry, Jesus was crucified as a messianic pretender and insurgent. Paul, writing around 20 years after Jesus' death, provides the earliest account of the
 After the death of Jesus, his followers established Christian groups in cities, such as Jerusalem. The movement quickly spread to
After the death of Jesus, his followers established Christian groups in cities, such as Jerusalem. The movement quickly spread to
 Jerusalem was the first center of the
Jerusalem was the first center of the

Time.com
Accessed October 8, 2009 and concludes that while Peter ''was'' the Primacy of Simon Peter, original head of the apostles, Peter was not the founder of any visible church succession.Cullmann, Oscar "In the New Testament [Jerusalem] is the only church of which we hear that Peter stood at its head. Of other episcopates of Peter we know nothing certain. Concerning Antioch, indeed ... there is a tradition, first appearing in the course of the second century, according to which Peter was its bishop. The assertion that he was Bishop of Rome we first find at a much later time. From the second half of the second century we do possess texts that mention the apostolic ''foundation'' of Rome, and at this time, which is indeed rather late, this foundation is traced back to Peter and Paul, an assertion that cannot be supported historically. Even here, however, nothing is said as yet of an episcopal office of Peter." The original seat of Roman imperial power soon became a center of church authority, grew in power decade by decade, and was recognized during the period of the Seven Ecumenical Councils, when the seat of government had been transferred to Constantinople, as the "head" of the church. Rome and Alexandria, which by tradition held authority over sees outside their own Roman province, province, were not yet referred to as patriarchates. The earliest Bishops of Rome were all Greek-speaking, the most notable of them being: Pope Clement I, Pope Clement I (c. 88–97), author of an First Epistle of Clement, Epistle to the Church in Corinth; Pope Telesphorus (c. 126–136), probably the only martyr among them; Pope Pius I, Pope Pius I (c. 141–154), said by the Muratorian fragment to have been the brother of the author of the Shepherd of Hermas; and Pope Anicetus (c. 155–160), who received Saint Polycarp and discussed with him the Easter controversy, dating of Easter. Pope Victor I, Pope Victor I (189–198) was the first ecclesiastical writer known to have written in Latin; however, his only extant works are his encyclicals, which would naturally have been issued in Latin and Greek. Greek New Testament texts were translated into Latin early on, well before Jerome, and are classified as the Vetus Latina and Western text-type. During the 2nd century, Christians and semi-Christians of diverse views congregated in Rome, notably Marcion and Valentinius, and in the following century there were schisms connected with Hippolytus of Rome and Novatian. The Roman church survived various persecutions. Among the prominent Christians executed as a result of their refusal to perform acts of worship to the Roman gods as ordered by emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian in 258 were Cyprian, bishop of Carthage. The last and most severe of the imperial persecutions was that Diocletianic Persecution, under Diocletian in 303; they ended in Rome, and the West in general, with the accession of Maxentius in 306.
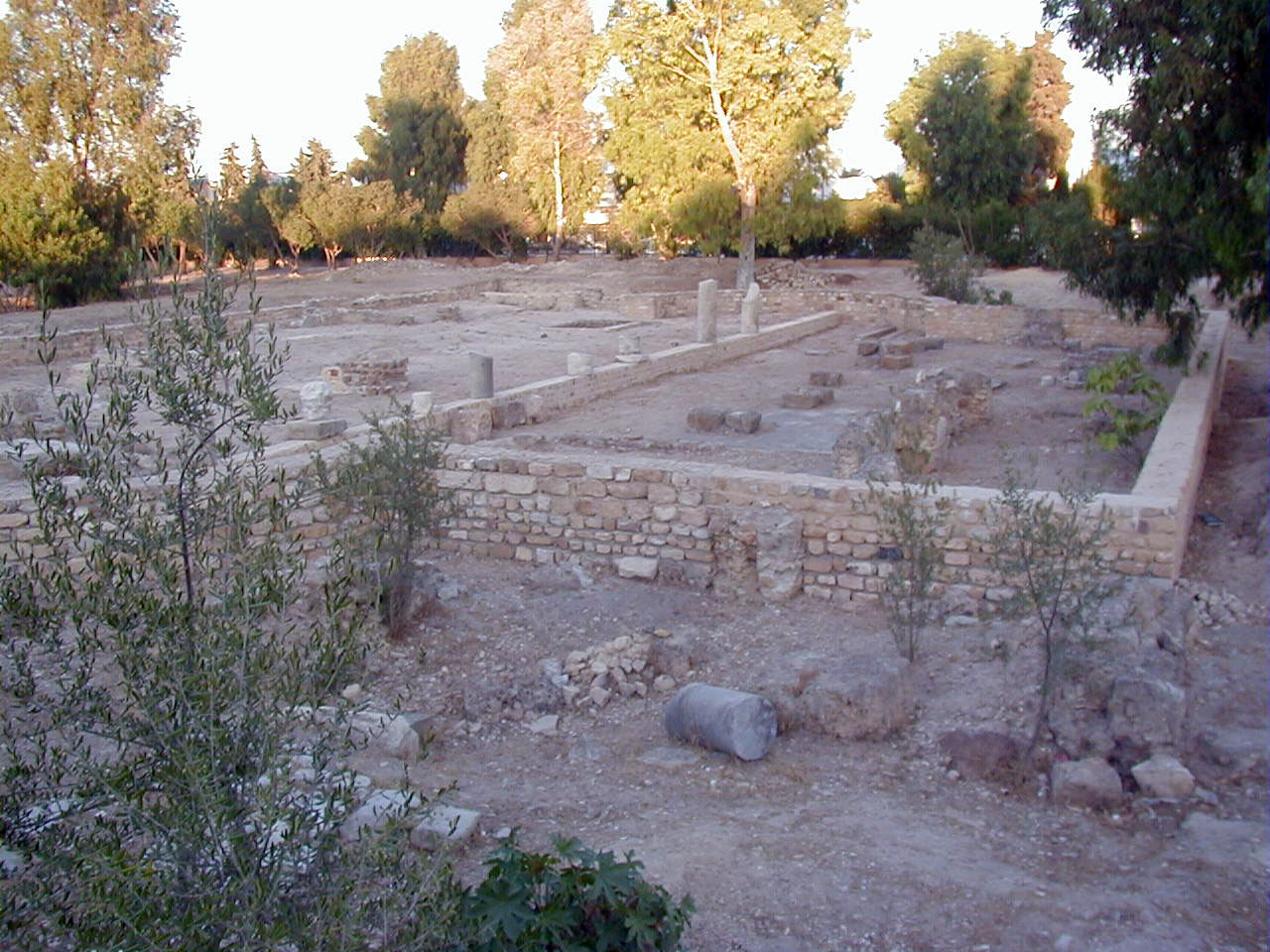 Carthage, in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa, south of the Mediterranean from Rome, gave the early church the Latin fathers Tertullian (c. 120 – c. 220) and Cyprian (d. 258). Carthage fell to Islam in 698.
The Church of Carthage thus was to the Early African church what the Diocese of Rome, Church of Rome was to the Catholic Church in Italy. The archdiocese used the African Rite, a variant of the Western liturgical rites in Latin language, possibly a local use of the primitive Roman Rite. Famous figures include Passion of Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions, Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions (died c. 203), Tertullian (c. 155–240), Cyprian (c. 200–258), Caecilianus (floruit 311), Aurelius of Carthage, Saint Aurelius (died 429), and Eugenius of Carthage (died 505). Tertullian and Cyprian are considered Church Fathers#Latin Fathers, Latin Church Fathers of the Latin Church. Tertullian, a theologian of part Berbers, Berber descent, was instrumental in the development of Trinity, trinitarian theology, and was the first to apply Latin language extensively in his theological writings. As such, Tertullian has been called "the father of Latin Christianity" and "the founder of Western theology". Carthage remained an important center of Christianity until 698, hosting several councils of Carthage.
Carthage, in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa, south of the Mediterranean from Rome, gave the early church the Latin fathers Tertullian (c. 120 – c. 220) and Cyprian (d. 258). Carthage fell to Islam in 698.
The Church of Carthage thus was to the Early African church what the Diocese of Rome, Church of Rome was to the Catholic Church in Italy. The archdiocese used the African Rite, a variant of the Western liturgical rites in Latin language, possibly a local use of the primitive Roman Rite. Famous figures include Passion of Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions, Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions (died c. 203), Tertullian (c. 155–240), Cyprian (c. 200–258), Caecilianus (floruit 311), Aurelius of Carthage, Saint Aurelius (died 429), and Eugenius of Carthage (died 505). Tertullian and Cyprian are considered Church Fathers#Latin Fathers, Latin Church Fathers of the Latin Church. Tertullian, a theologian of part Berbers, Berber descent, was instrumental in the development of Trinity, trinitarian theology, and was the first to apply Latin language extensively in his theological writings. As such, Tertullian has been called "the father of Latin Christianity" and "the founder of Western theology". Carthage remained an important center of Christianity until 698, hosting several councils of Carthage.
 According to Acts, Paul was shipwrecked and ministered on an island which some scholars have identified as Malta (an island just south of Sicily) for three months during which time he is said to have been bitten by a poisonous viper and survived (; ), an event usually dated c. AD 60. Paul had been allowed passage from #Caesarea, Caesarea Maritima to Rome by Porcius Festus, Procurator (Roman), procurator of Iudaea Province, to stand trial before the Emperor. Many traditions are associated with this episode, and Rabat, Malta#Catacombs, catacombs in Rabat testify to an Early Christian community on the islands. According to tradition, Saint Publius, Publius, the Roman Governor of Malta at the time of Saint Paul's shipwreck, became the first ''Bishop of Malta'' following his conversion to Christianity. After ruling the Maltese Church for thirty-one years, Publius was transferred to the See of Athens in AD 90, where he was martyred in AD 125. There is scant information about the continuity of Christianity in Malta in subsequent years, although tradition has it that there was a continuous line of bishops from the days of St. Paul to the time of Emperor Constantine.
According to Acts, Paul was shipwrecked and ministered on an island which some scholars have identified as Malta (an island just south of Sicily) for three months during which time he is said to have been bitten by a poisonous viper and survived (; ), an event usually dated c. AD 60. Paul had been allowed passage from #Caesarea, Caesarea Maritima to Rome by Porcius Festus, Procurator (Roman), procurator of Iudaea Province, to stand trial before the Emperor. Many traditions are associated with this episode, and Rabat, Malta#Catacombs, catacombs in Rabat testify to an Early Christian community on the islands. According to tradition, Saint Publius, Publius, the Roman Governor of Malta at the time of Saint Paul's shipwreck, became the first ''Bishop of Malta'' following his conversion to Christianity. After ruling the Maltese Church for thirty-one years, Publius was transferred to the See of Athens in AD 90, where he was martyred in AD 125. There is scant information about the continuity of Christianity in Malta in subsequent years, although tradition has it that there was a continuous line of bishops from the days of St. Paul to the time of Emperor Constantine.
 According to Church History (Eusebius), Eusebius' record, the apostles Thomas the Apostle, Thomas and Bartholomew the Apostle, Bartholomew were assigned to Parthia (modern Iran) and India.
A. E. Medlycott, ''India and The Apostle Thomas'', pp. 18–71;
M. R. James, ''Apocryphal New Testament'', pp. 364–436;
A. E. Medlycott, ''India and The Apostle Thomas'', pp. 1–17, 213–97;
Eusebius, ''History'', chapter 4:30;
J. N. Farquhar, ''The Apostle Thomas in North India'', chapter 4:30;
V. A. Smith, ''Early History of India'', p. 235;
L. W. Brown, ''The Indian Christians of St. Thomas'', pp. 49–59. By the time of the establishment of the Second Persian Empire (AD 226), there were bishops of the Church of the East in northwest India, Afghanistan and Balochistan (region), Baluchistan (including parts of Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan), with laymen and clergy alike engaging in missionary activity.
An early third-century Syriac work known as the ''Acts of Thomas'' connects the apostle's Indian ministry with two kings, one in the north and the other in the south. According to the ''Acts'', Thomas was at first reluctant to accept this mission, but the Lord appeared to him in a night vision and compelled him to accompany an Indian merchant, Abbanes (or Habban), to his native place in northwest India. There, Thomas found himself in the service of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom, Indo-Parthian King, Gondophares. The Apostle's ministry resulted in many conversions throughout the kingdom, including the king and his brother.
Thomas thereafter went south to Kerala and baptized the natives, whose descendants form the Saint Thomas Christians or the Syrian Malabar Nasranis.James, M. R. (1966) "The Acts of Thomas" in ''The Apocryphal New Testament'', pp. 365−77; 434−38. Oxford.
Piecing together the various traditions, the story suggests that Thomas left northwest India when invasion threatened, and traveled by vessel to the Malabar Coast along the southwestern coast of the Indian continent, possibly visiting southeast
According to Church History (Eusebius), Eusebius' record, the apostles Thomas the Apostle, Thomas and Bartholomew the Apostle, Bartholomew were assigned to Parthia (modern Iran) and India.
A. E. Medlycott, ''India and The Apostle Thomas'', pp. 18–71;
M. R. James, ''Apocryphal New Testament'', pp. 364–436;
A. E. Medlycott, ''India and The Apostle Thomas'', pp. 1–17, 213–97;
Eusebius, ''History'', chapter 4:30;
J. N. Farquhar, ''The Apostle Thomas in North India'', chapter 4:30;
V. A. Smith, ''Early History of India'', p. 235;
L. W. Brown, ''The Indian Christians of St. Thomas'', pp. 49–59. By the time of the establishment of the Second Persian Empire (AD 226), there were bishops of the Church of the East in northwest India, Afghanistan and Balochistan (region), Baluchistan (including parts of Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan), with laymen and clergy alike engaging in missionary activity.
An early third-century Syriac work known as the ''Acts of Thomas'' connects the apostle's Indian ministry with two kings, one in the north and the other in the south. According to the ''Acts'', Thomas was at first reluctant to accept this mission, but the Lord appeared to him in a night vision and compelled him to accompany an Indian merchant, Abbanes (or Habban), to his native place in northwest India. There, Thomas found himself in the service of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom, Indo-Parthian King, Gondophares. The Apostle's ministry resulted in many conversions throughout the kingdom, including the king and his brother.
Thomas thereafter went south to Kerala and baptized the natives, whose descendants form the Saint Thomas Christians or the Syrian Malabar Nasranis.James, M. R. (1966) "The Acts of Thomas" in ''The Apocryphal New Testament'', pp. 365−77; 434−38. Oxford.
Piecing together the various traditions, the story suggests that Thomas left northwest India when invasion threatened, and traveled by vessel to the Malabar Coast along the southwestern coast of the Indian continent, possibly visiting southeast
Early Christian Sources
English translations of the surviving writings of the early Christians.
Early Christians
(archived 1 September 2014)
PBS Frontline: The First Christians
First Christians and Rome
Cave in Jordan Said to Have Been Used by Early Christians
Biblical Archaeology Review (archived 7 January 2010) {{DEFAULTSORT:History of early Christianity Early Christianity, 1st-century Christianity 2nd-century Christianity 3rd-century Christianity 4th-century Christianity Dioceses established in the 1st century,
First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
in 325. Christianity spread from the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, across the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
and the Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( ), alternatively the dispersion ( ) or the exile ( ; ), consists of Jews who reside outside of the Land of Israel. Historically, it refers to the expansive scattering of the Israelites out of their homeland in the Southe ...
throughout the Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey ...
. The first followers of Christianity were Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
who had converted to the faith, i.e. Jewish Christian
Jewish Christians were the followers of a Jewish religious sect that emerged in Roman Judea during the late Second Temple period, under the Herodian tetrarchy (1st century AD). These Jews believed that Jesus was the prophesied Messiah and ...
s, as well as Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civi ...
, i.e. Lebanese Christians. Early Christianity contains the Apostolic Age
Christianity in the 1st century covers the formative history of Christianity from the start of the ministry of Jesus (–29 AD) to the death of the last of the Twelve Apostles () and is thus also known as the Apostolic Age. Early Christianity ...
and is followed by, and substantially overlaps with, the Patristic era.
The Apostolic see
An apostolic see is an episcopal see whose foundation is attributed to one or more of the apostles of Jesus or to one of their close associates. In Catholicism, the phrase "The Apostolic See" when capitalized refers specifically to the See of ...
s claim to have been founded by one or more of the apostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary. The word is derived from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", itself derived from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to se ...
of Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
, who are said to have dispersed from Jerusalem sometime after the crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion of Jesus was the death of Jesus by being crucifixion, nailed to a cross.The instrument of Jesus' crucifixion, instrument of crucifixion is taken to be an upright wooden beam to which was added a transverse wooden beam, thus f ...
, c. 26–33, perhaps following the Great Commission
In Christianity, the Great Commission is the instruction of the Resurrection appearances of Jesus, resurrected Jesus Christ to his disciple (Christianity), disciples to spread the gospel to all the nations of the world. The Great Commission i ...
. Early Christians gathered in small private homes,Paul, for example, greets a house church in . known as house church
A house church or home church is a label used to describe a group of Christians who regularly gather for worship in private homes. The group may be part of a larger Christian body, such as a parish, but some have been independent groups that se ...
es, but a city's whole Christian community would also be called a "church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
"—the Greek noun ἐκκλησία (''ekklesia'') literally means "assembly", "gathering", or "congregation" but is translated as "church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
" in most English translations of the New Testament.
Many early Christians were merchants and others who had practical reasons for traveling to Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, and other regions. Over 40 such communities were established by the year 100, many in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, also known as Asia Minor, such as the Seven churches of Asia
The Seven Churches of Revelation, also known as the Seven Churches of the Apocalypse and the Seven Churches of Asia, are seven churches of early Christianity mentioned in the New Testament Book of Revelation. All of them were located in Asia Min ...
. By the end of the first century
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; T ...
, Christianity had already spread to Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
, Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, and Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, serving as foundations for the expansive spread of Christianity
Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century in the Roman province of Judea, from where it spread throughout and beyond the Roman Empire.
Origins
Christianity "emerged as a sect of Judaism in Roman Judea" in the sy ...
, eventually throughout the world.
History
Origins
Second Temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism is the Judaism, Jewish religion as it developed during the Second Temple period, which began with the construction of the Second Temple around 516 BCE and ended with the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destruction of Jerusalem in ...
, the form of Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
existing from the end of the Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile was the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were forcibly relocated to Babylonia by the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The deportations occurred ...
( to the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 AD. The central tenets of Second Temple Judaism revolved around monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
and the belief that Jews were a chosen people. As part of their covenant with God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
, Jews were obligated to obey the Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
. In return, they were given the land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine. The definition ...
and the city of Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, where God dwelled in the Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
.
The Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
ended the Babylonian captivity, permitting exiled Jews to return to their homeland and rebuild the Temple . Nevertheless, the native Jewish monarchy was not restored. Instead, political power devolved to the high priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious organisation.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many god ...
, who served as an intermediary between the Jewish people and the empire. This arrangement continued after the region was conquered by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
(356–323 BC).
Alexander's conquests initiated the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
when the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
underwent Hellenization
Hellenization or Hellenification is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language, and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonisation often led to the Hellenisation of indigenous people in the Hellenistic period, many of the ...
(the spread of Greek culture
The culture of Greece has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Minoan and later in Mycenaean Greece, continuing most notably into Classical Greece, while influencing the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Empire. Other cultu ...
). Judaism was thereafter both culturally and politically part of the Hellenistic world; however, Hellenistic Judaism
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Hellenistic culture and religion. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellen ...
was stronger among diaspora Jews than among those living in the land of Israel. Diaspora Jews spoke Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
, and the Jews of Alexandria produced a Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Septuagint The Septuagint ( ), sometimes referred to as the Greek Old Testament or The Translation of the Seventy (), and abbreviated as LXX, is the earliest extant Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible from the original Biblical Hebrew. The full Greek ...
. The Septuagint was the translation of the . '' Septuagint The Septuagint ( ), sometimes referred to as the Greek Old Testament or The Translation of the Seventy (), and abbreviated as LXX, is the earliest extant Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible from the original Biblical Hebrew. The full Greek ...
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
used by early Christians. Diaspora Jews continued to make pilgrimage to the Temple, but they started forming local religious institutions called synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
s as early as the 3rd century BC.
After Alexander's death, the region was ruled by Ptolemaic Egypt Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
*Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
() and then the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
(). The anti-Jewish policies of Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes ( 215 BC–November/December 164 BC) was king of the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. Notable events during Antiochus' reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of ...
() sparked the Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt () was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167 to 160 BCE and ended with the Seleucids in control of ...
in 167BC, which culminated in the establishment of an independent Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
under the Hasmoneans, who ruled as kings and high priests. This independence would last until 63BC when Judea became a client state
A client state in the context of international relations is a State (polity), state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
.
Apocalyptic literature
Apocalyptic literature is a genre of prophetical writing that developed in post- Exilic Jewish culture and was popular among millennialist early Christians. '' Apocalypse'' () is a Greek word meaning "revelation", "an unveiling or unfolding o ...
and thought had a major influence on Second Temple Judaism and early Christianity. Apocalypticism
Apocalypticism is the religious belief that the Eschatology, end of the world is imminent, even within one's own lifetime. This belief is usually accompanied by the idea that civilization will soon come to a tumultuous end due to some sort of ...
grew out of resistance to Hellenistic and later Roman rule. Apocalyptic writers considered themselves to be living in the end times and expected God to intervene in history, end the present sufferings, and restore his kingdom. Frequently, this was accomplished by a savior figure (such as a messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
or " Son of Man") who wins the final battle against the forces of evil and is appointed by God to rule. ''Messiah'' (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
: ) means "anointed" and is used in the Old Testament to designate Jewish kings and in some cases priests
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, ...
and prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
whose status was symbolized by being anointed with holy anointing oil
In the ancient Israelite religion, the holy anointing oil () formed an integral part of the ordination of the priesthood and the High Priest as well as in the consecration of the articles of the Tabernacle ( Exodus 30:26) and subsequent temple ...
. The term is most associated with King David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
, to whom God promised an eternal kingdom ( 2 Samuel 7:11–17). After the destruction of David's kingdom and lineage, this promise was reaffirmed by the prophets Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "Yahweh is salvation"; also known as Isaias or Esaias from ) was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
The text of the Book of Isaiah refers to Isaiah as "the prophet" ...
, Jeremiah
Jeremiah ( – ), also called Jeremias, was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition, Jeremiah authored the Book of Jeremiah, book that bears his name, the Books of Kings, and the Book of Lamentations, with t ...
, and Ezekiel
Ezekiel, also spelled Ezechiel (; ; ), was an Israelite priest. The Book of Ezekiel, relating his visions and acts, is named after him.
The Abrahamic religions acknowledge Ezekiel as a prophet. According to the narrative, Ezekiel prophesied ...
, who foresaw a future king from the House of David who would establish and reign over an idealized kingdom.
Jesus
 Christianity centers on the
Christianity centers on the life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
and ministry of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religi ...
, who lived . Jesus left no writings of his own, and most information about him comes from early Christian writings that now form part of the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
. The earliest of these are the Pauline epistles
The Pauline epistles, also known as Epistles of Paul or Letters of Paul, are the thirteen books of the New Testament attributed to Paul the Apostle, although the authorship of some is in dispute. Among these epistles are some of the earliest ext ...
, letters written to various Christian congregations by Paul the Apostle
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Apostles in the New Testament, Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the Ministry of Jesus, teachings of Jesus in the Christianity in the 1st century, first ...
in the 50s AD. The four canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the second century AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message was reported. In this sen ...
of Matthew (), Mark
Mark may refer to:
In the Bible
* Mark the Evangelist (5–68), traditionally ascribed author of the Gospel of Mark
* Gospel of Mark, one of the four canonical gospels and one of the three synoptic gospels
Currencies
* Mark (currency), a currenc ...
(), Luke (), and John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
(written at the end of the 1st century) are ancient biographies of Jesus' life.
Jesus grew up in Nazareth
Nazareth is the largest Cities in Israel, city in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. In its population was . Known as "the Arab capital of Israel", Nazareth serves as a cultural, political, religious, economic and ...
, a village in Galilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
. He started his public ministry when he was around 30 years old. Traveling through the Galilee, the Decapolis
The Decapolis (Greek: ) was a group of ten Greek Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Greek and late Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BC and AD. Most of the cities were located to the east of the Jordan ...
, and to Jerusalem, Jesus preached a message directed at other Jews. This message centered on the imminent arrival of the Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms kingdom of God and kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
. He urged followers to repent in preparation for its coming and taught them how to live while waiting. This ethical teaching is summarized in the Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer, also known by its incipit Our Father (, ), is a central Christian prayer attributed to Jesus. It contains petitions to God focused on God’s holiness, will, and kingdom, as well as human needs, with variations across manusc ...
and the Great Commandment
The Great Commandment (or Greatest Commandment) is a name used in the New Testament to describe the first of two commandments cited by Jesus in Matthew 22 (), Mark 12 (), and in answer to him in Luke 10 (),
According to Jesus of Nazareth, th ...
to love God and to "love your neighbor as yourself" ( Matthew 22:37–39). Jesus chose twelve disciples, representing the twelve tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( , ) are described in the Hebrew Bible as being the descendants of Jacob, a Patriarchs (Bible), Hebrew patriarch who was a son of Isaac and thereby a grandson of Abraham. Jacob, later known as Israel (name), Israel, ...
, from among his followers. They symbolized the full restoration of Israel, including the Ten Lost Tribes
The Ten Lost Tribes were those from the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been exiled from the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel after it was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire around 720 BCE. They were the following ...
, that would be accomplished through him.
The gospel accounts provide insight into what early Christians believed about Jesus. As the Christ or "Anointed One" (Greek: ), Jesus is identified as the fulfillment of messianic prophecies in the Hebrew scriptures. Through the accounts of his miraculous virgin birth, the gospels present Jesus as the Son of God
Historically, many rulers have assumed titles such as the son of God, the son of a god or the son of heaven.
The term "Son of God" is used in the Hebrew Bible as another way to refer to humans who have a special relationship with God. In Exo ...
. The gospels describe the miracles of Jesus
The miracles of Jesus are the many miraculous deeds attributed to Jesus in Christian texts, with the majority of these miracles being faith healings, exorcisms, resurrections, and control over nature.
In the Gospel of John, Jesus is said to ...
which served to authenticate his message and reveal a foretaste of the coming kingdom.
 After three years of ministry, Jesus was crucified as a messianic pretender and insurgent. Paul, writing around 20 years after Jesus' death, provides the earliest account of the
After three years of ministry, Jesus was crucified as a messianic pretender and insurgent. Paul, writing around 20 years after Jesus' death, provides the earliest account of the resurrection of Jesus
The resurrection of Jesus () is Christianity, Christian belief that God in Christianity, God Resurrection, raised Jesus in Christianity, Jesus from the dead on the third day after Crucifixion of Jesus, his crucifixion, starting—or Preexis ...
in 1 Corinthians 15:3–8. The gospel accounts provide narratives of the resurrection, ultimately leading to the ascension of Jesus
The Ascension of Jesus (anglicized from the Vulgate ) is the Christianity, Christian and Islamic belief that Jesus entering heaven alive, ascended to Heaven. Christian doctrine, as reflected in the major Christian creeds and confessional stateme ...
into Heaven
Heaven, or the Heavens, is a common Religious cosmology, religious cosmological or supernatural place where beings such as deity, deities, angels, souls, saints, or Veneration of the dead, venerated ancestors are said to originate, be throne, ...
. Jesus' victory over death became the central belief of Christianity. For his followers, Jesus inaugurated a New Covenant
The New Covenant () is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a Book of Jeremiah#Sections of the Book, phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah (Jeremiah 31:31–34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the ...
between God and his people. The Pauline epistles teach that Jesus makes salvation
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
possible. Through faith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or concept. In the context of religion, faith is " belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
According to the Merriam-Webster's Dictionary, faith has multiple definitions, inc ...
, believers experience union with Jesus and both share in his suffering and the hope
Hope is an optimistic state of mind that is based on an expectation of positive outcomes with respect to events and circumstances in one's own life, or the world at large.
As a verb, Merriam-Webster defines ''hope'' as "to expect with confid ...
of his resurrection.
While they do not provide new information, non-Christian sources do confirm certain information found in the gospels. The Jewish historian Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of pr ...
referenced Jesus in his ''Antiquities of the Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' (; , ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by the Roman-Jewish historian Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, which was 94 CE. It cont ...
'' written . The paragraph, known as the '' Testimonium Flavianum'', provides a brief summary of Jesus' life, but the original text has been altered by Christian interpolation
In textual criticism, Christian interpolation generally refers to textual insertion and textual damage to Jewish and pagan source texts during Christian scribal transmission.
Old Testament pseudepigrapha
Notable examples among the body of texts k ...
. The first Roman author to reference Jesus is Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
(), who wrote that Christians "took their name from who was executed in the reign of Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
by the procurator Pontius Pilate" .
1st century
The decades after the crucifixion of Jesus are known as the Apostolic Age because the Disciples (also known asApostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary. The word is derived from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", itself derived from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to se ...
) were still alive. Important Christian sources for this period are the Pauline epistles
The Pauline epistles, also known as Epistles of Paul or Letters of Paul, are the thirteen books of the New Testament attributed to Paul the Apostle, although the authorship of some is in dispute. Among these epistles are some of the earliest ext ...
and the Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
, as well as the Didache
The ''Didache'' (; ), also known as ''The Lord's Teaching Through the Twelve Apostles to the Nations'' (), is a brief anonymous early Christian treatise ( ancient church order) written in Koine Greek, dated by modern scholars to the first or (l ...
and the Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical peri ...
' writtings.Initial spread
 After the death of Jesus, his followers established Christian groups in cities, such as Jerusalem. The movement quickly spread to
After the death of Jesus, his followers established Christian groups in cities, such as Jerusalem. The movement quickly spread to Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
and Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
, capital of Roman Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great, who had become the protector of the Hellenistic kingdom of Syria.
...
and one of the most important cities in the empire. Early Christians referred to themselves as brethren, '' disciples'' or ''saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the ...
s'', but it was in Antioch, according to Acts 11:26, that they were first called Christians (Greek: ).
According to the New Testament, Paul the apostle established Christian communities throughout the Mediterranean world. He is known to have also spent some time in Arabia. After preaching in Syria, he turned his attention to the cities of Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. By the early 50s, he had moved on to Europe where he stopped in Philippi
Philippi (; , ''Phílippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides (, ''Krēnĩdes'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colonists in 360/359 BC. The city was renamed by Phili ...
and then traveled to Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
in Roman Macedonia. He then moved into mainland Greece, spending time in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
. While in Corinth, Paul wrote his Epistle to the Romans
The Epistle to the Romans is the sixth book in the New Testament, and the longest of the thirteen Pauline epistles. Biblical scholars agree that it was composed by Paul the Apostle to explain that Salvation (Christianity), salvation is offered ...
, indicating that there were already Christian groups in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
. Some of these groups had been started by Paul's missionary associates Priscilla and Aquila and Epainetus.
Social and professional networks played an important part in spreading the religion as members invited interested outsiders to secret Christian assemblies (Greek: ) that met in private homes (see house church
A house church or home church is a label used to describe a group of Christians who regularly gather for worship in private homes. The group may be part of a larger Christian body, such as a parish, but some have been independent groups that se ...
). Commerce and trade also played a role in Christianity's spread as Christian merchants traveled for business. Christianity appealed to marginalized groups (women, slaves) with its message that "in Christ there is neither Jew nor Greek, neither male nor female, neither slave nor free" ( Galatians 3:28). Christians also provided social services to the poor, sick, and widows. Women actively contributed to the Christian faith as disciples, missionaries, and more due to the large acceptance early Christianity offered.
Historian Keith Hopkins estimated that by AD 100 there were around 7,000 Christians (about 0.01 percent of the Roman Empire's population of 60 million). Separate Christian groups maintained contact with each other through letters, visits from itinerant preacher
An itinerant preacher (also known as an itinerant minister) is a Christian evangelist who preaches the basic Christian redemption message while traveling around to different groups of people within a relatively short period of time. The usage of ...
s, and the sharing of common texts, some of which were later collected in the New Testament.
Jerusalem church
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus Christ. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a syn ...
according to the Book of Acts
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
. The apostles lived and taught there for some time after Pentecost. According to Acts, the early church
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the historical era of the Christian religion up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. Christianity spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and bey ...
was led by the Apostles, foremost among them Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a su ...
and John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
. When Peter left Jerusalem after Herod Agrippa I tried to kill him, James, brother of Jesus
James the Just, or a variation of James, brother of the Lord ( from , and , , can also be Anglicized as "Jacob"), was, according to the New Testament, a brother of Jesus. He was the first Jewish bishop of Jerusalem. Traditionally, it is bel ...
appears as the leader of the Jerusalem church. Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A ...
() called him Bishop of Jerusalem. Peter, John and James were collectively recognized as the three pillars of the church
A triumvirate () or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs (). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are notionally equal, the actual distr ...
( Galatians 2:9).
At this early date, Christianity was still a Jewish sect. Christians in Jerusalem kept the Jewish Sabbath
Shabbat (, , or ; , , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Friday–Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical stories describing the cre ...
and continued to worship at the Temple. In commemoration of Jesus' resurrection, they gathered on Sunday for a communion meal. Initially, Christians kept the Jewish custom of fasting on Mondays and Thursdays. Later, the Christian fast days shifted to Wednesdays and Fridays (see Friday fast) in remembrance of Judas' betrayal and the crucifixion.
James was killed on the order of the high priest in AD 62. He was succeeded as leader of the Jerusalem church by Simeon
Simeon () is a given name, from the Hebrew (Biblical Hebrew, Biblical ''Šimʿon'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Šimʿôn''), usually transliterated in English as Shimon. In Greek, it is written Συμεών, hence the Latinized spelling Sy ...
, another relative of Jesus. During the First Jewish-Roman War
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
(AD66–73), Jerusalem and the Temple were destroyed after a brutal siege in AD70. Prophecies of the Second Temple's destruction are found in the synoptic gospels
The gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark, and Gospel of Luke, Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical ...
, Harris, Stephen L., Understanding the Bible. Palo Alto: Mayfield. 1985. specifically in the Olivet Discourse
The Olivet Discourse or Olivet prophecy is a biblical passage found in the Synoptic Gospels in Matthew 24 and 25, Mark 13, and Luke 21. It is also known as the Little Apocalypse because it includes the use of apocalyptic language, and it inc ...
.
According to a tradition recorded by Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
and Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis (; – 403) was the bishop of Salamis, Cyprus, at the end of the Christianity in the 4th century, 4th century. He is considered a saint and a Church Father by the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic Churche ...
, the Jerusalem church fled to Pella at the outbreak of the First Jewish Revolt.Eusebius, ''Church History'' 3, 5, 3; Epiphanius, ''Panarion'' 29,7,7–8; 30, 2, 7; O''n Weights and Measures'' 15. On the flight to Pella see: Jonathan Bourgel, "'The Jewish Christians' Move from Jerusalem as a pragmatic choice", in: Dan Jaffé (ed), ''Studies in Rabbinic Judaism and Early Christianity'', (Leyden: Brill, 2010), pp. 107–138 (https://www.academia.edu/4909339/THE_JEWISH_CHRISTIANS_MOVE_FROM_JERUSALEM_AS_A_PRAGMATIC_CHOICE).P. H. R. van Houwelingen, "Fleeing forward: The departure of Christians from Jerusalem to Pella", ''Westminster Theological Journal'' 65 (2003), 181–200. The church had returned to Jerusalem by AD 135, but the disruptions severely weakened the Jerusalem church's influence over the wider Christian church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus Christ. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a syn ...
.
Gentile Christians
James the Just, brother of Jesus, was leader of the early Christian community in Jerusalem, and his other kinsmen likely held leadership positions in the surrounding area after the destruction of the city until its rebuilding as ''Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina (Latin: ''Colonia Aelia Capitolina'' ɔˈloːni.a ˈae̯li.a kapɪtoːˈliːna was a Roman colony founded during the Roman emperor Hadrian's visit to Judaea in 129/130 CE. It was founded on the ruins of Jerusalem, which had b ...
'' in , when all Jews were banished from Jerusalem.
The first Gentiles to become Christians were God-fearers, people who believed in the truth of Judaism but had not become proselytes (see Cornelius the Centurion
Cornelius (; ; fl. 1st century AD) was a Roman centurion who is considered by some Christians to be the first Gentile to convert to the faith, as related in Acts of the Apostles (see Ethiopian eunuch for the competing tradition). The baptism o ...
). As Gentiles joined the young Christian movement, the question of whether they should convert to Judaism and observe the Torah (such as food laws, male circumcision
Circumcision is a Medical procedure, procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the fores ...
, and Sabbath observance) gave rise to various answers. Some Christians demanded full observance of the Torah and required Gentile converts to become Jews. Others, such as Paul, believed that the Torah was no longer binding because of Jesus' death and resurrection. In the middle were Christians who believed Gentiles should follow some of the Torah but not all of it.
In , Barnabas
Barnabas (; ; ), born Joseph () or Joses (), was according to tradition an early Christians, Christian, one of the prominent Disciple (Christianity), Christian disciples in Jerusalem. According to Acts 4:36, Barnabas was a Cypriot Jews, Cyprio ...
and Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
went to Jerusalem to meet with the three Pillars of the Church
A triumvirate () or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs (). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are notionally equal, the actual distr ...
: James the Just, Peter, and John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
. Later called the Council of Jerusalem
The Council of Jerusalem or Apostolic Council is a council described in chapter 15 of the Acts of the Apostles, held in Jerusalem .
The council decided that Gentiles who converted to Christianity were not obligated to keep most of the rule ...
, according to Pauline Christians, this meeting (among other things) confirmed the legitimacy of the evangelizing mission of Barnabas and Paul to the Gentiles
''Gentile'' () is a word that today usually means someone who is not Jewish. Other Groups claiming affiliation with Israelites, groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, have historically used the term ''gentile'' to describe outsider ...
. It also confirmed that Gentile converts were not obligated to follow the Mosaic Law
The Law of Moses ( ), also called the Mosaic Law, is the law said to have been revealed to Moses by God. The term primarily refers to the Torah or the first five books of the Hebrew Bible.
Terminology
The Law of Moses or Torah of Moses (Hebr ...
, especially the practice of male circumcision
Circumcision is a Medical procedure, procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the fores ...
, which was condemned as execrable and repulsive in the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world , also Greco-Roman civilization, Greco-Roman culture or Greco-Latin culture (spelled Græco-Roman or Graeco-Roman in British English), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and co ...
during the period of Hellenization
Hellenization or Hellenification is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language, and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonisation often led to the Hellenisation of indigenous people in the Hellenistic period, many of the ...
of the Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey ...
, and was especially adversed in Classical civilization
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilization ...
from ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically re ...
and Romans, who valued the foreskin
In male Human body, human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce (), is the double-layered fold of Human skin, skin, Mucous membrane, mucosal and Muscle tissue, muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans ...
positively. The resulting Apostolic Decree in Acts 15 is theorized to parallel the seven Noahide laws found in the Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
. However, modern scholars dispute the connection between Acts 15 and the seven Noahide laws. In roughly the same time period, rabbinic Jewish legal authorities made their circumcision requirement for Jewish boys even stricter."peri'ah", (Shab. xxx. 6)
The primary issue which was addressed related to the requirement of circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. T ...
, as the author of Acts relates, but other important matters arose as well, as the Apostolic Decree indicates. The dispute was between those, such as the followers of the "Pillars of the Church", led by James, who believed, following his interpretation of the Great Commission
In Christianity, the Great Commission is the instruction of the Resurrection appearances of Jesus, resurrected Jesus Christ to his disciple (Christianity), disciples to spread the gospel to all the nations of the world. The Great Commission i ...
, that the church must observe the Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
, i.e. the rules of traditional Judaism, and Paul the Apostle
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Apostles in the New Testament, Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the Ministry of Jesus, teachings of Jesus in the Christianity in the 1st century, first ...
, who called himself "Apostle to the Gentiles", who believed there was no such necessity. The main concern for the Apostle Paul, which he subsequently expressed in greater detail with his letters directed to the early Christian communities in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, was the inclusion of Gentiles into God's New Covenant
The New Covenant () is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a Book of Jeremiah#Sections of the Book, phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah (Jeremiah 31:31–34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the ...
, sending the message that faith in Christ is sufficient for salvation
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
. (''See also'': Supersessionism, New Covenant
The New Covenant () is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a Book of Jeremiah#Sections of the Book, phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah (Jeremiah 31:31–34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the ...
, Antinomianism, Hellenistic Judaism
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Hellenistic culture and religion. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellen ...
, and Paul the Apostle and Judaism).
The Council of Jerusalem did not end the dispute, however. There are indications that James still believed the Torah was binding on Jewish Christians. Galatians 2:11–14 describes "people from James" causing Peter and other Jewish Christians in Antioch to break table fellowship with Gentiles. (''See also'': Incident at Antioch). Joel Marcus, professor of Christian origins, suggests that Peter's position may have lain somewhere between James and Paul, but that he probably leaned more toward James. This is the start of a split between Jewish Christian
Jewish Christians were the followers of a Jewish religious sect that emerged in Roman Judea during the late Second Temple period, under the Herodian tetrarchy (1st century AD). These Jews believed that Jesus was the prophesied Messiah and ...
ity and Pauline Christianity, Gentile (or Pauline) Christianity. While Jewish Christianity would remain important through the next few centuries, it would ultimately be pushed to the margins as Gentile Christianity became dominant. Jewish Christianity was also opposed by early Rabbinic Judaism, the successor to the Pharisees. When Peter left Jerusalem after Herod Agrippa I tried to kill him, James appears as the principal authority of the early Christian church. Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A ...
() called him Bishop of Jerusalem. A Christianity in the ante-Nicene period, 2nd-century church historian, Hegesippus (chronicler), Hegesippus, wrote that the Sanhedrin martyred him in AD 62.
In 66 AD, the First Jewish Revolt, Jews revolted against Rome. After a brutal siege, Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), Jerusalem fell in AD 70. The city, including the Jewish Temple, was destroyed and the population was mostly killed or removed. According to a tradition recorded by Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
and Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis (; – 403) was the bishop of Salamis, Cyprus, at the end of the Christianity in the 4th century, 4th century. He is considered a saint and a Church Father by the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic Churche ...
, the Jerusalem church fled to Pella at the outbreak of the First Jewish Revolt. According to Epiphanius of Salamis, the Cenacle survived at least to Hadrian#Second Roman-Jewish War, Hadrian's visit in AD 130. A scattered population survived. The Council of Jamnia, Sanhedrin relocated to Jamnia. Prophecies of the Second Temple's destruction are found in the Synoptic Gospels, specifically in Jesus's Olivet Discourse
The Olivet Discourse or Olivet prophecy is a biblical passage found in the Synoptic Gospels in Matthew 24 and 25, Mark 13, and Luke 21. It is also known as the Little Apocalypse because it includes the use of apocalyptic language, and it inc ...
.
1st century persecution
Romans had a negative perception of early Christians. The Roman historian Tacitus wrote that Christians were despised for their "abominations" and "hatred of humankind". The belief that Christians hated humankind could refer to their refusal to participate in social activities connected to pagan worship—these included most social activities such as the Theatre of ancient Rome, theater, the army, sports, and classical literature. They also refused to Roman imperial cult, worship the Roman emperor, like Jews. Nonetheless, Romans were more lenient to Jews compared to Gentile Christians. Some anti-Christian Romans further distinguished between Jews and Christians by claiming that Christianity was "apostasy" from Judaism. Celsus, for example, considered Jewish Christians to be hypocrites for claiming that they embraced their Jewish heritage. Emperor Nero persecuted Christians in Rome, whom he blamed for starting the Great Fire of Rome, Great Fire of AD 64. It is possible that Peter and Paul were in Rome and were Christian martyr, martyred at this time. Nero was deposed in AD 68, and the persecution of Christians ceased. Under the emperors Vespasian () and Titus (), Christians were largely ignored by the Roman government. The Emperor Domitian () authorized a new persecution against the Christians. It was at this time that the Book of Revelation was written by John of Patmos.Early centers
Eastern Roman Empire
Jerusalem
In the 2nd century, Roman Emperor Hadrian rebuilt Jerusalem as a Religion in ancient Rome, Pagan city and renamed it ''Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina (Latin: ''Colonia Aelia Capitolina'' ɔˈloːni.a ˈae̯li.a kapɪtoːˈliːna was a Roman colony founded during the Roman emperor Hadrian's visit to Judaea in 129/130 CE. It was founded on the ruins of Jerusalem, which had b ...
'', erecting statues of Jupiter Capitolinus, Jupiter and Imperial cult (ancient Rome), himself on the site of the former Jewish Temple, the Temple Mount. In the years AD 132–136, Bar Kokhba revolt, Bar Kokhba led an unsuccessful revolt as a Jewish Messiah claimant, but Christians refused to acknowledge him as such. When Bar Kokhba was defeated, Hadrian barred Jews from the city, except for the day of Tisha B'Av, thus the Early bishops of Jerusalem, subsequent Jerusalem bishops were Gentiles ("uncircumcised") for the first time.
The Jerusalem in Christianity, general significance of Jerusalem to Christians entered a period of decline during the persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. According to Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
, Jerusalem Christians escaped to Pella, Jordan, Pella, in the Decapolis
The Decapolis (Greek: ) was a group of ten Greek Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Greek and late Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BC and AD. Most of the cities were located to the east of the Jordan ...
(Transjordan (region), Transjordan), at the beginning of the First Jewish–Roman War in AD 66. Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem#Bishops of Aelia Capitolina, Jerusalem's bishops became Suffragan bishop, suffragans (subordinates) of the Metropolitan bishop in nearby #Caesarea, Caesarea, Interest in Jerusalem resumed with the Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage of the Roman Empress Helena (Empress), Helena to the Holy Land (). According to the church historian Socrates of Constantinople, Helena (with the assistance of Bishop Macarius of Jerusalem) claimed to have found the True Cross, ''cross of Christ'', after removing a Temple to Venus (mythology), Venus (attributed to Hadrian) that had been built over the site. Jerusalem had received special recognition in Canon VII of the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
in AD 325. The traditional founding date for the Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre (which guards the Holy places#Christianity, Christian Holy places in the Holy Land) is 313, which corresponds with the date of the Edict of Milan promulgated by the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great, which legalized Christianity in the Roman Empire. Jerusalem was later named as one of the Pentarchy, but this was never accepted by the #Rome, Church of Rome. (''See also'': East–West Schism#Prospects for reconciliation).
Antioch
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
(modern Antakya, Turkey) was the capital of the Syria (Roman province), Roman province of Syria and a center of Hellenistic period, Greek culture in the Eastern Mediterranean, as well as a key locus of trade that made it the third-most important city of the Roman Empire. In the Book of Acts
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
, it is said that it was at Antioch where followers of Jesus were first called Christians; it was also the location of the Incident at Antioch, described in the Epistle to the Galatians. It was the site of an early church traditionally said to be founded by Peter; later traditions also attributed the role of Bishop of Antioch as first being held by Peter. The Gospel of Matthew and the Apostolic Constitutions may have been written there. The church father Ignatius of Antioch was its third bishop. The School of Antioch, founded in 270, was one of two major centers of early church learning. The Curetonian Gospels and the Syriac Sinaiticus are two early (pre-Peshitta) New Testament text types associated with Syriac Christianity. It was one of the three whose bishops were recognized at the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
(325) as exercising jurisdiction over the adjoining territories.
Alexandria
The city of Alexandria in the Nile delta was established byAlexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
in 331 BC. Its famous libraries made it a center of Hellenistic learning. The Septuagint
The Septuagint ( ), sometimes referred to as the Greek Old Testament or The Translation of the Seventy (), and abbreviated as LXX, is the earliest extant Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible from the original Biblical Hebrew. The full Greek ...
translation of the Old Testament began there, and the Alexandrian text-type is recognized by scholars as one of the earliest New Testament types. It had a History of the Jews in Egypt, significant Jewish population, of which Philo of Alexandria is probably the most known author. It produced superior scripture and notable church fathers, such as Clement, Origen, and Athanasius; also noteworthy were the Desert Fathers of Egypt. By the end of the early-Christian era, Alexandria, Rome, and Antioch were accorded authority over nearby Metropolitan bishop, metropolitans. The Council of Nicaea in canon VI affirmed Alexandria's traditional authority over Egypt, Libya, and #Cyrene, Pentapolis (North Africa) (the Byzantine Diocese of Egypt, Diocese of Egypt) and probably granted Alexandria the right to declare a universal date for the observance of Easter (see also Easter controversy). Some postulate that Alexandria was not only a center of Christianity, but was also, as a cradle of Gnosticism,
a center for Christian-based Gnosticism, Gnostic sects.
Asia Minor
The tradition of John the Apostle was strong in Anatolia (the ''near-east'', part of modern Turkey, the western part was called the Asia (Roman province), Roman province of Asia). The authorship of the Johannine works traditionally and plausibly occurred in Ephesus, c. 90–110, although some scholars argue for an origin inSyria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
. This includes the Book of Revelation, although modern Bible scholars believe that it to be authored by a different John, John of Patmos (a Greek island about 30 miles off the Anatolian coast), that mentions Seven churches of Asia
The Seven Churches of Revelation, also known as the Seven Churches of the Apocalypse and the Seven Churches of Asia, are seven churches of early Christianity mentioned in the New Testament Book of Revelation. All of them were located in Asia Min ...
. According to the New Testament, the Apostle Paul was from Tarsus (city), Tarsus (in south-central Anatolia) and Paul of Tarsus#Conversion and mission, his missionary journeys were primarily in Anatolia. The First Epistle of Peter () is addressed to Anatolian regions. On the southeast shore of the Black Sea, Helenopontus, Pontus was a Greek colony mentioned three times in the New Testament. Inhabitants of Pontus were some of the first converts to Christianity. Pliny the Younger on Christ, Pliny, governor in 110, in his letters, addressed Christians in Pontus. Of the extant Ignatius of Antioch#Letters, letters of Ignatius of Antioch considered authentic, five of seven are to Anatolian cities, the sixth is to Polycarp. Smyrna was home to Polycarp, the bishop who reportedly knew the Apostle John personally, and probably also to his student Irenaeus. Papias of Hierapolis is also believed to have been a student of John the Apostle. In the 2nd century, Anatolia was home to Quartodecimanism, Montanism, Marcion of Sinope, and Melito of Sardis who recorded an early Development of the Christian Biblical canon, Christian Biblical canon. After the Crisis of the Third Century, Nicomedia became the capital of the History of the Eastern Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire in 286. The Synod of Ancyra was held in 314. In 325 the emperor Constantine I and Christianity, Constantine convoked the first Christian ecumenical council in Nicaea and in 330 moved the capital of the reunified empire to Byzantium (also an early Christian center and just across the Bosphorus from ''Anatolia'', later called Constantinople), referred to as the Byzantine Empire, which lasted till 1453. The First seven Ecumenical Councils were held either in Western Anatolia or across the Bosphorus in Constantinople.
Caesarea
Caesarea Maritima, Caesarea, on the seacoast just northwest of Jerusalem, at first ''Caesarea Maritima'', then after 133 ''Caesarea Palaestina'', was built by Herod the Great, c. 25–13 BC, and was the capital of Iudaea Province (6–132) and later ''Palaestina Prima''. It was there that Peter baptized the Cornelius the Centurion, centurion Cornelius, considered the first gentile convert. Paul sought refuge there, once staying at the house of Philip the Evangelist, and later being imprisoned there for two years (estimated to be 57–59). The Apostolic Constitutions (7.46) state that the first Bishop of Caesarea was Zacchaeus, Zacchaeus the Publican. After Hadrian's siege of Jerusalem (c. 133), Caesarea became the metropolitan see with the bishop of Jerusalem as one of its Suffragan bishop, ''"suffragans"'' (subordinates). Origen (d. 254) compiled his Hexapla there and it held a Theological Library of Caesarea Maritima, famous library and theological school, Pamphilus of Caesarea, St. Pamphilus (d. 309) was a noted scholar-priest. St. Gregory the Wonder-Worker (d. 270), St. Basil the Great (d. 379), and St. Jerome (d. 420) visited and studied at the library which was later destroyed, probably by the Sasanian Empire, Persians in 614 or the Saracens around 637. The first major church historian, Eusebius of Caesarea, was a bishop, c. 314–339. Fenton John Anthony Hort, F. J. A. Hort and Adolf von Harnack have argued that the Nicene Creed originated in Caesarea. The Caesarean text-type is recognized by many textual scholars as one of the earliest New Testament types.Cyprus
Paphos was the capital of the island of Cyprus during the Roman years and seat of a Roman commander. In AD 45, the apostles Paul andBarnabas
Barnabas (; ; ), born Joseph () or Joses (), was according to tradition an early Christians, Christian, one of the prominent Disciple (Christianity), Christian disciples in Jerusalem. According to Acts 4:36, Barnabas was a Cypriot Jews, Cyprio ...
, who according to was "a native of Cyprus", came to Cyprus and reached Paphos preaching the message of Jesus, see also . According to Acts, the apostles were persecuted by the Romans but eventually succeeded in convincing the Roman commander Sergius Paulus to renounce his old religion in favour of Christianity. Barnabas is traditionally identified as the founder of the Cypriot Orthodox Church.
Damascus
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
is the capital of Syria and claims to be the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world. According to the New Testament, the Apostle Paul was converted on the Road to Damascus. In the three accounts (, , ), he is described as being led by those he was traveling with, blinded by the light, to Damascus where his sight was restored by a disciple called Ananias of Damascus, Ananias (who is thought to have been the first bishop of Damascus) then he was baptized.
Greece
Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
, the major northern Greek city where it is believed Christianity was founded by Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
, thus an Apostolic See, and the surrounding regions of Macedonia (region), Macedonia, Thrace, and Epirus, which also extend into the neighboring Balkan states of Albania and Bulgaria, were early centers of Christianity. Of note are Paul's Epistles to the ''Thessalonians'' and to Philippi
Philippi (; , ''Phílippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides (, ''Krēnĩdes'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colonists in 360/359 BC. The city was renamed by Phili ...
, which is often considered the first contact of Christianity with Europe. The ''Apostolic Father'' Polycarp Polycarp's letter to the Philippians, wrote a letter to the Philippians, c. 125.
Nicopolis was a city in the Roman province of Epirus Vetus, today a ruin on the northern part of the western Greek coast. In the Epistle to Titus, Paul said he intended to go there. It is possible that there were some Christians in its population. According to Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
, Origen (c. 185–254) stayed there for some time
Ancient Corinth#Biblical Corinth, Ancient Corinth, today a ruin near modern Corinth in southern Greece, was an early center of Christianity. According to the Acts of Apostles, Paul stayed eighteen months in Corinth to preach. He initially stayed with Aquila and Priscilla, and was later joined by Silas and Saint Timothy, Timothy. After he left Corinth, Apollos, Apollo was sent from Ephesus by Priscilla to replace him. Paul returned to Corinth at least once. He wrote the First Epistle to the Corinthians from Ephesus approximately in 54–55, which focused on sexual immorality, divorces, lawsuits, and resurrections. The Second Epistle to the Corinthians from Macedonia (Roman province), Macedonia was written around 56 as a fourth letter discussing his proposed plans for the future, instructions, unity, and his defense of apostolic authority. The earliest evidence of the Papal primacy, primacy of the Roman Church can be seen in the First Epistle of Clement written to the Corinthian church, dated around 96. The bishops in Corinth include Apollo, Sosthenes, and Dionysius the Areopagite, Dionysius.
Athens, the capital and largest city in Greece, was visited by Paul. He probably traveled by sea, arriving at Piraeus, the harbor of Athens, coming from Berea (Bible), Berœa of Macedonia around the year 53. According to Acts 17, when he arrived at Athens, he immediately sent for Silas and Timotheos who had stayed behind in Berœa. While waiting for them, Paul explored Athens and visited the synagogue, as there was a History of the Jews in Greece, local Jewish community. A Christian community was quickly established in Athens, although it may not have been large initially. A common tradition identifies the Dionysius the Areopagite, Areopagite as the first bishop of the Christian community in Athens, while another tradition mentions Hierotheos the Thesmothete. The succeeding bishops were not all of Athenian descent: Narkissos was believed to have come from Palestine, and Saint Publius, Publius from Malta. Quadratus of Athens, Quadratus is known for an apology addressed to Emperor Hadrian during his visit to Athens, contributing to early Christian literature. Aristides of Athens, Aristeides and Athenagoras of Athens, Athenagoras also wrote apologies during this time. By the second century, Athens likely had a significant Christian community, as Pope Hyginus, Hygeinos, bishop of Rome, write a letter to the community in Athens in the year 139.
Gortyn on Crete was allied with Rome and was thus made capital of Roman Creta et Cyrenaica. St. Titus is believed to have been the first bishop. The city was sacked by the pirate Abu Hafs (pirate), Abu Hafs in 828.
Thrace
Paul the Apostle
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Apostles in the New Testament, Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the Ministry of Jesus, teachings of Jesus in the Christianity in the 1st century, first ...
preached in Macedonia (region), Macedonia, and also in Philippi
Philippi (; , ''Phílippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides (, ''Krēnĩdes'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colonists in 360/359 BC. The city was renamed by Phili ...
, located in Thrace on the Thracian Sea coast. According to Hippolytus of Rome, Andrew the Apostle preached in Thrace, on the Black Sea coast and along the lower course of the Danube River. The spread of Christianity among the Thracians and the emergence of centers of Christianity like Serdica (present day Sofia), History of Plovdiv, Philippopolis (present day Plovdiv) and Durostorum (present day Silistra) was likely to have begun with these early Apostolic Age, Apostolic missions. The Monastery of Saint Athanasius, first Christian monastery in Europe was founded in Thrace in 344 by Saint Athanasius near modern-day Chirpan, Bulgaria, following the Council of Serdica.
Libya
Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene and the surrounding region of Cyrenaica#Christianity, Cyrenaica or the North African "Pentapolis (North Africa), Pentapolis", south of the Mediterranean from Greece, the northeastern part of modern Libya, was a Greek colony in North Africa later converted to a Roman province. In addition to Greeks and Romans, there was also a History of the Jews in Libya, significant Jewish population, at least up to the Kitos War (115–117). According to , Simon of Cyrene carried Jesus' cross. ''Cyrenians'' are also mentioned in , , , . According to Byzantine legend, the first bishop was Lucius of Cyrene, Lucius, mentioned in Acts 13:1.Western Roman Empire
Rome
Exactly when Christians first appeared in Rome is difficult to determine. TheActs of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
claims that the Jewish Christian
Jewish Christians were the followers of a Jewish religious sect that emerged in Roman Judea during the late Second Temple period, under the Herodian tetrarchy (1st century AD). These Jews believed that Jesus was the prophesied Messiah and ...
couple Priscilla and Aquila had recently come from Rome to Ancient Corinth#Biblical Corinth, Corinth when, in about the year 50, Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
reached the latter city, indicating that belief in Jesus in Rome had preceded Paul.
Historians consistently consider Peter and Paul to have been martyred in Rome under the reign of Nero"Paul, St" Cross, F. L., ed. ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church''. New York: Oxford University Press. 2005 in 64, after the Great Fire of Rome which, according to Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
, the Emperor Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, blamed on the Christians. In the Christianity in the 2nd century, second century Irenaeus of Lyons, reflecting the ancient view that the church could not be fully present anywhere without a bishop, recorded that Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a su ...
and Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
had been the founders of the Church in Rome and had appointed Pope Linus, Linus as bishop.
However, Irenaeus does not say that either Peter or Paul was "bishop" of the Church in Rome and several historians have questioned whether Peter spent much time in Rome before his martyrdom. While the church in Rome was already flourishing when Paul wrote his Epistle to the Romans
The Epistle to the Romans is the sixth book in the New Testament, and the longest of the thirteen Pauline epistles. Biblical scholars agree that it was composed by Paul the Apostle to explain that Salvation (Christianity), salvation is offered ...
to them from Corinth (c. 58) he attests to a large Christian community already thereThe Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (Oxford University Press 2005 ), article ''Rome (early Christian)'' and greets some fifty people in Rome by name, but not Peter, Incident at Antioch, whom he knew. There is also no mention of Peter in Rome later during Paul's two-year stay there in , about 60–62. Most likely he did not spend any major time at Rome before 58 when Paul wrote to the Romans, and so it may have been only in the 60s and relatively shortly before his martyrdom that Peter came to the capital.
Oscar Cullmann sharply rejected the claim that Peter Historical development of the doctrine of Papal Primacy, began the papal succession,"In the life of Peter there is no starting point for a chain of succession to the leadership of the church at large." While Cullmann believed the Matthew 16:18 text is entirely valid and is in no way spurious, he says it cannot be used as "warrant of the papal succession."— "Religion: Peter & the Rock." ''Time'', December 7, 1953Time.com
Accessed October 8, 2009 and concludes that while Peter ''was'' the Primacy of Simon Peter, original head of the apostles, Peter was not the founder of any visible church succession.Cullmann, Oscar "In the New Testament [Jerusalem] is the only church of which we hear that Peter stood at its head. Of other episcopates of Peter we know nothing certain. Concerning Antioch, indeed ... there is a tradition, first appearing in the course of the second century, according to which Peter was its bishop. The assertion that he was Bishop of Rome we first find at a much later time. From the second half of the second century we do possess texts that mention the apostolic ''foundation'' of Rome, and at this time, which is indeed rather late, this foundation is traced back to Peter and Paul, an assertion that cannot be supported historically. Even here, however, nothing is said as yet of an episcopal office of Peter." The original seat of Roman imperial power soon became a center of church authority, grew in power decade by decade, and was recognized during the period of the Seven Ecumenical Councils, when the seat of government had been transferred to Constantinople, as the "head" of the church. Rome and Alexandria, which by tradition held authority over sees outside their own Roman province, province, were not yet referred to as patriarchates. The earliest Bishops of Rome were all Greek-speaking, the most notable of them being: Pope Clement I, Pope Clement I (c. 88–97), author of an First Epistle of Clement, Epistle to the Church in Corinth; Pope Telesphorus (c. 126–136), probably the only martyr among them; Pope Pius I, Pope Pius I (c. 141–154), said by the Muratorian fragment to have been the brother of the author of the Shepherd of Hermas; and Pope Anicetus (c. 155–160), who received Saint Polycarp and discussed with him the Easter controversy, dating of Easter. Pope Victor I, Pope Victor I (189–198) was the first ecclesiastical writer known to have written in Latin; however, his only extant works are his encyclicals, which would naturally have been issued in Latin and Greek. Greek New Testament texts were translated into Latin early on, well before Jerome, and are classified as the Vetus Latina and Western text-type. During the 2nd century, Christians and semi-Christians of diverse views congregated in Rome, notably Marcion and Valentinius, and in the following century there were schisms connected with Hippolytus of Rome and Novatian. The Roman church survived various persecutions. Among the prominent Christians executed as a result of their refusal to perform acts of worship to the Roman gods as ordered by emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian in 258 were Cyprian, bishop of Carthage. The last and most severe of the imperial persecutions was that Diocletianic Persecution, under Diocletian in 303; they ended in Rome, and the West in general, with the accession of Maxentius in 306.
Carthage
 Carthage, in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa, south of the Mediterranean from Rome, gave the early church the Latin fathers Tertullian (c. 120 – c. 220) and Cyprian (d. 258). Carthage fell to Islam in 698.
The Church of Carthage thus was to the Early African church what the Diocese of Rome, Church of Rome was to the Catholic Church in Italy. The archdiocese used the African Rite, a variant of the Western liturgical rites in Latin language, possibly a local use of the primitive Roman Rite. Famous figures include Passion of Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions, Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions (died c. 203), Tertullian (c. 155–240), Cyprian (c. 200–258), Caecilianus (floruit 311), Aurelius of Carthage, Saint Aurelius (died 429), and Eugenius of Carthage (died 505). Tertullian and Cyprian are considered Church Fathers#Latin Fathers, Latin Church Fathers of the Latin Church. Tertullian, a theologian of part Berbers, Berber descent, was instrumental in the development of Trinity, trinitarian theology, and was the first to apply Latin language extensively in his theological writings. As such, Tertullian has been called "the father of Latin Christianity" and "the founder of Western theology". Carthage remained an important center of Christianity until 698, hosting several councils of Carthage.
Carthage, in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa, south of the Mediterranean from Rome, gave the early church the Latin fathers Tertullian (c. 120 – c. 220) and Cyprian (d. 258). Carthage fell to Islam in 698.
The Church of Carthage thus was to the Early African church what the Diocese of Rome, Church of Rome was to the Catholic Church in Italy. The archdiocese used the African Rite, a variant of the Western liturgical rites in Latin language, possibly a local use of the primitive Roman Rite. Famous figures include Passion of Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions, Saint Perpetua, Saint Felicitas, and their Companions (died c. 203), Tertullian (c. 155–240), Cyprian (c. 200–258), Caecilianus (floruit 311), Aurelius of Carthage, Saint Aurelius (died 429), and Eugenius of Carthage (died 505). Tertullian and Cyprian are considered Church Fathers#Latin Fathers, Latin Church Fathers of the Latin Church. Tertullian, a theologian of part Berbers, Berber descent, was instrumental in the development of Trinity, trinitarian theology, and was the first to apply Latin language extensively in his theological writings. As such, Tertullian has been called "the father of Latin Christianity" and "the founder of Western theology". Carthage remained an important center of Christianity until 698, hosting several councils of Carthage.
Southern Gaul
The Mediterranean coast of France and the Rhone valley, then part of Roman Gallia Narbonensis, were early centers of Christianity. Major Christian communities were found in Arles, Avignon, Vienne, Isère, Vienne, Lyon, and Marseille (the oldest city in France). The Persecution in Lyon occurred in 177. The Apostolic Father Irenaeus from Smyrna ofAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
was Bishop of Lyon near the end of the 2nd century and he claimed Saint Pothinus was his predecessor. The Council of Arles (314), Council of Arles in 314 is considered a forerunner of the ecumenical councils. The Gallican Rite#Ephesine theory, Ephesine theory attributes the Gallican Rite to Lyon.
Aquileia
The ancient Roman city of Aquileia at the head of the Adriatic Sea, today one of the main archaeological sites of Northern Italy, was an early center of Christianity said to be founded by Mark the Evangelist, Mark before his mission to Alexandria. Hermagoras of Aquileia is believed to be its first bishop. The Aquileian Rite is associated with Aquileia.Milan
It is believed that the Church of Milan in northwest Italy was founded by the apostleBarnabas
Barnabas (; ; ), born Joseph () or Joses (), was according to tradition an early Christians, Christian, one of the prominent Disciple (Christianity), Christian disciples in Jerusalem. According to Acts 4:36, Barnabas was a Cypriot Jews, Cyprio ...
in the 1st century. Gervasius and Protasius and others were martyred there. It has long maintained its own rite known as the Ambrosian Rite attributed to Ambrose (born c. 330) who was bishop in 374–397 and one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. Duchesne argues that the Gallican Rite#Ambrosian theory, Gallican Rite originated in Milan.
Syracuse and Calabria
Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse was founded by Greek colonists in 734 or 733 BC, part of Magna Graecia. Syracuse is one of the first Christian communities established byPeter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a su ...
, preceded only by Antioch. Paul also preached in Syracuse. Historical evidence from the middle of the third century, during the time of Cyprian, suggests that Christianity was thriving in Syracuse, and the presence of catacombs provides clear indications of Christian activity in the second century as well. Across the Strait of Messina, Calabria on the mainland was also probably an early center of Christianity.
Malta
 According to Acts, Paul was shipwrecked and ministered on an island which some scholars have identified as Malta (an island just south of Sicily) for three months during which time he is said to have been bitten by a poisonous viper and survived (; ), an event usually dated c. AD 60. Paul had been allowed passage from #Caesarea, Caesarea Maritima to Rome by Porcius Festus, Procurator (Roman), procurator of Iudaea Province, to stand trial before the Emperor. Many traditions are associated with this episode, and Rabat, Malta#Catacombs, catacombs in Rabat testify to an Early Christian community on the islands. According to tradition, Saint Publius, Publius, the Roman Governor of Malta at the time of Saint Paul's shipwreck, became the first ''Bishop of Malta'' following his conversion to Christianity. After ruling the Maltese Church for thirty-one years, Publius was transferred to the See of Athens in AD 90, where he was martyred in AD 125. There is scant information about the continuity of Christianity in Malta in subsequent years, although tradition has it that there was a continuous line of bishops from the days of St. Paul to the time of Emperor Constantine.
According to Acts, Paul was shipwrecked and ministered on an island which some scholars have identified as Malta (an island just south of Sicily) for three months during which time he is said to have been bitten by a poisonous viper and survived (; ), an event usually dated c. AD 60. Paul had been allowed passage from #Caesarea, Caesarea Maritima to Rome by Porcius Festus, Procurator (Roman), procurator of Iudaea Province, to stand trial before the Emperor. Many traditions are associated with this episode, and Rabat, Malta#Catacombs, catacombs in Rabat testify to an Early Christian community on the islands. According to tradition, Saint Publius, Publius, the Roman Governor of Malta at the time of Saint Paul's shipwreck, became the first ''Bishop of Malta'' following his conversion to Christianity. After ruling the Maltese Church for thirty-one years, Publius was transferred to the See of Athens in AD 90, where he was martyred in AD 125. There is scant information about the continuity of Christianity in Malta in subsequent years, although tradition has it that there was a continuous line of bishops from the days of St. Paul to the time of Emperor Constantine.
Salona
Salona, the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea, was an early center of Christianity and today is a ruin in modern Croatia. Titus (biblical), Titus, a disciple of Paul, preached there. Some Christians suffered martyrdom. Salona emerged as a center for the spread of Christianity, with Andronicus of Pannonia, Andronicus establishing the See of Syrmium (Sremska Mitrovica, Mitrovica) in Pannonia, followed by those in Siscia and Mursia. The Diocletianic Persecution left deep marks in Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and Pannonia (Roman province), Pannonia. Quirinus of Sescia, Quirinus, bishop of Siscia, died a martyr in AD 303.Seville
Seville was the capital of Hispania Baetica or the Roman province of southern Spain. The origin of the diocese of Seville can be traced back to Apostolic times, or at least to the first century AD. Gerontius, the bishop of Italica, near Hispalis (Seville), likely appointed a pastor for Seville. A bishop of Seville named Sabinus participated in the Council of Illiberis in 287. He was the bishop when Justa and Rufina were martyred in 303 for refusing to worship the idol Salambo. Prior to Sabinus, Marcellus is listed as a bishop of Seville in an ancient catalogue of prelates preserved in the "Codex Emilianensis". After the Edict of Milan in 313, Evodius became the bishop of Seville and undertook the task of rebuilding the churches that had been damaged. It is believed that he may have constructed the church of San Vicente, which could have been the first cathedral of Seville. Early Christianity also spread from the Iberian Peninsula south across the Strait of Gibraltar into Roman Mauretania Tingitana, of note is Marcellus of Tangier who was martyred in 298.Roman Britain
Christianity reached Roman Britain by the third century of the Christian era, the first recorded martyrs in Britain being Saint Alban, St. Alban of Verulamium and Julius and Aaron of Caerleon, during the reign of Diocletian (284–305). Gildas dated the faith's arrival to the latter part of the reign ofTiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
, although stories connecting it with Joseph of Arimathea#Britain, Joseph of Arimathea, Lucius of Britain, Lucius, or Fagan (saint), Fagan are now generally considered pious forgeries. Restitutus, Bishop of London, is recorded as attending the Council of Arles (314), 314 Council of Arles, along with the Bishop of Lincoln and Bishop of York.
Christianisation intensified and evolved into Celtic Christianity after the End of Roman rule in Britain, Romans left Britain c. 410.
Outside the Roman Empire
Christianity also spread beyond the Roman Empire during the early Christian period.Armenia
It is accepted that the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia became the first polity to adopt Christianity as its state religion. Although it has long been claimed that Armenia was the first Christian kingdom, according to some scholars this has relied on a source by Agathangelos titled "The History of the Armenians", which has recently been redated, casting some doubt. Christianity became the official religion of the Kingdom of Armenia in 301, when it was still illegal in the Roman Empire. According to church tradition, the Armenian Apostolic Church was founded by Gregory the Illuminator of the late third – early fourth centuries after the conversion of Tiridates III of Armenia, Tiridates III. The church traces its origins to the missions of Bartholomew the Apostle and Thaddeus (Jude the Apostle) in the 1st century. Tiridates III was the first Christian king in Armenia from 298 to 330.Georgia
According to Orthodox tradition, Christianity was first preached in Georgia (country), Georgia by the Apostles Simon the Zealot, Simon and Andrew the Apostle, Andrew in the 1st century. It became the state religion of Kartli (Caucasian Iberia, Iberia) in 319. The conversion of Kartli to Christianity is credited to a Greek lady called St. Nino of Cappadocia. The Georgian Orthodox Church, originally part of the Church of Antioch, gained its autocephaly and developed its doctrinal specificity progressively between the 5th and 10th centuries. The Bible was also translated into Georgian in the 5th century, as the Georgian alphabet was developed for that purpose.India
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
and Socotra en route, and landing at the former flourishing port of Muziris on an island near Cochin in 52. From there he preached the gospel throughout the Malabar Coast. The various churches he founded were located mainly on the Periyar River and its tributaries and along the coast. He preached to all classes of people and had about 170 converts, including members of the four principal castes. Later, stone crosses were erected at the places where churches were founded, and they became pilgrimage centres. In accordance with apostolic custom, Thomas ordained teachers and leaders or elders, who were reported to be the earliest ministry of the Malabar church.
Thomas next proceeded overland to the Coromandel Coast in southeastern India, and ministered in what is now Chennai (earlier Madras), where a local king and many people were converted. One tradition related that he went from there to China via Malacca in Malaysia, and after spending some time there, returned to the Chennai area. Apparently his renewed ministry outraged the Brahmins, who were fearful lest Christianity undermine their social caste system. So according to the Syriac version of the ''Acts of Thomas'', Mazdai, the local king at Mylapore, after questioning the Apostle condemned him to death about the year AD 72. Anxious to avoid popular excitement, the King ordered Thomas conducted to a nearby mountain, where, after being allowed to pray, he was then stoned and stabbed to death with a lance wielded by an angry Brahmin.
Mesopotamia and the Parthian Empire
Edessa, Mesopotamia, Edessa, which was held by Rome from 116 to 118 and 212 to 214, but was mostly a client kingdom associated either with Rome or Persia, was an important Christian city. Shortly after 201 or even earlier, its royal house became Christian. Edessa (now Şanlıurfa) in northwestern Mesopotamia was from apostolic times the principal center of Syriac language, Syriac-speaking Christianity. it was the capital of an independent kingdom from 132 BC to AD 216, when it became tributary to Rome. Celebrated as an important centre of Greco-Syrian culture, Edessa was also noted for its Jewish community, with proselytes in the royal family. Strategically located on the main trade routes of the Fertile Crescent, it was easily accessible fromAntioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
, where the mission to the Gentiles was inaugurated. When early Christians were scattered abroad because of persecution, some found refuge at Edessa. Thus the Edessan church traced its origin to the Apostolic Age
Christianity in the 1st century covers the formative history of Christianity from the start of the ministry of Jesus (–29 AD) to the death of the last of the Twelve Apostles () and is thus also known as the Apostolic Age. Early Christianity ...
(which may account for its rapid growth), and Christianity even became the state religion for a time.
The Church of the East had its inception at a very early date in the buffer zone between the Parthian Empire, Parthian and Roman Empires in Upper Mesopotamia, known as the Assyrian Church of the East. The vicissitudes of its later growth were rooted in its minority status in a situation of international tension. The rulers of the Parthian Empire (250 BC – AD 226) were on the whole tolerant in spirit, and with the older faiths of Babylonia and Assyria in a state of decay, the time was ripe for a new and vital faith. The rulers of the Second Persian empire (226–640) also followed a policy of religious toleration to begin with, though later they gave Christians the same status as a subject race. However, these rulers also encouraged the revival of the ancient Persian dualistic faith of Zoroastrianism and established it as the state religion, with the result that the Christians were increasingly subjected to repressive measures. Nevertheless, it was not until Christianity became the state religion in the West (380) that enmity toward Rome was focused on the Eastern Christians. After the Muslim conquest in the 7th century, the caliphate tolerated other faiths but forbade proselytism and subjected Christians to heavy taxation.
The missionary Addai evangelized Mesopotamia (modern Iraq) about the middle of the 2nd century. An ancient legend recorded by Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
(AD 260–340) and also found in the ''Doctrine of Addai'' (c. AD 400) (from information in the royal archives of Edessa) describes how King Abgar V of Edessa, Abgar V of Edessa communicated to Jesus, requesting he come and heal him, to which appeal he received a reply. It is said that after the resurrection, Thomas the Apostle, Thomas sent Addai (or Thaddaeus), to the king, with the result that the city was won to the Christian faith. In this mission he was accompanied by a disciple, Mari, and the two are regarded as co-founders of the church, according to the ''Liturgy of Addai and Mari'' (c. AD 200), which is still the normal liturgy of the Assyrian church. The ''Doctrine of Addai'' further states that Thomas was regarded as an apostle of the church in Edessa.
Addai, who became the first bishop of Edessa, was succeeded by Mar Aggai, Aggai, then by Palut, who was ordained about 200 by Serapion of Antioch. Thence came to us in the 2nd century the famous ''Peshitta'', or Syriac translation of the Old Testament; also Tatian's ''Diatessaron'', which was compiled about 172 and in common use until St. Rabbula, Bishop of Edessa (412–435), forbade its use. This arrangement of the four canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the second century AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message was reported. In this sen ...
as a continuous narrative, whose original language may have been Syriac, Greek, or even Latin, circulated widely in Syriac-speaking Churches.
A Christian council was held at Edessa as early as 197. In 201 the city was devastated by a great flood, and the Christian church was destroyed. In 232, the Syriac Acts were written supposedly on the event of the relics of the Apostle Thomas being handed to the church in Edessa. Under Roman domination many martyrs suffered at Edessa: Sts. Scharbîl and Barsamya, under Decius; Sts. Gûrja, Schâmôna, Habib, and others under Diocletian. In the meanwhile Christian priests from Edessa had evangelized Eastern Mesopotamia and Iran, Persia, and established the first churches in the kingdom of the Sasanian dynasty, Sasanians. Atillâtiâ, Bishop of Edessa, assisted at the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
(325).
Persia and Central Asia
By the latter half of the 2nd century, Christianity had spread east throughout Medes, Media, Persia, Parthia, and Bactria. The twenty bishops and many presbyters were more of the order of itinerant missionaries, passing from place to place as Paul did and supplying their needs with such occupations as merchant or craftsman. By AD 280 the metropolis of Seleucia assumed the title of "Catholicos" and in AD 424 a council of the church at Seleucia elected the first patriarch to have jurisdiction over the whole church of the East. The seat of the Patriarchate was fixed at Seleucia-Ctesiphon, since this was an important point on the east–west trade routes which extended to India and China, Java and Japan. Thus the shift of ecclesiastical authority was away from Edessa, which in AD 216 had become tributary to Rome. the establishment of an independent patriarchate with nine subordinate metropoli contributed to a more favourable attitude by the Persian government, which no longer had to fear an ecclesiastical alliance with the common enemy, Rome. By the time that Edessa was incorporated into the Sasanian Empire, Persian Empire in 258, the city of Arbil, Arbela, situated on the Tigris in what is now Iraq, had taken on more and more the role that Edessa had played in the early years, as a centre from which Christianity spread to the rest of the Persian Empire. Bardaisan, writing about 196, speaks of Christians throughout Medea, Media, Parthia and Bactria (modern-day Afghanistan) and, according to Tertullian (c. 160–230), there were already a number of bishoprics within the Persian Empire by 220. By 315, the bishop of Seleucia–Ctesiphon had assumed the title "Catholicos". By this time, neither Edessa nor Arbela was the centre of the Church of the East anymore; ecclesiastical authority had moved east to the heart of the Persian Empire. The twin cities of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, well-situated on the main trade routes between East and West, became, in the words of John Stewart, "a magnificent centre for the missionary church that was entering on its great task of carrying the gospel to the far east". During the reign of Shapur II of the Sasanian Empire, he was not initially hostile to his Christian subjects, who were led by Shemon Bar Sabbae, the Patriarch of the Church of the East, however, the conversion of Constantine the Great to Christianity caused Shapur to start distrusting his Christian subjects. He started seeing them as agents of a foreign enemy. The wars between the Sasanian and Roman empires turned Shapur's mistrust into hostility. After the death of Constantine, Shapur II, who had been preparing for a war against the Romans for several years, imposed a double tax on his Christian subjects to finance the conflict. Shemon, however, refused to pay the double tax. Shapur started pressuring Shemon and his clergy to convert to Zoroastrianism, which they refused to do. It was during this period the "cycle of the martyrs" began during which "many thousands of Christians" were put to death. During the following years, Shemon's successors, Shahdost and Barba'shmin, were also martyred. A near-contemporary 5th-century Christian work, the ''Ecclesiastical History'' of Sozomen, contains considerable detail on the Persian Christians martyred under Shapur II. Sozomen estimates the total number of Christians killed as follows:Arabian Peninsula
To understand the penetration of the Christianity in Eastern Arabia, Arabian Peninsula by the Christian gospel, it is helpful to distinguish between the Bedouin nomads of the interior, who were chiefly herdsmen and unreceptive to foreign control, and the inhabitants of the settled communities of the coastal areas and oases, who were either middlemen traders or farmers and were receptive to influences from abroad. Christianity apparently gained its strongest foothold in the ancient center of Semitic civilization in South-west Arabia or Yemen (sometimes known as Seba or Sheba, whose queen visited Solomon). Because of geographic proximity, acculturation with Ethiopia was always strong, and the royal family traces its ancestry to this queen. The presence of Arabians at Pentecost and Paul's three-year sojourn in Arabia suggest a very early gospel witness. A 4th-century church history, states that the apostle Bartholomew preached in Arabia and that Himyarites were among his converts. The Al-Jubail Church in what is now Saudi Arabia was built in the 4th century. Arabia's close relations with Ethiopia give significance to the conversion of Ethiopian eunuch, the treasurer to the queen of Ethiopia, not to mention the tradition that the Apostle Matthew was assigned to this land.Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
says that "one Pantaenus, Pantaneous (c. AD 190) was sent from Alexandria as a missionary to the nations of the East", including southwest Arabia, on his way to India.
Nubia
Christianity arrived early in Nubia. In theNew Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
of the Christian Bible, Ethiopian eunuch, a treasury official of "Candace, queen of the Ethiopians" returning from a trip to Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
was baptism, baptised by Philip the Evangelist:
: Then the Angel of the Lord said to Philip, Start out and go south to the road that leads down from Jerusalem to Gaza, which is desert. And he arose and went: And behold, a Ethiopian eunuch, man of Ethiopia, an Eunuch of great authority under Candace, Queen of E-thi-o'pi-ans, who had the charge of all her treasure, and had come to Jerusalem to worship.
Ethiopia at that time meant any upper Nile region. Kandake, Candace was the title and perhaps, name for the Meroë or Kingdom of Kush, Kushite queens.
In the fourth century, bishop Athanasius of Alexandria, Athanasius of Alexandria consecrated Marcus as bishop of Philae before his death in 373, showing that Christianity had permanently penetrated the region. John of Ephesus records that a Monophysite priest named Julian converted the king and his nobles of Nobatia around 545 and another kingdom of Alodia converted around 569. By the 7th century Makuria expanded becoming the dominant power in the region so strong enough to halt the southern expansion of Islam after the Arabs had taken Egypt. After several failed invasions the new rulers agreed to a treaty with Dongola allowing for peaceful coexistence and trade. This treaty held for six hundred years allowing Arab traders introducing Islam to Nubia and it gradually supplanted Christianity. The last recorded bishop was Timothy of Faras, Timothy at Qasr Ibrim in 1372.
See also
* Baptism in early Christianity * Christianity in the ante-Nicene period * Christianity in the 4th century * Diversity in early Christian theology * Early Christian art and architecture * History of Christianity * Proto-orthodox Christianity * Split of Christianity and Judaism * Historiography of early ChristianityReferences
Bibliography
* * * * James D.G. Dunn, Dunn, James D.G. ''Jews and Christians: The Parting of the Ways'', AD 70 to 135. pp 33–34. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing (1999). . * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * *External links
Early Christian Sources
English translations of the surviving writings of the early Christians.
Early Christians
(archived 1 September 2014)
PBS Frontline: The First Christians
First Christians and Rome
Cave in Jordan Said to Have Been Used by Early Christians
Biblical Archaeology Review (archived 7 January 2010) {{DEFAULTSORT:History of early Christianity Early Christianity, 1st-century Christianity 2nd-century Christianity 3rd-century Christianity 4th-century Christianity Dioceses established in the 1st century,