|
Flight To Pella
The fourth-century Church Father Eusebius of Caesarea and Epiphanius of Salamis cite a tradition that before the destruction of Jerusalem in AD 70 the early Christians had been warned to flee to Pella in the region of the Decapolis across the Jordan River. The flight to Pella probably did not include the Ebionites.G. Uhlhorn, "Ebionites", in: ''A Religious Encyclopaedia or Dictionary of Biblical, Historical, Doctrinal, and Practical Theology'', 3rd ed. (edited by Philip Schaff), p. 684–685 (vol. 2).O. Cullmann, "Ebioniten", in: ''Religion in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', p. 7435 (vol. 2). The authenticity of this tradition has been a much debated question since 1951 when S. G. F. Brandon in his work ''The Fall of Jerusalem and the Christian Church'' argued that the Christians would have been allied to their compatriots, the Zealots; only after the destruction of the Jewish community would Christianity have emerged as a universalist religion. The Christian–Zealot alliance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Father
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical period in which they worked became known as the Patristic Era and spans approximately from the late 1st to mid-8th centuries, flourishing in particular during the 4th and 5th centuries, when Christianity was in the process of establishing itself as the state church of the Roman Empire. For many denominations of Christianity, the writings of the Ante-Nicene Fathers, Nicene Fathers and Post-Nicene Fathers are included in Sacred Tradition. As such, in traditional dogmatic theology, authors considered Church Fathers are treated as authoritative for the establishment of doctrine. The academic field of patristics, the study of the Church Fathers, has extended the scope of the term, and there is no definitive list. Some, such as Origen and Ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
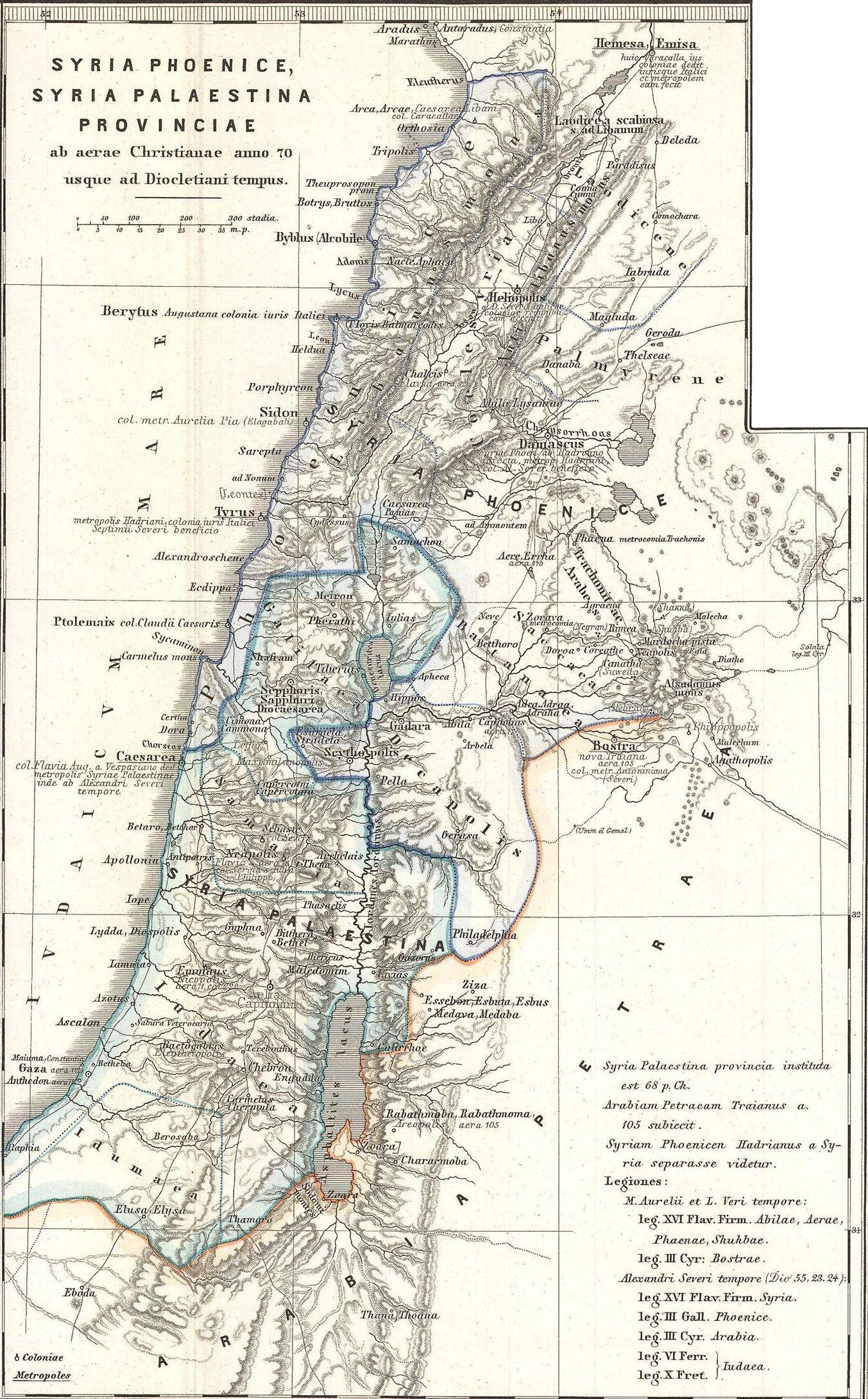
Coele Syria
Coele-Syria () was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. The term originally referred to the "hollow" Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges, but sometimes it was applied to a broader area of the region of Syria. The area is now part of modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ܟܠ ''kul'' , such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grabbe, p173 "Yet the suggestion is widely accepted that the name actually derives from Aramaic for "all Syria", which was then assimilated by the Greeks to a more usual pattern for place names" The word "Coele", with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
70s In The Roman Empire
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. 7 is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Evolution of the Arabic digit For early Brahmi numerals, 7 was written more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted (ᒉ). The western Arab peoples' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arab peoples developed the digit from a form that looked something like 6 to one that looked like an uppercase V. Both modern Arab forms influenced the European form, a two-stroke form consisting of a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Jaffé
Dan Jaffé (; born in 1970) is a Franco-Israeli specialist in the history of religions and teaches at Bar-Ilan University (Tel-Aviv) and Ashkelon Academic College. He is a researcher attached to the CNRS The French National Centre for Scientific Research (, , CNRS) is the French state research organisation and is the largest fundamental science agency in Europe. In 2016, it employed 31,637 staff, including 11,137 tenured researchers, 13,415 eng .... His work focuses on the Jewish world in the first centuries of the Common Era, the Talmud and the origins of Christianity. He has published extensively on relations between Rabbinic Judaism and Early Christianity. He directs the collection ''Judaïsme ancien et christianisme primitif'' published by Éditions du Cerf. Life Education In 1998 Jaffé earned a Masters Degree at Bar-Ilan University. From 2004 he holds a PhD in Studies and History of Religion from the University of Paris X with the thesis entitled ''Orthodoxie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed Hasmonean royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Roman Empire during the First Jewish–Roman War as general of the Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in AD 67 to the Roman army led by military commander Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Roman emperor. In response, Vespasian decided to keep him as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became emperor in AD 69, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the Emperor's family name of '' Flavius''. Flavius Josephus fully defected to the Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abomination Of Desolation
"Abomination of desolation" is a phrase from the Book of Daniel describing the pagan sacrifices with which the 2nd century BC Greek king Antiochus IV Epiphanes replaced the twice-daily offering in the Second Temple, Jewish temple, or alternatively the altar on which such offerings were made. In the 1st century AD it was taken up by the authors of the gospels in the context of Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), the Roman destruction of Jerusalem and the temple in the year 70, with the Gospel of Mark placing the "abomination of desolation" into a speech by Jesus concerning the Second Coming. It is widely accepted that Mark was the primary source used by the authors of the Gospel of Matthew and of Gospel of Luke, Luke for their parallel passages, with Matthew 24:15–16 adding a reference to Daniel and Luke 21:20–21 giving a description of the Roman armies ("But when you see Jerusalem surrounded by armies..."); in all three it is likely that the authors had in mind a future Christian esch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Luke
The Gospel of Luke is the third of the New Testament's four canonical Gospels. It tells of the origins, Nativity of Jesus, birth, Ministry of Jesus, ministry, Crucifixion of Jesus, death, Resurrection of Jesus, resurrection, and Ascension of Jesus, ascension of Jesus. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-volume work which scholars call Luke–Acts, accounting for 27.5% of the New Testament. The combined work divides the Christianity in the 1st century, history of first-century Christianity into three stages, with the gospel making up the first two of these – the life of Jesus the messiah (Christ (title), Christ) from his birth to the beginning of his mission in the meeting with John the Baptist, followed by his ministry with events such as the Sermon on the Plain and its Beatitudes, and his Passion of Jesus, Passion, death, and resurrection. Most modern scholars agree that the main sources used for Luke were (1) the Gospel of Mark; (2) a hypothetical col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells the story of who the author believes is Israel's messiah (Christ (title), Christ), Jesus, resurrection of Jesus, his resurrection, and his Great Commission, mission to the world. Matthew wishes to emphasize that the Jewish Christianity, Jewish tradition should not be lost in a church that was increasingly becoming gentile. The gospel reflects the struggles and conflicts between the evangelist's community and the other Jews, particularly with its sharp criticism of the scribes, chief priests and Pharisees with the position that the Kingdom of God (Christianity), Kingdom of Heaven has been taken away from them and given instead to the church. Scholars find numerous problems with the traditional attribution to the Matthew the Apostle, Apostle Matthew, though it is possible the gospel incorporates a source written by the disciple. The predominant scholarly view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the Major religious groups, world's largest religion. Most Christians consider Jesus to be the Incarnation (Christianity), incarnation of God the Son and awaited Messiah#Christianity, messiah, or Christ (title), Christ, a descendant from the Davidic line that is prophesied in the Old Testament. Virtually all modern scholars of classical antiquity, antiquity agree that Historicity of Jesus, Jesus existed historically. Accounts of Life of Jesus, Jesus's life are contained in the Gospels, especially the four canonical Gospels in the New Testament. Since the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, Quest for the historical Jesus, academic research has yielded various views on the historical reliability of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transjordan (region)
Transjordan, also known as the East Bank or the Transjordanian Highlands (), is the part of the Southern Levant east of the Jordan River, mostly contained in present-day Jordan. The region, known as Transjordan, was controlled by numerous powers throughout history. During the early modern period, the region of Transjordan was included under the jurisdiction of Ottoman Syrian provinces. After the Great Arab Revolt against Ottoman rule during the 1910s, the Emirate of Transjordan was established in 1921 by Hashemite Emir Abdullah, and the emirate became a British protectorate. In 1946, the emirate achieved independence from the British and in 1949 the country changed its name to the "Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan", after the Jordanian annexation of the West Bank following the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Name The prefix ''trans-'' is Latin and means "across" or beyond, and so "Transjordan" refers to the land ''on the other side of'' the Jordan River. The equivalent term for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panarion
In early Christianity, early Christian heresiology, the ''Panarion'' (, derived from Latin , meaning "bread basket"), to which 16th-century Latin translations gave the name ''Adversus Haereses'' (Latin: "Against Heresies"), is the most important of the works of Epiphanius of Salamis. It was written in Koine Greek beginning in 374 or 375, and issued about three years later,Williams, Frank; translator. "Introduction". The Panarion of Epiphanius of Salamis, Book I (Sects 1-46)'. 1987. (E.J. Brill, Leiden) . as a treatise on heresy, heresies, with its title referring to the text as a "stock of remedies to offset the poisons of heresy." It treats 80 religious sects, either organized groups or philosophies, from the time of Adam to the latter part of the fourth century, detailing their histories, and rebutting their beliefs.Long, G. ed. ''The penny cyclopædia''. Society for the diffusion of useful knowledge. 1833. p 477. The ''Panarion'' is an important source of information on the Jewis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |