Coele Syria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Coele-Syria () was a region of
"Yet the suggestion is widely accepted that the name actually derives from Aramaic for "all Syria", which was then assimilated by the Greeks to a more usual pattern for place names" The word "Coele", with κοῖλος (''koĩlos''), fem. κοίλη (''koílē'') literally meaning in Ancient and
 *Circa 36 CE Philo of Alexandria in his written work, ''On the Life of Moses'' ;
*Circa 36 CE Philo of Alexandria in his written work, ''On the Life of Moses'' ;  :
*Circa 70 CE
:
*Circa 70 CE
662
chapter=VII. Coele-Syria
Palestine: From Alexander the Great to 70 CE. Encyclopedia Britannica.
History of Palestine (region) Ptolemaic Kingdom Seleucid Empire 4th century BC 3rd century BC 2nd century BC 1st century BC Historical regions of Asia
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
. The term originally referred to the "hollow" Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges, but sometimes it was applied to a broader area of the region of Syria. The area is now part of modern-day Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
.
Name
It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription ofAramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
ܟܠ ''kul'' , such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grabbe, p173"Yet the suggestion is widely accepted that the name actually derives from Aramaic for "all Syria", which was then assimilated by the Greeks to a more usual pattern for place names" The word "Coele", with κοῖλος (''koĩlos''), fem. κοίλη (''koílē'') literally meaning in Ancient and
Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
, is thought to have come about via a folk-etymological reinterpretation referring to the "hollow" Beqaa Valley between Mount Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains. However, the term Coele-Syria was also used in a wider sense to indicate or , by the writers Pliny, Arrian, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
and also Diodorus Siculus, who indicated Coele-Syria to at least stretch as far south as Joppa, while Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
stated that the border between Egypt and Coele-Syria lay between the towns of Rhinocolara and Rhaphia.
The first and only official use of the term was during the period of Seleucid rule of the region, between c. 200 BCE and 64 BCE. During this period, the term ''Coele Syria and Phoenicia'' or ''Coele Syria'' was also used in a narrower sense to refer to the former Ptolemaic territory which the Seleucids now controlled, being the area south of the river Eleutherus. This usage was adopted by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
and the Books of the Maccabees. Later during the Roman period , Eunapius wrote that the capital of Coele-Syria was the Seleucid city of Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
, north of the Eleutherus.
Official usage
According toPolybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
, a former officer of the Ptolemaic Empire named Ptolemy Thrasea, having fought in the 217 BCE Battle of Raphia, defected to the Seleucid king Antiochus III the Great. Antiochus gave him the title "Strategos
''Strategos'' (), also known by its Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized form ''strategus'', is a Greek language, Greek term to mean 'military General officer, general'. In the Hellenistic world and in the Byzantine Empire, the term was also use ...
and Archiereus of Coele-Syria and Phoenicia". Some scholars speculate that this title may have been used previously by the Ptolemies, but no direct evidence exists to support this.
Syrian Wars
The region was disputed between the Seleucid dynasty and the Ptolemaic dynasty during the Syrian Wars.Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
's general Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
first occupied Coele-Syria in 318 BC. However, when Ptolemy joined the coalition against Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( , "Antigonus the One-Eyed"; 382 – 301 BC) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control lar ...
in 313 BC, he quickly withdrew from Coele-Syria. In 312 BC Seleucus I Nicator, defeated Demetrius, the son of Antigonus, in the Battle of Gaza which again allowed Ptolemy to occupy Coele-Syria. Though he was again to pull out after only a few months, after Demetrius had won a battle over his general and Antigonus entered Syria in force up to Antigonuses, this brief success had enabled Seleucus to make a dash for Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
which Seleucus secured. In 302 BC, Ptolemy joined a new coalition against Antigonus and reoccupied Coele-Syria, but quickly withdrew on hearing a false report that Antigonus had won a victory. He was only to return when Antigonus had been defeated at Ipsus in 301 BC. Coele-Syria was assigned to Seleucus, by the victors of Ipsus, as Ptolemy had added nothing to the victory. Though, given Ptolemy's track record, he was unlikely to organize a serious defense of Coele-Syria, Seleucus acquiesced in Ptolemy's occupation, probably because Seleucus remembered how it had been with Ptolemy's help he had reestablished himself in Babylonia.
The later Seleucids were not to be so understanding, resulting in the century of Syrian Wars between the Ptolemies and Seleucids. The Battle of Panium in 200 BC, during the Fifth Syrian War, was the final decisive battle between the two sides in ending Ptolemaic control over the region. The 171–168 BC conflicts over Coele-Syria, between Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes ( 215 BC–November/December 164 BC) was king of the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. Notable events during Antiochus' reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of ...
and Ptolemy VI Philometor, are discussed in Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
's history of Rome (in XLII. 29 and XLV. 11–12).
Seleucid control over the area of Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
began diminishing with the eruption of the Maccabean Revolt in 165 BC. With Seleucid troops being involved in warfare on the Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
n front, Judea succeeded in securing its independence by 140 BC. Despite attempts of Seleucid rulers to regain territories, the conquests of Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
in 64 BC were a decisive blow to them, and Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
became part of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
.
Nomenclatures of Syria
Judging from Arrian and '' The Anabasis of Alexander'', the historians ofAlexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, as well as more ancient authors, gave the name of Syria to all the country comprehended between the Tigris and the Mediterranean. The part to the east of the Euphrates, afterwards named Mesopotamia was called "Syria between the rivers;" that to the west was called by the general name Coele-Syria, and although Phoenicia and Palestine were sometimes separated from it. Yet, it was often comprehended as the whole country as far as Egypt.
:
*Circa 323 BCE Laomedon of Mytilene takes control of Coele-Syria (dissolving Eber-Nari).
*Circa 323 BCE The Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax lists several cities on the Palestinian coast (Dor, Jaffa, Ascalon, and Acre) that are incorporated into Coele-Syria.
In the Wars of the Diadochi, Coele-Syria came under the control of Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( , "Antigonus the One-Eyed"; 382 – 301 BC) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control lar ...
. Then in 301 BCE, Ptolemy I Soter exploited events surrounding the Battle of Ipsus to take control of the region. The victors at Ipsus finalized the breakup of Alexander's empire. Coele-Syria was allocated to Ptolemy's former ally Seleucus I Nicator, who—having been previously aided by Ptolemy—took no military action to gain control of the region. Their successors, however, became embroiled in a series of conflicts over this issue.
:Wars over Coele-Syria given by Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
c. 150 BCE
::Ptolemy, marching on Pelusium, made his first halt at that city, and after picking up stragglers and serving out rations to his men moved on marching through the desert and skirting Mount Casius and the marshes called Barathra. Reaching the spot he was bound for on the fifth day he encamped at a distance of fifty stades from Raphia, (Modern Rafah at the border of Egypt and Israel, north of Rhinocolara ( El Arish)) which is the first city of Coele-Syria on the Egyptian side after Rhinocolura.
*Circa 120 BCE In the written work, '' 1 Maccabees'' ;And king Demetrius made Apollonius his general, who was governor of Celesyria: and he gathered together a great army, and came to Jamnia.*Circa 100 BCE In the written work, '' 2 Maccabees'' ;
And when he could not overcome Onias, he went to Apollonius, the son of Tharseas, who at that time was governor of Celesyria, and Phenicia.:Boundaries of Egypt given by Diodorus Siculus c. 50 BCE ::Having spoken of the three boundaries of Egypt, by which it is distinguished from the rest of the continent, we now proceed to the next. The fourth side is nearly surrounded with a vast sea, without any harbours, being a very long and tedious voyage, and very difficult to find any place of landing. For from Parcetonium in Africa, to Joppa in Cœlo-Syria, for the space almost of five thousand furlongs, there is not one safe harbour to be found, except Pharus. *Circa 25 BCE
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
in his history of Rome ;Antiochus was so incensed, ...He at once sent his fleet to Cyprus, and in the first days of spring set his army in motion for Egypt and advanced into Coelo-Syria. When near Rhinocolura he was met by envoys from Ptolemy, who ...begged him to say clearly what he wanted rather than to attack Ptolemy as an enemy—by force of arms—after previously being his friend.
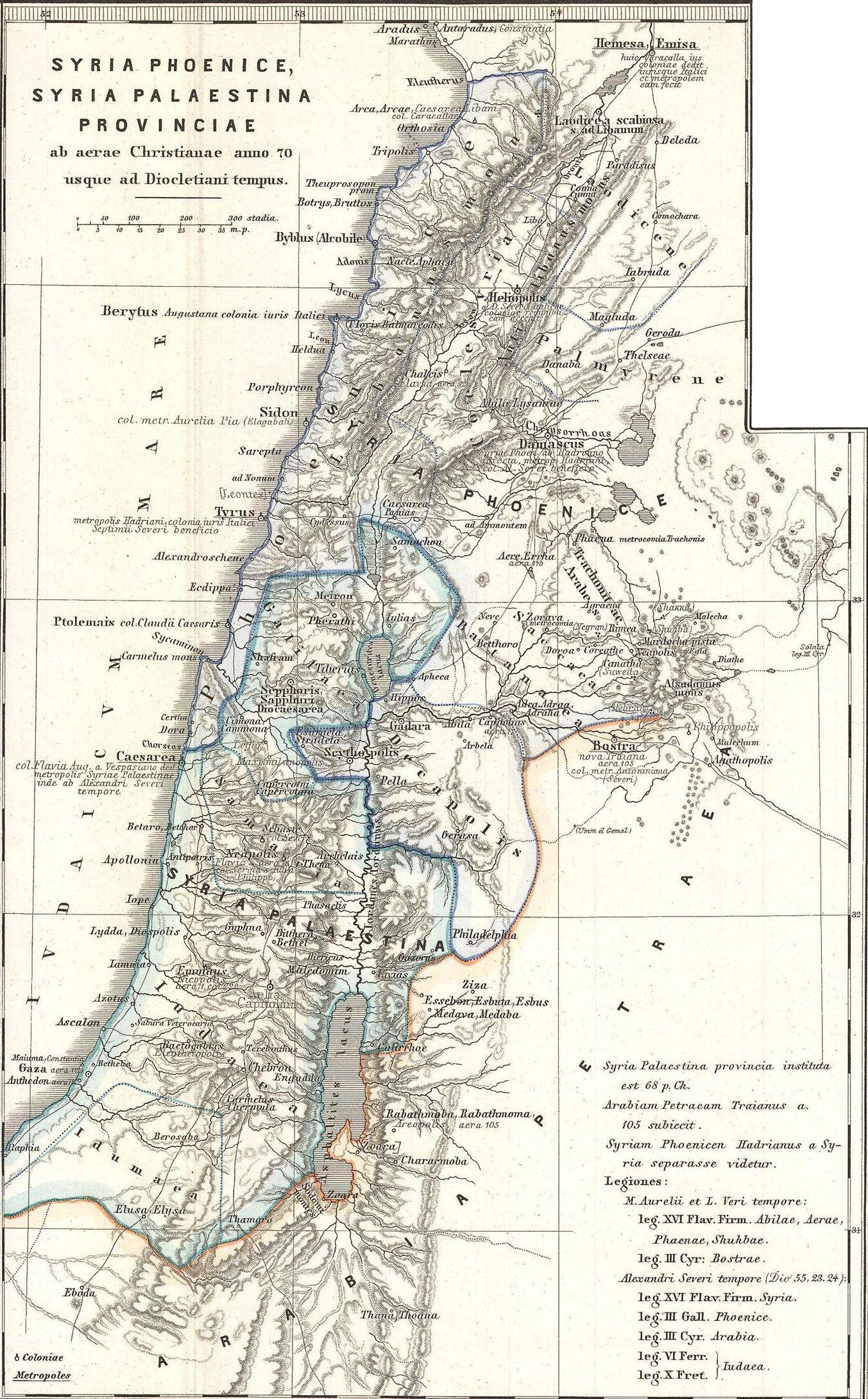
Coele-Syria Proper
Authors of the Roman period differ on the limits of Coele-Syria, some extending and others contracting them. The ''Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
'' of Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
notes that ''Coele Syria Propria (Proper)'' is defined by the ''Libanus'' and ''Anti-libanus'' mountain ranges, running parallel to each other. In the wars between the Ptolemies and the Seleucidæ, the name Cœle Syria was applied to the whole of the southern portion of Syria, but under the Romans, it was confined to "Cœlesyria Proper" and variously included the district east of Anti-Libanus, about Damascus, and a portion of Palestine east of the Jordan river (possibly of: Trans-Jordan, Perea, or the Decapolis).
:
 *Circa 36 CE Philo of Alexandria in his written work, ''On the Life of Moses'' ;
*Circa 36 CE Philo of Alexandria in his written work, ''On the Life of Moses'' ; When then oseshe received the supreme authority, with the good will of all his subjects, God himself being the regulator and approver of all his actions, he conducted his people as a colony into Phoenicia, and into the hollow Syria (Coele-syria), and Palestine, which was at that time called the land of the Canaanites, the borders of which country were three days' journey distant from Egypt.*Circa 43 CE Pomponius Mela in his written work, ''Description of the World'' ;
Syria holds a broad expanse of the littoral, as well as lands that extend rather broadly into the interior, and it is designated by different names in different places. For example, it is called Coele, Mesopotamia, Judaea, Commagene, and Sophene. It is Palestine at the point where Syria abuts the Arabs, then Phoenicia, and then—where it reaches Cilicia—Antiochia. ..In Palestine, however, is Gaza, a mighty and well fortified city.The name Syria comes from the
ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
regional name for the Levantine colonies and colonial territories which they had established and which were "formerly comprehended as part of Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
" (see Name of Syria). Syria had an uncertain border to the northeast that Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
describes as including from west to east; Commagene, Sophene, and Adiabene. In Pliny's time, Syria was administratively divided into a number of provinces with various degrees of autonomy under the Roman Empire, such as the Ityraei or Ituraei, who were a people of Coelo-Syria famous for shooting with a bow, he wood of the trees called" yews are bent into Ituraean bows".
 :
*Circa 70 CE
:
*Circa 70 CE Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
in his written work, '' Natural History'' ; Next to these countries on the coast is Syria, once the greatest of lands. It had a multitude of divisions with different names, the part adjacent to Arabia was previously known as Palestine (who's northernmost city was Caesarea, Plin. NH 5.69: "Caesarea ..finis Palastine") or Judaea or Cœle.*Circa 100 CE Josephus in his written work, '' Antiquities of the Jews, notes that in 46 BCE
Herod the Great
Herod I or Herod the Great () was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman Jewish client king of the Herodian kingdom of Judea. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea. Among these works are the rebuilding of the ...
was appointed as the "stratēgos" of Coele Syria, by the governor of Syria, Sextus Julius Caesar. And he also writes'' ; Antiochus made a friendship and league with*Circa 125 CE The Roman emperorPtolemy Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ..., and gave him his daughterCleopatra Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was ...in marriage, and yielded up to him Cœle-Syria and Samaria and Judæa and Phœnicia by way of dowry.
Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
promotes the city of Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
to "Metropolis of Coele-Syria".
*Circa 150 CE Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; ; ; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who prospered during the reigns of the Roman Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius.
He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the pr ...
in his written work, ''Roman History'' ; Intending to write the history of the Romans, I have deemed it necessary to begin with the boundaries of the nations under their sway.... Here turning our course and passing round, we take in Palestine-Syria, and beyond it a part of Arabia. The Phoenicians hold the country next to Palestine on the sea, and beyond the Phoenician territory are Coele-Syria, and the parts stretching from the sea as far inland as the river Euphrates, namely Palmyra and the sandy country round about, extending even to the Euphrates itself.The Decapolis was so called from its ten cities enumerated by Pliny. What ''Pliny'' calls ''Decapolis'', ''Ptolemy'' makes his ''Cœle-Syria''; and the ''Cœle-Syria'' of ''Pliny'', is that part of ''Syria'' about ''Aleppo''. :Towns in Coelesyria given by
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
c. 150 CE that are distinct from Pliny's Decapolis
#Heliopolis
#Abila which is called Lysinia (Abila Lysanios)
#Saana
#Ina
#Samulis (Samoulis)
#Abida
#Capitolias
#Adra
#Canatha
Provincia Syria Coele
The governor of Syria retained the civil administration of the whole large province undiminished, and held for long alone in all Asia a command of the first rank. It was only in the course of the second century that a diminution of his prerogatives occurred, when Hadrian took one of the four legions from the governor of Syria and handed it over to the governor of Palestine. It was Severus who at length withdrew the first place in the Roman military hierarchy from the Syrian governor. After having subdued the province —which had wished at that time to make Niger emperor, as it had formerly done with its governor Vespasian —amidst resistance from the capital Antioch in particular, he ordained its partition into a northern and a southern half, and gave to the governor of the former, which was called Coele-Syria, two legions, to the governor of the latter, the province of Syro-Phoenicia, one egion : *Circa 200 CE. Ulpian, On Taxes, Book I;There is also the colony of Laodicea, in Coele Syria, to which also the divine Severus granted the Italian Law on account of its services in the Civil War.:Boundaries of the 'Promised Land' given by
Jerome
Jerome (; ; ; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
He is best known ...
c. 400 CE
You may delineate the*Circa 400 CE Eunapius in his written work, ''Lives of Philosophers and Sophists'' ;Promised Land In the Abrahamic religions, the "Promised Land" ( ) refers to a swath of territory in the Levant that was bestowed upon Abraham and his descendants by God in Abrahamic religions, God. In the context of the Bible, these descendants are originally ...ofMoses In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...from the Book of Numbers (ch. 34): as bounded on the south by the desert tract called Sina, between the Dead Sea and the city of Kadesh-barnea, hich is located with the Arabah to the east">Arabah.html" ;"title="hich is located with the Arabah">hich is located with the Arabah to the eastand continues to the west, as far as the river of Egypt, that discharges into the open sea near the city of Rhinocolara; as bounded on the west by the sea along the coasts of Palestine, Phoenicia, Coele-Syria, and Cilicia; as bounded on the north by the circle formed by the Taurus Mountains and Zephyrium and extending to Hamath, called Epiphany-Syria; as bounded on the east by the city of Hippos, Israel, Antioch Hippos and Lake Kinneret, now called Sea of Galilee, Tiberias, and then the Jordan River which discharges into the salt sea, now called the Dead Sea.
Libanius (died 392 CE) was born at Antioch, the capital of Coele Syria as it is called. This city was founded by Seleucus surnamed Nicator.:*Capital of the Seleucid Empire was Antioch (240–63 BCE) :*Capital of the Syria Coele (Roman province) was Antioch (200–600 CE)
See also
* Hasmonean kingdom * Roman Syria * Herodian kingdom * Herodian tetrarchy *Judaea (Roman province)
Judaea was a Roman province from 6 to 135 CE, which at its height encompassed the regions of Judea, Idumea, Peraea, Samaria, and Galilee, as well as parts of the coastal plain of the southern Levant. At its height, it encompassed much ...
*Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina ( ) was the renamed Roman province formerly known as Judaea, following the Roman suppression of the Bar Kokhba revolt, in what then became known as the Palestine region between the early 2nd and late 4th centuries AD. The pr ...
Notes
Further reading
*External links
* *{{cite book, author=Barclay Vincent Head, title=Historia Numorum: A Manual of Greek Numismatics, publisher=Clarendon Press, url=https://archive.org/details/historianumorumm00headrich, year=1887, pag662
chapter=VII. Coele-Syria
Palestine: From Alexander the Great to 70 CE. Encyclopedia Britannica.
History of Palestine (region) Ptolemaic Kingdom Seleucid Empire 4th century BC 3rd century BC 2nd century BC 1st century BC Historical regions of Asia