Paleo-Indian Period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Paleo-Indians were the
This allowed land animals, followed by humans, to migrate south into the interior of the continent. The people went on foot or used boats along the coastline. The dates and routes of the
 Researchers continue to study and discuss the specifics of Paleo-Indian migration to and throughout the Americas, including the dates and routes traveled. The traditional theory holds that these early migrants moved into
Researchers continue to study and discuss the specifics of Paleo-Indian migration to and throughout the Americas, including the dates and routes traveled. The traditional theory holds that these early migrants moved into
 The Palaeoindian culture lasts 4000 years, from 12,000 to 8000 BP. It is divided into Early Palaeoindian (12,000-10,000 BP) and Late Palaeoindian (10,000-8000 BP), ending with early events of the Early Archaic period in some regions.
Sites in Alaska (eastern Beringia) exhibit some of the earliest evidence of Paleo-Indians, followed by archaeological sites in northern
The Palaeoindian culture lasts 4000 years, from 12,000 to 8000 BP. It is divided into Early Palaeoindian (12,000-10,000 BP) and Late Palaeoindian (10,000-8000 BP), ending with early events of the Early Archaic period in some regions.
Sites in Alaska (eastern Beringia) exhibit some of the earliest evidence of Paleo-Indians, followed by archaeological sites in northern  The
The
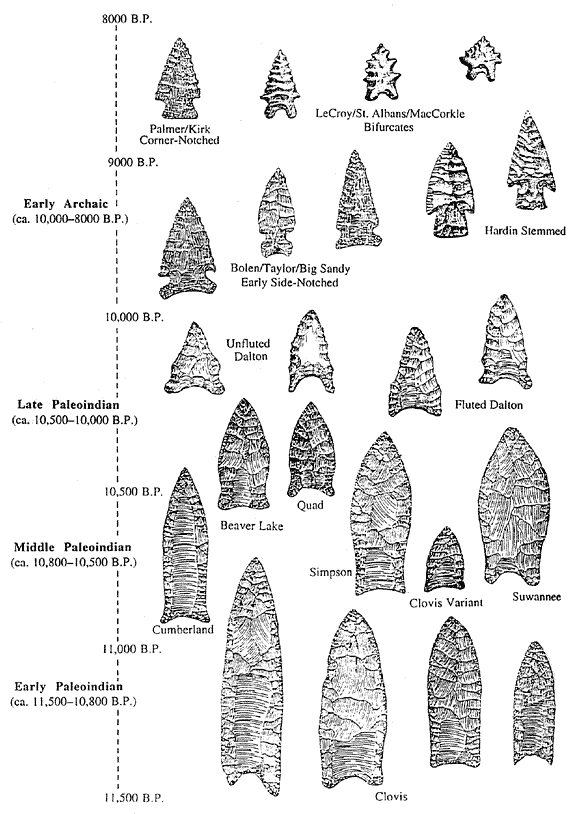 Paleo-Indians are generally classified by lithic reduction or
Paleo-Indians are generally classified by lithic reduction or
The micro-satellite diversity and distributions of the Y lineage specific to South America indicates that certain Amerindian populations have been isolated since the initial colonization of the region. The
Survey of professional opionions regarding the peopling of the Americas
" ''The SAA Archaeological Record'' Volume 12, No. 2 March 2012
 The Archaic period in the Americas saw a changing environment featuring a warmer, more arid climate and the disappearance of the last megafauna. The majority of population groups at this time were still highly mobile hunter-gatherers, but now individual groups started to focus on resources available to them locally. Thus with the passage of time there is a pattern of increasing regional generalization like the
The Archaic period in the Americas saw a changing environment featuring a warmer, more arid climate and the disappearance of the last megafauna. The majority of population groups at this time were still highly mobile hunter-gatherers, but now individual groups started to focus on resources available to them locally. Thus with the passage of time there is a pattern of increasing regional generalization like the
Atlas of the Human Journey
Journey of Mankind – Genetic Map
–
The Paleoindian Period
– United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service
Alabama Archaeology: Prehistoric Alabama
– The University of Alabama, Department of Archaeology
The Paleoindian Database
– The University of Tennessee, Department of Anthropology.
Paleoindians and the Great Pleistocene Die-Off
– American Academy of Arts and Sciences, National Humanities Center {{Cultural areas of indigenous North Americans +1 +1 +1 History of Indigenous peoples of North America History of Indigenous peoples in Canada Native American history History of the Americas History of North America History of South America Hunter-gatherers Hunter-gatherers of the United States Hunter-gatherers of Canada Hunter-gatherers of South America Late Pleistocene Mesoamerica Pleistocene life Pleistocene North America Pleistocene South America Pre-Columbian archaeology
first peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
towards the end of the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
and is distinct from the term ''Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
''.''Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
'' specifically refers to the period between million years ago and the end of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
in the Eastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to p ...
. It is not used in New World archaeology.
Traditional theories suggest that big-animal hunters crossed the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
from North Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia () is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geography, geographical terms and consists of three federal districts of Russia: Ural Federal District, Ural, Siberian Federal District, Siberian, and the Far E ...
into the Americas over a land bridge (Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south ...
). This bridge existed from 45,000 to 12,000 BCE (47,000–14,000 BP). Small isolated groups of hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s migrated alongside herds of large herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat ...
s far into Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. From BCE ( BP), ice-free corridors developed along the Pacific coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas North America
Countries on the western side of North America have a Pacific coast as their western or south-western border. One of th ...
and valleys of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
.page 2This allowed land animals, followed by humans, to migrate south into the interior of the continent. The people went on foot or used boats along the coastline. The dates and routes of the
peopling of the Americas
It is believed that the peopling of the Americas began when Paleolithic hunter-gatherers (Paleo-Indians) entered North America from the North Asian Mammoth steppe via the Beringia land bridge, which had formed between northeastern Siberia and we ...
remain subjects of ongoing debate. There were likely three waves of ancient settlers from the Bering Sea
The Bering Sea ( , ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre, p=ˈbʲerʲɪnɡəvə ˈmorʲe) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasse ...
to the American continent.
Stone tool
Stone tools have been used throughout human history but are most closely associated with prehistoric cultures and in particular those of the Stone Age. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a ...
s, particularly projectile point
In archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have been kept in the ...
s and scrapers, are the primary evidence of the earliest human activity in the Americas. Archeologists and anthropologists use surviving crafted lithic flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock (geology), rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and ...
d tools to classify cultural periods. Scientific evidence links Indigenous Americans to eastern Siberian populations by the distribution of blood types, and genetic composition as indicated by molecular data, such as DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. There is evidence for at least two separate migrations.
Paleoindians lived alongside and hunted many now extinct megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
(large animals), with most large animals across the Americas becoming extinct towards the end of the Paleoindian period as part of the Late Pleistocene megafauna extinctions
The Late Pleistocene to the beginning of the Holocene saw the extinction of the majority of the world's megafauna, typically defined as animal species having body masses over , which resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity acro ...
. The potential role of human hunting in the extinctions has been the subject of much controversy.
From 8000 to 7000 BCE (10,000–9,000 BP) the climate stabilized, leading to a rise in population and lithic technology
In archaeology, lithic technology includes a broad array of techniques used to produce usable tools from various types of stone. The earliest stone tools to date have been found at the site of Lomekwi 3 (LOM3) in Kenya and they have been dated to ...
advances, resulting in a more sedentary lifestyle during the following Archaic Period.
Migration into the Americas
Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south ...
between eastern Siberia and present-day Alaska 17,000 years ago, at a time when the Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million ...
significantly lowered sea levels. These people are believed to have followed herds of now-extinct pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
along ice-free corridors that stretched between the Laurentide and Cordilleran ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s. An alternative proposed scenario involves migration, either on foot or using boats
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
, down the Pacific coast to South America. Evidence of the latter would have been submerged by a sea-level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
of more than a hundred meters following the end of the Last Glacial Period.
The time range of the peopling of the Americas remains a source of substantial debate. Conventional estimates have it that humans reached North America at some point between 15,000 and 20,000 years ago. However, some groups of humans may have reached South America as early as 25,000 years ago. One of the few areas of agreement is the origin from Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
, with widespread habitation of the Americas during the end of the Last Glacial Period, and more specifically after the end of the Last Glacial Maximum around 16,000 to 13,000 years before present.
Periodization
 The Palaeoindian culture lasts 4000 years, from 12,000 to 8000 BP. It is divided into Early Palaeoindian (12,000-10,000 BP) and Late Palaeoindian (10,000-8000 BP), ending with early events of the Early Archaic period in some regions.
Sites in Alaska (eastern Beringia) exhibit some of the earliest evidence of Paleo-Indians, followed by archaeological sites in northern
The Palaeoindian culture lasts 4000 years, from 12,000 to 8000 BP. It is divided into Early Palaeoindian (12,000-10,000 BP) and Late Palaeoindian (10,000-8000 BP), ending with early events of the Early Archaic period in some regions.
Sites in Alaska (eastern Beringia) exhibit some of the earliest evidence of Paleo-Indians, followed by archaeological sites in northern British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, western Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
and the Old Crow Flats
Old Crow Flats (''Van Tat'' in the Gwichʼin language) is a wetland complex in northern Yukon, Canada along the Old Crow River. It is north of the Arctic Circle and south of the Beaufort Sea, and is nearly surrounded by mountains.
Site
The site ...
region of the Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
territory. The Paleo-Indians would eventually flourish all over the Americas. These peoples were spread over a wide geographical area; thus there were regional variations in lifestyles. However, all the individual groups shared a common style of stone tool production, making knapping
Knapping is the shaping of flint, chert, obsidian, or other conchoidal fracturing stone through the process of lithic reduction to manufacture stone tools, strikers for flintlock firearms, or to produce flat-faced stones for building or facing w ...
styles and progress identifiable. This early Paleo-Indian period's lithic reduction
In archaeology, in particular of the Stone Age, lithic reduction is the process of fashioning stones or rocks from their natural state into tools or weapons by removing some parts. It has been intensely studied and many archaeological industrie ...
tool adaptations have been found across the Americas, utilized by highly mobile bands consisting of approximately 20 to 60 members of an extended family. Food would have been plentiful during the few warm months of the year. Lakes and rivers were teeming with many species of fish, birds and aquatic mammals. Nuts, berries and edible roots could be found in the forests and marshes. The fall would have been a busy time because foodstuffs would have to be stored and clothing made ready for the winter. During the winter, coastal fishing groups moved inland to hunt and trap fresh food and furs.
Late ice-age climatic changes caused plant communities and animal populations to change. Groups moved and sought new supplies as preferred resources were depleted. Small bands utilized hunting and gathering during the spring and summer months, then broke into smaller direct family groups for the fall and winter. Family groups moved every 3–6 days, possibly traveling up to per year. Diets were often sustaining and rich in protein; clothing was made from a variety of animal hides that were also used for shelter construction. During much of the early and middle Paleo-Indian periods, inland bands are thought to have subsisted primarily through hunting now-extinct megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
. Large Pleistocene mammals included the giant beaver, steppe wisent
The steppe bison (''Bison'' ''priscus'', also less commonly known as the steppe wisent and the primeval bison) is an extinct species of bison which lived from the Middle Pleistocene to the Holocene. During the Late Pleistocene, it was widely dist ...
, giant muskox, mastodon
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to ...
, woolly mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived from the Middle Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with the African ...
and ancient reindeer.
 The
The Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is an archaeological culture from the Paleoindian period of North America, spanning around 13,050 to 12,750 years Before Present (BP). The type site is Blackwater Draw locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, where stone too ...
, appearing around 11,500 BCE ( BP) in North America, is one of the most notable Paleo-Indian archaeological cultures. It has been disputed whether the Clovis culture were specialist big-game hunters or employed a mixed foraging strategy that included smaller terrestrial game, aquatic animals, and a variety of flora. Paleo-Indian groups were efficient hunters and carried a variety of tools. These included highly efficient fluted-style spear points, as well as microblades used for butchering and hide processing. Projectile points and hammerstone
In archaeology, a hammerstone is a hard cobble
used to strike off lithic flakes from a lump of tool stone during the process of lithic reduction. The hammerstone is a rather universal stone tool which appeared early in most regions of the wo ...
s made from many sources are found traded or moved to new locations. Stone tools were traded and/or left behind from North Dakota
North Dakota ( ) is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota people, Dakota and Sioux peoples. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minneso ...
and Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
, to Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, an ...
and Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
. Trade routes also have been found from the British Columbia Interior
The British Columbia Interior, popularly referred to as the BC Interior or simply the Interior, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. While the exact boundaries are variously defined, the British Columbia Interior ...
to the coast of California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
.
The glaciers that covered the northern half of the continent began to gradually melt, exposing new land for occupation around 17,500–14,500 years ago. At the same time as this was occurring, worldwide extinctions among the large mammals began. In North America, camelids
Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant members of this group are: dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, ...
and equids eventually died off, the latter not to reappear on the continent until the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
reintroduced the horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
near the end of the 15th century CE. As the Quaternary extinction event
The Late Pleistocene to the beginning of the Holocene saw the extinction of the majority of the world's megafauna, typically defined as animal species having body masses over , which resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity acro ...
was happening, the late Paleo-Indians would have relied more on other means of subsistence.
From BCE ( BP), the broad-spectrum big game hunters of the Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
began to focus on a single animal species: the bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
(an early cousin of the American bison
The American bison (''Bison bison''; : ''bison''), commonly known as the American buffalo, or simply buffalo (not to be confused with Bubalina, true buffalo), is a species of bison that is endemic species, endemic (or native) to North America. ...
). The earliest known of these bison-oriented hunting traditions is the Folsom tradition
The Folsom tradition is a Paleo-Indian archaeological culture that occupied much of central North America from to c. 10200 BCE. The term was first used in 1927 by Jesse Dade Figgins, director of the Denver Museum of Nature and Scien ...
. Folsom peoples traveled in small family groups for most of the year, returning yearly to the same springs and other favored locations on higher ground. There they would camp for a few days, perhaps erecting a temporary shelter, making and/or repairing some stone tools, or processing some meat, then moving on. Paleo-Indians were not numerous, and population densities were quite low.
Classification
 Paleo-Indians are generally classified by lithic reduction or
Paleo-Indians are generally classified by lithic reduction or lithic core
In archaeology, a lithic core is a distinctive Artifact (archaeology), artifact that results from the practice of lithic reduction. In this sense, a core is the scarred nucleus resulting from the detachment of one or more lithic flake, flakes fr ...
"styles" and by regional adaptations. Lithic technology
In archaeology, lithic technology includes a broad array of techniques used to produce usable tools from various types of stone. The earliest stone tools to date have been found at the site of Lomekwi 3 (LOM3) in Kenya and they have been dated to ...
fluted spear points, like other spear points, are collectively called projectile points
In archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have been kept in the ...
. The projectiles are constructed from chipped stones that have a long groove called a "flute". The spear points would typically be made by chipping a single flake from each side of the point. The point was then tied onto a spear of wood or bone. As the environment changed with the ice age ending around 17–13 Ka BP on short, and around 25–27 Ka BP on the long, many animals migrated overland to take advantage of the new sources of food. Humans following these animals, such as bison, mammoth and mastodon, thus gained the name ''big-game hunters''. Pacific coastal groups of the period would have relied on fishing as the prime source of sustenance.
Archaeologists are piecing together evidence that the earliest human settlements in North America were thousands of years before the appearance of the current Paleo-Indian time frame (before the late glacial maximum 20,000-plus years ago). Evidence indicates that people were living as far east as Beringia before 30,000 BCE (32,000 BP). Until recently, it was generally believed that the first Paleo-Indian people to arrive in North America belonged to the Clovis culture. This archaeological phase was named after the city of Clovis, New Mexico
Clovis is a city in and the county seat of Curry County, New Mexico. The population was 38,567 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Clovis is located in the New Mexico portion of the Llano Estacado, in the eastern part of the state.
A ...
, where in 1936 unique Clovis point
Clovis points are the characteristically fluted projectile points associated with the New World Clovis culture, a prehistoric Paleo-American culture. They are present in dense concentrations across much of North America and they are largely restr ...
s were found in situ at the site of Blackwater Draw
Blackwater Draw is an intermittent stream channel about long, with headwaters in Roosevelt County, New Mexico, about southwest of Clovis, New Mexico, and flows southeastward across the Llano Estacado toward the city of Lubbock, Texas, where ...
, where they were directly associated with the bones of Pleistocene animals.
Recent data from a series of archaeological sites throughout the Americas suggest that Clovis (thus the "Paleo-Indians") time range should be re-examined. In particular, sites such as Cooper's Ferry in Idaho, Cactus Hill
Cactus Hill is an archaeological site in southeastern Virginia, United States, located on sand dunes above the Nottoway River about 45 miles south of Richmond. The site receives its name from the prickly pear cacti that can be found growing abunda ...
in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, Meadowcroft Rockshelter
The Meadowcroft Rockshelter is an archaeological site which is located near Avella in Jefferson Township, Pennsylvania. The site is a rock shelter in a bluff overlooking Cross Creek (a tributary of the Ohio River), and contains evidence that the ...
in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Bear Spirit Mountain in West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
, Catamarca and Salta
Salta () is the capital and largest city in the Provinces of Argentina, Argentine province of Salta Province, the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the List of cities in Argentina, 7th most-populous ...
in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Pilauco and Monte Verde
Monte Verde is a Paleolithic archaeological site in the Llanquihue Province in southern Chile, located near Puerto Montt, Los Lagos Region. The site is primarily known for Monte Verde II, dating to approximately 14,550–14,500 calibrated years ...
in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, Topper in South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, and Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 administrative divisions of Mexico, federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into municipalities of ...
in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
have generated early dates for wide-ranging Paleo-Indian occupation. Some sites significantly predate the migration time frame of ice-free corridors, thus suggesting that there were additional coastal migration routes available, traversed either on foot and/or in boats. Geological evidence suggests the Pacific coastal route was open for overland travel before 23,000 years ago and after 16,000 years ago.
South America
In South America, the site ofMonte Verde
Monte Verde is a Paleolithic archaeological site in the Llanquihue Province in southern Chile, located near Puerto Montt, Los Lagos Region. The site is primarily known for Monte Verde II, dating to approximately 14,550–14,500 calibrated years ...
indicates that its population was probably territorial and resided in their river basin for most of the year. Some other South American groups, on the other hand, were highly mobile and hunted big-game animals such as gomphothere
Gomphotheres are an extinct group of proboscideans related to modern elephants. First appearing in Africa during the Oligocene, they dispersed into Eurasia and North America during the Miocene and arrived in South America during the Pleistocene a ...
s and giant sloths. They used classic bifacial projectile point technology, such as Fishtail points.
The primary examples are populations associated with El Jobo points (The dating for these sites ranges from BP (forVenezuela Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...), fish-tail or Magallanes points (various parts of the continent, but mainly the southern half), and Paijan points (Peru Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...andEcuador Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...) at sites in grasslands, savanna plains, and patchy forests.
Taima-Taima
Taima-Taima is a Late Pleistocene archaeological site located about 20 kilometers east of Santa Ana de Coro, in the Falcón State of Venezuela. The human settlement at Taima-Taima started about 14,000 years ago.
History of research
The site was ...
in Venezuela) to BP. The bi-pointed El Jobo projectile points were mostly distributed in north-western Venezuela; from the Gulf of Venezuela
The Gulf of Venezuela is a gulf of the Caribbean Sea bounded by the Venezuelan states of Zulia and Falcón and by La Guajira Department, Colombia. The western side is formed by the Guajira Peninsula. A strait connects it with Maracaibo Lake to ...
to the high mountains and valleys. The population using them were hunter-gatherers that seemed to remain within a certain circumscribed territory. El Jobo points were probably the earliest, going back to BP and they were used for hunting large mammals. In contrast, the fish-tail points, dating to c. 11,000 B.P. in Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
, had a much wider geographical distribution, but mostly in the central and southern part of the continent.
Archaeogenetics
Thehaplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a sing ...
most commonly associated with Amerindian genetics is Haplogroup Q-M3
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346.
In 1996 the research group at Stanfo ...
. Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the Y ...
, like (mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the DNA contained in ...
), differs from other nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s in that the majority of the Y chromosome is unique and does not recombine during meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
. This allows the historical pattern of mutations to be easily studied. The pattern indicates Indigenous Amerindians experienced two very distinctive genetic episodes: first with the initial peopling of the Americas, and secondly with European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale colonization of the Americas, involving a number of European countries, took place primarily between the late 15th century and the early 19th century. The Norse explored and colonized areas of Europe a ...
. The former is the determinant factor for the number of gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
lineages and founding haplotype
A haplotype (haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material (DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA orga ...
s present in today's Indigenous Amerindian populations.
Human settlement of the Americas occurred in stages from the Bering sea coast line, with an initial layover on Beringia for the founding population
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
.page 2The micro-satellite diversity and distributions of the Y lineage specific to South America indicates that certain Amerindian populations have been isolated since the initial colonization of the region. The
Na-Dené
Na-Dene ( ; also Nadene, Na-Dené, Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit, Tlina–Dene) is a family of Native American languages that includes at least the Athabaskan languages, Eyak, and Tlingit languages. Haida was formerly included but is now general ...
, Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
and Indigenous Alaskan populations, however, exhibit haplogroup Q (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q or Q-M242 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It has two primary subclades: Q1/Q-L472 (also known as Q-MEH2) and Q2/Q-L275). These include numerous subclades that have been sampled and identified in males among modern populations.
Q ...
mutations that are distinct from other Amerindians with various mtDNA mutations. This suggests that the earliest migrants into the northern extremes of North America and Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
derived from later migrant populations.
Evidence from full genomic studies suggests that the first people in the Americas diverged from Ancient East Asians about 36,000 years ago and expanded northwards into Siberia, where they encountered and interacted with a different Paleolithic Siberian population (known as Ancient North Eurasian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) refers to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture () and populations closely related to them, such as the Upper Paleolithic individ ...
s), giving rise to both Paleosiberian peoples
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Paleo-Siberian is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the hunter-gatherer people of the 15th-10th millennia before present, in northern and northeastern Siberia. The Ancien ...
and Ancient Native Americans, which later migrated towards the Beringian region, became isolated from other populations, and subsequently populated the Americas.
Debate about megafauna extinction
Due to the evidence that Paleoindians hunted now extinct megafauna (large animals), and that following a period of overlap, most large animals across the Americas became extinct as part of theLate Pleistocene megafauna extinctions
The Late Pleistocene to the beginning of the Holocene saw the extinction of the majority of the world's megafauna, typically defined as animal species having body masses over , which resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity acro ...
, it has been argued by many authors that hunting by Paleoindians was an important factor in the extinctions, though this suggestion is controversial, with other authors placing the blame on climatic change. In a 2012 survey of archaeologists in ''The SAA Archaeological Record,'' 63% of respondents said that megafauna extinctions were likely the result of a "combination of factors".Amber D. Wheat Survey of professional opionions regarding the peopling of the Americas
" ''The SAA Archaeological Record'' Volume 12, No. 2 March 2012
Transition to archaic period
 The Archaic period in the Americas saw a changing environment featuring a warmer, more arid climate and the disappearance of the last megafauna. The majority of population groups at this time were still highly mobile hunter-gatherers, but now individual groups started to focus on resources available to them locally. Thus with the passage of time there is a pattern of increasing regional generalization like the
The Archaic period in the Americas saw a changing environment featuring a warmer, more arid climate and the disappearance of the last megafauna. The majority of population groups at this time were still highly mobile hunter-gatherers, but now individual groups started to focus on resources available to them locally. Thus with the passage of time there is a pattern of increasing regional generalization like the Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west— ...
, Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
, Poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
, Dalton
Dalton may refer to:
Science
* Dalton (crater), a lunar crater
* Dalton (program), chemistry software
* Dalton (unit) (Da), a.k.a. unified atomic mass unit
* John Dalton, chemist, physicist and meteorologist
* 12292 Dalton, an asteroid
Ent ...
, and Plano traditions. These regional adaptations would become the norm, with reliance less on hunting and gathering, and a more mixed economy of small game, fish, seasonally wild vegetables, and harvested plant foods. Many groups continued to hunt big game but their hunting traditions became more varied and meat procurement methods more sophisticated. The placement of artifacts and materials within an Archaic burial site indicated social differentiation based upon status in some groups.
See also
* Adams County Paleo-Indian District – (Archeological site) *Arlington Springs Man
Arlington Springs Man was an ancient Paleoindian, most likely a man, whose remains were found in 1959 on Santa Rosa Island, one of the Channel Islands located off the coast of Southern California. He lived about 13,000 years Before Present, maki ...
– (Human remains)
* Blackwater Draw
Blackwater Draw is an intermittent stream channel about long, with headwaters in Roosevelt County, New Mexico, about southwest of Clovis, New Mexico, and flows southeastward across the Llano Estacado toward the city of Lubbock, Texas, where ...
– (Archeological site)
* Borax Lake Site – (Archeological site)
* Buhl woman – (Human remains)
* Calico Early Man Site – (Archeological site)
* Caverna da Pedra Pintada – (Archeological site)
* Cody complex
The Cody complex is a Paleo-Indian culture group first identified at a ''Bison antiquus'' kill site near Cody, Wyoming, in 1951. Points possessing characteristics of Cody Complex flaking have been found all across North America from Canada to ...
– (Culture group)
* Cueva de las Manos
Cueva de las Manos ( Spanish for Cave of the Hands or Cave of Hands) is a cave and complex of rock art sites in the province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, south of the town of Perito Moreno. It is named for the hundreds of paintings of hands s ...
– (Cave paintings)
* East Fork Site
The East Fork Site is an archaeological site in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Ohio. Located south of Batavia, it has yielded artifacts from more cultures than has any other site in Clermont County.Owen, Lorrie K., ed. ''Dictio ...
– (Archeological site)
* Folsom Tradition
The Folsom tradition is a Paleo-Indian archaeological culture that occupied much of central North America from to c. 10200 BCE. The term was first used in 1927 by Jesse Dade Figgins, director of the Denver Museum of Nature and Scien ...
– (Culture group)
* Fort Rock Cave
Fort Rock Cave was the site of the earliest evidence of human habitation in the US state of Oregon before the excavation of the Paisley Caves. Fort Rock Cave featured numerous well-preserved sagebrush sandals, ranging from 9,000 to 13,000 years ...
– (Archeological site)
* Hiscock Site – (Archeological site)
* Kennewick Man
Kennewick Man or Ancient One was a Native American man who lived during the early Holocene, whose skeletal remains were found in 1996 washed out on a bank of the Columbia River near Kennewick, Washington. Radiocarbon tests show the man lived a ...
– (Human remains)
* Leanderthal Lady
Leanderthal Lady is the skeletal remains of a prehistoric woman discovered in January 1983 near the city of Leander, Texas. The remains were alternatively labeled "Leanne". Both names were inspired by the proximity of the site to the town of Leande ...
– (Human remains)
* Lehner Mammoth-Kill Site – (Archeological site)
* Lindenmeier site – (Archeological site)
* Luzia Woman
Luzia Woman () is the name for an Upper Paleolithic period skeleton of a Paleo-Indians, Paleo-Indian woman who was found in a cave in Brazil. The 11,500-year-old skeleton was found in a cave in the Lapa Vermelha archeological site in Pedro Leopol ...
– (Human remains)
* Marmes Rockshelter
The Marmes Rockshelter (also known as (45-FR-50)) is an archaeological site first excavated in 1962, near Lyons Ferry Park and the confluence of the Snake and Palouse Rivers, in Franklin County, southeastern Washington. This rockshelter is re ...
– (Archeological site)
* Mastodon State Historic Site – (Archeological site)
* Mummy Cave – (Archeological site)
* Naia – (Human remains)
* Paisley Caves
The Paisley Caves or the Paisley Five Mile Point Caves complex is a system of eight caves in an arid, desolate region of south-central Oregon, United States north of the present-day city of Paisley, Oregon. The caves are located in the Summer L ...
– (Archeological site)
* Peñon woman
Peñon woman or Peñon Woman III is the name for the human remains, specifically a skull, of a Paleo-Indian woman found by an ancient lake bed in Pueblo Peñón de los Baños in Mexico City in 1959.
Discovery
Peñon Woman III was found on an islan ...
– (Human remains)
* Post Pattern :''Post pattern also may refer to a particular American football strategy, the Post (route).''
The Post Pattern refers to a Paleo-Indian archaeological culture of artifacts found in northwest California dating between 9,000 and 13,000 years ago. ...
– (Archaeological culture)
* San Dieguito complex
The San Dieguito complex is an archaeological pattern left by early Holocene inhabitants of Southern California and surrounding portions of the Southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. Radiocarbon dating places a 10,200 BP (Before Pres ...
– (Archeological site)
* Sandia Man Cave – (Archeological site)
* Upward Sun River site – (Archeological site)
* Witt Site – (Archeological site)
* X̲áːytem – (Archeological site)
* Quad site – (Archeological site)
Notes
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Atlas of the Human Journey
Genographic Project
The Genographic Project, launched on 13 April 2005 by the National Geographic Society and IBM, was a Molecular anthropology, genetic anthropological study (sales discontinued on 31 May 2019) that aimed to map historical human migrations patter ...
, National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly ''The National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as ''Nat Geo'') is an American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine ...
Journey of Mankind – Genetic Map
–
Bradshaw Foundation
The Gwion Gwion rock paintings, Gwion figures, Kiro Kiro or Kujon (also known as the Bradshaw rock paintings, Bradshaw rock art, Bradshaw figures and the Bradshaws) are one of the two major regional traditions of rock art found in the north-wes ...
The Paleoindian Period
– United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service
Alabama Archaeology: Prehistoric Alabama
– The University of Alabama, Department of Archaeology
The Paleoindian Database
– The University of Tennessee, Department of Anthropology.
Paleoindians and the Great Pleistocene Die-Off
– American Academy of Arts and Sciences, National Humanities Center {{Cultural areas of indigenous North Americans +1 +1 +1 History of Indigenous peoples of North America History of Indigenous peoples in Canada Native American history History of the Americas History of North America History of South America Hunter-gatherers Hunter-gatherers of the United States Hunter-gatherers of Canada Hunter-gatherers of South America Late Pleistocene Mesoamerica Pleistocene life Pleistocene North America Pleistocene South America Pre-Columbian archaeology