Ozone Layer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of
 The Earth's ozone layer formed about 500 million years ago, when the
The Earth's ozone layer formed about 500 million years ago, when the O2 + \mathit\nu_ -> 2O
: O + O2 <-> O3
About 90% of the ozone in the atmosphere is contained in the stratosphere. Ozone concentrations are greatest between about , where they range from about 2 to 8 parts per million. If all of the ozone were compressed to the pressure of the air at sea level, it would be only thick.

 Although the concentration of the ozone in the ozone layer is very small, it is vitally important to life because it absorbs biologically harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation coming from the Sun. Extremely short or vacuum UV (10–100 nm) is screened out by nitrogen. UV radiation capable of penetrating nitrogen is divided into three categories, based on its wavelength; these are referred to as UV-A (400–315 nm), UV-B (315–280 nm), and UV-C (280–100 nm).
UV-C, which is very harmful to all living things, is entirely screened out by a combination of dioxygen (< 200 nm) and ozone (> about 200 nm) by around altitude. UV-B radiation can be harmful to the skin and is the main cause of
Although the concentration of the ozone in the ozone layer is very small, it is vitally important to life because it absorbs biologically harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation coming from the Sun. Extremely short or vacuum UV (10–100 nm) is screened out by nitrogen. UV radiation capable of penetrating nitrogen is divided into three categories, based on its wavelength; these are referred to as UV-A (400–315 nm), UV-B (315–280 nm), and UV-C (280–100 nm).
UV-C, which is very harmful to all living things, is entirely screened out by a combination of dioxygen (< 200 nm) and ozone (> about 200 nm) by around altitude. UV-B radiation can be harmful to the skin and is the main cause of
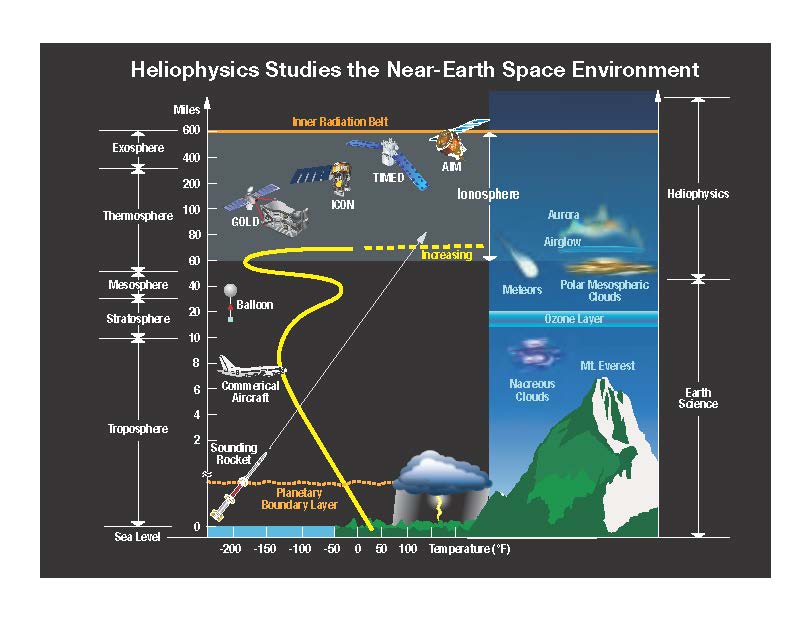 The thickness of the ozone layer varies worldwide and is generally thinner near the equator and thicker near the poles. Thickness refers to how much ozone is in a column over a given area and varies from season to season. The reasons for these variations are due to atmospheric circulation patterns and solar intensity.
The ozone layer ends gradually, but in general its upper limit is where air becomes too thin for UV light to generate much ozone, and its lower limit is where generated ozone blocks enough UV light to stop most ozone production.
In the homosphere, wind-driven movement is more important than relative gas weight. The majority of ozone is produced over the
The thickness of the ozone layer varies worldwide and is generally thinner near the equator and thicker near the poles. Thickness refers to how much ozone is in a column over a given area and varies from season to season. The reasons for these variations are due to atmospheric circulation patterns and solar intensity.
The ozone layer ends gradually, but in general its upper limit is where air becomes too thin for UV light to generate much ozone, and its lower limit is where generated ozone blocks enough UV light to stop most ozone production.
In the homosphere, wind-driven movement is more important than relative gas weight. The majority of ozone is produced over the 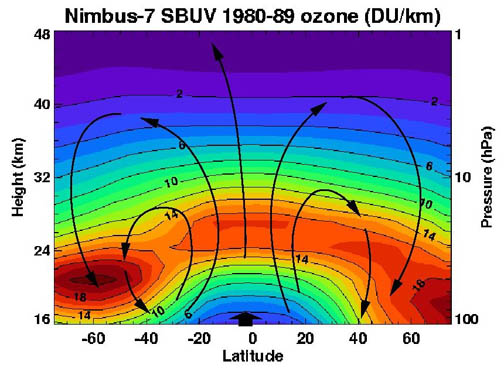
 The ozone layer can be depleted by
The ozone layer can be depleted by
National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
with ozone pollutions being one of six criteria pollutants. This regulation has proven to be effective since counties, cities, and tribal regions must abide by these standards and the EPA also provides assistance for each region to regulate contaminants. Effective presentation of information has also proven to be important in order to educate the general population of the existence and regulation of ozone depletion and contaminants. A scientific paper was written by Sheldon Ungar in which the author explores and studies how information about the depletion of the ozone, In 1978, the United States, Canada, and
In 1978, the United States, Canada, and
File:Ultraviolet image of the Cygnus Loop Nebula crop.jpg, This GALEX image of the Cygnus Loop nebula could not have been taken from the surface of the Earth because the ozone layer blocks the ultra-violet radiation emitted by the nebula.
Stratospheric ozone: an electronic textbookOzone Layer Info
(archived July 2, 2004) *Th
CAMS stratospheric ozone service
delivers maps, datasets, and validation reports about the past and current state of the ozone layer. {{Authority control Layer Ultraviolet radiation
 The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
that absorbs most of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
's ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
(O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in relation to other gases in the stratosphere. The ozone layer peaks at 8 to 15 parts per million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantity, dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction (chemistry), mass fraction.
Since t ...
of ozone, while the average ozone concentration in Earth's atmosphere as a whole is about 0.3 parts per million. The ozone layer is mainly found in the lower portion of the stratosphere, from approximately above Earth, although its thickness varies seasonally and geographically.
The ozone layer was discovered in 1913 by French physicists Charles Fabry and Henri Buisson. Measurements of the sun showed that the radiation sent out from its surface and reaching the ground on Earth is usually consistent with the spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
of a black body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium with its environment is ...
with a temperature in the range of , except that there was no radiation below a wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of about 310 nm at the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
end of the spectrum. It was deduced that the missing radiation was being absorbed by something in the atmosphere. Eventually the spectrum of the missing radiation was matched to only one known chemical, ozone. Its properties were explored in detail by the British meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists ...
G. M. B. Dobson, who developed a simple spectrophotometer (the Dobsonmeter) that could be used to measure stratospheric ozone from the ground. Between 1928 and 1958, Dobson established a worldwide network of ozone monitoring stations, which continue to operate to this day. The " Dobson unit" (DU), a convenient measure of the amount of ozone overhead, is named in his honor.
The ozone layer absorbs 97 to 99 percent of the Sun's medium-frequency ultraviolet light (from about 200 nm to 315 nm wavelength), which otherwise would potentially damage exposed life forms near the surface.
In 1985, atmospheric research revealed that the ozone layer was being depleted by chemicals released by industry, mainly chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volat ...
s (CFCs). Concerns that increased UV radiation due to ozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar ...
threatened life on Earth, including increased skin cancer in humans and other ecological problems, led to bans on the chemicals, and the latest evidence is that ozone depletion has slowed or stopped. The United Nations General Assembly has designated September 16 as the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer.
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
also has a thin ozone layer at an altitude of 100 kilometers above the planet's surface.
Sources
neoproterozoic oxygenation event
The Neoproterozoic Oxygenation Event (NOE), also called the Second Great Oxidation Event, was a geologic time interval between around 850 and 540 million years ago during the Neoproterozoic era, which saw a very significant increase in oxygen le ...
brought the fraction of oxygen in the atmosphere to about 20%.
The photochemical mechanisms that give rise to the ozone layer were discovered by the British physicist Sydney Chapman in 1930. Ozone in the Earth's stratosphere is created by ultraviolet light striking ordinary oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s containing two oxygen atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s (O2), splitting them into individual oxygen atoms ( atomic oxygen); the atomic oxygen then combines with unbroken O2 to create ozone, O3. The ozone molecule is unstable (although, in the stratosphere, long-lived) and when ultraviolet light hits ozone it splits into a molecule of O2 and an individual atom of oxygen, a continuing process called the ozone–oxygen cycle. Chemically, this can be described as:
: Ultraviolet light

sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin tha ...
; excessive exposure can also cause cataracts, immune system suppression, and genetic damage, resulting in problems such as skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
. The ozone layer (which absorbs from about 200 nm to 310 nm with a maximal absorption at about 250 nm) is very effective at screening out UV-B; for radiation with a wavelength of 290 nm, the intensity at the top of the atmosphere is 350 million times stronger than at the Earth's surface. Nevertheless, some UV-B, particularly at its longest wavelengths, reaches the surface, and is important for the skin's production of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
in mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
.
Ozone is transparent to most UV-A, so most of this longer-wavelength UV radiation reaches the surface, and it constitutes most of the UV reaching the Earth. This type of UV radiation is significantly less harmful to DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, although it may still potentially cause physical damage, premature aging of the skin, indirect genetic damage, and skin cancer.
Distribution in the stratosphere
 The thickness of the ozone layer varies worldwide and is generally thinner near the equator and thicker near the poles. Thickness refers to how much ozone is in a column over a given area and varies from season to season. The reasons for these variations are due to atmospheric circulation patterns and solar intensity.
The ozone layer ends gradually, but in general its upper limit is where air becomes too thin for UV light to generate much ozone, and its lower limit is where generated ozone blocks enough UV light to stop most ozone production.
In the homosphere, wind-driven movement is more important than relative gas weight. The majority of ozone is produced over the
The thickness of the ozone layer varies worldwide and is generally thinner near the equator and thicker near the poles. Thickness refers to how much ozone is in a column over a given area and varies from season to season. The reasons for these variations are due to atmospheric circulation patterns and solar intensity.
The ozone layer ends gradually, but in general its upper limit is where air becomes too thin for UV light to generate much ozone, and its lower limit is where generated ozone blocks enough UV light to stop most ozone production.
In the homosphere, wind-driven movement is more important than relative gas weight. The majority of ozone is produced over the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
and is transported toward the poles by stratospheric wind patterns. In the northern hemisphere these patterns, known as the Brewer–Dobson circulation, make the ozone layer thickest in the spring and thinnest in the fall. When ozone is produced by solar UV radiation in the tropics, it is done so by circulation lifting ozone-poor air out of the troposphere and into the stratosphere where the sun photolyzes oxygen molecules and turns them into ozone. Then, the ozone-rich air is carried to higher latitudes and drops into lower layers of the atmosphere.
Research has found that the ozone levels in the United States are highest in the spring months of April and May and lowest in October. While the total amount of ozone increases moving from the tropics to higher latitudes, the concentrations are greater in high northern latitudes than in high southern latitudes, with spring ozone columns in high northern latitudes occasionally exceeding 600 DU and averaging 450 DU whereas 400 DU constituted a usual maximum in the Antarctic before anthropogenic ozone depletion. This difference occurred naturally because of the weaker polar vortex and stronger Brewer–Dobson circulation in the northern hemisphere owing to that hemisphere's large mountain ranges and greater contrasts between land and ocean temperatures. The difference between high northern and southern latitudes has increased since the 1970s due to the ozone hole
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar ...
phenomenon. The highest amounts of ozone are found over the Arctic during the spring months of March and April, but the Antarctic has the lowest amounts of ozone during the summer months of September and October,

Depletion
 The ozone layer can be depleted by
The ozone layer can be depleted by free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabolic disorders
Metabolism
...
catalysts
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst ...
, including nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
(NO), nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
(N2O), hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
(OH), atomic chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
(Cl), and atomic bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
(Br). While there are natural sources for all of these species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, the concentrations of chlorine and bromine increased markedly in recent decades because of the release of large quantities of man-made organohalogen compounds, especially chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volat ...
s (CFCs) and bromofluorocarbons. Atmospheric components are not sorted out by weight in the homosphere because of wind-driven mixing that extends to an altitude of about 90 km, well above the ozone layer. So despite being heavier than diatomic nitrogen and oxygen, these highly stable compounds rise into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
, where Cl and Br radicals are liberated by the action of ultraviolet light. Each radical is then free to initiate and catalyze a chain reaction capable of breaking down over 100,000 ozone molecules. By 2009, nitrous oxide was the largest ozone-depleting substance (ODS) emitted through human activities.
The breakdown of ozone in the stratosphere results in reduced absorption of ultraviolet radiation. Consequently, unabsorbed and dangerous ultraviolet radiation reaches the Earth's surface at a higher intensity. Ozone levels have dropped by a worldwide average of about 4 percent since the late 1970s. For approximately 5 percent of the Earth's surface, around the north and south poles, much larger seasonal declines have been seen, and are described as "ozone holes". "Ozone holes" are actually patches in the ozone layer in which the ozone is thinner. The thinnest parts of the ozone are at the polar points of Earth's axis. The discovery of the annual depletion of ozone above the Antarctic was first announced by Joe Farman
Joseph Charles Farman CBE (7 August 1930 – 11 May 2013) was a British geophysicist who worked for the British Antarctic Survey. Together with Brian Gardiner and Jon Shanklin, he published the discovery of the ozone hole over Antarctica, having ...
, Brian Gardiner, and Jonathan Shanklin
Jonathan Shanklin (born 29 September 1953) is a meteorologist who has worked at the British Antarctic Survey since 1977. Together with Joe Farman and Brian G. Gardiner he discovered the "Ozone Hole" in the 1980s.
Shanklin has described his ro ...
, in a paper which appeared in ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' on May 16, 1985.
Regulation attempts have included but not have been limited to the Clean Air Act implemented by the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
. The Clean Air Act introduced the requirement oNational Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
with ozone pollutions being one of six criteria pollutants. This regulation has proven to be effective since counties, cities, and tribal regions must abide by these standards and the EPA also provides assistance for each region to regulate contaminants. Effective presentation of information has also proven to be important in order to educate the general population of the existence and regulation of ozone depletion and contaminants. A scientific paper was written by Sheldon Ungar in which the author explores and studies how information about the depletion of the ozone,
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, and various related topics. The ozone case was communicated to lay persons "with easy-to-understand bridging metaphors derived from the popular culture" and related to "immediate risks with everyday relevance". The specific metaphors used in the discussion (ozone shield, ozone hole) proved quite useful and, compared to global climate change, the ozone case was much more seen as a "hot issue" and imminent risk. Lay people were cautious about a depletion of the ozone layer and the risks of skin cancer.
Satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s burning up upon re-entry into Earth's atmosphere produce aluminum oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly ...
(Al2O3) nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s that endure in the atmosphere for decades. Estimates for 2022 alone were ~17 metric tons (~30kg of nanoparticles per ~250kg satellite). Increasing populations of satellite constellation
A satellite constellation is a group of artificial satellites working together as a system. Unlike a single satellite, a constellation can provide permanent global or near-global pass (spaceflight), coverage, such that at any time everywhere on E ...
s can eventually lead to significant ozone depletion.
"Bad" ozone can cause adverse health risks respiratory effects (difficulty breathing) and is proven to be an aggravator of respiratory illnesses such as asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
, and emphysema
Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the permanent enlargement of air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.
Emphysema is a lower respiratory tract di ...
. That is why many countries have set in place regulations to improve "good" ozone and prevent the increase of "bad" ozone in urban or residential areas. In terms of ozone protection (the preservation of "good" ozone) the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
has strict guidelines on what products are allowed to be bought, distributed, or used in specific areas. With effective regulation, the ozone is expected to heal over time.
 In 1978, the United States, Canada, and
In 1978, the United States, Canada, and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
enacted bans on CFC-containing aerosol spray
Aerosol spray is a type of dispensing system which creates an aerosol mist of liquid particles. It comprises a can or bottle that contains a payload, and a propellant under pressure. When the container's valve is opened, the payload is forced out ...
s that damage the ozone layer but the European Community rejected a similar proposal. In the U.S., chlorofluorocarbons continued to be used in other applications, such as refrigeration and industrial cleaning, until after the discovery of the Antarctic ozone hole in 1985. After negotiation of an international treaty (the Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol on Substances That Deplete the Ozone Layer is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 ...
), CFC production was capped at 1986 levels with commitments to long-term reductions. This allowed for a ten-year phase-in for developing countries (identified in Article 5 of the protocol). Since then, the treaty was amended to ban CFC production after 1995 in developed countries, and later in developing countries. All of the world's 197 countries have signed the treaty. Beginning January 1, 1996, only recycled or stockpiled CFCs were available for use in developed countries like the US. The production phaseout was possible because of efforts to ensure that there would be substitute chemicals and technologies for all ODS uses.
On August 2, 2003, scientists announced that the global depletion of the ozone layer might be slowing because of the international regulation of ozone-depleting substances. In a study organized by the American Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, Atmospheric science, atmospheric, Oceanography, ocean, Hydrology, hydrologic, Astronomy, space, and Planetary science, planetary scientists and enthusiasts that ...
, three satellites and three ground stations confirmed that the upper-atmosphere ozone-depletion rate slowed significantly over the previous decade. Some breakdown was expected to continue because of ODSs used by nations which have not banned them, and because of gases already in the stratosphere. Some ODSs, including CFCs, have very long atmospheric lifetimes ranging from 50 to over 100 years. It has been estimated that the ozone layer will recover to 1980 levels near the middle of the 21st century. A gradual trend toward "healing" was reported in 2016.
Compounds containing C–H bonds (such as hydrochlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, ...
s, or HCFCs) have been designed to replace CFCs in certain applications. These replacement compounds are more reactive and less likely to survive long enough in the atmosphere to reach the stratosphere where they could affect the ozone layer. While being less damaging than CFCs, HCFCs can have a negative impact on the ozone layer, so they are also being phased out. These in turn are being replaced by hydrofluorocarbon
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are synthetic organic compounds that contain fluorine and hydrogen atoms, and are the most common type of organofluorine compounds. Most are gases at room temperature and pressure. They are frequently used in air condit ...
s (HFCs) and other compounds that do not destroy stratospheric ozone at all.
The residual effects of CFCs accumulating within the atmosphere lead to a concentration gradient between the atmosphere and the ocean. This organohalogen compound dissolves into the ocean's surface waters and acts as a time-dependent tracer. This tracer helps scientists study ocean circulation by tracing biological, physical, and chemical pathways.
Implications for astronomy
As ozone in the atmosphere prevents most energetic ultraviolet radiation reaching the surface of the Earth, astronomical data in these wavelengths have to be gathered from satellites orbiting above the atmosphere and ozone layer. Most of the light from young hot stars is in the ultraviolet and so study of these wavelengths is important for studying the origins of galaxies. The Galaxy Evolution Explorer, GALEX, is an orbiting ultraviolet space telescope launched on April 28, 2003, which operated until early 2012.See also
* Cambrian explosion *Nuclear winter
Nuclear winter is a severe and prolonged anti-greenhouse effect, global climatic cooling effect that is hypothesized to occur after widespread firestorms following a large-scale Nuclear warfare, nuclear war. The hypothesis is based on the fact ...
*Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
* Short-lived climate pollutants
*United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
References
Further reading
; Science * * * Ritchie, Hannah, "What We Learned from Acid Rain: By working together, the nations of the world can solve climate change", ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...
'', vol. 330, no. 1 (January 2024), pp. 75–76. " untries will act only if they know others are willing to do the same. With acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists b ...
, they did act collectively.... We did something similar to restore Earth's protective ozone layer.... e cost of technology really matters.... In the past decade the price of solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
has fallen by more than 90 percent and that of wind energy
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity ...
by more than 70 percent. Battery costs have tumbled by 98 percent since 1990, bringing the price of electric car
An electric car or electric vehicle (EV) is a passenger car, passenger automobile that is propelled by an electric motor, electric traction motor, using electrical energy as the primary source of propulsion. The term normally refers to a p ...
s down with them.... e stance of elected officials matters more than their party
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a Hospitality, host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will oft ...
affiliation.... Change can happen – but not on its own. We need to drive it." (p. 76.)
* United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
(2010). ''Environmental Effects of Ozone Depletion and its Interactions with Climate Change: 2010 Assessment''. Nairobi: UNEP.
*
*
; Policy
*
*
*
*
* (Ambassador Benedick was the Chief U.S. Negotiator at the meetings that resulted in the Montreal Protocol.)
*
*
*
External links
Stratospheric ozone: an electronic textbook
(archived July 2, 2004) *Th
CAMS stratospheric ozone service
delivers maps, datasets, and validation reports about the past and current state of the ozone layer. {{Authority control Layer Ultraviolet radiation