Oxazines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Oxazines are
Oxazines are

File:Structural formula of morpholine.svg,
Development of polymeric materials as a class of benzoxazines
heterocyclic
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, proper ...
organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s containing one oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and one nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
atom in a cyclohexa-1,4-diene
1,4-Cyclohexadiene is an organic compound with the formula C6H8. It is a colourless, flammable liquid that is of academic interest as a prototype of a large class of related compounds called terpenoids, an example being γ-terpinene. An isomer of ...
ring (a doubly unsaturated six-membered ring). Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
s exist depending on the relative position of the heteroatom
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen.
Organic chemistry
In practice, the term is mainly used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecular ...
s and relative position of the double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
s.
By extension, the derivatives are also referred to as oxazines; examples include ifosfamide
Ifosfamide, sold under the brand name Ifex among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, small cell lung cancer, c ...
and morpholine
Morpholine is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound having the chemical formula oxygen, O(carbon, Chydrogen, H2CH2)2nitrogen, NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a bas ...
(tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine). A commercially available dihydro-1,3-oxazine is a reagent in the Meyers synthesis of aldehydes. Fluorescent dyes such as Nile red
Nile red (also known as Nile blue oxazone) is a lipophilic stain. Nile red stains intracellular lipid droplets yellow. In most polar solvents, Nile red will not fluoresce; however, when in a lipid-rich environment, it can be intensely fluoresce ...
and Nile blue are based on the aromatic compound benzophenoxazine. Cinnabarine and cinnabaric acid are two naturally occurring dioxazines, being derived from biodegradation of tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
.
Dioxazines
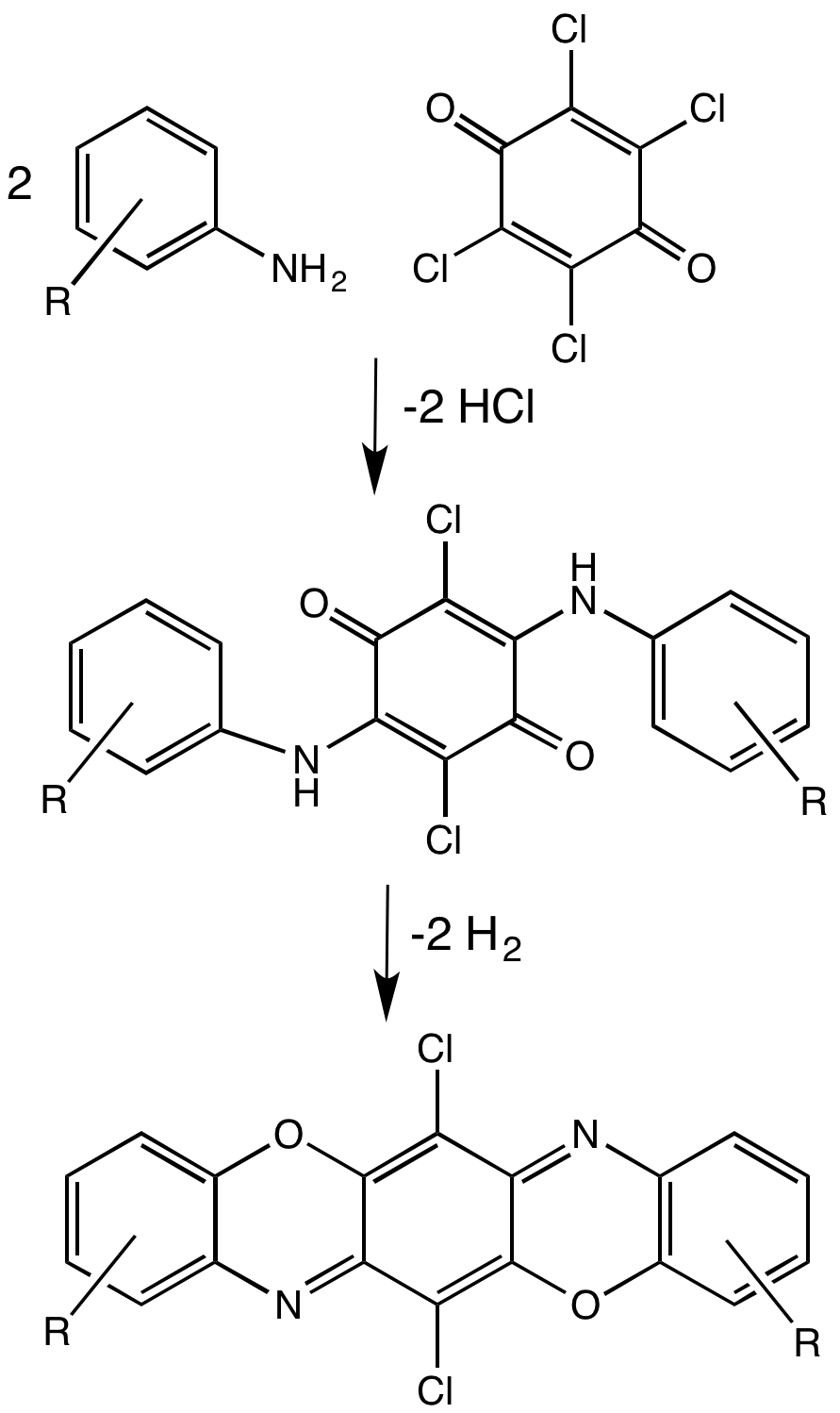
Dioxazines are pentacyclic compounds consisting of two oxazine subunits. A commercially important example is the pigmentpigment violet 23
Pigment violet 23 is an organic compound that is a commercial pigment. It is member of the dioxazine family of heterocyclic compounds, but derived from carbazoles. It is prepared by condensation of chloranil and 3-amino-''N''-ethylcarbazole. It ...
.

Benzoxazines

Benzoxazine
Benzoxazines are a group of isomeric bicyclic heterocyclic chemical compounds that consist of a benzene ring fused to an oxazine ring. The different isomers depend on the relative positions of the oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the oxazine ring, on ...
s are bicyclic compounds formed by the ring fusion of a benzene ring with an oxazine. Polybenzoxazine
Polybenzoxazines, also called benzoxazine resins, are cured polymerization products derived from benzoxazine monomers.
Monomers
Benzoxazines are bicyclic heterocyclic compounds containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom in a doubly unsaturated ...
s are a class of polymers formed by the reaction of phenols, formaldehyde, and primary amines which on heating to ~200 °C (~400 °F) polymerise to produce polybenzoxazine networks. The resulting high molecular weight thermoset polymer matrix
A thermoset polymer matrix is a synthetic polymer reinforcement where polymers act as binder or matrix to secure in place incorporated particulates, fibres or other reinforcements. They were first developed for structural applications, such as gla ...
composites are used where enhanced mechanical performance, flame and fire resistance compared to epoxy and phenolic resins is required.
Physical properties
Oxazine dyes exhibitsolvatochromism
In chemistry, solvatochromism is the phenomenon observed when the colour of a solution is different when the solute is dissolved in different solvents.
The solvatochromic effect is the way the spectrum of a substance (the solute) varies when th ...
.
Images
Morpholine
Morpholine is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound having the chemical formula oxygen, O(carbon, Chydrogen, H2CH2)2nitrogen, NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a bas ...
File:10H-phenoxazine 200.svg, Phenoxazine
Phenoxazine is a heterocyclic compound. The structure of phenoxazine consists of an oxazine fused to two benzene rings. It occurs as the central core of a number of naturally occurring chemical compounds such as dactinomycin and litmus. The dyes ...
File:C.I. Pigment Violet 23.svg, Pigment violet 23
Pigment violet 23 is an organic compound that is a commercial pigment. It is member of the dioxazine family of heterocyclic compounds, but derived from carbazoles. It is prepared by condensation of chloranil and 3-amino-''N''-ethylcarbazole. It ...
is a commercially useful pigment.
References
External links
* {{MeshName, OxazinesDevelopment of polymeric materials as a class of benzoxazines