|
Pigment Violet 23
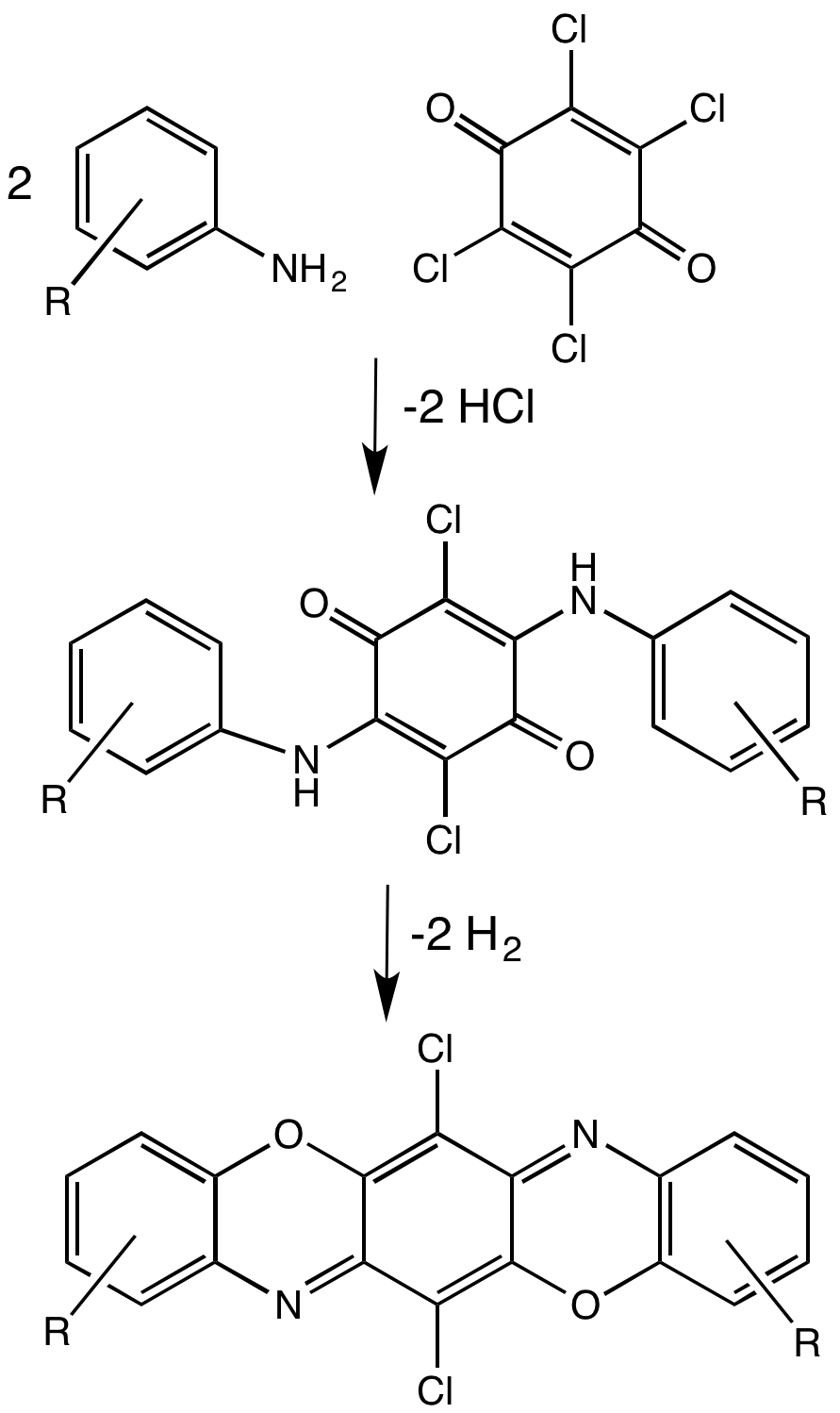
Pigment violet 23 is an organic compound that is a commercial pigment. It is member of the dioxazine family of heterocyclic compounds, but derived from carbazoles. It is prepared by condensation of chloranil and 3-amino-''N''-ethylcarbazole. It has a centrosymmetric angular structure. For many years, the structure was assigned, incorrectly, as having a "linear structure" ( EC no. 228-767-9, CAS RN 6358-30-1) which differ in terms of the carbazole ring fusion. Pigment violet 23 is prepared by condensation of an aniline with chloranil Chloranil is a quinone with the molecular formula C6Cl4O2. Also known as tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone, it is a yellow solid. Like the parent benzoquinone, chloranil is a planar molecule J.-M. Lü, S. V. Rosokha, I. S. Neretin and J. K. Kochi, "Qui ....Horst Tappe, Walter Helmling, Peter Mischke, Karl Rebsamen, Uwe Reiher, Werner Russ, Ludwig Schläfer and Petra Vermehren "Reactive Dyes"in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2000, Wiley-V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compound, inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic chemistry, inorganic, organic chemistry, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazine
Oxazines are heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compounds containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom in a cyclohexa-1,4-diene ring (a doubly unsaturated six-membered ring). Isomers exist depending on the relative position of the heteroatoms and relative position of the double bonds. By extension, the derivatives are also referred to as oxazines; examples include ifosfamide and morpholine (tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine). A commercially available dihydro-1,3-oxazine is a reagent in the Meyers synthesis of aldehydes. Fluorescent dyes such as Nile red and Nile blue are based on the aromatic compound benzophenoxazine. Cinnabarine and cinnabaric acid are two naturally occurring dioxazines, being derived from biodegradation of tryptophan. Dioxazines Dioxazines are pentacyclic compounds consisting of two oxazine subunits. A commercially important example is the pigment pigment violet 23. Benzoxazines Benzoxazines are bicyclic compounds formed by the ring fusion of a benzene ring w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compound
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbazole
Carbazole is an aromatic Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound. It has a tricyclic structure, consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused on either side of a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound's structure is based on the indole structure, but in which a second benzene ring is fused onto the five-membered ring at the 2–3 position of indole (equivalent to the 9a–4a double bond in carbazole, respectively). Carbazole is a constituent of tobacco smoke. History Carl Graebe and Carl Andreas Glaser, Carl Glaser first isolated the compound from coal tar in 1872. Production Few carbazole production methods are economically viable, due to limited demand. During coal tar distillation, carbazole concentrates in the anthracene distillate and must be removed before anthraquinone production; that waste product is the major industrial carbazole source. Polar compounds (e.g., ketones) selectively precipitate it from the anthracene; a more modern techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloranil
Chloranil is a quinone with the molecular formula C6Cl4O2. Also known as tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone, it is a yellow solid. Like the parent benzoquinone, chloranil is a planar molecule J.-M. Lü, S. V. Rosokha, I. S. Neretin and J. K. Kochi, "Quinones as Electron Acceptors. X-Ray Structures, Spectral (EPR, UV-vis) Characteristics and Electron-Transfer Reactivities of Their Reduced Anion Radicals as Separated vs Contact Ion Pairs" Journal of the American Chemical Society 2006 128, 16708-16719. that functions as a mild oxidant. Synthesis and use as reagent Chloranil is produced by chlorination of phenol to give hexachlorocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one ("hexachlorophenol"). Hydrolysis of the dichloromethylene group in this dienone gives chloranil: :C6H5OH + 6 Cl2 → C6Cl6O + 6 HCl :C6Cl6O + H2O → C6Cl4O2 + 2 HCl Chloroanil serves as a hydrogen acceptor. It is more electrophilic than quinone itself. It is used for the aromatization reactions, such as the conversion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Community Number
European, or Europeans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** European Union citizenship ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (other) * The Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Fusion
In organic chemistry, annulation (; occasionally annelation) is a chemical reaction in which a new Ring (chemistry), ring is constructed on a molecule. : Examples are the Robinson annulation, Danheiser annulation and certain cycloadditions. Annular molecules are constructed from side-on condensed cyclic segments, for example helicenes and acenes. In transannulation a bicyclic molecule is created by Intramolecular reaction, intramolecular carbon-carbon bond formation in a large monocyclic ring. An example is the samarium(II) iodide induced ketone - alkene cyclization of ''5-methylenecyclooctanone'' which proceeds through a ketyl intermediate: : Benzannulation The term benzannulated compounds refers to derivatives of cyclic compounds (usually aromatic) which are fused to a benzene ring. Examples are listed in the table below: In contemporary chemical literature, the term benzannulation also means "construction of benzene rings from acyclic precursors".image:VerkadeProtn.svg, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |