Over-determined System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In mathematics, a system of equations is considered overdetermined if there are more equations than unknowns. An overdetermined system is almost always inconsistent (it has no solution) when constructed with random coefficients. However, an overdetermined system will have solutions in some cases, for example if some equation occurs several times in the system, or if some equations are linear combinations of the others.
The terminology can be described in terms of the concept of
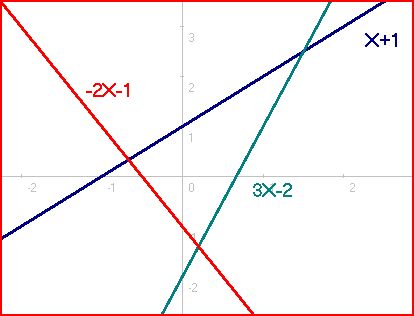



 Consider the system of 3 equations and 2 unknowns ( and ), which is overdetermined because 3 > 2, and which corresponds to Diagram #1:
There is one solution for each pair of linear equations: for the first and second equations (0.2, −1.4), for the first and third (−2/3, 1/3), and for the second and third (1.5, 2.5). However, there is no solution that satisfies all three simultaneously. Diagrams #2 and 3 show other configurations that are inconsistent because no point is on all of the lines. Systems of this variety are deemed inconsistent.
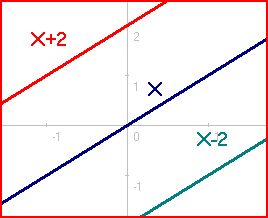
The only cases where the overdetermined system does in fact have a solution are demonstrated in Diagrams #4, 5, and 6. These exceptions can occur only when the overdetermined system contains enough linearly dependent equations that the number of independent equations does not exceed the number of unknowns. Linear dependence means that some equations can be obtained from linearly combining other equations. For example, ''Y'' = ''X'' + 1 and 2''Y'' = 2''X'' + 2 are linearly dependent equations because the second one can be obtained by taking twice the first one.
Consider the system of 3 equations and 2 unknowns ( and ), which is overdetermined because 3 > 2, and which corresponds to Diagram #1:
There is one solution for each pair of linear equations: for the first and second equations (0.2, −1.4), for the first and third (−2/3, 1/3), and for the second and third (1.5, 2.5). However, there is no solution that satisfies all three simultaneously. Diagrams #2 and 3 show other configurations that are inconsistent because no point is on all of the lines. Systems of this variety are deemed inconsistent.
The only cases where the overdetermined system does in fact have a solution are demonstrated in Diagrams #4, 5, and 6. These exceptions can occur only when the overdetermined system contains enough linearly dependent equations that the number of independent equations does not exceed the number of unknowns. Linear dependence means that some equations can be obtained from linearly combining other equations. For example, ''Y'' = ''X'' + 1 and 2''Y'' = 2''X'' + 2 are linearly dependent equations because the second one can be obtained by taking twice the first one.
constraint counting In mathematics, constraint counting is counting the number of constraints in order to compare it with the number of variables, parameters, etc. that are free to be determined, the idea being that in most cases the number of independent choices tha ...
. Each unknown can be seen as an available degree of freedom. Each equation introduced into the system can be viewed as a constraint
Constraint may refer to:
* Constraint (computer-aided design), a demarcation of geometrical characteristics between two or more entities or solid modeling bodies
* Constraint (mathematics), a condition of an optimization problem that the solution ...
that restricts one degree of freedom.
Therefore, the critical case occurs when the number of equations and the number of free variables are equal. For every variable giving a degree of freedom, there exists a corresponding constraint. The ''overdetermined'' case occurs when the system has been overconstrained — that is, when the equations outnumber the unknowns. In contrast, the '' underdetermined'' case occurs when the system has been underconstrained — that is, when the number of equations is fewer than the number of unknowns. Such systems usually have an infinite number of solutions.
Systems of equations
An example in two dimensions
Matrix form
Any system of linear equations can be written as amatrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
equation.
The previous system of equations (in Diagram #1) can be written as follows:
Notice that the rows of the coefficient matrix (corresponding to equations) outnumber the columns (corresponding to unknowns), meaning that the system is overdetermined. The rank of this matrix is 2, which corresponds to the number of dependent variables in the system. A linear system is consistent if and only if
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (shortened as "iff") is a biconditional logical connective between statements, where either both statements are true or both are false.
The connective is bi ...
the coefficient matrix has the same rank as its augmented matrix (the coefficient matrix with an extra column added, that column being the column vector of constants). The augmented matrix has rank 3, so the system is inconsistent. The nullity is 0, which means that the null space contains only the zero vector and thus has no basis.
In linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as:
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as:
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matric ...
the concepts of row space, column space
In linear algebra, the column space (also called the range or image) of a matrix ''A'' is the span (set of all possible linear combinations) of its column vectors. The column space of a matrix is the image or range of the corresponding mat ...
and null space are important for determining the properties of matrices. The informal discussion of constraints and degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
above relates directly to these more formal concepts.
Homogeneous case
The homogeneous case (in which all constant terms are zero) is always consistent (because there is a trivial, all-zero solution). There are two cases, depending on the number of linearly dependent equations: either there is just the trivial solution, or there is the trivial solution plus an infinite set of other solutions. Consider the system of linear equations: ''L''''i'' = 0 for 1 ≤ ''i'' ≤ ''M'', and variables ''X''1, ''X''2, ..., ''X''''N'', where each ''L''''i'' is a weighted sum of the ''X''''i''s. Then ''X''1 = ''X''2 = ⋯ = ''X''''N'' = 0 is always a solution. When ''M'' < ''N'' the system is ''underdetermined'' and there are always an infinitude of further solutions. In fact the dimension of the space of solutions is always at least ''N'' − ''M''. For ''M'' ≥ ''N'', there may be no solution other than all values being 0. There will be an infinitude of other solutions only when the system of equations has enough dependencies (linearly dependent equations) that the number of independent equations is at most ''N'' − 1. But with ''M'' ≥ ''N'' the number of independent equations could be as high as ''N'', in which case the trivial solution is the only one.Non-homogeneous case
In systems of linear equations, ''L''''i''=''c''''i'' for 1 ≤ ''i'' ≤ ''M'', in variables ''X''1, ''X''2, ..., ''X''''N'' the equations are sometimes linearly dependent; in fact the number of linearly independent equations cannot exceed ''N''+1. We have the following possible cases for an overdetermined system with ''N'' unknowns and ''M'' equations (''M''>''N''). * ''M'' = ''N''+1 and all M equations arelinearly independent
In the theory of vector spaces, a set of vectors is said to be if there is a nontrivial linear combination of the vectors that equals the zero vector. If no such linear combination exists, then the vectors are said to be . These concepts ...
. This case yields no solution. Example: ''x'' = 1, ''x'' = 2.
* ''M'' > ''N'' but only ''K'' equations (''K'' < ''M'' and ''K'' ≤ ''N''+1) are linearly independent. There exist three possible sub-cases of this:
**''K'' = ''N''+1. This case yields no solutions. Example: 2''x'' = 2, ''x'' = 1, ''x'' = 2.
**''K'' = ''N''. This case yields either a single solution or no solution, the latter occurring when the coefficient vector of one equation can be replicated by a weighted sum of the coefficient vectors of the other equations but that weighted sum applied to the constant terms of the other equations does not replicate the one equation's constant term. Example with one solution: 2''x'' = 2, ''x'' = 1. Example with no solution: 2''x'' + 2''y'' = 2, ''x'' + ''y'' = 1, ''x'' + ''y'' = 3.
**''K'' < ''N''. This case yields either infinitely many solutions or no solution, the latter occurring as in the previous sub-case. Example with infinitely many solutions: 3''x'' + 3''y'' = 3, 2''x'' + 2''y'' = 2, ''x'' + ''y'' = 1. Example with no solution: 3''x'' + 3''y'' + 3''z'' = 3, 2''x'' + 2''y'' + 2''z'' = 2, ''x'' + ''y'' + ''z'' = 1, ''x'' + ''y'' + ''z'' = 4.
These results may be easier to understand by putting the augmented matrix of the coefficients of the system in row echelon form by using Gaussian elimination
In mathematics, Gaussian elimination, also known as row reduction, is an algorithm for solving systems of linear equations. It consists of a sequence of operations performed on the corresponding matrix of coefficients. This method can also be used ...
. This row echelon form is the augmented matrix of a system of equations that is equivalent to the given system (it has exactly the same solutions). The number of independent equations in the original system is the number of non-zero rows in the echelon form. The system is inconsistent (no solution) if and only if the last non-zero row in echelon form has only one non-zero entry that is in the last column (giving an equation 0 = c where c is a non-zero constant). Otherwise, there is exactly one solution when the number of non-zero rows in echelon form is equal to the number of unknowns, and there are infinitely many solutions when the number of non-zero rows is lower than the number of variables.
Putting it another way, according to the Rouché–Capelli theorem, any system of equations (overdetermined or otherwise) is inconsistent if the rank of the augmented matrix is greater than the rank of the coefficient matrix. If, on the other hand, the ranks of these two matrices are equal, the system must have at least one solution. The solution is unique if and only if the rank equals the number of variables. Otherwise the general solution has ''k'' free parameters where ''k'' is the difference between the number of variables and the rank; hence in such a case there are an infinitude of solutions.
Exact solutions
All exact solutions can be obtained, or it can be shown that none exist, using matrix algebra. See System of linear equations#Matrix solution.Approximate solutions
The method of ordinary least squares can be used to find an approximate solution to overdetermined systems. For the system the least squares formula is obtained from the problem the solution of which can be written with thenormal equations
In statistics, ordinary least squares (OLS) is a type of linear least squares method for choosing the unknown parameters in a linear regression model (with fixed level-one effects of a linear function of a set of explanatory variables) by the ...
,
where indicates a matrix transpose, ''provided'' exists (that is, provided ''A'' has full column rank). With this formula an approximate solution is found when no exact solution exists, and it gives an exact solution when one does exist. However, to achieve good numerical accuracy, using the QR factorization of ''A'' to solve the least squares problem is preferred.
In general use
The concept can also be applied to more general systems of equations, such assystems of polynomial equations
A system of polynomial equations (sometimes simply a polynomial system) is a set of simultaneous equations where the are polynomials in several variables, say , over some field .
A ''solution'' of a polynomial system is a set of values for the s ...
or partial differential equations
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function.
The function is often thought of as an "unknown" to be solved for, similarly to ...
. In the case of the systems of polynomial equations, it may happen that an overdetermined system has a solution, but that no one equation is a consequence of the others and that, when removing any equation, the new system has more solutions. For example, has the single solution but each equation by itself has two solutions.
See also
* Underdetermined system * Rouché-Capelli (or, Rouché-Frobenius) theorem *Integrability condition In mathematics, certain systems of partial differential equations are usefully formulated, from the point of view of their underlying geometric and algebraic structure, in terms of a system of differential forms. The idea is to take advantage of t ...
*Least squares
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems (sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns) by minimizing the sum of the squares of the r ...
* Consistency proof
* Compressed sensing
* Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse
References
{{reflist Curve fitting Linear algebra Partial differential equations