Osmium Compounds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Osmium compounds are compounds containing the element

Os + 2O2 ->
OsO4 is a 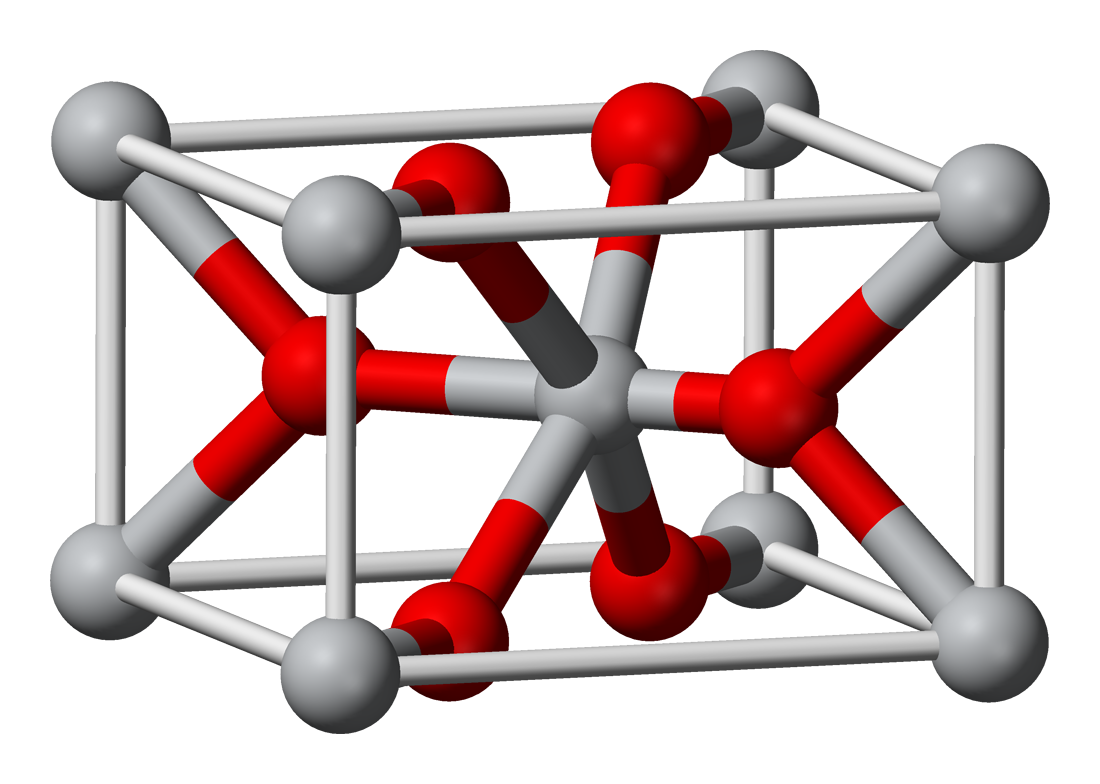 Osmium dioxide is another known oxide of osmium, which can be obtained by the reaction of
Osmium dioxide is another known oxide of osmium, which can be obtained by the reaction of
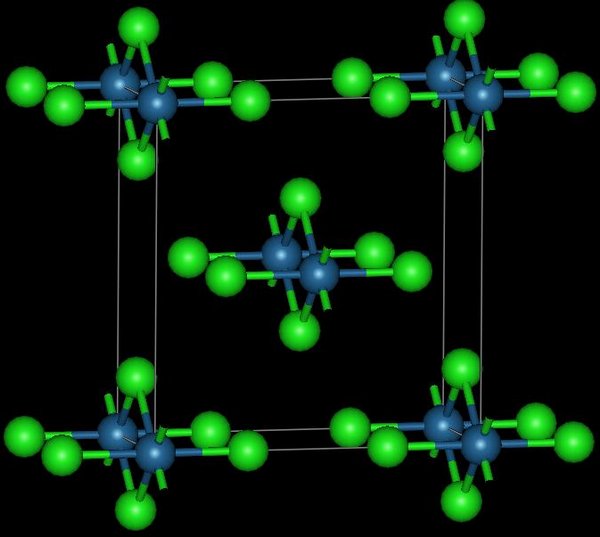 Osmium tetrachloride exists in two crystalline forms, and is used to prepare other osmium complexes. It was first reported in 1909 as the product of chlorination of osmium metal.
This route affords the high temperature polymorph:
:Os + 2 Cl2 → OsCl4
This reddish-black polymorph is
Osmium tetrachloride exists in two crystalline forms, and is used to prepare other osmium complexes. It was first reported in 1909 as the product of chlorination of osmium metal.
This route affords the high temperature polymorph:
:Os + 2 Cl2 → OsCl4
This reddish-black polymorph is
 Osmium borides are notable for their potentially high hardness. It is thought that a combination of high electron density of osmium with the strength of boron-osmium
Osmium borides are notable for their potentially high hardness. It is thought that a combination of high electron density of osmium with the strength of boron-osmium
osmium
Osmium () is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, trace element in a ...
(Os). Osmium forms compounds with oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
s ranging from −2 to +8. The most common oxidation states are +2, +3, +4, and +8. The +8 oxidation state is notable for being the highest attained by any chemical element aside from iridium's +9 and is encountered only in xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
, ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is unreactive to most chem ...
, hassium
Hassium is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Hs and atomic number 108. It is highly radioactive: its most stable known isotopes have half-life, half-lives of about ten seconds. One of its isotopes, Hs ...
, iridium
Iridium is a chemical element; it has the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. This very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density ...
, and plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four ...
. The oxidation states −1 and −2 represented by the two reactive compounds and are used in the synthesis of osmium cluster compounds.
Oxides

Osmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ...
is the most notable compound of osmium, having many uses. The name "osmium" even derives from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
"" because of the smell of osmium tetroxide. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the solid is volatile. Its volatility, along with its strong oxidizing power, is the origin of its quite serious toxicity - inhalation provides a very effective route for the compound to react with tissue. The compound is colourless, but most samples appear yellow. This is most likely due to the presence of the impurity OsO2, which is yellow-brown in colour. In biology, its property of binding to lipids has made it a widely used stain in electron microscopy. OsO4 is formed slowly when osmium powder reacts with O2 at ambient temperature. Reaction of bulk solid requires heating to 400 °C.
:Delta T
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier
...
OsO4Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any ...
and a mild oxidant. It reacts with alkaline aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water ...
to give the perosmate anion . This species is easily reduced to osmate
Osmate was a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Varese in the Italian region Lombardy, located about northwest of Milan and about southwest of Varese. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 550 and an area of .All demographics ...
anion, . When the Lewis base
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
is an amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
, adducts are also formed. Thus OsO4 can be stored in the form of osmeth, in which OsO4 is complexed with hexamine
Hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA), also known as 1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane, is a heterocyclic organic compound with diverse applications. It has the chemical formula (CH2)6N4 and is a white crystalline compound that is highly soluble in water and p ...
. Osmeth can be dissolved in tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
(THF) and diluted in an aqueous buffer solution
A buffer solution is a solution where the pH does not change significantly on dilution or if an acid or base is added at constant temperature. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solution ...
to make a dilute (0.25%) working solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solu ...
of OsO4. With tert-BuNH2, the imido
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications ...
derivative is produced:
:OsO4 + Me3CNH2 → OsO3(NCMe3) + H2O
Similarly, with NH3 one obtains the nitrido complex
Metal nitrido complexes are coordination compounds and metal clusters that contain an atom of nitrogen bound only to transition metals. These compounds are ''molecular'', i.e. discrete in contrast to the polymeric, dense nitride materials that are ...
:
:OsO4 + NH3 + KOH → K s(N)O3+ 2 H2O
The s(N)O3sup>− anion is isoelectronic and isostructural with OsO4. OsO4 is very soluble in tert-butyl alcohol
''tert''-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as ''t''-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. ''tert''-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near ...
. In solution, it is readily reduced by hydrogen to osmium metal. The suspended osmium metal can be used to catalyze
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated ...
of a wide variety of organic chemicals containing double or triple bonds.
:OsO4 + 4 H2 → Os + 4 H2O
OsO4 undergoes "reductive carbonylation" with carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
in methanol at 400 K and 200 sbar to produce the triangular cluster Os3(CO)12:
:3 OsO4 + 24 CO → Os3(CO)12 + 12 CO2
 Osmium dioxide is another known oxide of osmium, which can be obtained by the reaction of
Osmium dioxide is another known oxide of osmium, which can be obtained by the reaction of osmium
Osmium () is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, trace element in a ...
with a variety of oxidizing agents, including, sodium chlorate
Sodium chlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na ClO3. It is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water. It is hygroscopic. It decomposes above 300 °C to release oxygen and leaves sodium chloride. Sever ...
, osmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ...
, and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
at about 600 °C. It does not dissolve in water, but is attacked by dilute hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
. The crystals have rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite.
Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at vis ...
structure. Unlike osmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ...
, OsO2 is not toxic.
Halides
Fluorides
Osmium hexafluoride
Osmium hexafluoride, also osmium(VI) fluoride, (OsF6) is a compound of osmium and fluorine, and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Synthesis
Osmium hexafluoride is made by a direct reaction of osmium metal exposed to an excess of e ...
is one of the 17 known binary hexafluorides, which can be made by the direct reaction of osmium metal exposed to an excess of elemental fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extre ...
gas at 300 °C. It is a yellow crystalline solid that melts at 33.4 °C and boils at 47.5 °C.''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
The ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' is a comprehensive one-volume reference resource for science research. First published in 1914, it is currently () in its 105th edition, published in 2024. It is known colloquially among chemists as ...
'', 90th Edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2009, , Section 4, ''Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds'', p. 4-85. The solid structure measured at −140 °C is orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, res ...
space group ''Pnma''. Lattice parameters are ''a'' = 9.387 Å, ''b'' = 8.543 Å, and ''c'' = 4.944 Å. There are four formula unit
In chemistry, a formula unit is the smallest unit of a non-molecular substance, such as an ionic compound, covalent network solid, or metal. It can also refer to the chemical formula for that unit. Those structures do not consist of discrete mol ...
s (in this case, discrete molecules) per unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector
In mathematics, a unit vector i ...
, giving a density of 5.09 g·cm−3. The OsF6 molecule itself (the form important for the liquid or gas phase) has octahedral molecular geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The o ...
, which has point group ('' Oh''). The Os–F bond length
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between Atomic nucleus, nuclei of two chemical bond, bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a Transferability (chemistry), transferable property of a bond between at ...
is 1.827 Å. Partial hydrolysis of OsF6 produces OsOF4. Osmium pentafluoride
Osmium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula OsF5. It is a blue-green solid. Like the pentafluorides of Ru, Rh, and Ir, OsF5 exists as a tetramer in the solid state.
Preparation
Osmium pentafluoride can be prepared by reducti ...
is a tetramer in the solid state that can be prepared by reduction of osmium hexafluoride
Osmium hexafluoride, also osmium(VI) fluoride, (OsF6) is a compound of osmium and fluorine, and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Synthesis
Osmium hexafluoride is made by a direct reaction of osmium metal exposed to an excess of e ...
with iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
as a solution in iodine pentafluoride
Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in speci ...
:
:10 OsF6 + I2 → 10 OsF5 + 2 IF5
Chlorides
 Osmium tetrachloride exists in two crystalline forms, and is used to prepare other osmium complexes. It was first reported in 1909 as the product of chlorination of osmium metal.
This route affords the high temperature polymorph:
:Os + 2 Cl2 → OsCl4
This reddish-black polymorph is
Osmium tetrachloride exists in two crystalline forms, and is used to prepare other osmium complexes. It was first reported in 1909 as the product of chlorination of osmium metal.
This route affords the high temperature polymorph:
:Os + 2 Cl2 → OsCl4
This reddish-black polymorph is orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, res ...
and adopts a structure in which osmium centres are octahedrally coordinated, sharing opposite edges of the OsCl6 octahedra to form a chain. A brown, apparently cubic polymorph forms upon reduction of osmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ...
with thionyl chloride
Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a moderately Volatility (chemistry), volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a Halogenation, chlorinating reagen ...
:
:OsO4 + 4 SOCl2 → OsCl4 + 2 Cl2 + 4 SO2
Osmium tetroxide dissolves in hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
to give the hexachloroosmate anion:
:OsO4 + 10 HCl → H2OsCl6 + 2 Cl2 + 4 H2O
Bromides
Osmium tetrabromide is a black solid that can be produced by heating osmium tetrachloride andbromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
under pressure. As determined by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
, osmium tetrabromide is an inorganic polymer. It is isomorphous with platinum tetrabromide and technetium tetrachloride. As such, osmium is in octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (: octahedra or octahedrons) is any polyhedron with eight faces. One special case is the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. Many types of i ...
coordination. Each osmium center bonds to four doubly bridging bromide ligands and two mutually cis terminal bromide ligands. Osmium tribromide, OsBr3, is the only other binary osmium bromide is that has been crystallized.
Iodides
Osmium(I) iodide is a metallic grey solid produced by the reaction ofosmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ...
and hydroiodic acid
Hydroiodic acid (or hydriodic acid) is a colorless liquid. It is an aqueous solution of hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula . It is a strong acid, in which hydrogen iodide is ionized completely in an aqueous solution. Concentrated aqueous ...
heated in a water bath for 48 hours in a carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
atmosphere. It is an amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is a characteristic of a crystal. The terms "glass" and "glassy solid" are sometimes used synonymousl ...
compound. Osmium(II) iodide is a black solid produced by the reaction of osmium tetroxide and hydroiodic acid at 250 °C in nitrogen:
:OsO4 + HI → OsI2 + H2O
This compound decomposes in contact with water. Osmium(III) iodide is a black solid that is produced by heating hexaiodoosmic acid (H2OsI6). This compound is insoluble in water. Osmium(IV) iodide has been claimed to exist, although the supposed way to prepare it (osmic acid, OsO2•2H2O, with hydroiodic acid
Hydroiodic acid (or hydriodic acid) is a colorless liquid. It is an aqueous solution of hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula . It is a strong acid, in which hydrogen iodide is ionized completely in an aqueous solution. Concentrated aqueous ...
) produced dihydroxonium hexaiodoosmate instead of the tetraiodo compound, and instead contained mono, di and tri-iodo osmium compounds.
Borides
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
s will make osmium borides superhard materials
A superhard material is a material with a hardness value exceeding 40 gigapascals ( GPa) when measured by the Vickers hardness test. They are virtually incompressible solids with high electron density and high bond covalency. As a result of their ...
, however this has not been demonstrated yet. For example, OsB2 is hard (hardness comparable to that of sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire ...
), but not superhard. These borides are produced in vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent formation
of osmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ...
, which is a hazardous compound. Synthesis occurs at high temperatures (~1000 °C) from a mixture of MgB2 and OsCl3. Three osmium borides are known: OsB, Os2B3 and OsB2. The first two have hexagonal structure, similar to that of rhenium diboride
Rhenium diboride (ReB2) is a synthetic high-hardness material that was first synthesized in 1962. The compound is formed from a mixture of rhenium, noted for its resistance to high pressure, and boron, which forms short, strong covalent bonds wi ...
. Osmium diboride was first also sought as hexagonal, but one of its phases was later reassigned to orthorhombic. In recent methods of synthesis, it has also been found that a hexagonal phase of OsB2 exists with a similar structure to ReB2.
See also
*Iron compounds
Iron shows the characteristic chemical properties of the transition metals, namely the ability to form variable oxidation states differing by steps of one and a very large Coordination complex, coordination and Organometallic chemistry, organomet ...
* Ruthenium compounds
Ruthenium compounds are compounds containing the element ruthenium (Ru). Ruthenium compounds can have oxidation states ranging from 0 to +8, and −2. The properties of ruthenium and osmium Chemical compound, compounds are often similar. The +2, ...
* Rhenium compounds Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from −3 to +7 except −2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are t ...
* Iridium compounds
Iridium compounds are compounds containing the element iridium (Ir). Iridium forms compounds in oxidation states between −3 and +9, but the most common oxidation states are +1, +2, +3, and +4. Well-characterized compounds containing iridium in ...
References
{{Chemical compounds by element Compounds Chemical compounds by element