Opportunity Rover on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Opportunity'', also known as MER-B (Mars Exploration Rover – B) or MER-1, and nicknamed Oppy, is a
 ''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the
''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the
 ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' were launched a month apart, on June 10 and July 8, 2003, and both reached the Martian surface by January 2004. ''Opportunity''s launch was managed by NASA's Launch Services Program. This was the first launch of the
''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' were launched a month apart, on June 10 and July 8, 2003, and both reached the Martian surface by January 2004. ''Opportunity''s launch was managed by NASA's Launch Services Program. This was the first launch of the  On January 25, 2004 (GMT) (January 24, 2004, PST), the airbag-protected landing craft settled onto the surface of Mars in the Eagle crater.
From its initial landing into an
On January 25, 2004 (GMT) (January 24, 2004, PST), the airbag-protected landing craft settled onto the surface of Mars in the Eagle crater.
From its initial landing into an  ''Opportunity''s total odometry by June 10, 2018 (sol 5111), was , while the dust factor was 10.8. Since January 2013, the solar array dust factor (one of the determinants of solar power production) varied from a relatively dusty 0.467 on December 5, 2013 (sol 3507), to a relatively clean 0.964 on May 13, 2014 (sol 3662).
In December 2014, NASA reported that ''Opportunity'' was suffering from "
''Opportunity''s total odometry by June 10, 2018 (sol 5111), was , while the dust factor was 10.8. Since January 2013, the solar array dust factor (one of the determinants of solar power production) varied from a relatively dusty 0.467 on December 5, 2013 (sol 3507), to a relatively clean 0.964 on May 13, 2014 (sol 3662).
In December 2014, NASA reported that ''Opportunity'' was suffering from "

 In early June 2018, a large planetary-scale dust storm developed, and within a few days the rover's solar panels were not generating enough power to maintain communications, with the last contact on June 10, 2018. NASA stated that they did not expect to resume communication until after the storm subsided, but the rover kept silent even after the storm ended in early October, suggesting either a catastrophic failure or a layer of dust covering its solar panels.Opportunity Rover Still Silent on Mars, 4 Months After Epic Dust Storm Began
In early June 2018, a large planetary-scale dust storm developed, and within a few days the rover's solar panels were not generating enough power to maintain communications, with the last contact on June 10, 2018. NASA stated that they did not expect to resume communication until after the storm subsided, but the rover kept silent even after the storm ended in early October, suggesting either a catastrophic failure or a layer of dust covering its solar panels.Opportunity Rover Still Silent on Mars, 4 Months After Epic Dust Storm Began
. Mike Wall, ''Space.com''. October 12, 2018. The team remained hopeful that a windy period between November 2018 and January 2019 might clear the dust from its solar panels, as had happened before. Wind was detected nearby on January 8, and on January 26 the mission team announced a plan to begin broadcasting a new set of commands to the rover in case its radio receiver failed. On February 12, 2019, past and present members of the mission team gathered in the
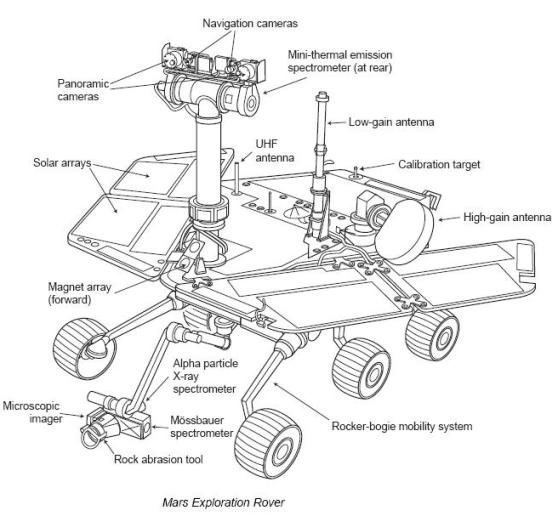
 ''Opportunity '' (and its twin, '' Spirit'') are six-wheeled,
''Opportunity '' (and its twin, '' Spirit'') are six-wheeled,
 ''Opportunity'' has provided substantial evidence in support of the mission's primary scientific goals: to search for and characterize a wide range of rocks and
''Opportunity'' has provided substantial evidence in support of the mission's primary scientific goals: to search for and characterize a wide range of rocks and
NASA/JPL Mission page
Sunrise on Mars – video (02:10)
(
(3:52) overview
�
(59:47) final panel
Finding ''Opportunity'': high-resolution images of landing site (Mars Global Surveyor – Mars Orbiter Camera)
MER Analyst's Notebook
Interactive access to mission data and documentation
Archive
of MER progress reports by A.J.S. Rayl at planetary.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Opportunity Rover * 2003 robots Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle Mars rovers Missions to Mars Robots of the United States Six-wheeled robots Solar-powered robots Space probes decommissioned in 2019 Space probes launched in 2003 Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets Derelict landers (spacecraft) Soft landings on Mars 2004 on Mars Mars robots
robotic
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
rover
Rover may refer to:
People Name
* Constance Rover (1910–2005), English historian
* Jolanda de Rover (born 1963), Dutch swimmer
* Rover Thomas (c. 1920–1998), Indigenous Australian artist
Stage name
* Rover (musician), French singer-songw ...
that was active on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
from 2004 until 2018. ''Opportunity'' was operational on Mars for sols ( on Earth). Launched on July 7, 2003, as part of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rove ...
program, it landed in Meridiani Planum
Meridiani Planum (alternatively Terra Meridiani) is a large plain straddling the equator of Mars. The plain sits on top of an enormous body of sediments that contains bound water. The iron oxide in the spherules is crystalline (grey) hematite (Fe ...
on January 25, 2004, three weeks after its twin, '' Spirit'' (MER-A), touched down on the other side of the planet. With a planned 90- sol duration of activity (slightly less than 92.5 Earth days), ''Spirit'' functioned until it got stuck in 2009 and ceased communications in 2010, while ''Opportunity'' was able to stay operational for sols after landing, maintaining its power and key systems through continual recharging of its batteries using solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
, and hibernating during events such as dust storms to save power. This careful operation allowed ''Opportunity'' to operate for 57 times its designed lifespan, exceeding the initial plan by (in Earth time). By June 10, 2018, when it last contacted NASA, the rover had traveled a distance of .
Mission highlights included the initial 90-sol mission, finding meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
s such as Heat Shield Rock
Heat Shield Rock is a basketball-sized iron-nickel meteorite found on the Meridiani Planum plain of Mars by the Mars rover ''Opportunity'' in January 2005.
Informally referred to as "Heat Shield Rock" by the Opportunity research team, the met ...
(Meridiani Planum meteorite), and over two years of exploring and studying Victoria crater
Victoria is an impact crater on Mars located at 2.05°S, 5.50°W in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain, lying situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. This crater was first visited by the Mars E ...
. The rover survived moderate dust storms and in 2011 reached Endeavour crater
Endeavour is an impact crater located in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. Endeavour is about in diameter. Using ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' data, phy ...
, which has been considered as a "second landing site". The ''Opportunity'' mission is considered one of NASA's most successful ventures.
Due to the planetary 2018 dust storm on Mars, ''Opportunity'' ceased communications on June 10 and entered hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic reduction entered by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It is mos ...
on June 12, 2018. It was hoped it would reboot once the weather cleared, but it did not, suggesting either a catastrophic failure or that a layer of dust had covered its solar panels. NASA hoped to re-establish contact with the rover, citing a recurring windy period which was forecast for November 2018 to January 2019, that could potentially clean off its solar panels. On February 13, 2019, NASA officials declared that the ''Opportunity'' mission was complete, after the spacecraft had failed to respond to over 1,000 signals sent since August 2018.
Objectives
The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to: *Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to pastwater
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
activity. In particular, samples sought include those that have minerals deposited by water-related processes such as precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
, evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
, sedimentary cementation, or hydrothermal activity.
*Determine the distribution and composition of minerals, rocks, and soils surrounding the landing sites.
*Determine what geologic processes have shaped the local terrain and influenced the chemistry. Such processes could include water or wind erosion, sedimentation, hydrothermal mechanisms, volcanism, and cratering.
*Perform calibration and validation of surface observations made by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
The ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (''MRO'') is a spacecraft designed to search for the existence of water on Mars and provide support for missions to Mars, as part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. It was launched from Cape Canaveral on Au ...
(MRO) instruments. This will help determine the accuracy and effectiveness of various instruments that survey Martian geology from orbit.
*Search for iron-containing minerals, and to identify and quantify relative amounts of specific mineral types that contain water or were formed in water, such as iron-bearing carbonates.
*Characterize the mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
and textures of rocks and soils to determine the processes that created them.
*Search for geological clues to the environmental conditions that existed when liquid water was present.
*Assess whether those environments were conducive to life.
Mission timeline
 ''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the
''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rove ...
program in the long-term Mars Exploration Program
Mars Exploration Program (MEP) is a long-term effort Exploration of Mars, to explore the planet Mars, funded and led by NASA. Formed in 1993, MEP has made use of orbital spacecraft, lander (spacecraft), landers, and Mars rovers to explore the p ...
. The Mars Exploration Program's four principal goals were to determine if the potential for life exists on Mars (in particular, whether recoverable water may be found on Mars), to characterize the Mars climate and its geology, and then to prepare for a potential human mission to Mars. The Mars Exploration Rovers were to travel across the Martian surface and perform periodic geologic analyses to determine if water ever existed on Mars as well as the types of minerals available, as well as to corroborate data taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
The ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (''MRO'') is a spacecraft designed to search for the existence of water on Mars and provide support for missions to Mars, as part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. It was launched from Cape Canaveral on Au ...
(MRO). Both rovers were designed with an expected 90 sols (92 Earth days) lifetime, but each lasted much longer than expected. ''Spirit'' mission lasted 20 times longer than its expected lifetime, and its mission was declared ended on May 25, 2011, after it got stuck in soft sand and expended its power reserves trying to free itself. ''Opportunity'' lasted 55 times longer than its 90 sol planned lifetime, operating for days from landing to mission end. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the ''Opportunity'' Update Archive.
Launch and landing
 ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' were launched a month apart, on June 10 and July 8, 2003, and both reached the Martian surface by January 2004. ''Opportunity''s launch was managed by NASA's Launch Services Program. This was the first launch of the
''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' were launched a month apart, on June 10 and July 8, 2003, and both reached the Martian surface by January 2004. ''Opportunity''s launch was managed by NASA's Launch Services Program. This was the first launch of the Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas, and sometimes known as the Thorad Delta 1. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family, derived directly from the Delta 3000, and entered service in ...
Heavy. The launch period went from June 25 to July 15, 2003. The first launch attempt occurred on June 28, 2003, but the spacecraft launched nine days later on July 7, 2003, due to delays for range safety and winds, then later to replace items on the rocket (insulation and a battery). Each day had two instantaneous launch opportunities. On the day of launch, the launch was delayed to the second opportunity (11:18 p.m. EDT) in order to fix a valve.
 On January 25, 2004 (GMT) (January 24, 2004, PST), the airbag-protected landing craft settled onto the surface of Mars in the Eagle crater.
From its initial landing into an
On January 25, 2004 (GMT) (January 24, 2004, PST), the airbag-protected landing craft settled onto the surface of Mars in the Eagle crater.
From its initial landing into an impact crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal c ...
amidst an otherwise generally flat plain, ''Opportunity'' successfully investigated regolith and rock samples and took panoramic photos of its landing site. Its sampling allowed NASA scientists to make hypotheses concerning the presence of hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
and past presence of water on the surface of Mars. Following this, it was directed to travel across the surface of Mars to investigate another crater site, Endurance crater, which it explored from June to December 2004. Subsequently, ''Opportunity'' examined the impact site of its own heat shield
In engineering, a heat shield is a component designed to protect an object or a human operator from being burnt or overheated by dissipating, reflecting, and/or absorbing heat. The term is most often used in reference to exhaust heat management a ...
and discovered an intact meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
, now known as Heat Shield Rock
Heat Shield Rock is a basketball-sized iron-nickel meteorite found on the Meridiani Planum plain of Mars by the Mars rover ''Opportunity'' in January 2005.
Informally referred to as "Heat Shield Rock" by the Opportunity research team, the met ...
, on the surface of Mars.
''Opportunity'' was directed to proceed in a southerly direction to Erebus crater, a large, shallow, partially buried crater and a stopover on the way south towards Victoria crater
Victoria is an impact crater on Mars located at 2.05°S, 5.50°W in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain, lying situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. This crater was first visited by the Mars E ...
, between October 2005 and March 2006. It experienced some mechanical problems with its robotic arm.
In late September 2006, ''Opportunity'' reached Victoria crater and explored along the rim in a clockwise direction. In June 2007 it returned to Duck Bay, its original arrival point at Victoria crater; in September 2007 it entered the crater to begin a detailed study. In August 2008, ''Opportunity'' left Victoria crater for Endeavour crater
Endeavour is an impact crater located in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. Endeavour is about in diameter. Using ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' data, phy ...
, which it reached on August 9, 2011.
At the rim of the Endeavour crater, the rover moved around a geographic feature named ''Cape York''. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter had detected phyllosilicate
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, the crystalline forms of silica (silicon dio ...
s there, and the rover analyzed the rocks with its instruments to check this sighting on the ground. This structure was analyzed in depth until summer 2013. In May 2013 the rover was heading south to a hill named '' Solander Point''.
 ''Opportunity''s total odometry by June 10, 2018 (sol 5111), was , while the dust factor was 10.8. Since January 2013, the solar array dust factor (one of the determinants of solar power production) varied from a relatively dusty 0.467 on December 5, 2013 (sol 3507), to a relatively clean 0.964 on May 13, 2014 (sol 3662).
In December 2014, NASA reported that ''Opportunity'' was suffering from "
''Opportunity''s total odometry by June 10, 2018 (sol 5111), was , while the dust factor was 10.8. Since January 2013, the solar array dust factor (one of the determinants of solar power production) varied from a relatively dusty 0.467 on December 5, 2013 (sol 3507), to a relatively clean 0.964 on May 13, 2014 (sol 3662).
In December 2014, NASA reported that ''Opportunity'' was suffering from "amnesia
Amnesia is a deficit in memory caused by brain damage or brain diseases,Gazzaniga, M., Ivry, R., & Mangun, G. (2009) Cognitive Neuroscience: The biology of the mind. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. but it can also be temporarily caused by t ...
" events in which the rover failed to write data, e.g. telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', 'far off', an ...
information, to non-volatile memory
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data.
Non-volatile memory typ ...
. The hardware failure was believed to be due to an age-related fault in one of the rover's seven memory banks. As a result, NASA had aimed to force the rover's software to ignore the failed memory bank; amnesia events continued to occur, however, which eventually resulted in vehicle resets. In light of this, on Sol 4027 (May 23, 2015), the rover was configured to operate in RAM-only mode, completely avoiding the use of non-volatile memory for storage.
End of mission

 In early June 2018, a large planetary-scale dust storm developed, and within a few days the rover's solar panels were not generating enough power to maintain communications, with the last contact on June 10, 2018. NASA stated that they did not expect to resume communication until after the storm subsided, but the rover kept silent even after the storm ended in early October, suggesting either a catastrophic failure or a layer of dust covering its solar panels.Opportunity Rover Still Silent on Mars, 4 Months After Epic Dust Storm Began
In early June 2018, a large planetary-scale dust storm developed, and within a few days the rover's solar panels were not generating enough power to maintain communications, with the last contact on June 10, 2018. NASA stated that they did not expect to resume communication until after the storm subsided, but the rover kept silent even after the storm ended in early October, suggesting either a catastrophic failure or a layer of dust covering its solar panels.Opportunity Rover Still Silent on Mars, 4 Months After Epic Dust Storm Began. Mike Wall, ''Space.com''. October 12, 2018. The team remained hopeful that a windy period between November 2018 and January 2019 might clear the dust from its solar panels, as had happened before. Wind was detected nearby on January 8, and on January 26 the mission team announced a plan to begin broadcasting a new set of commands to the rover in case its radio receiver failed. On February 12, 2019, past and present members of the mission team gathered in the
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
(JPL)'s Space Flight Operations Facility
The Space Flight Operations Facility (SFOF) is a building containing a control room and related computing and communications equipment areas at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. NASA's Deep Space Network is operated from this ...
to watch final commands being transmitted to Opportunity via the dish of the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex
The Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex (GDSCC), commonly called the Goldstone Observatory, is a satellite ground station located in Fort Irwin in the U.S. state of California. Operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), its ...
in California. Following 25 minutes of transmission of the final 4 sets of commands, communication attempts with the rover were handed off to Canberra, Australia
Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city, and the eighth-largest Australian city b ...
.
More than 835 recovery commands were transmitted since losing signal in June 2018 to the end of January 2019 with over 1000 recovery commands transmitted before February 13, 2019. NASA officials held a press conference on February 13 to declare an official end to the mission. NASA associate administrator Thomas Zurbuchen said, "It is therefore that I am standing here with a deep sense of appreciation and gratitude that I declare the ''Opportunity'' mission is complete." As NASA ended their attempts to contact the rover, the last data sent was the song " I'll Be Seeing You" performed by Billie Holiday
Billie Holiday (born Eleanora Fagan; April 7, 1915 – July 17, 1959) was an American jazz and swing music singer. Nicknamed "Lady Day" by her friend and music partner, Lester Young, Holiday made significant contributions to jazz music and pop ...
. Assets that had been needed to support ''Opportunity'' were transitioned to support the ''Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin , from "careful, diligent, curious", akin to "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking, such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident in humans and other animals. Curiosity helps Developmental psyc ...
'' rover and the then-upcoming '' Perseverance'' rover.
The final communication from the rover came on June 10, 2018 (sol 5111) from Perseverance Valley, and indicated a solar array energy production of 22 Watt-hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a non-SI unit of energy equal to 3.6 megajoules (MJ) in SI units, which is the energy delivered by one kilowatt of power for one hour. Kilowatt-hours are a commo ...
s for the sol, and the highest atmospheric opacity (tau) ever measured on Mars: 10.8.
Design and construction

solar-powered
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to conve ...
robots standing high, wide and long and weighing . Six wheels on a rocker-bogie system enabled mobility over rough terrain. Each wheel had its own motor. The vehicle was steered at front and rear and was designed to operate safely at tilts of up to 30 degrees. The maximum speed was ; , although the average speed was about . Both ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' have pieces of the fallen World Trade Center's metal on them that were "turned into shields to protect cables on the drilling mechanisms".
Solar arrays generated about 140 watts for up to fourteen hours per sol, while rechargeable lithium ion batteries stored energy for use at night. ''Opportunity''s onboard computer uses a 20 MHz RAD6000 CPU with 128 MB of DRAM and 3 MB of EEPROM. The rover's operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
ranges from and radioisotope heaters provide a base level of heating, assisted by electrical heaters when necessary.
Communications depended on an omnidirectional low-gain antenna communicating at a low data rate and a steerable high-gain antenna, both in direct contact with the Deep Space Network
The NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide Telecommunications network, network of spacecraft communication ground segment facilities, located in the United States (California), Spain (Madrid), and Australia (Canberra), that supports NASA' ...
on Earth. A low-gain antenna was also used to relay data to spacecraft orbiting Mars.
Science payload
The science instruments included: * Panoramic Camera (Pancam) – examined the texture, color, mineralogy, and structure of the local terrain. * Navigation Camera (Navcam) – monochrome with a higher field of view but lower resolution, for navigation and driving. * Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer (Mini-TES) – identified promising rocks and soils for closer examination, and determined the processes that formed them. * Hazcams, two B&W cameras with 120 degree field of view, that provided additional data about the rover's surroundings. The rover arm held the following instruments: * Mössbauer spectrometer (MB)MIMOS II
MIMOS II is the miniaturised Mössbauer spectrometer, developed by Dr. Göstar Klingelhöfer at the Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, that is used on the Mars Exploration Rovers '' Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' for close-up investig ...
– used for close-up investigations of the mineralogy of iron-bearing rocks and soils.
* Alpha particle X-ray spectrometer
:''APXS is also an abbreviation for APache eXtenSion tool, an extension for Apache web servers.''
An alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) is a spectrometer that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from scattered alpha parti ...
(APXS) – close-up analysis of the abundances of elements that make up rocks and soils.
* Magnets – for collecting magnetic dust particles.
* Microscopic Imager (MI) – obtained close-up, high-resolution images of rocks and soils.
* Rock Abrasion Tool
The Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) is a grinding and brushing installation on NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers, '' Spirit'' (MER-A) and '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on Mars in January 2004. It was designed, developed and continues to be o ...
(RAT) – exposed fresh material for examination by instruments on board.
''Opportunity'' was 'driven' by several operators throughout its mission, including JPL roboticist Vandi Verma.
Power
The rover uses a combination of solar cells and a rechargeable chemical battery. This class of rover has two rechargeablelithium batteries
Lithium battery may refer to:
* Lithium metal battery, a non-rechargeable battery with lithium as an anode
** Lithium–air battery
** Lithium–iron disulfide battery
** Lithium–sulfur battery
** Nickel–lithium battery
** Rechargeable l ...
, each composed of 8 cells with 8 amp-hour capacity. At the start of the mission the solar panels could provide up to around 900 watt-hours (Wh) per day to recharge the battery and power system in one Sol, but this could vary due to a variety of factors. In Eagle crater the cells were producing about 840 Wh per day, but by Sol 319 in December 2004, it had dropped to 730 Wh per day.
Like Earth, Mars has seasonal variations that reduce sunlight during winter. However, since the Martian year is longer than that of the Earth, the seasons fully rotate roughly once every 2 Earth years. By 2016, MER-B had endured seven Martian winters, during which times power levels drop which can mean the rover avoids doing activities that use a lot of power. During its first winter power levels dropped to under 300 Wh per day for two months, but some later winters were not as bad.
Another factor that can reduce received power is dust in the atmosphere, especially dust storms. Dust storms have occurred quite frequently when Mars is closest to the Sun. Global dust storms in 2007 reduced power levels for ''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' so much they could only run for a few minutes each day. Due to the 2018 dust storms on Mars, ''Opportunity'' entered hibernation mode on June 12, but it remained silent after the storm subsided in early October.
Scientific findings
 ''Opportunity'' has provided substantial evidence in support of the mission's primary scientific goals: to search for and characterize a wide range of rocks and
''Opportunity'' has provided substantial evidence in support of the mission's primary scientific goals: to search for and characterize a wide range of rocks and regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestria ...
that hold clues to past water activity on Mars. In addition to investigating the water, ''Opportunity'' has also obtained astronomical observations and atmospheric data.
Legacy and honors
Following its launch, ''Opportunity'' was anthropomorphized by its operators: the rover was called a "she," drawing from nautical tradition, and given an affectionate nickname, "Oppy." One scientist, who worked with ''Opportunity'' for over a decade, attributed this to the rover's unexpectedly long lifespan, which he called a story of "an underdog beating the odds," and its "familiar, almost biologically inspired shape." The media attention surrounding ''Opportunitys shutdown spread this usage to the general public. With word on February 12, 2019, that NASA was likely to conclude the ''Opportunity'' mission, many media outlets and commentators issued statements praising the mission's success and stating their goodbyes to the rover. One journalist, Jacob Margolis, tweeted his translation of the last data transmission sent by ''Opportunity'' on June 10, 2018, as "My battery is low and it's getting dark." The phrase struck a chord with the public, inspiring a period of mourning, artwork, and tributes to the memory of ''Opportunity''. When the quote became widely reported, some news reports mistakenly asserted that the rover sent that exact message in English, resulting in NASA being inundated with additional questions. Margolis wrote a clarifying article on February 16, making it clear he had taken statements from NASA officials who were interpreting the data sent by ''Opportunity'', both on the state of its low power and Mars's high atmospheric opacity, and rephrased them in a poetic manner, never to imply the rover had sent the specific words. Honoring ''Opportunitys great contribution to the exploration of Mars, anasteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
was named Opportunity: 39382 Opportunity. The name was proposed by Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld
Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld (; ; 21 October 1921 – 30 March 2015) was a Dutch astronomer.
Background
In a jointly credited trio with Tom Gehrels and her husband Cornelis Johannes van Houten, she was the discoverer of many thousands of as ...
who, along with Cornelis Johannes van Houten
Cornelis Johannes "Kees" van Houten (18 February 1920 – 24 August 2002) was a Dutch people, Dutch astronomer.
Early life and education
Born in The Hague, he spent his entire career at Leiden University except for a brief period (1954–1956) as ...
and Tom Gehrels, discovered the asteroid on September 24, 1960. ''Opportunity''s lander is ''Challenger Memorial Station''.
On March 24, 2015, NASA celebrated ''Opportunity'' having traveled the distance of a marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of kilometres ( 26 mi 385 yd), usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There ...
race, . The rover covered the distance in 11 years and 2 months. The JPL technicians celebrated the occasion by running a race. The location in Mars where the rover reached the distance was aptly named Marathon Valley.
A documentary
A documentary film (often described simply as a documentary) is a nonfiction Film, motion picture intended to "document reality, primarily for instruction, education or maintaining a Recorded history, historical record". The American author and ...
film, '' Good Night Oppy'', about the ''Opportunity'', ''Spirit'', and their long missions, was directed by Ryan White
Ryan Wayne White (December 6, 1971 – April 8, 1990) was an American teenager from Kokomo, Indiana, who became a national poster child for HIV/AIDS in the United States after his school barred him from attending classes following a diagn ...
, and included support from JPL and Industrial Light & Magic
Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) is an American Film, motion picture visual effects, computer animation and stereo conversion digital studio founded by George Lucas on May 26, 1975. It is a division of the film production company Lucasfilm, which Lu ...
. It was released in 2022.
Images
The rover could take pictures with its different cameras, but only the PanCam camera had the ability to photograph a scene with different color filters. The panorama views are usually built up from PanCam images. By February 3, 2018, ''Opportunity'' had returned 224,642 pictures. A selection of panoramas from the mission:See also
* * * * * List of surface features of Mars visited by ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' * * ''Perseverance'' (rover) * * ** * * Comparison of embedded computer systems on board the Mars rovers * * ''Zhurong'' roverReferences
External links
NASA links
NASA/JPL Mission page
Sunrise on Mars – video (02:10)
(
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
; November 7, 2018)
* End of ''Opportunity'' Mission (February 13, 2019; videos) �(3:52) overview
�
(59:47) final panel
MSSS and WUSTL links
Finding ''Opportunity'': high-resolution images of landing site (Mars Global Surveyor – Mars Orbiter Camera)
MER Analyst's Notebook
Interactive access to mission data and documentation
Other links
Archive
of MER progress reports by A.J.S. Rayl at planetary.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Opportunity Rover * 2003 robots Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle Mars rovers Missions to Mars Robots of the United States Six-wheeled robots Solar-powered robots Space probes decommissioned in 2019 Space probes launched in 2003 Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets Derelict landers (spacecraft) Soft landings on Mars 2004 on Mars Mars robots