Old Salt Route on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Old Salt Route was a
The Old Salt Route was a
 Historians generally recognize the Old Salt Route as part of a much longer path, which functioned as an important connection between the northern and southern reaches of the country. One of the oldest documents that confirms
Historians generally recognize the Old Salt Route as part of a much longer path, which functioned as an important connection between the northern and southern reaches of the country. One of the oldest documents that confirms
/ref> In 1398, though, the Stecknitz Canal, one of the first manmade waterways in
Lüneburg’s Website
Network Old Salt Street
– has English and German content.
20.000 tons of white gold
– German article {{Authority control Geography of Schleswig-Holstein German tourist routes Hanseatic League History of Lübeck Trade routes Medieval economic history Roads in Schleswig-Holstein Cycle paths in Schleswig-Holstein Tourist attractions in Schleswig-Holstein Tourist attractions in Lower Saxony History of salt Otto the Great
 The Old Salt Route was a
The Old Salt Route was a medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
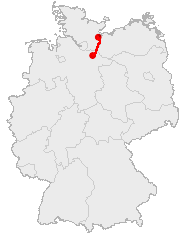
trade route in Northern Germany
Northern Germany (, ) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony and the two city-states Hambur ...
, one of the ancient network of salt roads which were used primarily for the transport of salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
and other staples. In Germany it was referred to as ''Alte Salzstraße''.
Salt was very valuable and essential at that time; it was sometimes referred to as "white gold." The vast majority of the salt transported on the road was produced from brine near Lüneburg
Lüneburg, officially the Hanseatic City of Lüneburg and also known in English as Lunenburg, is a town in the German Bundesland (Germany), state of Lower Saxony. It is located about southeast of another Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city, Hambur ...
, a city in the northern central part of the country and then transported to Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
, a major seaport on Germany's Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
coast.
History
 Historians generally recognize the Old Salt Route as part of a much longer path, which functioned as an important connection between the northern and southern reaches of the country. One of the oldest documents that confirms
Historians generally recognize the Old Salt Route as part of a much longer path, which functioned as an important connection between the northern and southern reaches of the country. One of the oldest documents that confirms Lüneburg
Lüneburg, officially the Hanseatic City of Lüneburg and also known in English as Lunenburg, is a town in the German Bundesland (Germany), state of Lower Saxony. It is located about southeast of another Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city, Hambur ...
and its role in refining and transporting salt dates from 956 A.D. According to that document, King Otto I the Great granted the St. Michaelis Monastery in Lüneburg the customs revenue from the saltworks. Even at those early times, the city's wealth was based in large part on the salt found in the area. 2003. The Old Salt Route attained its peak of success between the 12th and the 16th century.
The trade route led from Lüneburg
Lüneburg, officially the Hanseatic City of Lüneburg and also known in English as Lunenburg, is a town in the German Bundesland (Germany), state of Lower Saxony. It is located about southeast of another Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city, Hambur ...
northward to Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
. From that port city, most of the salt was shipped to numerous destinations that also lie on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, including Falsterbo, which boasted a Scania Market. There it was used for the preservation of herring
Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the Order (biology), order Clupeiformes.
Herring often move in large Shoaling and schooling, schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate wate ...
, an immensely important food in the Middle Ages, as well as for other foods. The salt trade was a major reason for the power of Lübeck and the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
.
Transport of salt
Horse-drawn carts brought the salt from Lüneburg to a crossing of theElbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
river at Artlenburg (near Lauenburg) and from there, via Mölln, to Lübeck. For the most part, however, the historic trade route was composed of unsurfaced, sandy and often muddy roads through heathland, woods and small villages, making the transport of salt an arduous task. In addition, the route was somewhat dangerous, since the valuable cargo attracted thieves, bandits and marauders. The dangers faced by those who make the long trek and the fact that only relatively small quantities of the precious crystalline substance could be carried in any single journey, made moving salt via overland routes very expensive.DHL. “The Old Salt Road – Logistics networks today and yesterday”/ref> In 1398, though, the Stecknitz Canal, one of the first manmade waterways in
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, was completed, making it possible to transport much more salt in a single shipment and to do so with much greater ease and safety. That change helped merchants satisfy the salt requirements of an ever-growing demand. In the 16th century, for example, about 19,000 tons of the product were carried from Lüneburg to Lübeck each year either by land or water. However, it still took about twenty days to complete each trip.
Tourism
In modern times, a trip along the Salt Road promises a rich blend of nature and culture. The trip can be made on foot or on bicycle and part of the distance can also be enjoyed on a paddle-wheeled steamer. There are many fascinating sights along the old trade route. These points of interest include the historical towns Lüneburg, Mölln and Lübeck, which are highlighted by beautiful façades and little alleyways, and are a major attraction to visitors.Bicycle route
As a bicycle route, there are the options of a main and a scenic route. The shorter main route (95 km) leads bicyclists through many picturesque little towns such as Lauenburg, Büchen, Mölln and Krummsee and also passes by the Lüne Monastery. The scenic route is especially attractive for nature lovers. The path diverges from the main thoroughfare at Witzeeze, continues on through the Lauenburg Nature Park and rejoins the main route just before Lübeck.Lüneburg Heath
Once, the area around Lüneburg was covered in lush woodlands. But because the medieval salt works depended on wood as a fuel used in boiling and purifying the saline water from which the salt was obtained, much of the forest was cut down. Heather then covered area, helping it to become a landscape that now attracts thousands of visitors when that foliage is in full bloom.See also
* German Salt Museum * Lüneburg Saltworks * Sülze SaltworksNotes
External links
Lüneburg’s Website
Network Old Salt Street
– has English and German content.
20.000 tons of white gold
– German article {{Authority control Geography of Schleswig-Holstein German tourist routes Hanseatic League History of Lübeck Trade routes Medieval economic history Roads in Schleswig-Holstein Cycle paths in Schleswig-Holstein Tourist attractions in Schleswig-Holstein Tourist attractions in Lower Saxony History of salt Otto the Great