Old Riyadh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Old Riyadh () is an umbrella term used for a loosely defined region that primarily lies in the southern portion of modern-day
 In 1744, Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab formed an alliance with Muhammad ibn Saud, the ruler of the nearby town of
In 1744, Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab formed an alliance with Muhammad ibn Saud, the ruler of the nearby town of
22
year=1990, publisher=Routledge, isbn=978-0-7103-0395-0 Geography of Riyadh History of Riyadh
Riyadh
Riyadh is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. Located on the eastern bank of Wadi Hanifa, the current form of the metropolis largely emerged in th ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
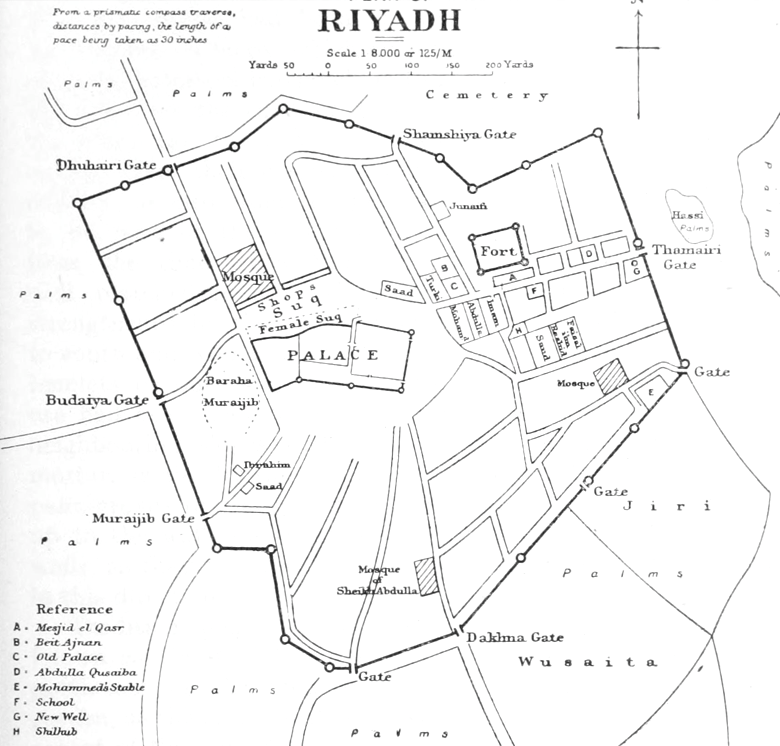
, encompassing neighborhoods and settlements that emerged from the ruins of Hajr al-Yamamah in late 16th century or existed during pre-Islamic era, the erstwhile walled town (today Qasr Al Hukm District) enclosed within the defensive fortifications and its immediate vicinity prior to its demolition in the 1950s, villages and not former towns located along the outskirts of Riyadh
Riyadh is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. Located on the eastern bank of Wadi Hanifa, the current form of the metropolis largely emerged in th ...
(such as Irqah and Manfuhah) that got incorporated into the metropolis following multiple phases of expansion and modernization between the 1950s and 1970s. To some extent, neighborhoods excluded during Riyadh's rapid urbanization during the same period are also categorized as part of old districts, with most of them situated in the modern downtown.
History
Early origins in pre-Islamic Arabia
Before the advent of Islam in the 7th century, the settlement upon which present-dayRiyadh
Riyadh is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. Located on the eastern bank of Wadi Hanifa, the current form of the metropolis largely emerged in th ...
is situated was known as Hajr al-Yamamah, or simply Hajr. The settlement was founded by the Banu Hanifa tribe in the 5th century several years after the purported obliteration of the lost Arabian tribes of Tasm and Jadis by Himyarite king Hassan Yuha'min. After the advent of Islam by 7th century, most of its inhabitants converted to Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
and became part of the new Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
and then the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
. After the overthrow of the Umayyads in the Abbasid Revolution in 8th century, Hajr became part of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
and was still the seat of al-Yamama region until it was seceded by the prevailing Ukhaydhirites in 866 AD when they made al-Kharj
Kharj () is a List of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate in central Saudi Arabia. It is one of the important governorates in Saudi Arabia. Located southeast of the capital, Riyadh, it covers an area of 7640 mi2 (19,790 km2) and has a popu ...
their new capital. Consequently, Hajr underwent severe economic and political decline due to prolonged droughts while simultaneously being indulged in feudalistic conflicts with its neighbors such as Diriyah
Diriyah (; formerly romanization of Arabic, romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya) is a towns in Saudi Arabia, town and governorate in Saudi Arabia. Located on the northwestern outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh, Diriyah was the original home of t ...
and Manfuhah. Hajr eventually witnessed steady fragmentation and was succeeded by various rival settlements such as Migrin (or Miqrin) and Miʼkal by the end of 16th century. The 14th-century Moroccan traveler and explorer Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
travelled to Hajr and described it as "a good, fertile city with rivers and trees, inhabited by sects of Arabs, and most of them are from Banu Hanifa, which is their country in the past, and their ruler is Tufail bin Ghanem".
Later on, Hajr broke up into several separate settlements and estates. The most notable of these were Migrin (or Muqrin) and Mi'kal, though the name '' Hajr'' continued to appear in local folk poetry. The earliest known reference to the area by the name ''Riyadh'' comes from a 17th-century chronicler reporting on an event from the year 1590. In 1737, Deham ibn Dawwas, a refugee from neighboring Manfuha, took control of Riyadh. Ibn Dawwas built a single wall to encircle the various oasis town in the area, making them effectively a single city. The name "Riyadh," meaning "gardens" refers to these earlier oasis towns.
First and second Saudi states
 In 1744, Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab formed an alliance with Muhammad ibn Saud, the ruler of the nearby town of
In 1744, Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab formed an alliance with Muhammad ibn Saud, the ruler of the nearby town of Diriyah
Diriyah (; formerly romanization of Arabic, romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya) is a towns in Saudi Arabia, town and governorate in Saudi Arabia. Located on the northwestern outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh, Diriyah was the original home of t ...
. Ibn Saud then set out to conquer the surrounding region with the goal of bringing it under the rule of a single Islamic state. Ibn Dawwas of Riyadh led the most determined resistance, allied with forces from Al Kharj, Al Ahsa, and the Banu Yam clan of Najran. However, Ibn Dawwas fled and Riyadh capitulated to the Saudis in 1774, ending long years of wars, and leading to the declaration of the First Saudi State, with Diriyah as its capital.
The First Saudi State was destroyed by forces sent by Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali (4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849) was the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Albanians, Albanian viceroy and governor who became the ''de facto'' ruler of History of Egypt under the Muhammad Ali dynasty, Egypt from 1805 to 1848, widely consi ...
, acting on behalf of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. Ottoman forces razed the Saudi capital Diriyah
Diriyah (; formerly romanization of Arabic, romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya) is a towns in Saudi Arabia, town and governorate in Saudi Arabia. Located on the northwestern outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh, Diriyah was the original home of t ...
in 1818. They had maintained a garrison at Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
. This marked the decline of the House of Saud for a short time. Turki bin Abdullah bin Muhammad
Chagatai (, ), also known as Turki, Eastern Turkic, or Chagatai Turkic (), is an Extinct language, extinct Turkic languages, Turkic language that was once widely spoken across Central Asia. It remained the shared literary language in the region u ...
became the first Amir of the Second Saudi State; the cousin of Saud bin Saud, he ruled for 19 years till 1834, leading to the consolidation of the area though they were notionally under the control of Muhammad Ali, the Viceroy of Egypt. In 1823, Turki ibn Abdallah chose Riyadh as the new capital. Following the assassination of Turki in 1834, his eldest son Faisal killed the assassin and took control, and refused to be controlled by the Viceroy of Egypt. Najd was then invaded and Faisal was taken captive and held in Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
. However, as Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
became independent of the Ottoman Empire, Faisal escaped after five years of incarceration, returned to Najd and resumed his reign, ruled till 1865, and consolidated the reign of the House of Saud.
Following the death of Faisal, there was rivalry among his sons which situation was exploited by Muhammad bin Rashid who took most of Najd, signed a treaty with the Ottomans, and also captured Hasa in 1871. In 1889, Abdul Rahman bin Faisal, the third son of Faisal again regained control over Najd and ruled till 1891, whereafter the control was regained by Muhammad bin Raschid.
Internecine struggles between Turki's grandsons led to the fall of the Second Saudi State in 1891 at the hand of the rival Al Rashid clan, which ruled from the northern city of Ha'il. The al-Masmak fort dates from that period.
Abdul Rahman bin Faisal al-Saud had sought refuge among a tribal community on the outskirts of Najd and then went to Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
with his family and stayed in exile. However, his son Abdul Aziz retrieved his ancestral kingdom of Najd in 1902 and consolidated his rule by 1926, and further expanded his kingdom to cover "most of the Arabian Peninsula." He named his kingdom as Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
in September 1932 with Riyadh as the capital. King Abdul Aziz died in 1953 and his son Saud took control as per the established succession rule of father to son from the time Muhammad bin Saud had established the Saud rule in 1744. However, this established line of succession was broken when King Saud was succeeded by his brother King Faisal in 1964. In 1975, Faisal was succeeded by his brother King Khalid. In 1982, King Fahd took the reins from his brother. This new line of succession is among the sons of King Abdul Aziz who has 35 sons; this large family of Ibn Saud hold all key positions in the large kingdom.
In modern times
The old city area in southern Riyadh today is characterized by its low-contour earth-structured derelict buildings inspired by the traditional Najdi architecture. Most of the residents of the area migrated to other neighborhoods during Riyadh's multiple phases of expansion in 1950s and after the1970s energy crisis
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period wer ...
. Some of the neighborhoods like Jabrah got inhabited by foreign workers after the influx of skilled labors into the country between the 1970s and 1980s in the aftermath of the 1973 oil embargo whereas some settlements such as Duhairah went extinct around the same period. Some of the neighborhoods like Hillat al-Ahrar also hosted a large population of Afro-Arabs who were emancipated in 1962 following the nationwide abolition of slavery during the reign of King Saud.
List of neighborhoods
Following is a list of neighborhoods of old Riyadh with respect to the modern metropolis based on different classificationsFormer towns and villages
These towns, estates and villages emerged from the ruins of Hajr in 16th century whereas some existed during pre-Islamic times * Migrin * Mi’kal * Jabrah * Masani * Manfuhah * Owd * Siyah * Beneyah * Irqah * Al-Jaz’ah * Al-KharabQuarters of the former walled town
These quarters and douars were part of the former walled town, the successor to the city-state of Migrin, prior to its dismantling in the 1950s. * Gadimah * Duhairah * Ajnab * Mugailiyah * Muraighib * Ghanaiy * Sharqiyah * Dakhna * Doho * MusadaQuarters and neighborhoods in close proximity to the walled town
* Al Murabba * Umm Sulaim * Wusaita * Al-Bat'ha * Al-Qiri * Skirina * Utaiqah * Thulaim * JabrahReferences
Sources
* * * * {{cite book, last=Farsy, first=Fouad, title=Modernity and Tradition: The Saudi Equation, url=https://archive.org/details/modernitytraditi0000fars, url-access=registration, pag22
year=1990, publisher=Routledge, isbn=978-0-7103-0395-0 Geography of Riyadh History of Riyadh