Obturator Internus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the
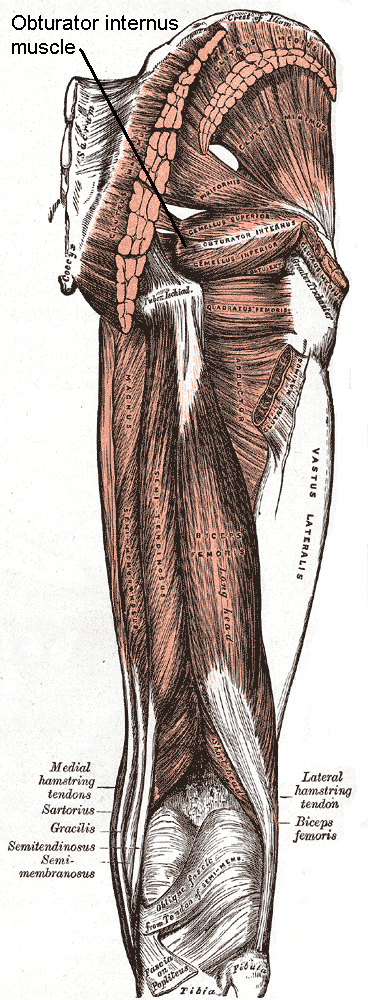
File:Obturator internus muscle.jpg, Obturator internus muscle
File:Slide10A.JPG, Obturator internus muscle
File:Braus 1921 251.png, "Triceps coxae"
Int. J. Morphol., 25(1):95-98, 2007
{{Authority control Hip muscles Hip lateral rotators Deep lateral rotators of the hip Muscles of the lower limb
ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.
It exits the pelvic cavity
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.
The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproduc ...
through the lesser sciatic foramen.
The internal obturator is situated partly within the lesser pelvis
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.
The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproduc ...
, and partly at the back of the hip-joint
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an list of human anatomical regions, ...
.
It functions to help laterally rotate femur with hip extension and abduct femur with hip flexion, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum.
Structure
Origin
The internal obturator muscle arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of thepelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
. It surrounds the obturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the large, Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, the obturator canal, through wh ...
. It is attached to the inferior pubic ramus and ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone) ...
below and behind the pelvic brim
The pelvic brim is the edge of the pelvic inlet. It is an approximately butterfly-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis.
Structure
The pelvic ...
. It reaches from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies ...
above and behind to the obturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the large, Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening, the obturator canal, through wh ...
below and in front.
It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane. This is except in the posterior part, from the tendinous arch which completes the canal for the passage of the obturator vessels and nerve, and to a slight extent from the obturator fascia, which covers the muscle.
Passage
The fibers converge through the lesser sciatic foramen. These end in four or five tendinous bands, which are found on the deep surface of the muscle. These bands are reflected at a right angle over the grooved surface of the ischium between its spine and tuberosity. The obturator nerve passes on the superficial surface of the internal obturator muscle. Thepudendal nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a Mixed nerve, mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic Autonomic nervous system, autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the exter ...
passes on the lateral surface of the internal obturator muscle and the coccygeus muscle
The coccygeus muscle or ischiococcygeus is a muscle of the pelvic floor located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament.
Structure
The coccygeus muscle is posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous liga ...
. The sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
passes superficial to the internal obturator muscle on the posterior surface.
Insertion
The tendon inserts on the greater trochanter of the proximalfemur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
.
Nerve supply
The internal obturator muscle is supplied by theobturator internus nerve
The nerve to obturator internus (also known as the obturator internus nerve) is a mixed (sensory and motor) nerve providing motor innervation to the obturator internus muscle and gemellus superior muscle, and sensory innervation to the hip join ...
( L5, S1, and S2).

Bursa/bands
This bony surface is covered by smooth cartilage, which is separated from the tendon by abursa
Bursa () is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the Marmara Region, Bursa is one of the industrial centers of the country. Most of ...
, and presents one or more ridges corresponding with the furrows between the tendinous bands.
These bands leave the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen and unite into a single flattened tendon, which passes horizontally across the capsule of the hip-joint, and, after receiving the attachments of the superior and inferior gemellus muscle
The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle
and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hi ...
s, is inserted into the forepart of the medial surface of the greater trochanter above the trochanteric fossa.
A bursa, narrow and elongated in form, is usually found between the tendon and the capsule of the hip-joint. It occasionally communicates with the bursa between the tendon and the ischium.
Function
The internal obturator muscle helps to support theurinary bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the ...
as part of the pelvic floor
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function, and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and ...
.
Additional images
References
External links
* - "Gluteal Region: Muscles" * - "The Female Pelvis: Muscles" * * (, ) * ()Int. J. Morphol., 25(1):95-98, 2007
{{Authority control Hip muscles Hip lateral rotators Deep lateral rotators of the hip Muscles of the lower limb