Nsp12 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nsp12 is a non-structural protein in the 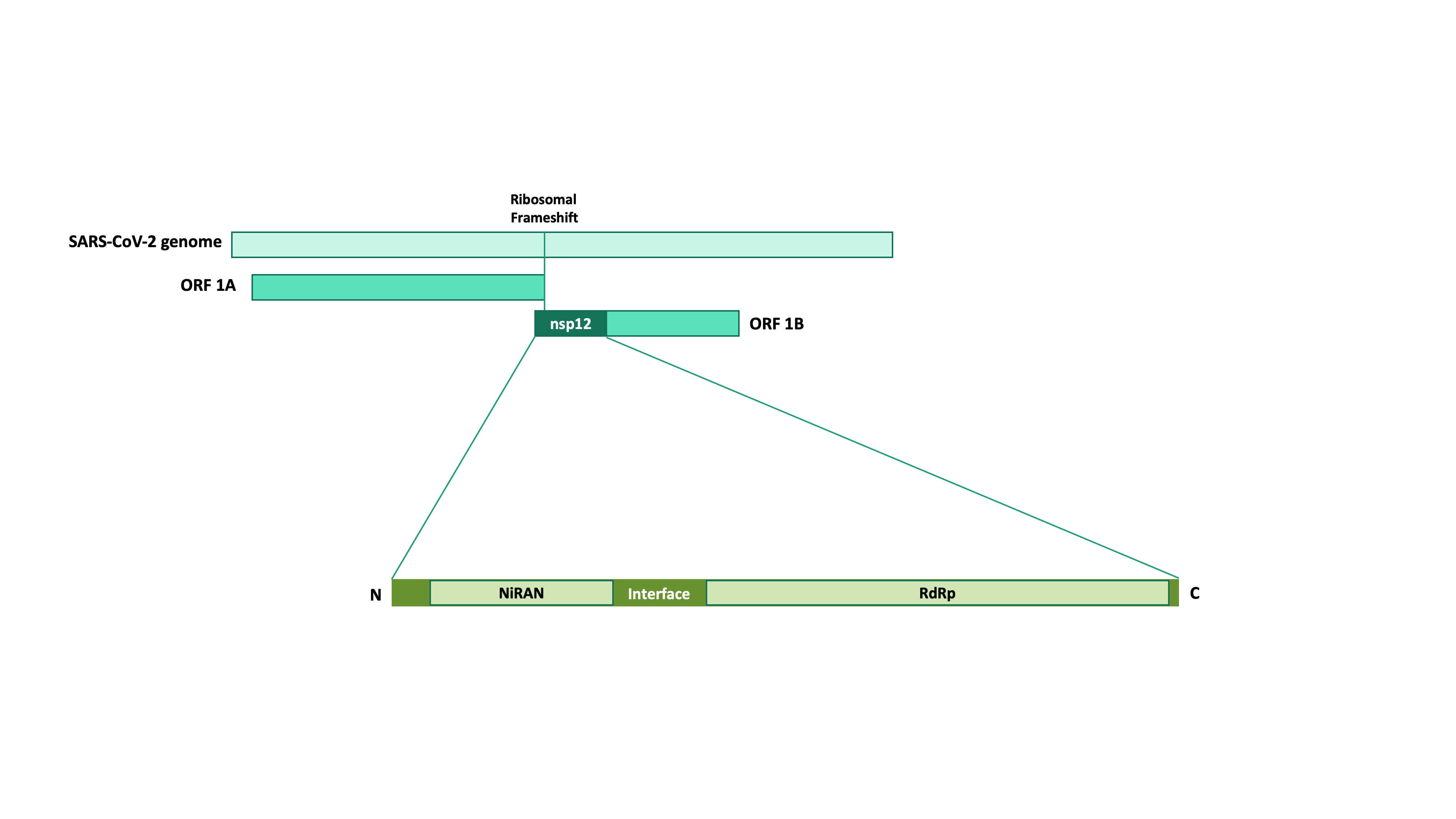 Coronavirus nsp12 also plays a role in host immune evasion; research has demonstrated that nsp12 inhibits the nuclear translocation of
Coronavirus nsp12 also plays a role in host immune evasion; research has demonstrated that nsp12 inhibits the nuclear translocation of
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
genome. Its gene is part of the ORF1ab
ORF1ab (also ORF1a/b) refers collectively to two open reading frames (ORFs), ORF1a and ORF1b, that are conserved in the genomes of nidoviruses, a group of viruses that includes coronaviruses. The genes express large polyproteins that undergo p ...
reading frame and it is part of the pp1ab polyprotein; it is cleaved by 3CLpro.
Nsp12 is a multi-domain subunit: it consists of an N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amin ...
nidovirus
''Nidovirales'' is an order of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrates and invertebrates. Host organisms include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, arthropods, molluscs, and helminths. The order includes the fami ...
-specific extension (NiRAN) domain, an interface domain, and a C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When t ...
RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase domain. The N-terminal portion of SARS-CoV-2 nsp12 additionally contains a β-hairpin
The beta hairpin (sometimes also called beta-ribbon or beta-beta unit) is a simple protein structural motif involving two beta strands that look like a hairpin. The motif consists of two strands that are adjacent in primary structure, oriented in ...
which is sandwiched between the NiRAN and RdRp domain.
 Coronavirus nsp12 also plays a role in host immune evasion; research has demonstrated that nsp12 inhibits the nuclear translocation of
Coronavirus nsp12 also plays a role in host immune evasion; research has demonstrated that nsp12 inhibits the nuclear translocation of IRF3
Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor.
Function
IRF3 is a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF3 was originally discovered as a homolog of IRF1 and IRF2. IR ...
.
RdRp Domain
The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase domain of nsp12 is C-terminal. InSARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
the domain spans residues 366 to 920. The structure of the RdRp domain shares common structural features with eukaryotic RNA polymerases
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the en ...
: the structure consists of a cupped right hand with subdomains referred to as fingers, palms, and thumbs. RdRp activity is dependent on two key zinc ions and conserved metal binding motifs of a histidine and two cysteines each.
The active site has seven catalytic motifs that are labeled A through G. Motif B serves as a hinge which allows the active site to associate with template RNA and Motif F directly interacts with the phosphate group of incoming free nucleotides.
RdRp has to interact with RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
, which is negatively charged, so multiple subdomains including the primer-template entry site, NTP entry site, and the RNA strand exit routes contain positively charged residues. RdRp is unique from host RNA polymerases in that it has to associate with RNA instead of DNA, many RdRp residues interact with RNA bases via 2’-OH groups on the ribose ring which provides a possibly structural explanation for its specificity for RNA.
Coronavirus nsp12 cannot function independently; it has two essential cofactor proteins, nsp7 and nsp8, that form a Replication and Transcription Complex (RTC). Structural studies of the RTC indicate that nsp7 and nsp8 form an 8:8 hexadecamer which acts as a primase
DNA primase is an enzyme involved in the replication of DNA and is a type of RNA polymerase. Primase catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA (or DNA in some
living organisms) segment called a primer complementary to a ssDNA (single-stranded ...
to initiate viral replication.
While nsp12 is relatively well conserved across the ''Coronavirus'' viral species, there are biochemical and structural differences between the RdRp domain of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 RdRp has lower enzymatic activity and lower thermal stability compared to the RdRp domain in SARS-CoV
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV'', Betacoronavirus pandemicum'')The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This m ...
.
Targeting by Remdesivir
Nsp12 is researched as a target for antiviral drugs as it is highly structurally conserved across related viruses and strains, and there are no human proteins with close structural homology. The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 and associated COVID19 disease led to the investigation ofRemdesivir
Remdesivir, sold under the brand name Veklury, Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. is a Broad-spectrum antiviral drug, broad-spectrum ...
as an antiviral drug for SARS-CoV-2. Remdesivir is a nucleoside analog which can compete with ATP for incorporation into the RNA strand and prematurely terminate RNA synthesis.
NiRAN Domain
Coronavirus nsp12 has an N-terminal nidovirus RdRp-associatednucleotidyltransferase
Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituents of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates. The general reaction of transferring a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from A to B, ca ...
(NiRAN) domain which is essential for viral replication. The NiRAN domain is capable of transferring nucleotides as functional groups and it contains three key motifs called A, B, and C with seven invariant residues.
The biological function of the nsp12 NiRAN domain is not as well characterized as RdRp, but recent research has elucidated a possible role for the NiRAN domain in viral RNA capping. An additional non-structural protein, nsp9, was shown to associate with nsp12. The biologically active form of nsp9 was additionally shown to be capable of binding nucleic acids with a preference for single-stranded RNA and could cleave nucleotide triphosphates and transfer the resulting nucleotide monophosphates to protein substrates in a process called NMPylation. Park and colleagues demonstrated that the SARS-CoV-2 NiRAN domain could cleave a pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate () and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (), among others. Often pyrophosphates a ...
from the end of an uncapped RNA genome and transfer the monophosphorylated RNA to nsp9 to RNAylate it. The domain can then transfer the monophosphorylated RNA from nsp9 to a Guanidine Diphosphate (GDP) to form the initial cap structure for SARS-CoV-2.
References
{{reflist Coronavirus proteins Viral nonstructural proteins