Nok civilization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nok culture is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham village of Nok in southern
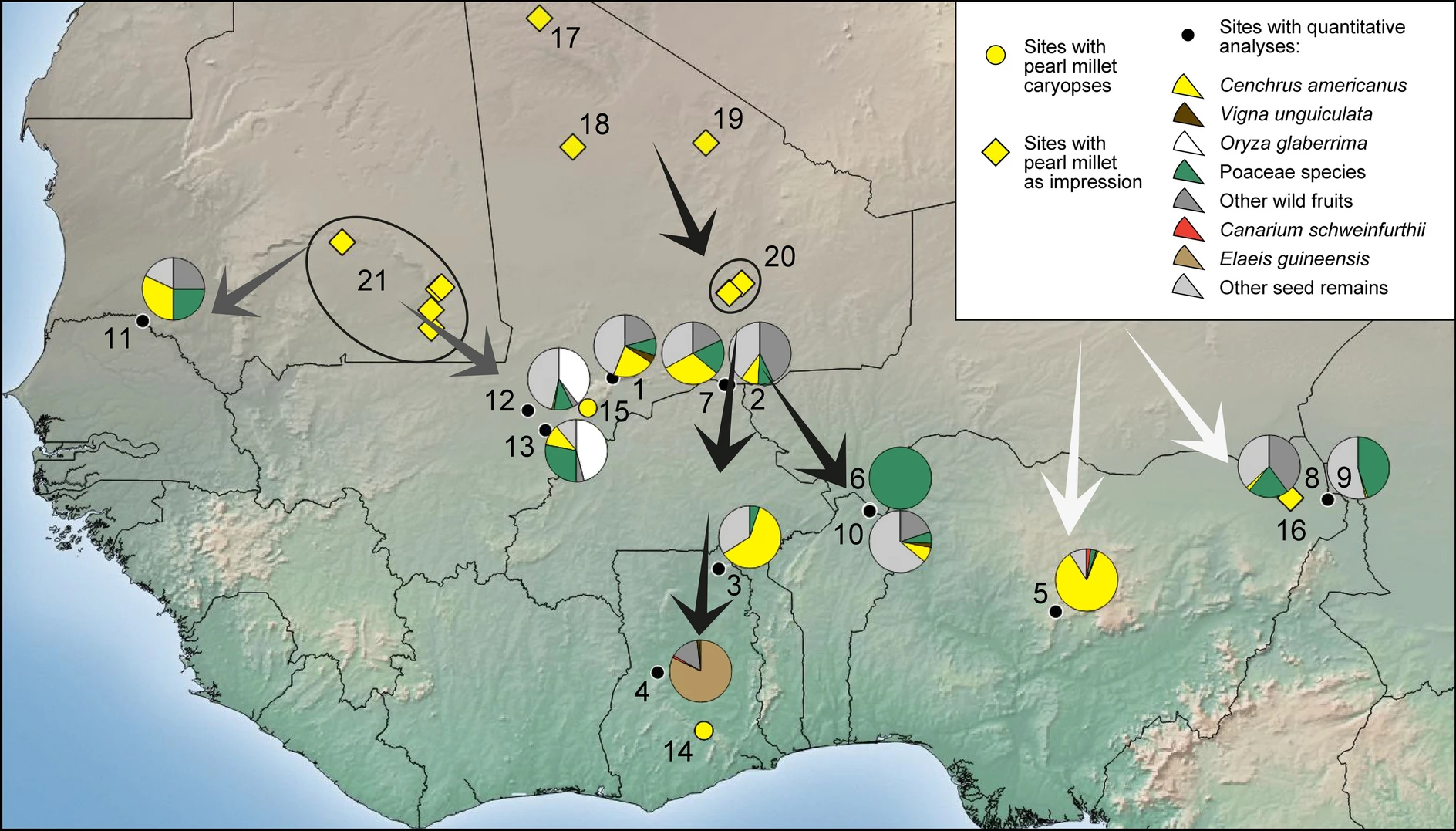
 Akin to the peoples of the Chad Basin and Kintampo culture, the people of the Nok culture employed a mixed cropping method of cultivating cowpeas and pearl millet as well as utilized oleaginous fruits. At Pangwari, pearl millet was
Akin to the peoples of the Chad Basin and Kintampo culture, the people of the Nok culture employed a mixed cropping method of cultivating cowpeas and pearl millet as well as utilized oleaginous fruits. At Pangwari, pearl millet was
Rupp, N.; Breunig, P.; Kahlheber, S. (2008). Exploring the Nok enigma. Antiquity, Project gallery.
*Shaw, T., (1981). The Nok sculptures of Nigeria. Scientific American 244(2): 154-166. *Tylecote, R. (1975a). The origin of iron smelting in Africa. Westafrican Journal of Archaeology. 5, 1-9. *Tylecote, R. (1975b). Iron smelting at Taruga, Nigeria. Journal of Historical Metallurgy 9 (2), 49-56. *Olubunmi A.O. (2007) The Rise and Fall of The Yoruba Race, The 199 Publishing Palace *Olubunmi A.O. (2009) On Ijesa Racial Purity, The 199 Publishing Palace *Ayoade J.O. (1983) Introduction To Climatology For The Tropics, John Wiley & Sons ltd UK
Kaduna State
Kaduna (, جىِهَر كَدُنا; مدينة كدونا; , ; ) is a States of Nigeria, state in the northwest geopolitical zone of Nigeria. The state capital is its namesake, the city of Kaduna (city), Kaduna, which was the List of Nigerian ...
of Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, where their terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
s were first discovered in 1928. The Nok people and the Gajiganna people may have migrated from the Central Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, along with pearl millet and pottery, and diverged prior to arriving in the northern region of modern-day Nigeria. This may have led to their respective settlements in the regions of Gajiganna and Nok. Nok people may have also migrated from the West African Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
to the region of Nok. Nok culture may have emerged in 1500 BCE and continued to persist until 1 BCE.
Nok people may have developed terracotta sculptures, through large-scale economic production, as part of a complex funerary culture that may have included practices such as feasting. The earliest Nok terracotta sculptures may have developed in 900 BCE. Some Nok terracotta sculptures portray figures wielding slingshots, as well as bows and arrows, which may be indicative of Nok people engaging in the hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
, or trapping
Animal trapping, or simply trapping or ginning, is the use of a device to remotely catch and often kill an animal. Animals may be trapped for a variety of purposes, including for meat, fur trade, fur/feathers, sport hunting, pest control, and w ...
, of undomesticated animals. A Nok sculpture portrays two individuals, along with their goods
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides welfare or utility to someone. Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs ...
, in a dugout canoe. Both of the anthropomorphic figures in the watercraft
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine.
Types
Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories.
*Raf ...
are paddling
Paddling, in regard to waterborne transport, is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using at least one hand-held paddle. The paddle, which consists of one or two blades joined to a shaft, is also used to steer the vessel via generatin ...
. The Nok terracotta depiction of a dugout canoe may indicate that Nok people used dugout canoes to transport cargo
In transportation, cargo refers to goods transported by land, water or air, while freight refers to its conveyance. In economics, freight refers to goods transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. The term cargo is also used in cas ...
, along tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
(e.g., Gurara River) of the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
, and exchanged them in a regional trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
network. The Nok terracotta depiction of a figure with a seashell on its head may indicate that the span of these riverine trade routes
A trade route is a Logistics, logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing Good (economics and accounting ...
may have extended to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
coast. In the maritime history
Maritime history is the study of human interaction with and activity at sea. It covers a broad thematic element of history that often uses a global approach, although national and regional histories remain predominant. As an academic subject, it ...
of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, there is the earlier Dufuna canoe, which was constructed approximately 8000 years ago in the northern region of Nigeria; as the second earliest form of water vessel known in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
, the Nok terracotta depiction of a dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed-out tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (tr ...
was created in the central region of Nigeria during the first millennium BCE. As part of Nok traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) refers to the knowledge, skills, and practices rooted in the cultural beliefs of various societies, especially Indigenous groups, used for maintaining health and treatin ...
, Nok ceramics may have been used to process root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
s and bark as medicinal plants
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including Plant defense against h ...
for the production of medicinal decoctions.
Excluding ancient Egyptian figurative art, Nok sculptures are regarded to be the earliest examples of large three-dimensional (sculptural) figurative art in continental Africa. Latter artistic traditions of West Africa – Bura of Niger (3rd century CE – 10th century CE), Koma of Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
(7th century CE – 15th century CE), Igbo-Ukwu of Nigeria (9th century CE – 10th century CE), Jenne-Jeno of Mali (11th century CE – 12th century CE), and Ile Ife of Nigeria (11th century CE – 15th century CE) – may have been shaped by the earlier West African clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
tradition of the Nok culture. Nok settlement sites are often found on mountaintops. Iron metallurgy may have independently developed in the Nok culture between 750 BCE and 550 BCE.
Origin
Breunig and Rupp (2016) stated: "Their origin is unknown, but since the plants they used as crops (especiallymillet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
) are indigenous to the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
region, a northern homeland is more probable than any other." Breunig (2017) expounded: "The people of the Nok culture must have come from somewhere else. So far, however, we have not found out what region, though we suspect the Sahel zone in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
." Champion et al. (2022) suggested that they may have come from the Central Sahara, and stated:
The cultivation of pearl millet diffused from the desiccating West and Central Sahara into the West African savanna zone after 2500 BCE, in the context of southwards population movements (Ozainne et al. 2014; Neumann 2018; Fuller et al. 2021)…The presence ofpearl millet Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...without roulette decorations or chaff temper, as seen in the Nok and early Gajiganna sites, suggests that the third diffusion originated directly from the centralSahara The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...and possibly split before reachingnorthern Nigeria Northern Nigeria (or Arewa, Arewancin Nijeriya) was an autonomous division within Nigeria, distinctly different from the southern part of the country, with independent customs, foreign relations and security structures. In 1962, it acquired t ..., accounting for the differences in Nok and Gajiganna pottery (Fig. 8; and see Champion 2020, p. 462).

Archaeology
The first Nok terracotta was discovered in 1928 by Colonel Dent Young, a co-owner of a mining partnership, near the village of Nok inKaduna State
Kaduna (, جىِهَر كَدُنا; مدينة كدونا; , ; ) is a States of Nigeria, state in the northwest geopolitical zone of Nigeria. The state capital is its namesake, the city of Kaduna (city), Kaduna, which was the List of Nigerian ...
, Nigeria. The terracotta was accidentally unearthed at a level of from an alluvial tin mine. Young presented the sculptures to the Museum of the Department of Mines in Jos.
Fifteen years later, in 1943 near the village of Nok, in the center of Nigeria, a new series of clay figurine
A figurine (a diminutive form of the word ''figure'') or statuette is a small, three-dimensional sculpture that represents a human, deity or animal, or, in practice, a pair or small group of them. Figurines have been made in many media, with cla ...
s were discovered by accident while mining tin. A clerk in charge of the mine had found a head and had taken it back to his home for use as a scarecrow, a role that it filled (successfully) for a year in a yam field. This scarecrow was eventually noticed by Bernard Fagg who at the time was an administrative officer who had studied archaeology at the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, wo ...
. Fagg noticed that the head on the scarecrow looked similar to the sculpture that Young had found. He traveled to Jos where Young showed Fagg other recently uncovered terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
figures. Eventually it became clear that the tin mining in Nok and Jema'a areas was revealing and destroying archaeological material.
Preliminary excavations at the beginning of January 1961 began near a remote valley named Taruga near the village of Takushara. The trial excavations took place during a period of eight days. The finds included objects of wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
, a quantity of iron slag, fragments of tuyere, pottery, figurine fragments, red ocher, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
hammer-stones, and small concentrations of charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
. The most famous finds at the site were the pottery graters which were shallow, flat-bottomed dishes which were deeply scored inside with diced patterns to produce a sharp abrasive surface. These pottery graters were probably used for food preparation. In the preliminary excavation a proton magnetometer
A proton magnetometer, also known as a proton precession magnetometer (PPM), uses the principle of Earth's field NMR, Earth's field nuclear magnetic resonance (EFNMR) to measure very small variations in the Earth's magnetic field, allowing ferrou ...
survey was used to try and locate furnaces. The survey revealed a total of 61 magnetic anomalies which were mostly located in a flat, central area which probably indicated the limits of actual occupation. Twenty of the anomalies revealed concentrations of slag
The general term slag may be a by-product or co-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and recycled metals depending on the type of material being produced. Slag is mainly a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. Broadly, it can be c ...
and nine of them contained in situ
is a Latin phrase meaning 'in place' or 'on site', derived from ' ('in') and ' ( ablative of ''situs'', ). The term typically refers to the examination or occurrence of a process within its original context, without relocation. The term is use ...
structures of furnace walls and bases. The most common type of artefact found was domestic pottery which can be divided into two different types. One type are bowls or shallow basins without lips and the other are globular pots which have averted lips. Because of this preliminary excavation, the Nok Culture would start being regarded as belonging to the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
.
In 1989, German scientists were working in northeastern Nigeria's Chad Basin as part of a cooperative project between the University of Maiduguri located in Borno State, Nigeria, and archaeologists of Goethe University Frankfurt
Goethe University Frankfurt () is a public research university located in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It was founded in 1914 as a citizens' university, which means it was founded and funded by the wealthy and active liberal citizenry of Frankfurt ...
. This project examined the beginnings of sedentary farming societies in the Chad Basin
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered approximately on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is approximately coterminous with the sedimenta ...
. Questions arose about whether there were other societies like those in the Chad Basin, and these questions led the team to investigate the Nok Culture. In the early steps of the Frankfurt Nok Project, researchers had difficulty finding sites to excavate. The team began collaborating with Umaru Yusuf Potiskum and they started finding distinct Nok culture sites, although most were looted.Breunig, Peter (editor). 2014. Nok: African sculpture in archaeological context. Africa Magna Verlag, Germany, October 15. Scientific field work began in 2005 to systematically investigate Nok archaeological sites and to better understand Nok terracotta sculptures within their Iron Age archaeological context, and was subsequently concluded in 2021.
Sculptures
The function of Nokterracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
sculptures is still unknown. For the most part, the terracotta is preserved in the form of scattered fragments. That is why Nok art is well known today only for the heads, both male and female, whose hairstyles are particularly detailed and refined. The statues are in fragments because the discoveries are usually made from alluvial mud, in terrain made by the erosion of water. The terracotta statues found there are hidden, rolled, polished, and broken. Rarely are works of great size conserved intact making them highly valued on the international art market.
The terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
figures are hollow, coil built, nearly life sized human heads and bodies that are depicted with highly stylized features, abundant jewelry
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the ...
, and varied postures. Because of the homogeneous composition of the scultptures across the Nok cultural, in contrast to the varying compositions of Nok pottery, it is thought that Nok sculpture was made from a few clay deposits, suggesting a centralized and specialized production.
Little is known of the original function of the pieces, but theories include ancestor portrayal, grave markers, and charms to prevent crop failure, infertility, and illness. Also, based on the dome-shaped bases found on several figures, they could have been used as finials for the roofs of ancient structures.
Margaret Young-Sanchez, Associate Curator of Art of the Americas, Africa, and Oceania in The Cleveland Museum of Art, explains that most Nok ceramics were shaped by hand from coarse-grained clay and subtractively sculpted in a manner that suggests an influence from wood carving. After some drying, the sculptures were covered with slip and burnished to produce a smooth, glossy surface. The figures are hollow, with several openings to facilitate thorough drying and firing. The firing process most likely resembled that used today in Nigeria, in which the pieces are covered with grass, twigs, and leaves and burned for several hours.
As a result of natural erosion and deposition, Nok terracottas were scattered at various depths throughout the Sahel grasslands, causing difficulty in the dating and classification of the mysterious artifacts. Luckily, two archaeological sites, Samun Dukiya and Taruga, were found containing Nok art that had remained unmoved. Radiocarbon and thermo-luminescence tests dated the sculptures to a range of dates between about 2,900 and 2,000 years ago, making them some of the oldest in Western Africa. Many further dates were retrieved in the course of new archaeological excavations, extending the beginnings of the Nok tradition even further back in time.
Because of the similarities between the two sites, archaeologist Graham Connah
Graham Edward Connah (11 August 1934 - 25 November 2023) was a British-born archaeologist who worked extensively in Britain, West Africa and Australia.
Connah was born in Cheshire, UK on 11 August 1934, and educated at Wirral Grammar School, an ...
believes that "Nok artwork represents a style that was adopted by a range of iron-using farming societies of varying cultures, rather than being the diagnostic feature of a particular human group as has often been claimed."
Nok people may have developed terracotta sculptures through large-scale economic production. Among Nok terracotta sculptures at Pangwari, there are sculptures portraying a large teeth-bearing therianthropic (human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
- feline) figure and the torso of a seated figure wearing a belt around their waist and a necklace, which had added features (e.g., bows, knots); there are also sculptures portraying the head of a human figure that has a bird beak and the head of a male figure with a seashell on it, which may have been created by the same sculptor. Additionally, there are sculptures portraying figures wielding slingshots, as well as bows and arrows, which may be indicative of Nok people engaging in the hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
, or trapping
Animal trapping, or simply trapping or ginning, is the use of a device to remotely catch and often kill an animal. Animals may be trapped for a variety of purposes, including for meat, fur trade, fur/feathers, sport hunting, pest control, and w ...
, of untamed animals.
One Nok sculpture portrays two individuals, along with their goods
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides welfare or utility to someone. Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs ...
, in a dugout canoe. Both of the anthropomorphic figures in the watercraft
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine.
Types
Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories.
*Raf ...
are paddling
Paddling, in regard to waterborne transport, is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using at least one hand-held paddle. The paddle, which consists of one or two blades joined to a shaft, is also used to steer the vessel via generatin ...
. The Nok terracotta depiction of a dugout canoe may indicate that Nok people utilized dugout canoes to transport cargo
In transportation, cargo refers to goods transported by land, water or air, while freight refers to its conveyance. In economics, freight refers to goods transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. The term cargo is also used in cas ...
, along tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
(e.g., Gurara River) of the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
, and exchanged them in a regional trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
network. The Nok terracotta depiction of a figure with a seashell on its head may indicate that the span of these riverine trade routes
A trade route is a Logistics, logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing Good (economics and accounting ...
may have extended to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
coast. In the maritime history
Maritime history is the study of human interaction with and activity at sea. It covers a broad thematic element of history that often uses a global approach, although national and regional histories remain predominant. As an academic subject, it ...
of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, there is the earlier Dufuna canoe, which was constructed approximately 8000 years ago in the northern region of Nigeria; as the second earliest form of water vessel known in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
, the Nok terracotta depiction of a dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed-out tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (tr ...
was created in the central region of Nigeria during the first millennium BCE.
Based on evidence from the sites of Nok archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
, such as considerable quantities of charcoal layered among Nok sculptures, goods (e.g., technically crafted ceramics, numerous stone-beaded necklaces) found in burial pits that support the view of them serving as grave
A grave is a location where a cadaver, dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is burial, buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of buria ...
sites, difference in soil coloring of burial pits and their immediate geographic area, and burial pits containing materials from organic substances, this supports the conclusion that Nok sculptures were part of a complex funerary culture.
Excluding ancient Egyptian figurative art, Nok sculptures are regarded to be the most early, large figurative art in continental Africa. Later artistic traditions of West Africa: Bura of Niger (3rd century CE – 10th century CE), Koma of Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
(7th century CE – 15th century CE), Igbo-Ukwu of Nigeria (9th century CE – 10th century CE), Jenne-Jeno of Mali (11th century CE – 12th century CE), and Ile Ife of Nigeria (11th century CE – 15th century CE) – may have been shaped by the earlier West African clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
tradition of the Nok culture.
Settlements and architecture
In the central region ofNigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, Nok archaeological sites
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
are determined to be settlement sites, on the basis of archaeological evidence discovered at the surface level of the sites, and determined to be of the Nok culture, on the basis of the type of archaeological evidence discovered, specifically, Nok terracotta remnants and Nok pottery. Nok settlement sites have been found in flat plains, on hilltops, and on the slopes and summits of mountains. There appears to have been a preference for specific topographic features like elevations and gentle slopes, possibly because they provided favourable drainage during the rainy season. In a preliminary study published in 2005, Rupp et al. stated that the foundation of a wall had been carved out of the underlying granite at the settlement site of Kochio, and that a 'megalithic
A megalith is a large Rock (geology), stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging ...
stone fence' had been erected around a central area in the settlement. However in a subsequent study published in 2016 the authors concluded that these were in fact misinterpreted natural geological features, and that there was no evidence for any stone architecture at Nok sites, apart from the rare exception of the circular stone foundation of a hut discovered in Puntun Dutse. The archaeological evidence indicates that Nok houses were built primarily of organic materials like wood, plant stalks, grasses, and animal hides, which decomposed without leaving visible traces in the soil. Typical Nok settlements were either hamlets or single compounds, similar in size to modern farmsteads found in the same area. There is no indication of agglomerations of people above village level, thus "no evidence that would warrant the existence of communities of a size that would be necessary to develop social stratification, which is regarded as one of the attributes of social complexity." Numerous excavations and prospections have indicated that no towns or any kind of urban environments existed in the Nok culture, and no evidence has been found for special buildings or areas occupied by high-ranking community members. The lack of substantial stratigraphies or evidence of mound formation processes further indicates that Nok sites had brief occupation episodes. In sum, the evidence indicates that Nok culture communities were small-scaled and organised in locally autonomous groups. According to Rupp et al. (2016):
Iron metallurgy
Iron metallurgy may have developed in the Nok culture between 750 BCE and 550 BCE. Nok people may have independently invented iron metallurgy in the 9th century BCE or 8th century BCE.Stone tools
The shapes of stone tools found at Nok sites change little throughout the entire span of the Nok Culture. What tends to strike researchers is a lack of cutting tools. Apart from stone axes, no tools with a cutting edge have been found.Projectile point
In archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have been kept in the ...
s made of either iron or stone are also absent from Nok sites.
Grinding tools are very common at Nok sites. They are rarely preserved in one piece, but can still illustrate the different shapes and sizes of tools used throughout the Nok Culture. Grinding stones were made of quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tecton ...
, granitic
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental ...
, or metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
. At the site of Ungwar Kura, grinding stones seem to have been placed in a certain order, and at the site of Ido huge grinding slabs were arranged in an upright position with pots and stone beads next to them. This context is assumed to have been ritual in some way. Most of the grinders are merely hand-sized. Throughout Nok sites, there is an abundance of grinding slabs but there seems to be a low number of hand stones. It is possible that members of the Nok Culture used these grinders until they reached a certain state of wear, and then repurposed them as pestles.
Ground stone axes were another tool commonly used by the Nok. They were typically made from fine-grained volcanic rock (siliceous rock is also sometimes seen), and may have been used in food preparation. These axe blades tend to be smallish in size, the largest reaching 20 centimeters. Stone balls are found at almost every Nok site and are approximately palm-sized. They were probably used as hammerstones or for roughening the surface of a grinding stone. Not all of them are ball shaped, however, and many have chipping marks all over or at least in one place. These stone balls likely would have served as mobile grinding stones.
Stone rings have also been found at Nok Culture sites. They are normally found as fragments but can be identified as rings because of their flat, oval or triangular cross-sections and their shapes. These stone rings are very rare and their purpose is unknown, but their use as currency or a medium of exchange has been suggested. Another rare find is stone beads, which are typically found as if strung on strings. Beads tend to be carefully made out of hard siliceous rock such as quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
, chalcedony
Chalcedony ( or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monoclinic ...
, jasper
Jasper, an aggregate of microgranular quartz and/or cryptocrystalline chalcedony and other mineral phases, is an opaque, impure variety of silica, usually red, yellow, brown or green in color; and rarely blue. The common red color is due to ...
, or carnelian. There are three different bead shapes: cylindrical, which is the most common shape, as well as rod and ring-shaped.
Ceramics
Potsherds (pottery shards) are the most abundant archaeological artifacts at Nok sites. Since 2009, excavated pottery has been undergoing systematic analysis with a central aim to try and establish a chronology. Certain attributes of the pottery such as decoration, shape, and size appear with an increasing frequency and then disappear, being replaced with different pottery attributes. This change can sometimes allow one to divide the progression into different intervals based on the different attributes. In total approximately 90,000 potsherds have been collected, of which 15,000 have been considered diagnostic, meaning that they are decorated, sherds from the rim or the bottom of the vessel, or they have handles or holes in them. The results of the pottery analysis can be delineated into three distinct time periods: Early, Middle, and Late.Early Nok Period ceramics
From approximately c. 1500–900 BC the pottery of the Early Nok Period are mostly small and not very well preserved. They seem to be richly decorated with various elaborate patterns directly below the vessels' rims and covering a large part of the ceramic body. The lines made on the pottery seem to be remarkably fine or curving lines. There tend to be many lines that are close together and some even have crisscrossing lines beneath the rim. Pottery frequently had everted and broad, thick rims.Middle Nok Period ceramics
The Middle Nok Period is approximately from c. 900–300 BC and in this time period there is a dramatic increase of sites, terracotta fragments and iron objects. Instead of the early period's decoration, which tended to cover most of the pot, instead, there is a decorative band which is bordered by deep horizontal lines. This band appears on the pots' upper half or directly under the rim of the bowls. Some bands have sharp ends as well as impressed zigzag lines or an incised wave or arc. Unlike the Early Nok period the Middle Nok ceramics tend to have more variety in the rim with everted rims, open bowls, bowls with inverted rims and incised line ornaments on the rims' lips.Late Nok Period ceramics
The Late Nok period is from approximately c. 300–1 BC and has only a few known sites. There is little pottery available for analysis but from the pottery that was found there is a decrease in the strictness of the ornamental band. While bands are still used, they are more complexly decorated with additional patterning. There also tends to be a returning pattern of body decoration. The variety of rim sizes and types seem to be increasing even more than in the Middle Nok period.Farming
 Akin to the peoples of the Chad Basin and Kintampo culture, the people of the Nok culture employed a mixed cropping method of cultivating cowpeas and pearl millet as well as utilized oleaginous fruits. At Pangwari, pearl millet was
Akin to the peoples of the Chad Basin and Kintampo culture, the people of the Nok culture employed a mixed cropping method of cultivating cowpeas and pearl millet as well as utilized oleaginous fruits. At Pangwari, pearl millet was domesticated
Domestication is a multi-generational mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a steady supply of reso ...
and cultivated, cowpeas were cultivated, and various forms of vegetation (e.g., Caesalpinioideae, Canarium schweinfurthii, Combretaceae
The Combretaceae, often called the white mangrove family, are a family of flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, G ...
, Phyllanthaceae, Vitex
''Vitex'' is a genus of flowering plants in the sage family Lamiaceae. It has about 250 species.Raymond M. Harley, Sandy Atkins, Andrey L. Budantsev, Philip D. Cantino, Barry J. Conn, Renée J. Grayer, Madeline M. Harley, Rogier P.J. de Kok, Tat ...
) were utilized. Hunting-gathering was another subsistence pattern
A subsistence pattern – alternatively known as a subsistence strategy – is the means by which a society satisfies its basic needs for survival. This encompasses the attainment of nutrition, water, and shelter. The five broad categories of sub ...
followed by the Nok people.
Grains
Nok peoples may have migrated into the central region of Nigeria and brought into the area the agricultural knowledge of cultivating tamed pearl millet between 1500 BCE and 900 BCE. At almost all Nok sites, there are charred plant remains consisting of firewood and plant material for cooking. Remains ofpearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
, one of Africa's oldest grain crops, are commonly found. Pearl millet is highly productive and resistant to adverse growing conditions, including drought. Cowpea
The cowpea (''Vigna unguiculata'') is an annual herbaceous legume from the genus '' Vigna''. Its tolerance for sandy soil and low rainfall have made it an important crop in the semiarid regions across Africa and Asia. It requires very few inpu ...
s, valued for their high protein content, are also found at some sites. So far, pearl millet and cowpeas are the only crops known to have been cultivated by the Nok people. It is unclear whether they ate or farmed tubers of any kind. The numerous grinding stones found at Nok sites suggest that the grains were ground into flour and made into a type of porridge.
Fruit
Hard pits from wild fruits have been found at many Nok sites. At some sites, fruit and seeds of other wild plants such as grasses andlegumes
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consu ...
were discovered. Overall there is not a huge selection of plant remains, but this could simply mean they were not preserved. More recent evidence of Carbonized plant remains of the Nok suggest that they foraged for tree fruits.
Trees and farming
The Nok people probably used an agroforestry system, combining cultivated crops with useful trees on the same plot of land. These plots are ecologically sustainable and inter-cropping of trees and several cultivated plant species were common from the savannas to the rain forest, with the origins of the practice going back to the first millennium BC, right at the time of the Nok culture. Most West African trees are not domesticated but are part of the wild vegetation which is left after farmers clear their fields of their crops. Because they are left to grow they multiply naturally without needing to be planted. Trees can produce food, medicine and animal feed.Animals
Because of the acidic soil, no animal bones from the Nok culture have been preserved, leaving no direct evidence of what species they might have domesticated (or hunted). The only evidence for animals during the Nok culture period is the depictions of animals as figurines or terracotta sculptures.Food
As of 3500 years ago, Nok agriculturalists gathered and utilized bee products (e.g., gatheredhoney
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several species of bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of pl ...
in pottery). The honey may have been utilized by Nok agriculturalists to add to West African cuisine
West African cuisine encompasses a diverse range of foods that are split between its 16 countries. In West Africa, many families grow and raise their own food, and within each there is a division of labor. Indigenous foods consist of a number of ...
s. As evidenced by remnants of beeswax
Bee hive wax complex
Beeswax (also known as cera alba) is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in o ...
and fats from animals on ceramics, the pottery may have been utilized to store meat, along with honey utilized for preservation
Preservation may refer to:
Heritage and conservation
* Preservation (library and archival science), activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record while making as few changes as possible
* ''Preservation'' (magazine), published by the Nat ...
purposes.
Traditional medicine
As part of Noktraditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) refers to the knowledge, skills, and practices rooted in the cultural beliefs of various societies, especially Indigenous groups, used for maintaining health and treatin ...
, Nok ceramics may have been used to process root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
s and bark as medicinal plants
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including Plant defense against h ...
for the production of medicinal decoctions.
Looting and repatriation
Since the 1970s, Nok terracotta figures have been heavily looted. Even larger-scalelooting
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
commenced in the Nok cultural area in 1994, and by 1995 two main local traders emerged. Each of the main traders could employ approximately 1,000 diggers to unearth terracottas every day. Although the majority of the terracottas were fragmented, some were intact and sellable.Brodie, Neil, and Donna Yates. 2012. Nok Terracottas. Trafficking Culture: Researching the Global Traffic in Looted Cultural Objects. Because of this, hundreds of Nok Culture sites have been illegally dug in search of these terracotta sculptures. Valuable information about the Nok Culture is lost when these objects are taken from out of the ground and removed from their archaeological contexts.
In 1979, Nigeria's National Commission of Museums and Monuments Decree established the National Commission for Museums and Monuments (NCMM), which is used to manage Nigeria's cultural heritage. NCMM Decree number 77 made it illegal for anyone other than authorized personnel to buy or sell antiquities within Nigeria or export an antiquity without a permit from the NCMM. Towards the end of the 1990s the federal government of Nigeria implemented the NCMM, which initiated a series of actions to work out strategies for combating the problems of looting and to map out a plan of action. The general consensus was that laws governing antiquities and penalties for offenders needed to be strictly enforced and that all archaeological sites should be monitored. The NCMM also recommended more aggressive public enlightenment campaigns as well as a series of sensitization programs across the nation. These programs are considered a success in terms of increased awareness by law enforcement agents, as well as the Nigerian customs authorities and Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization – INTERPOL (abbreviated as ICPO–INTERPOL), commonly known as Interpol ( , ; stylized in allcaps), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and crime cont ...
. However, not all of the recommendations were implemented, because the Nigerian government did not have the resources to face the large scale of some of the challenges. For example, the government did not have the resources to place monitors at all archaeological sites, and terracotta figures still slip through Nigeria's borders.
Today, the terracotta sculptures are very highly sought after on the international art market, and so artifacts continue to be dug up without documentation of the contexts in which they were buried. A lack of extensive archaeological study has also severely limited our understanding of the Nok cultures. A joint research project with Goethe University and the National Commission for Museums and Monuments conducted since 2005 showed that more than 90% of Nok Culture sites known in the research area have been illegally looted. Art historical studies carried out shows that over 1,000 Nok terracotta sculptures have been illegally excavated and smuggled into Europe, the USA, Japan, and elsewhere. In February 2013, Daily Trust
Media Trust is a privately held Nigerian newspaper publishing company based in Abuja that publishes the English-language ''Daily Trust'', ''Weekly Trust'', ''Sunday Trust'' and the Hausa-language ''Aminiya'' newspapers, as well as a new pan-Afric ...
reported that the Nigerian Federal Ministry of Information and National Orientation repossessed five Nok statuettes looted by a French thief in August 2010. The pieces had been seized by French customs agents and were repatriated following a Nigerian Government Directive. What further complicates the problem are the many workshops which fake Nok sculptures and then put them on the market as authentic.
Descendants
As each share cultural and artistic similarity with the Nok culture found in Nok, Sokoto, and Katsina, the Niger-Congo-speaking Yoruba, Jukun, or Dakakari peoples and Bassa people may be descendants of the Nok peoples. Based on stylistic similarities with the Nok terracottas, the bronze figurines of the Yoruba Ife Empire and the Binikingdom of Benin
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as Great Benin, is a traditional kingdom in southern Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was known as Dahomey from the 17th century until 1975. The Kingdom of Benin's c ...
may also be continuations of the traditions of the earlier Nok culture.
See also
* Early Nigerian historyReferences
Bibliography
*Further reading
*Atwood, R. (2011). The NOK of Nigeria.Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
July/August 2011, 34-38.
*
*Breunig, P. & Rupp, N. (2006). Nichts als Kunst. Archäologische Forschungen zur früheisenzeitlichen Nok-Kultur in Zentral-Nigeria. Forschung Frankfurt 2-3, 73-76.
*Boullier, C.; A. Person; J.-F. Saliège & J. Polet (2001). Bilan chronologique de la culture Nok et nouvelle datations sur des sculptures. Afrique: Archéologie & Arts 2, 9-28.
*Fagg, A. (1972). A preliminary report on an occupation site in the Nok valley, Nigeria: Samun Dukiya, AF/70/1. West African Journal of Archaeology 2, 75-79.
*Fagg, B. (1959). The Nok Culture in prehistory. Journal of the Historical Society of Nigeria 1 (4), 288-293.
*Fagg, B. (1968). The Nok Culture: Excavations at Taruga. The West African Archaeological Newsletter 10, 27-30.
*Fagg, B. (1969). Recent work in West Africa: new light on the Nok Culture. World Archaeology 1 (1), 41-50.
*Fagg, B., (1990): Nok terracottas. Lagos: National Commission for Museums and Monuments.
*Jemkur, J. (1992). Aspects of the Nok Culture. Zaria.
*Rupp, N.; Ameje, J.; Breunig, P. (2005). New studies on the Nok Culture of Central Nigeria. Journal of African Archaeology 3, 2: 283-290.Rupp, N.; Breunig, P.; Kahlheber, S. (2008). Exploring the Nok enigma. Antiquity, Project gallery.
*Shaw, T., (1981). The Nok sculptures of Nigeria. Scientific American 244(2): 154-166. *Tylecote, R. (1975a). The origin of iron smelting in Africa. Westafrican Journal of Archaeology. 5, 1-9. *Tylecote, R. (1975b). Iron smelting at Taruga, Nigeria. Journal of Historical Metallurgy 9 (2), 49-56. *Olubunmi A.O. (2007) The Rise and Fall of The Yoruba Race, The 199 Publishing Palace *Olubunmi A.O. (2009) On Ijesa Racial Purity, The 199 Publishing Palace *Ayoade J.O. (1983) Introduction To Climatology For The Tropics, John Wiley & Sons ltd UK
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Nok Culture Archaeology of Nigeria African art Terracotta 10th-century BC establishments 3rd-century disestablishments 1928 archaeological discoveries Iron Age cultures of Africa