Noisy Data on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Noisy data are data that are corrupted, distorted, or have a low
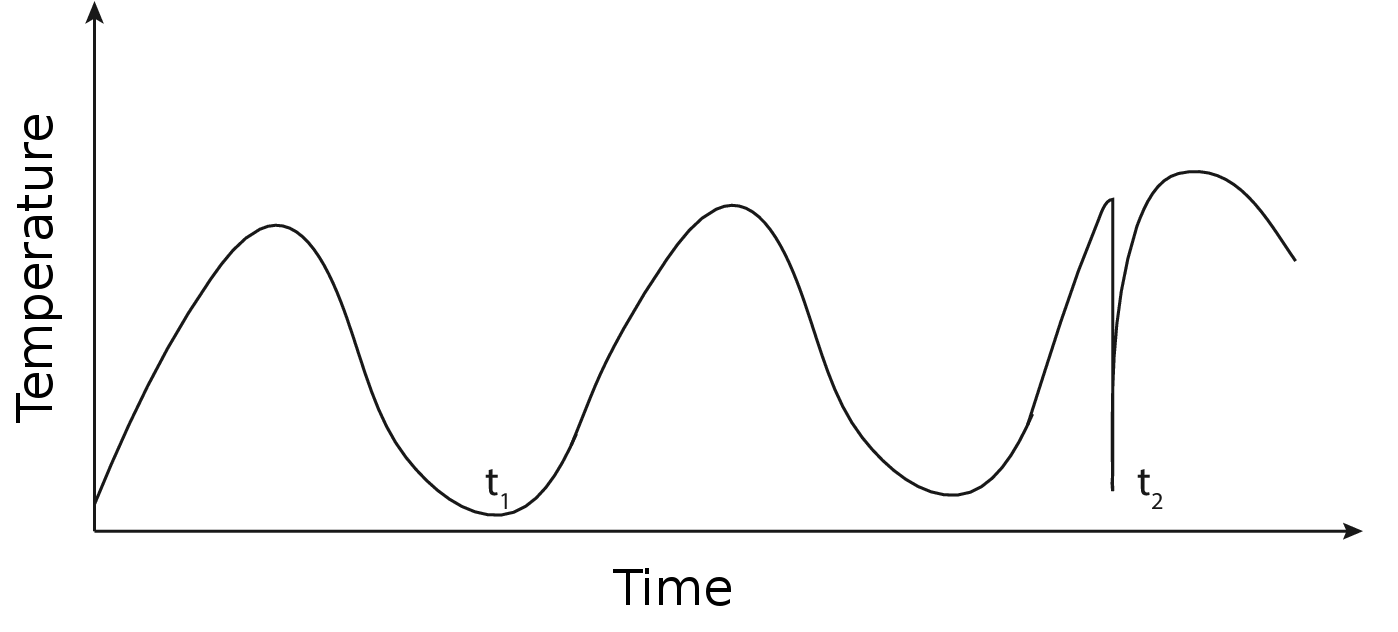 Differences in real-world measured data from the true values come about from by multiple factors affecting the measurement.
Differences in real-world measured data from the true values come about from by multiple factors affecting the measurement.
signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to noise power, often expressed in deci ...
. Improper procedures (or improperly documented procedures) to subtract out the noise in data can lead to a false sense of accuracy or false conclusions.
Noisy data are data with a large amount of additional meaningless information in them, known as noise. This includes data corruption
Data corruption refers to errors in computer data that occur during writing, reading, storage, transmission, or processing, which introduce unintended changes to the original data. Computer, transmission, and storage systems use a number of meas ...
and the term is often used as a synonym for corrupt data. It also includes any data that a user system cannot understand and interpret correctly. Many systems, for example, cannot use un structured text.
Noisy data can adversely affect the results of any data analysis and skew conclusions if not handled properly. Statistical analysis is sometimes used to weed the noise out of noisy data.
Sources of noise
 Differences in real-world measured data from the true values come about from by multiple factors affecting the measurement.
Differences in real-world measured data from the true values come about from by multiple factors affecting the measurement.
Random noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal.
Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects.
In particular, noise is inherent in physics and central to thermod ...
is often a large component of the noise in data.R.Y. Wang, V.C. Storey, C.P. Firth, A Framework for Analysis of Data Quality Research, IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 7 (1995) 623-640 doi: 10.1109/69.404034) Random noise in a signal is quantified as the signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to noise power, often expressed in deci ...
. Random noise contains a wide range of frequencies, and is also called ''white noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, i ...
'' (as wide range of colors of light combine to make ''white'').
Random noise affects the data collection and data preparation processes, where errors commonly occur. Noise has two main sources: errors introduced by measurement tools and random errors introduced by processing or by experts when the data is gathered.
Improper filtering can add noise if the filtered signal is treated as if it were a directly measured signal. As an example, Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two ...
-type digital filter
In signal processing, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a Sampling (signal processing), sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other ma ...
s such a moving average
In statistics, a moving average (rolling average or running average or moving mean or rolling mean) is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different selections of the full data set. Variations include: #Simpl ...
can have side effects such as lags or truncation of peaks. Differentiating digital filters ''amplifies'' random noise in the original data.
Outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are ...
data are data that appear to not belong in the data set. It can be caused by human error such as transposing numerals, mislabeling, programming bugs, etc. If actual outliers are not removed from the data set, they corrupt the results to a small or large degree, depending on circumstances. If valid data is identified as an outlier and is mistakenly removed, that also corrupts results.
Individuals may deliberately skew data to influence the results toward a desired conclusion. Data that looks good with few outliers reflects well on the individual collecting it, and so there may be incentive to remove more data as outliers or make the data look smoother than it is.
References
{{reflist Noise Digital audio