Nipple-sparing Mastectomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Nipple-sparing
Nipple-sparing
 Nipple-sparing
Nipple-sparing mastectomy
Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. A mastectomy is usually carried out to treat breast cancer. In some cases, women believed to be at high risk of breast cancer choose to have ...
(NSM), also known as nipple delay, is one of the surgical approaches for treating or preventing breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
. It involves the removal of all breast tissue, except the nipple-areolar complex (NAC), and the creation of new circulatory connections from the breast skin to NAC. By preserving the NAC, NSM has provided patients with higher cosmetic expectations and the opportunity to undergo a mastectomy while maintaining a more natural appearance.
The concept and technique of NSM were originally introduced by Freeman in the 1960s. This technique has offered a viable alternative for patients who prioritize cosmetic outcomes, taking into consideration factors such as tumour size, breast size, and the presence of inflammatory signs.
At the beginning of the surgery, various incision methods can be performed. Followed by flap dissection for removal of the breast tissue, NAC is preserved during the whole procedure. Breast reconstruction options, such as implant-based or flap-based reconstruction, can be pursued at last. After the surgery, proper monitoring of blood pressure and psychological support are needed.
NSM is generally safe involving a low risk of necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the NAC or surrounding skin due to interruptions of blood supply to it. Necrosis has been reported from 6%-30% of patients. The increased rates have an association with risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
s, including ptotic breasts, periareolar scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, t ...
s, large cup size, and previous radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
.
History
The concept and technique of NSM were first described by Freeman in 1962. The procedure was fraught with complications, unsatisfying cosmetic outcomes, and concerns about its oncologic safety. It was thus not widely accepted by surgeons. After the identification of the BRCA gene in the 1990s, together with the reintroduction by Hartmann et al. in their published research, the procedure regained popularity. The bulk of the study's patients had undergone NSM, and only 1% of them went on to acquire breast cancer subsequently. Whether the nipple was removed or kept, there was no difference in risk reduction. However, the suitability of NSM for individuals with excessively large or ptotic breasts has been a topic of debate. In 2009, Spear et al. conducted an initial study and concluded that NSM should not be offered to such patients. Nevertheless, in the same year, a critique of Spear challenged this conclusion by presenting a case of a patient withmacromastia
Breast hypertrophy is a rare medical condition of the breast connective tissues in which the breasts become excessively large. The condition is often divided based on the severity into two types, macromastia and gigantomastia. Hypertrophy of the ...
who underwent NSM safely following a pre-mastectomy delay procedure.
In 2020, Jay Arthur Jensen presented a new strategy that combines NSM with subtotal mastectomy. This approach not only achieves post-mastectomy nipple positioning but also avoids the potential drawbacks associated with a separate reduction mammoplasty
Mammaplasty (also called mammoplasty or mastoplasty) refers to a group of surgical procedures, the goal of which is to reshape or otherwise modify the appearance of the breast. There are three main types of mammoplasty:
# Augmentation mammaplast ...
followed by NSM or a specialized delay procedure. Importantly, all patients undergo full oncologic mastectomies, ensuring that nipple sparing can be achieved in this high-risk group within two procedures without compromising oncologic safety.
Indication
Therapeutic Candidate
Patients suffering from benign ormalignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
breast cancer can receive NSM treatment. The goal of NSM is to obtain negative margins and achieve a satisfying cosmetic outcome at the same time. NSM was ideally aimed at small breast cancer where the location of tumour is far away from the Nipple Areolar Complex (NAC), and without clinical lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
involvement. Selection of NSM candidates is based on preoperative and intraoperative
The perioperative period is the period of a patient's surgical procedure. It commonly includes ward admission, anesthesia, surgery, and recovery. Perioperative may refer to the three phases of surgery: preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperat ...
assessment.
Preoperative Assessment
Source:= Patients who have
= * undergone tumour margin evaluation by using radiological distance (mammogram
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer ...
or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
)
* a tumour size smaller than 3 cm
* a distance between tumour and NAC farther than 2 cm
* tumour located outside of the areola area
* no nipple retraction
* no blood discharge from the nipple
* no inflammatory signs
* no previous irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. An irradiator is a device used to expose an object to radiation, most often gamma radiation, for a variety of purposes. Irradiators may be used for sterilizing medical and p ...
and no micro calcifications on radiologic assessment
* no or minimal ptosis (grade 0 or 1)
* A or B cup breast size
* a BMI < 30 kg/m2
= Patients with
= * bilateral cancer *benign tumour
A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have rel ...
* preoperative radio- or chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
= Patients who are not an active smoker
= are recommended to receive this surgery. Nonetheless, patients withcontraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition (a situation or factor) that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a rea ...
s have shown positive results when using some of the more recent approaches to these difficult cases. NSM is now feasible even for patients with different contraindications. Currently, only women with inflammatory signs and nipple involvement are the absolute contraindications for conducting an NSM.
Intraoperative Assessment
Patients will undergo a frozen section examination of retroareolar tissue during the operation. The intraoperative frozen section is highly specific and moderately sensitive for identifying positive sub-areolarbiopsies
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of ...
in NSM. The examination can act as a guide for intraoperative reconstructive planning. The importance of conducting sub-areolar biopsies in all nipple-sparing mastectomies can be shown by the existence of positive sub-areolar biopsies in contralateral and high-risk prophylactic mastectomy specimens.
Prophylactic Candidate
High risk genetic mutationsBRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a ...
and BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are human genes and their protein products, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associate ...
carriers can receive preventative mastectomy as a risk-reduction treatment. The operation can reduce their overall risk of developing future breast cancer by more than 90%.
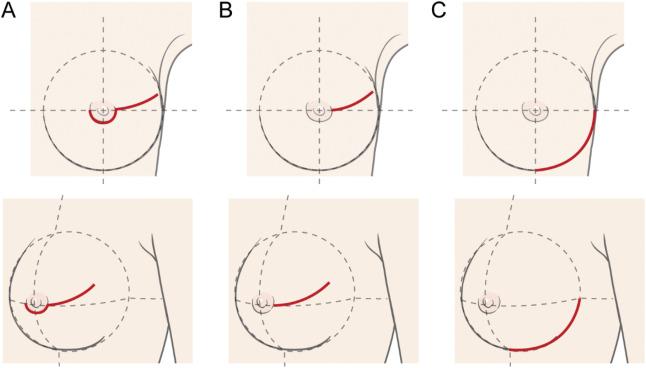
Technique
There are various ways ofincision
Incision may refer to:
* Cutting, the separation of an object, into two or more portions, through the application of an acutely directed force
* A type of open wound caused by a clean, sharp-edged object such as a knife, razor, or glass splinter
* ...
. The selection of incision methods depends on the skin perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer t ...
and cosmetic factors.

Inframammary fold (IMF) incision
This is the most common incision approach. An approximately 9 cm incision is performed inferiorly to the nipple. It then extends laterally along the IMF. The incision can be displaced 4 cm medially if theinternal mammary arteries
The internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurc ...
are desired as the recipient vessel for autologous reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
.
Vertical radial incision
A vertical radial incision extends from the bottom of the areola border to theinframammary fold
In human anatomy, the inframammary fold (IMF), inframammary crease or inframammary line is the natural lower boundary of the breast; the place where the breast and the chest meet. The choice of the term depends on the prominence of the feature. I ...
. This incision is preferable by plastic surgeons as it allows upward positioning of the nipple for ptosis correction.
Circumareolar with lateral extension incision
The incision is performed around the button half portion of the areolar border to the inframammary fold laterally. This approach is preferred by surgeons who routinely perform skin-sparing mastectomies via circumareolar incision.Preexisting scars incision
NSM can be performed through preexisting incision for prevention of additional scarring. After incision, mastectomy flap dissection is performed. Exposure is created by retraction of the skin flap with counter-tension by countertraction of the breast gland. This technique allows better visualization and access to the underlying breast tissue. Breast and ductal tissues are removed from the chest wall and the pectoralis muscle, including the pectoralis fascia. Through the whole procedure, the NAC is preserved by dissecting the tissues away from the underlying structures to maintain the blood supply and nerve connections to the nipple. Any breast reconstruction approaches, including implant-based reconstruction and flap-based reconstruction, may be done after the surgery. Implant-based reconstructions are most commonly selected as they allow the rebuilding of a moderate size of breast. Flap-based reconstruction utilizes autologous tissue, such as muscle or subcutaneous from alternative body regions for reconstructing the breast mound.Postoperative management
Physical
Monitoring ofblood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
is vital after the surgery. If any hypotensive situation occurs in patients, intravascular fluid injection is required for replenishment of blood pressure. Drugs containing epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
should be avoided to prevent vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vesse ...
and reduced blood flow through the anastomosis
An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (su ...
. Physical assessment, such as skin colour, capillary refill time
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the inn ...
, skin turgor
The skin turgor (associated with capillary refilling) is a term used to describe the ability of the skin to restore its shape after being deformed. The dehydration reduces the skin Elasticity (physics), elasticity and causes lower skin turgor, one ...
, skin temperature
Skin temperature is the temperature of the outermost surface of the body. Normal human skin temperature on the trunk of the body varies between 33.5 and 36.9 °C (92.3 and 98.4 °F), though the skin's temperature is lower over protrud ...
, and sensation of the breast, are used for blood pressure examination at NAC.
Psychological
Patients often suffer from depression andanxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
due to the stress of surgery and loss of breast tissue. Mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
education and self-compassion are important as a protective mechanism for body image disturbance
Body image disturbance (BID) is a common symptom in patients with eating disorders and is characterized by an altered Body image, perception of one's own body.
The onset is mainly attributed to patients with anorexia nervosa who persistently t ...
and psychological distress
Mental distress or psychological distress encompasses the symptoms and experiences of a person's internal life that are commonly held to be troubling, confusing or out of the ordinary. Mental distress can potentially lead to a change of behavior, ...
. However, this surgical approach provides greater psychological benefits than other mastectomy due to the preservation of the NAC and women’s body image.
Risk and complication
NSM has the same perioperative complications as skin-sparing mastectomy and breast reconstruction. One of the most common risks would benecrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the NAC and the surrounding skin tissues. This is affected by the oxygenating ability of the breast skin, which relates to the blood supply. The blood supply to the NAC particularly may be interfered with by the NSM. The average rate of partial or full skin flap necrosis is 9.5%. This is likely due to the surgical techniques and patient selection. BMI, breast mass, and sternal notch to nipple length are more adversely affecting the risk of necrosis.
Although breast reconstruction is known to be safe, there might still be some complications, including infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, seroma
A seroma is a pocket of clear serous fluid (filtered blood plasma). They may sometimes develop in the body after surgery, particularly after breast surgery, abdominal surgery, and reconstructive surgery. They can be diagnosed by physical sign ...
, hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
, and capsule contracture
In pathology, a contracture is a shortening of muscles, tendons, skin, and nearby soft tissues that causes the joints to shorten and become very stiff, preventing normal movement. A contracture is usually permanent, but less commonly can be temp ...
.
The risk of NAC necrosis can be reduced by the ‘delayed’ procedure. It consists of the creation of new circulatory connections from the breast skin to the NAC. In this way, the NAC may no longer be completely dependent on the breast tissue underneath for its blood supply.
As the NAC is preserved, patients may encounter a higher risk of occult NAC tumour. The retroareolar tissue is not removed completely and thus more terminal duct lobular units are left in patient’ s body, which induces higher oncological risk.
Significance
The difference between NSM and skin-sparing mastectomy (SSM) is that NSM allows preservation of the NAC but SSM does not. One of the main reasons to preserve the NAC is for patients’ satisfaction and psychological benefits. It is a crucial component of the breast, given its aesthetics and contribution tosexual pleasure
Sexual stimulation is anything that leads to sexual arousal or orgasm. This thing can be physical or of other senses, and is known as a stimulus.
Sexual stimulation is a broad term, usually understood to mean physical touching of the genitals ...
. Even though the NAC can be reconstructed after performing SSM, the reconstruction is difficult due to the unique appearance of every NAC. Overall, NSM can result in higher sexual and psychosocial well-being.
References
{{Reflist Breast surgery