Nile River Flow Bayesian Changepoint Detection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing
Of the world's major rivers, the Nile has one of the lowest average annual flow rates. About long, its
 With a total length of about between the region of
With a total length of about between the region of
 The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At
The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At

 The Blue Nile (, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile come from the Atbarah and Blue Nile, both of which originate in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water coming from the Blue Nile. The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian
The Blue Nile (, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile come from the Atbarah and Blue Nile, both of which originate in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water coming from the Blue Nile. The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian

 The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the
The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the
 The Nile has been the lifeline of civilization in Egypt since the
The Nile has been the lifeline of civilization in Egypt since the
 The Greek historian
The Greek historian
 To the ancient Greeks and Romans, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown, as they failed to penetrate the ''
To the ancient Greeks and Romans, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown, as they failed to penetrate the '' Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt,
Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt,
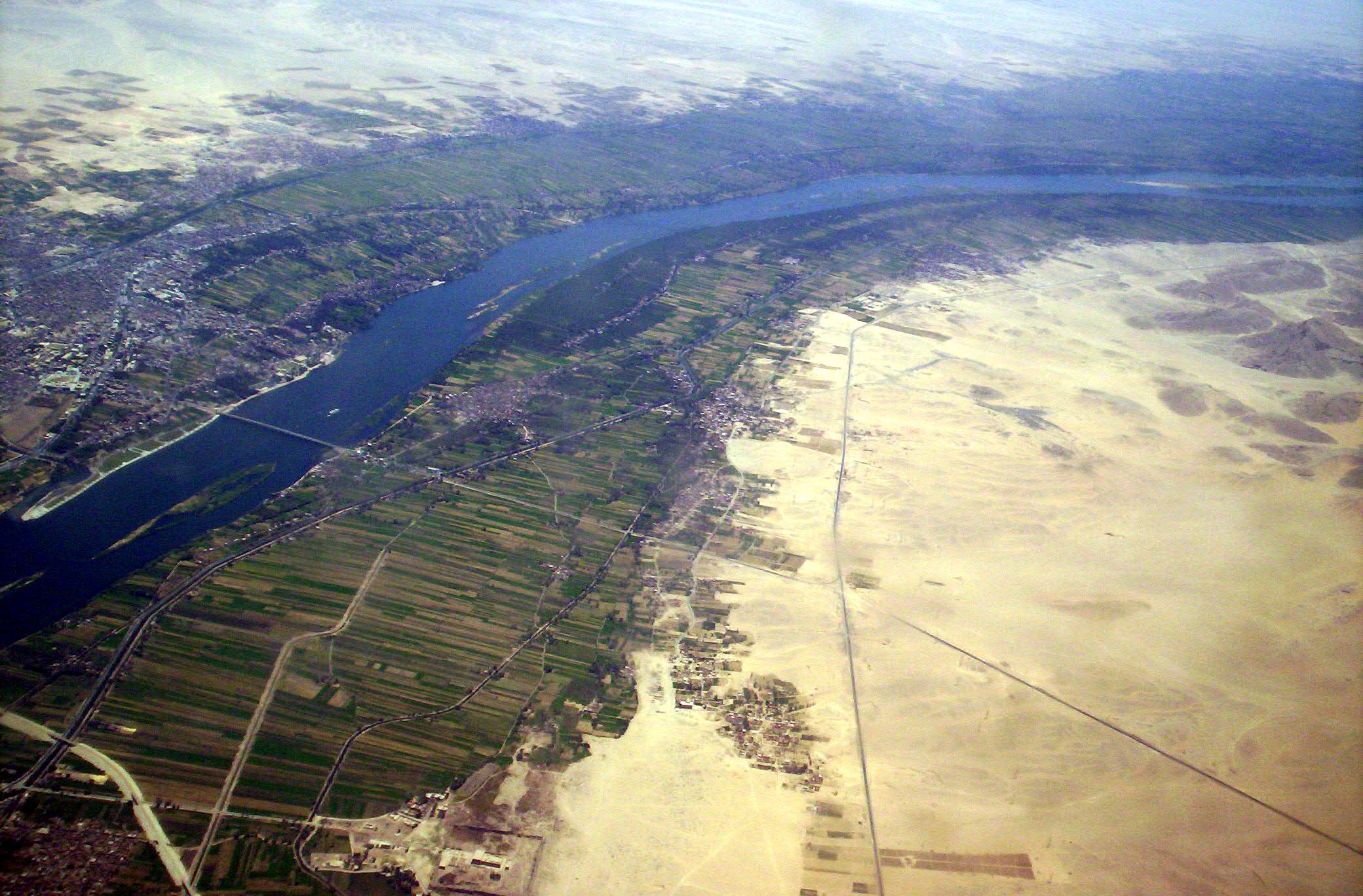
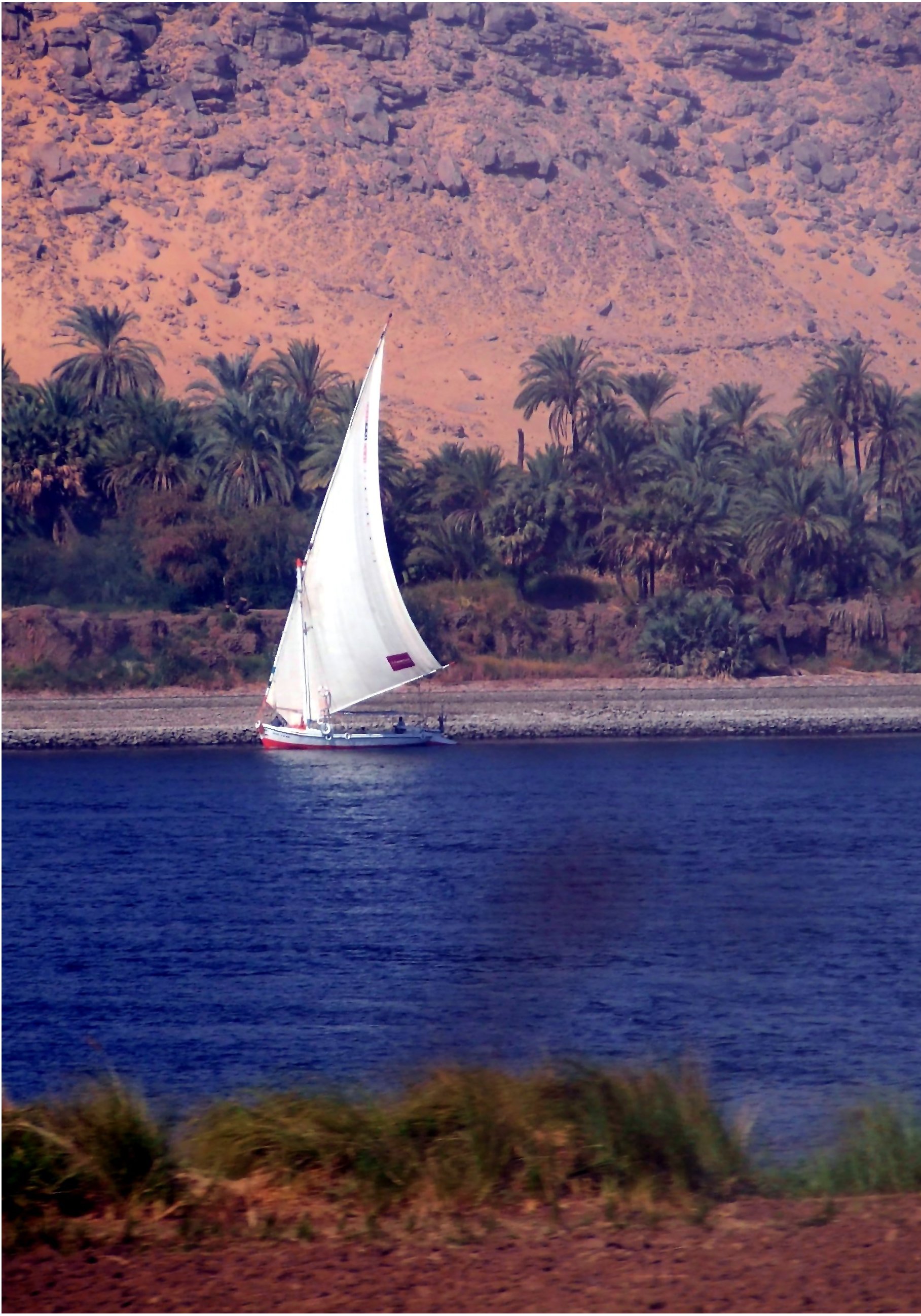
 The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the
The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the
; Report by Strategic Foresight Group From the 70 incidents of drought which took place between 1900 and 2012, 55 incidents took place in Ethiopia, Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya and Tanzania.
 The Nile waters have affected the populations, cultures, economies, and politics of
The Nile waters have affected the populations, cultures, economies, and politics of
 The following bridges cross the Blue Nile and connect Khartoum to Khartoum North:
* Mac Nimir Bridge
* Blue Nile Road & Railway Bridge
* Burri Bridge
* Elmansheya Bridge
*
The following bridges cross the Blue Nile and connect Khartoum to Khartoum North:
* Mac Nimir Bridge
* Blue Nile Road & Railway Bridge
* Burri Bridge
* Elmansheya Bridge
*
A Struggle Over the Nile
– slideshow by ''
Thesis Analyzing Nile River Negotiations
(archived 10 January 2016) *
Old maps of the Nile
from the Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The
river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
in northeastern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river in the world,
though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists SayOf the world's major rivers, the Nile has one of the lowest average annual flow rates. About long, its
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, Burundi
Burundi, officially the Republic of Burundi, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is located in the Great Rift Valley at the junction between the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa, with a population of over 14 million peop ...
, Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
, South Sudan
South Sudan (), officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered on the north by Sudan; on the east by Ethiopia; on the south by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Kenya; and on the ...
, Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
.
In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan.
In these countries it is an important economic factor in agriculture and fishing.
The Nile has two major tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
: the White Nile
The White Nile ( ') is a river in Africa, the minor of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the larger being the Blue Nile. The name "White" comes from the clay sediment carried in the water that changes the water to a pale color.
In the stri ...
and the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major Tributary, tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the wa ...
. The White Nile, being the longer, is traditionally considered to be the headwaters
The headwater of a river or stream is the geographical point of its beginning, specifically where surface runoff water begins to accumulate into a flowing channel of water. A river or stream into which one or many tributary rivers or streams flo ...
stream, while the Blue Nile actually contributes 80% of the water and silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
below the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also ''conflux'') occurs where two or more watercourses join to form a single channel (geography), channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main ...
of the two. The White Nile rises in the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
region. It begins at Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropics, tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface are ...
and flows through Uganda and South Sudan. The Blue Nile begins at Lake Tana
Lake Tana (; previously transcribed Tsana) is the largest lake in Ethiopia and a source of the Blue Nile. Located in Amhara Region in the north-western Ethiopian Highlands, the lake is approximately long and wide, with a maximum depth of , and ...
in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast. The two rivers meet at the Sudanese capital of Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum is the capital city of Sudan as well as Khartoum State. With an estimated population of 7.1 million people, Greater Khartoum is the largest urban area in Sudan.
Khartoum is located at the confluence of the White Nile – flo ...
.
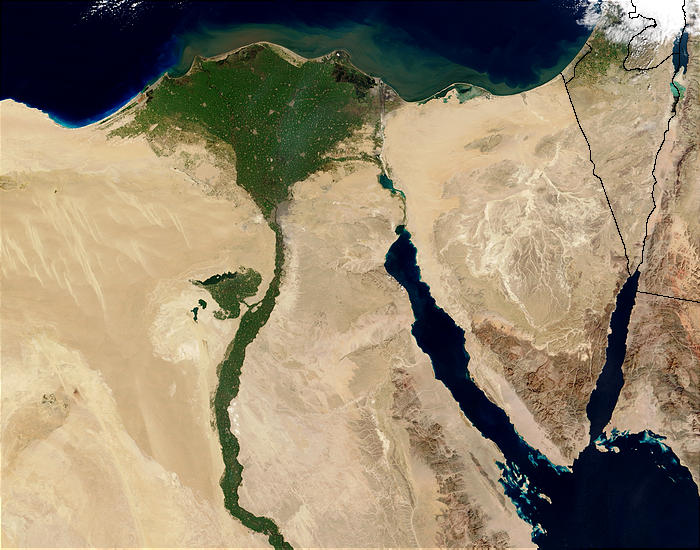
After Khartoum the river flows north, almost entirely through the Nubian Desert
The Nubian Desert ( ) is in the eastern region of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, spanning approximately 400,000 km2 of northeastern Sudan and northern Eritrea, between the Nile and the Red Sea. The arid region is rugged and rocky and contains s ...
, to Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
and its large delta, joining the Mediterranean Sea at Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
. Egyptian civilization and Sudanese kingdoms have depended on the river and its annual flooding since ancient times. Most of the population and cities of Egypt lie along those parts of the Nile valley north of the Aswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. When it was completed, it was the tallest earthen dam in the world, surpassing the Chatuge D ...
. Nearly all the cultural and historical sites of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
developed and are found along river banks. The Nile is, with the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Ròse''; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''Rôno'') is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and Southeastern France before dischargi ...
and Po, one of the three Mediterranean rivers with the largest water discharge.
Etymology
In the ancientEgyptian language
The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian (; ), is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world ...
, the Nile is called ''Ḥꜥpy'' (Hapy) or ''Jtrw'' (Iteru), meaning "river". In Coptic, the word ⲫⲓⲁⲣⲟ, pronounced ''piaro'' ( Sahidic) or ''phiaro'' ( Bohairic), means "the river" (lit. p(h).iar-o "the-canal-great"), and comes from the same ancient name. In Nobiin, the river is called ''Áman Dawū'', meaning "the great water". In Luganda
Ganda or Luganda ( ; ) is a Bantu language spoken in the African Great Lakes region. It is one of the major languages in Uganda and is spoken by more than 5.56 million Ganda people, Baganda and other people principally in central Uganda, includ ...
, the river is called ''Kiira'' or ''Kiyira''. In Runyoro, it is called ''Kihiira''. In Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian, or simply as Masri, is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic variety in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The esti ...
, the Nile is called ''en-Nīl'', while in Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages also the variety of spoken Arabic that ...
it is called ''an-Nīl''. In Biblical Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew ( or ), also called Classical Hebrew, is an archaic form of the Hebrew language, a language in the Canaanite languages, Canaanitic branch of the Semitic languages spoken by the Israelites in the area known as the Land of Isra ...
, it is , ''Ha-Ye'or'' or , ''Ha-Shiḥor''.
The English name ''Nile'' and the Arabic names ''en-Nîl'' and ''an-Nîl'' both derive from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
' and the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
. Beyond that, however, the etymology is disputed. Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
called the river , ''Aiguptos'', but in subsequent periods, Greek authors referred to its lower course as ''Neilos''; this term later became generalized for the entire river system. Thus, the name may derive from Ancient Egyptian expression ''n''ꜣ ''r''ꜣ''w-ḥ''ꜣ''w(t)'' (), which referred specifically to the branches of the Nile transversing the Delta, and would have been pronounced ''ni-lo-he'' in the area around Memphis in the 8th century BCE. Hesiod
Hesiod ( or ; ''Hēsíodos''; ) was an ancient Greece, Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer.M. L. West, ''Hesiod: Theogony'', Oxford University Press (1966), p. 40.Jasper Gr ...
at his ''Theogony
The ''Theogony'' () is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogy, genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Homeric Greek, epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contains 1,022 lines. It is one ...
'' refers to Nilus (Νεῖλος) as one of the river gods
A water deity is a deity in mythology associated with water or various bodies of water. Water deities are common in mythology and were usually more important among civilizations in which the sea or ocean, or a great river was more important. Anoth ...
, son of Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus ( ; , also , , or ) was a Titans, Titan son of Uranus (mythology), Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys (mythology), Tethys, and the father of the River gods (Greek mythology), river gods ...
and Tethys.
Another derivation of ''Nile'' might be related to the term ''Nil'' (; ), which refers to ''Indigofera tinctoria
''Indigofera tinctoria'', also called true indigo, is a species of plant from the bean family that was one of the original sources of indigo dye.
Description
True indigo is a shrub high. It may be an annual plant, annual, biennial plant, bie ...
'', one of the original sources of indigo dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive indigo, blue color. Indigo is a natural dye obtained from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera#Uses, ''Indigofera'' genus, in particular ''Indigofera tinctoria''. Dye-bearing ''Indigofer ...
. Another possible etymology derives from the Semitic term ''Nahal'', meaning "river". Old Libyan has the term ''lilu'', meaning water (in modern Berber ''ilel'' ⵉⵍⴻⵍ means ''sea'').
Courses
 With a total length of about between the region of
With a total length of about between the region of Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropics, tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface are ...
and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, the Nile is among the longest rivers on Earth. The drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of the Nile covers , about 10% of the area of Africa. Compared to other major rivers, though, the Nile carries little water (5% of that of the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
, for example). The Nile basin is complex, and because of this, the discharge at any given point along the main stem
In hydrology, a main stem or mainstem (also known as a trunk) is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". The mainstem extends all the way from one specific headwater to the outlet of the river, although t ...
depends on many factors including weather, diversions, evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
and evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) refers to the combined processes which move water from the Earth's surface (open water and ice surfaces, bare soil and vegetation) into the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of w ...
, and groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
flow.
Upstream from Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum is the capital city of Sudan as well as Khartoum State. With an estimated population of 7.1 million people, Greater Khartoum is the largest urban area in Sudan.
Khartoum is located at the confluence of the White Nile – flo ...
(to the south), the river is known as the White Nile
The White Nile ( ') is a river in Africa, the minor of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the larger being the Blue Nile. The name "White" comes from the clay sediment carried in the water that changes the water to a pale color.
In the stri ...
, a term also used in a limited sense to describe the section between Lake No and Khartoum. At Khartoum, the river is joined by the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major Tributary, tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the wa ...
. The White Nile starts in equatorial East Africa, and the Blue Nile begins in Ethiopia. Both branches are on the western flanks of the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
.
Sources
The source of the Blue Nile isLake Tana
Lake Tana (; previously transcribed Tsana) is the largest lake in Ethiopia and a source of the Blue Nile. Located in Amhara Region in the north-western Ethiopian Highlands, the lake is approximately long and wide, with a maximum depth of , and ...
in the Gish Abay
Gish Abay is a town in west-central Ethiopia. Located in the Mirab Gojjam Zone, Mirab (West) Gojjam Zone of the Amhara Region, it is the administrative center of Sekela (woreda), Sekela woreda. The town is named after the nearby Mount Gish and the ...
region in the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
.
The source of the White Nile, even after centuries of exploration, remains in dispute. The most remote source that is indisputably a source for the White Nile is of the Kagera River
The Kagera River, also known as Akagera River, or Alexandra Nile, is an East African river, forming part of the upper headwaters of the Nile and carrying water from its most distant source.Stanley, H.M., 1899, Through the Dark Continent, London: ...
; however, the Kagera has multiple tributaries that are in contention for the farthest source of the White Nile. Two start in Burundi: the Ruvyironza River (also known as the Luvironza) and the Rurubu River. In addition, in 2010, an exploration party in Rwanda went to a place described as the source of the Rukarara tributary, and by hacking a path up steep jungle-choked mountain slopes in the Nyungwe Forest found (in the dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
) an appreciable incoming surface flow for many kilometres upstream, thence finding a new source, giving the Nile a length of .
In Uganda
The White Nile leavesLake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropics, tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface are ...
at Ripon Falls near Jinja, Uganda
Jinja is a city in the Eastern Region, Uganda, Eastern Region of Uganda, located on the north shore of Lake Victoria.
Location
Jinja is in Jinja District, Busoga sub-region, in the Eastern Region of Uganda. It is approximately east of Kampala, ...
, as the "Victoria Nile." It flows north for some to Lake Kyoga
Lake Kyoga or Lake Kioga (literally 'the place of bathing' in Runyoro language) is a large shallow lake in Uganda, about in area and at an elevation of 1,033 metres. The Victoria Nile flows through the lake on its way from Lake Victoria to Lake ...
. The last part of the approximately river section starts from the western shores of the lake and flows at first to the west until just south of Masindi Port, where the river turns north, then makes a great half circle to the east and north to Karuma Falls. For the remaining part, it flows westerly through the Murchison Falls
Murchison Falls, also known as Kabalega Falls, is a waterfall in Uganda, located at the apex of Lake Albert on the White Nile. At the top of Murchison Falls, the Nile forces its way through a gap in the rocks, only wide, and tumbles , before fl ...
until it reaches the northern shores of Lake Albert where it forms a significant river delta. Lake Albert is on the border of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, but the Nile is not a border river at this point. After leaving Lake Albert, the river continues north through Uganda and is known as the Albert Nile.
In South Sudan
The White Nile flows into South Sudan just south ofNimule
Nimule is a city in the southern part of South Sudan in Magwi County, Eastern Equatoria. It lies approximately , by road, southeast of Juba, the capital of South Sudan and largest city in the country. The town also lies approximately , by road, n ...
, where it is known as the ''Bahr al Jabal'' ("Mountain River"). Just south of the town is the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also ''conflux'') occurs where two or more watercourses join to form a single channel (geography), channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main ...
with the Achwa River. The Bahr al Ghazal, long, joins the Bahr al Jabal at a small lagoon called Lake No, after which the Nile becomes known as the ''Bahr al Abyad'', or the White Nile, from the whitish clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
suspended in its waters. When the Nile floods it leaves a rich silty deposit which fertilizes the soil. The Nile no longer floods in Egypt since the completion of the Aswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. When it was completed, it was the tallest earthen dam in the world, surpassing the Chatuge D ...
in 1970. An anabranch
An anabranch is a section of a river or stream that diverts from the main channel or stem of the watercourse and rejoins the main stem downstream. Local anabranches can be the result of small islands in the watercourse. In larger anabranches, ...
river, the Bahr el Zeraf, flows out of the Nile's Bahr al Jabal section and rejoins the White Nile.
The flow rate of the Bahr al Jabal at Mongalla is almost constant throughout the year and averages . After Mongalla, the Bahr Al Jabal enters the enormous swamps of the Sudd
The Sudd (, Nuer: Baki̱ec, Dinka: Toc) is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile's '' Baḥr al-Jabal'' section. The Arabic word ' is derived from ' (), meaning "barrier" or "obstruction". The term "the sudd" has come to ref ...
region. More than half of the Nile's water is lost in this swamp to evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
and transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. It is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. Transpiration also cools plants, c ...
. The average flow rate of the White Nile at the tails of the swamps is about . From here it meets with the Sobat River
The Sobat River is a river of the Greater Upper Nile region in northeastern South Sudan, Africa. It is the most southerly of the great eastern tributaries of the White Nile, before the confluence with the Blue Nile.
Geography
The Sobat River is ...
at Malakal
Malakal is a city in South Sudan, serving as the capital of Upper Nile (state), Upper Nile State in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan, along the White Nile, White Nile River. It also serves as the headquarter of Malakal County and it us ...
. On an annual basis, the White Nile upstream of Malakal contributes about 15% of the total outflow of the Nile.
The average flow of the White Nile at Lake Kawaki Malakal, just below the Sobat River, is ; the peak flow is approximately in October and minimum flow is about in April. This fluctuation is caused by the substantial variation in the flow of the Sobat, which has a minimum flow of about in March and a peak flow of over in October. During the dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
(January to June) the White Nile contributes between 70% and 90% of the total discharge from the Nile.
In Sudan
BelowRenk
The Renk Group AG is a German global manufacturer of transmissions, engines, hybrid drive systems, vehicle suspension systems, plain bearings, couplings, and testing systems. The company builds special gearboxes for tanks, frigates, icebreakers, ...
, the White Nile enters Sudan, it flows north to Khartoum and meets the Blue Nile.
The course of the Nile in Sudan is distinctive. It flows over six groups of cataracts, from the sixth at Sabaloka just north of Khartoum northward to Abu Hamad. The tectonic uplift of the Nubian Swell
The Nubian Swell is a geologic structural uplift in northern Africa that trends east to west and separates the lower Nile of Egypt from the Sudan basin. The Nubian Swell has been geologically active since early Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the ...
diverts the river south-west for over 300 km, following the structure of the Central African Shear Zone
The Central African Shear Zone (CASZ) (or Shear System) is a wrench fault system extending in an ENE direction from the Gulf of Guinea through Cameroon into Sudan.
The structure is not well understood.
, there was still no general agreement about ...
embracing the Bayuda Desert
The Bayuda Desert, located at , is in the eastern region of the Sahara Desert, spanning approximately 100,000 km2 of northeast Sudan north of Omdurman and south of Korti, embraced by the great bend of the Nile in the north, east, and sout ...
. At Al Dabbah it resumes its northward course towards the first cataract at Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the Nile at the first cataract. The modern city ha ...
forming the S-shaped Great Bend of the Nile mentioned by Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
.
In the north of Sudan, the river enters Lake Nasser
Lake Nasser ( ', ) is a large reservoir (water), reservoir in southern Egypt and northern Sudan. It was created by the construction of the Aswan Dam, Aswan High Dam and is one of the List of reservoirs by volume, largest man-made lakes in the wo ...
(known in Sudan as Lake Nubia), the larger part of which is in Egypt.
In Egypt
Below theAswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. When it was completed, it was the tallest earthen dam in the world, surpassing the Chatuge D ...
, at the northern limit of Lake Nasser, the Nile resumes its historic course. North of Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
, the Nile splits into two branches (or distributaries) that feed the Mediterranean: the Rosetta
Rosetta ( ) or Rashid (, ; ) is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799.
Founded around the 9th century on the site of the ancient town of Bolbitine, R ...
Branch (an anglicized version of the name Rashid) to the west and the Damietta
Damietta ( ' ) is a harbor, port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt. It is located at the Damietta branch, an eastern distributary of the Nile Delta, from the Mediterranean Sea, and about north of Cairo. It was a Cath ...
to the east, forming the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the eas ...
.
Sediment transport
 The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At
The annual sediment transport by the Nile in Egypt has been quantified.
* At Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the Nile at the first cataract. The modern city ha ...
: 0.14 million tonnes of suspended sediment
The suspended load of a flow of fluid, such as a river, is the portion of its sediment uplifted by the fluid's flow in the process of sediment transportation. It is kept suspended by the fluid's turbulence. The suspended load generally consists of ...
and an additional 28% of bedload
The term bed load or bedload describes particles in a flowing fluid (usually water) that are transported along the stream bed. Bed load is complementary to suspended load and wash load.
Bed load moves by rolling, sliding, and/or saltating (hop ...
* At Beni Sweif: 0.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 20% of bedload
* At Qena: 0.27 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 27% of bedload
* At Sohag
Sohag (, , ), also spelled as Suhag or Suhaj, is a city on the west bank of the Nile in Egypt. It has been the capital of Sohag Governorate since 1960, before which the capital was Girga and the name of the governorate was Girga Governorate. I ...
: 1.5 million tonnes of suspended sediment and an additional 13% of bedload
Tributaries
Atbarah River
Below the confluence with the Blue Nile the only major tributary is the Atbarah River, also known as the Red Nile. Roughly halfway to the sea, it originates in Ethiopia north ofLake Tana
Lake Tana (; previously transcribed Tsana) is the largest lake in Ethiopia and a source of the Blue Nile. Located in Amhara Region in the north-western Ethiopian Highlands, the lake is approximately long and wide, with a maximum depth of , and ...
, and is around long. The Atbarah flows only while there is rain in Ethiopia and dries very rapidly. During the dry period of January to June, it typically dries up north of Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum is the capital city of Sudan as well as Khartoum State. With an estimated population of 7.1 million people, Greater Khartoum is the largest urban area in Sudan.
Khartoum is located at the confluence of the White Nile – flo ...
.
Blue Nile

 The Blue Nile (, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile come from the Atbarah and Blue Nile, both of which originate in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water coming from the Blue Nile. The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian
The Blue Nile (, ''ʿĀbay'') springs from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. The Blue Nile flows about 1,400 kilometres to Khartoum, where the Blue Nile and White Nile join to form the Nile. Ninety percent of the water and ninety-six percent of the transported sediment carried by the Nile come from the Atbarah and Blue Nile, both of which originate in Ethiopia, with fifty-nine percent of the water coming from the Blue Nile. The erosion and transportation of silt only occurs during the Ethiopian rainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* '' ...
when rainfall is especially high in the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
; the rest of the year, the great rivers draining Ethiopia into the Nile have a weaker flow. In harsh and arid seasons and droughts, the Blue Nile dries out completely.
The flow of the Blue Nile varies considerably over its yearly cycle and is the main contribution to the large natural variation of the Nile flow. During the dry season the natural discharge of the Blue Nile can be as low as , although upstream dams regulate the flow of the river. During the wet season, the peak flow of the Blue Nile often exceeds in late August (a difference of a factor of 50).
Before the placement of dams on the river the yearly discharge varied by a factor of 15 at Aswan. Peak flows of over occurred during late August and early September, and minimum flows of about occurred during late April and early May.
Bahr el Ghazal and Sobat River
The Bahr al Ghazal and theSobat River
The Sobat River is a river of the Greater Upper Nile region in northeastern South Sudan, Africa. It is the most southerly of the great eastern tributaries of the White Nile, before the confluence with the Blue Nile.
Geography
The Sobat River is ...
are the two most important tributaries of the White Nile in terms of discharge.
The Bahr al Ghazal's drainage basin is the largest of any of the Nile's sub-basins, measuring in size, but it contributes a relatively small amount of water, about annually, because tremendous volumes of water are lost in the Sudd wetlands.
The Sobat River, which joins the Nile a short distance below Lake No, drains about half as much land, , but contributes annually to the Nile. When in flood the Sobat carries a large amount of sediment, adding greatly to the White Nile's color.
Yellow Nile

 The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the
The Yellow Nile is a former tributary that connected the Ouaddaï highlands Ouaddaï may refer to:
* Ouaddaï highlands, an area in eastern Chad along the border with Sudan
* Ouaddaï Prefecture Ouaddaï may refer to:
* Ouaddaï highlands, an area in eastern Chad along the border with Sudan
* Ouaddaï Prefecture, a for ...
of eastern Chad to the Nile River Valley to . Its remains are known as the Wadi Howar
Wadi Howar (Wadi Howa or Yellow Nile) is a wadi in Sudan and Chad.
Geography
Originating in the Ennedi Region of Chad ''Wadi Howar'' runs through the Sudanese states of North Darfur and Northern to join the Nile north of the great bend opposi ...
. The wadi passes through Gharb Darfur near the northern border with Chad and meets up with the Nile near the southern point of the Great Bend.
History
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, with most of the population and all of the cities of Egypt developing along those parts of the Nile valley lying north of Aswan. However, the Nile used to run much more westerly through what is now Wadi Hamim and Wadi al Maqar in Libya and flow into the Gulf of Sidra
The Gulf of Sidra (), also known as the Gulf of Sirte (), is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya, named after the oil port of Sidra or the city of Sirte. It was also historically known as the Great Sirte or G ...
. As the sea level rose at the end of the most recent ice age, the stream which is now the northern Nile captured the ancestral Nile near Asyut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut''. ( ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at , while the ancient city i ...
. This change in climate also led to the current extents of the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
desert, around 3400 BCE.
Khufu branch
TheGiza pyramid complex
The Giza pyramid complex (also called the Giza necropolis) in Egypt is home to the Great Pyramid of Giza, Great Pyramid, the pyramid of Khafre, and the pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx of G ...
originally overlooked a branch of the Nile that no longer exists. This branch was highest during the African Humid Period
The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) was a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grass ...
.
Ancient Niles
The existing Nile has five earlier phases: *i) the Upper Miocenian Eonile, of about 6 million years BP; *ii) the Upper Pliocenian Paleonile, commencing about 3.32 million years BP, and during thePleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
;
*iii) The Nile phases, including the Proto-Nile, commencing about 600,000 years BP;
*iv) Pre-Nile;
*v) transitioning at about 400,000 years BP to the Neo-Nile.
Flowing north from the Ethiopian Highlands, satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell im ...
was used to identify dry watercourses in the desert to the west of the Nile. A canyon, now filled by surface drift, represents the Eonile that flowed during 23–5.3 million years before present. The Eonile transported clastic sediments to the Mediterranean; several natural gas fields have been discovered within these sediments.
During the late-Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
Messinian salinity crisis
In the Messinian salinity crisis (also referred to as the Messinian event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event) the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (drying-up) throughout the latter part of ...
, when the Mediterranean Sea was a closed basin
Closed may refer to:
Mathematics
* Closure (mathematics), a set, along with operations, for which applying those operations on members always results in a member of the set
* Closed set, a set which contains all its limit points
* Closed interval, ...
and evaporated to the point of being empty or nearly so, the Nile cut its course down to the new base level until it was several hundred metres below world ocean level at Aswan and below Cairo. This created a very long and deep canyon which was filled with sediment after the Mediterranean was recreated. At some point the sediments raised the riverbed sufficiently for the river to overflow westward into a depression to create Lake Moeris
Lake Moeris (, genitive Μοίριδος) was an ancient endorheic freshwater lake located in the Faiyum Oasis, southwest of Cairo, Egypt, which persists today at a fraction of its former size as the hypersaline Lake Qarun (Arabic: بركة ق� ...
.
Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika ( ; ) is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake. It is the world's List of lakes by volume, second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the List of lakes by depth, second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. ...
drained northwards into the Nile until the Virunga Volcanoes blocked its course in Rwanda. The Nile was much longer at that time, with its furthest headwaters in northern Zambia. The currently existing Nile first flowed during the former parts of the Würm glaciation
The Würm glaciation or Würm stage ( or ''Würm-Glazial'', colloquially often also ''Würmeiszeit'' or ''Würmzeit''; cf. ice age), usually referred to in the literature as the Würm (often spelled "Wurm"), was the last glacial period in the ...
period.
Affad 23 is an archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or recorded history, historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline ...
located in alluvial deposits formed by an ancient channel of the Nile in the Affad region of southern Dongola Reach
The Dongola Reach is a reach of approximately 160 km in length stretching from the Fourth downriver to the Third Cataracts of the Nile in Upper Nubia, Sudan. Named after the Sudanese town of Dongola which dominates this part of the river, the r ...
, Sudan.
Integrated Nile
There are two theories about the age of the integrated Nile. One is that the integrated drainage of the Nile is of young age and that the Nile basin was formerly broken into series of separate basins, only the most northerly of which fed a river following the present course of the Nile in Egypt and Sudan. Rushdi Said postulates that Egypt supplied most of the waters of the Nile during the early part of its history.Said, R. (1981). ''The geological evolution of the River Nile''.Springer Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing.
Originally founded in 1842 in ...
.
The other theory is that the drainage from Ethiopia via rivers equivalent to the Blue Nile, the Atbara and the Takazze flowed to the Mediterranean via the Egyptian Nile since well back into Tertiary
Tertiary (from Latin, meaning 'third' or 'of the third degree/order..') may refer to:
* Tertiary period, an obsolete geologic period spanning from 66 to 2.6 million years ago
* Tertiary (chemistry), a term describing bonding patterns in organic ch ...
times.Williams, M.A.J.; Williams, F. (1980). ''Evolution of Nile Basin''. In M.A.J. Williams and H. Faure (eds). ''The Sahara and the Nile''. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 207–224.
R. B. Salama suggests that a series of separate closed continental basins each occupied one of the major parts of the Sudanese Rift System that during the Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
and Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of th ...
periods (66 million to 2.588 million years ago): Mellut rift, White Nile rift, Blue Nile rift, Atbara rift and Sag El Naam rift.
The Mellut Basin is nearly deep at its central part. This rift could possibly be still active, with reported tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
activity in its northern and southern boundaries. The Sudd
The Sudd (, Nuer: Baki̱ec, Dinka: Toc) is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile's '' Baḥr al-Jabal'' section. The Arabic word ' is derived from ' (), meaning "barrier" or "obstruction". The term "the sudd" has come to ref ...
swamp which forms the central part of the basin may still be subsiding. The White Nile Rift system, although shallower than the Bahr el Arab rift, is about deep. Geophysical exploration of the Blue Nile Rift System estimated the depth of the sediments to be . These basins were not interconnected until their subsidence ceased, and the rate of sediment deposition was enough to fill and connect them.
The Egyptian Nile connected to the Sudanese Nile, which captures the Ethiopian and Equatorial headwaters during the current stages of tectonic activity in the Eastern, Central and Sudanese Rift systems.Salama, R.B. (1997). ''Rift Basins of Sudan. African Basins, Sedimentary Basins of the World. 3.'' Edited by R.C. Selley (Series Editor K.J. Hsu) pp. 105–149. ElSevier, Amsterdam. The connection of the different Niles occurred during cyclic wet periods. The Atbarah overflowed its closed basin during the wet periods that occurred about 100,000 to 120,000 years ago. The Blue Nile connected to the main Nile during the 70,000–80,000 years B.P. wet period. The White Nile system in Bahr El Arab and White Nile Rifts remained a closed lake until the connection of the Victoria Nile to the main system some 12,500 years ago during the African humid period
The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) was a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grass ...
.
Role in the founding of Egyptian civilization

 The Greek historian
The Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
wrote that "Egypt was the gift of the Nile". An unending source of sustenance, it played a crucial role in the development of Egyptian civilization. Because the river overflowed its banks annually and deposited new layers of silt, the surrounding land was very fertile. The Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
ians cultivated and traded wheat, flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
, papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
and other crops around the Nile. Wheat was a crucial crop in the famine-plagued Middle East. This trading system secured Egypt's diplomatic relationships with other countries and contributed to economic stability. Far-reaching trade has been carried on along the Nile since ancient times. A tune, Hymn to the Nile, was created and sung by the ancient Egyptian peoples about the flooding of the Nile River and all of the miracles it brought to Ancient Egyptian civilization.
Water buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called domestic water buffalo, Asian water buffalo and Asiatic water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also kept in Italy, the Balkans ...
were introduced from Asia, and the Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
introduced camels in the 7th century BCE. These animals were raised for meat and were domesticated and used for ploughing—or in the camels' case, carriage. Water was vital to both people and livestock. The Nile was also a convenient and efficient means of transportation for people and goods.
The Nile was also an important part of ancient Egyptian spiritual life. Hapi was the god of the annual floods, and both he and the pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
were thought to control the flooding. The Nile was considered to be a causeway from life to death and the afterlife. The east was thought of as a place of birth and growth, and the west was considered the place of death, as the god Ra, the Sun, underwent birth, death, and resurrection each day as he crossed the sky. Thus, all tombs were west of the Nile, because the Egyptians believed that in order to enter the afterlife, they had to be buried on the side that symbolized death.
As the Nile was such an important factor in Egyptian life, the ancient calendar was even based on the three cycles of the Nile. These seasons, each consisting of four months of thirty days each, were called Akhet, Peret
Pedro Pubill Calaf (, ; 24 March 1935 – 27 August 2014), better known as Peret, was a Spanish Romani singer, guitar player and composer of Catalan rumba from Mataró (Barcelona).
Known for his 1971 single, "Borriquito" ( Ariola Records), ...
, and Shemu. Akhet, which means inundation, was the time of the year when the Nile flooded, leaving several layers of fertile soil behind, aiding in agricultural growth. Peret was the growing season, and Shemu, the last season, was the harvest season when there were no rains.
European search for the source
 To the ancient Greeks and Romans, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown, as they failed to penetrate the ''
To the ancient Greeks and Romans, the upper reaches of the White Nile remained largely unknown, as they failed to penetrate the ''Sudd
The Sudd (, Nuer: Baki̱ec, Dinka: Toc) is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile's '' Baḥr al-Jabal'' section. The Arabic word ' is derived from ' (), meaning "barrier" or "obstruction". The term "the sudd" has come to ref ...
'' wetlands of South Sudan. Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
thought that source of the Nile was in Mauritania, on the "other" (south) side of the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
. Various expeditions failed to determine the river's source. Agatharchides
Agatharchides or Agatharchus ( or , ''Agatharchos'') of Cnidus was a Greek historian and geographer (flourished 2nd century BC).
Life
Agatharchides is believed to have been born at Cnidus, hence his appellation. As Stanley M. Burstein notes, the ...
records that in the time of Ptolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
, a military expedition had penetrated far enough along the course of the Blue Nile to determine that the summer floods were caused by heavy seasonal rainstorms in the Ethiopian Highlands, but no European of antiquity is known to have reached Lake Tana. The '' Tabula Rogeriana'' depicted the source as three lakes in 1154.
Europeans began to learn about the origins of the Nile in the 14th century when the Pope sent monks as emissaries to Mongolia who passed India, the Middle East and Africa, and described being told of the source of the Nile in Abyssinia (Ethiopia). Later in the 15th and 16th centuries, travelers to Ethiopia visited Lake Tana and the source of the Blue Nile in the mountains south of the lake. Supposedly, Paolo Trevisani (–1483), a Venetian traveller in Ethiopia, wrote a journal of his travels to the ''origin of the Nile'' that has since been lost.
James Bruce
James Bruce of Kinnaird (14 December 1730 – 27 April 1794) was a Scottish traveller and travel writer who physically confirmed the source of the Blue Nile. He spent more than a dozen years in North and East Africa and in 1770 became the fir ...
claimed to be the first European to have visited the headwaters.
Modern writers give the credit to the Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
Pedro Páez. Páez's account of the source of the Nile is a long and vivid account of Ethiopia. It was published in full only in the early 20th century, but was featured in works of Páez's contemporaries, like Baltazar Téllez, Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Society of Jesus, Jesuit scholar and polymath who published around 40 major works of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fellow Jes ...
and Johann Michael Vansleb.
Europeans had been resident in Ethiopia since the late 15th century, and one of them may have visited the headwaters even earlier without leaving a written trace. The Portuguese João Bermudes published the first description of the Tis Issat Falls in his 1565 memoirs, compared them to the Nile Falls alluded to in Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
's ''De Republica''. Jerónimo Lobo
Jerónimo Lobo (1595 – 29 January 1678) was a Portuguese Jesuit missionary. He took part in the unsuccessful efforts to convert Ethiopia from the native Ethiopian church to Roman Catholicism until the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1643. Afterw ...
describes the source of the Blue Nile, visiting shortly after Pedro Páez. Telles also uses his account.
The White Nile was even less understood. The ancients mistakenly believed that the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
represented the upper reaches of the White Nile. For example, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
writes that the Nile had its origins "in a mountain of lower Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It extended from central present-day Algeria to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, encompassing northern present-day Morocco, and from the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean in the ...
", flowed above ground for "many days" distance, then went underground, reappeared as a large lake in the territories of the Masaesyli
The Masaesyli were a Berber tribe of western Numidia (central and western Algeria) and the main antagonists of the Massylii in eastern Numidia.
During the Second Punic War the Masaesyli initially supported the Roman Republic and were led by Sy ...
, then sank again below the desert to flow underground "for a distance of 20 days' journey till it reaches the nearest Ethiopians."
 Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt,
Modern exploration of the Nile basin began with the conquest of the northern and central Sudan by the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and social activist. A global cultural icon, widely known by the nickname "The Greatest", he is often regarded as the gr ...
, and his sons from 1821 onward. As a result of this, the Blue Nile was known as far as its exit from the Ethiopian foothills and the White Nile as far as the mouth of the Sobat River. Three expeditions under a Turkish officer, Selim Bimbashi, were made between 1839 and 1842, and two got to the point about beyond the present port of Juba
Juba is the capital and largest city of South Sudan. The city is situated on the White Nile and also serves as the capital of the Central Equatoria, Central Equatoria State. It is the most recently declared national capital and had a populatio ...
, where the country rises and rapids make navigation very difficult.
Lake Victoria was first sighted by Europeans in 1858 when British explorer John Hanning Speke
Captain John Hanning Speke (4 May 1827 – 15 September 1864) was an English explorer and army officer who made three exploratory expeditions to Africa. He is most associated with the search for the source of the Nile and was the first Eu ...
reached its southern shore while traveling with Richard Francis Burton
Captain (British Army and Royal Marines), Captain Sir Richard Francis Burton, Order of St Michael and St George, KCMG, Royal Geographical Society#Fellowship, FRGS, (19 March 1821 – 20 October 1890) was a British explorer, army officer, orien ...
to explore central Africa and locate the great lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
. Burton, recovering from illness and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika ( ; ) is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake. It is the world's List of lakes by volume, second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the List of lakes by depth, second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. ...
, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proven his discovery to be the true source of the Nile when Burton regarded this as still unsettled. A quarrel ensued which sparked intense debate within the scientific community and interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Speke's discovery. British explorer and missionary David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, and an explorer in Africa. Livingstone was married to Mary Moffat Livings ...
pushed too far west and entered the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
system instead. It was ultimately Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley
Sir Henry Morton Stanley (born John Rowlands; 28 January 1841 – 10 May 1904) was a Welsh-American explorer, journalist, soldier, colonial administrator, author, and politician famous for his exploration of Central Africa and search for missi ...
who confirmed Speke's discovery, circumnavigating Lake Victoria and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the lake's northern shore.
Since 1950
 The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the
The Nile has long been used to transport goods along its length. Winter winds blow south, up river, so ships could sail up river using sails and down river using the flow of the river. While most Egyptians still live in the Nile valley, the 1970 completion of the Aswan Dam ended the summer floods and their renewal of the fertile soil, fundamentally changing farming practices. The Nile supports much of the population living along its banks, enabling Egyptians to live in otherwise inhospitable regions of the Sahara. The river's flow is disturbed at several points by the Cataracts of the Nile which form an obstacle to navigation by boats. The Sudd also forms a formidable navigation obstacle and impedes water flow, to the extent that Sudan had once attempted to build the Jonglei Canal
The Jonglei Canal was a canal project started, but never completed, to divert water from the vast Sudd wetlands of South Sudan so as to deliver more water downstream to Sudan and Egypt for use in agriculture. Sir William Garstin proposed the ...
to bypass the swamp.
Nile cities include Khartoum, Aswan, Luxor
Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt. Luxor had a population of 263,109 in 2020, with an area of approximately and is the capital of the Luxor Governorate. It is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited c ...
(Thebes), and the Giza
Giza (; sometimes spelled ''Gizah, Gizeh, Geeza, Jiza''; , , ' ) is the third-largest city in Egypt by area after Cairo and Alexandria; and fourth-largest city in Africa by population after Kinshasa, Lagos, and Cairo. It is the capital of ...
Cairo conurbation
A conurbation is a region consisting of a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which, through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ...
. The first cataract, the closest to the mouth of the river, is at Aswan, north of the Aswan Dam. This part of the river is a regular tourist route, with cruise ships and traditional wooden sailing boats known as felucca
A felucca is a traditional wooden sailing boat with a single sail used in the Mediterranean, including around Malta and Tunisia. However, in Egypt, Iraq and Sudan (particularly along the Nile and in the Sudanese protected areas of the Red Sea), ...
s. Many cruise ships ply the route between Luxor and Aswan, stopping at Edfu
Edfu (, , , ; also spelt Idfu, or in modern French as Edfou) is an Egyptian city, located on the west bank of the Nile River between Esna and Aswan, with a population of approximately 60,000 people. Edfu is the site of the Ptolemaic Temple of H ...
and Kom Ombo
Kom Ombo (; Coptic: or ; Ancient Greek: or ; or and ) is an agricultural town in Egypt famous for the Temple of Kom Ombo. It was originally an Egyptian city called Nubt, meaning City of Gold (not to be confused with the city north of ...
along the way. Security concerns have limited cruising on the northernmost portion for many years.
A computer simulation study to plan the economic development of the Nile was directed by H.A.W. Morrice and W.N. Allan, for the Ministry of Hydro-power of Sudan, during 1955–57 Morrice was their hydrological adviser, and Allan his predecessor. The calculations were enabled by accurate monthly inflow data collected for 50 years. The underlying principle was the use of over-year storage, to conserve water from rainy years for use in dry years. Irrigation, navigation and other needs were considered. Each computer run postulated a set of reservoirs and operating equations for the release of water as a function of the month and the levels upstream. The behavior that would have resulted given the inflow data was modeled. Over 600 models were run. Recommendations were made to the Sudanese authorities. The calculations were run on an IBM 650
The IBM 650 Magnetic Drum Data-Processing Machine is an early digital computer produced by IBM in the mid-1950s. It was the first mass-produced computer in the world. Almost 2,000 systems were produced, the last in 1962, and it was the firs ...
computer. Simulation studies to design water resources are discussed further in the article on hydrology transport models, which have been used since the 1980s to analyze water quality.
Despite the development of many reservoirs, drought during the 1980s led to widespread starvation in Ethiopia and Sudan, but Egypt was nourished by water impounded in Lake Nasser. Drought has proven to be a major cause of fatality in the Nile river basin. According to a report by the Strategic Foresight Group, droughts in the last century have affected around 170 million people and killed half a million people.Blue Peace for the Nile, 2009; Report by Strategic Foresight Group From the 70 incidents of drought which took place between 1900 and 2012, 55 incidents took place in Ethiopia, Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya and Tanzania.
Water sharing dispute
 The Nile waters have affected the populations, cultures, economies, and politics of
The Nile waters have affected the populations, cultures, economies, and politics of Northeast Africa
Northeast Africa, or Northeastern Africa, or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, encompasses the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North Africa and East Africa, and encompasses ...
and the Nile Basin
The Nile Basin is the part of Africa drained by the Nile River and its tributaries.
Besides being the second largest hydrographic basin in Africa, the Nile Basin is effectively the most notable drainage basin on the continent. It covers approxi ...
for many decades. The most recent water sharing dispute is the dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over the $4.5 billion Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD or TaIHiGe; , , ), formerly known as the Millennium Dam and sometimes referred to as the Hidase Dam (, ), is a gravity dam on the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia. The dam is in the Benishangul-Gumuz Region ...
, which has become a national preoccupation in both countries, stoking patriotism
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and a sense of attachment to one's country or state. This attachment can be a combination of different feelings for things such as the language of one's homeland, and its ethnic, cultural, politic ...
, deep-seated fears and even murmurs of war. In both Egypt and Ethiopia the Nile and the Grand Ethiopian Renaisance Dam are parts of the national identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language".
National identity ...
. In Ethiopia it is seen as a path towards increased development, whereas in Egypt fears of drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
and water shortage
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity. One is ''physical.'' The other is ''economic water scarcity''. Physic ...
prevail. For Egypt, to justify its excessive access to Nile waters, three treaties signed in 1902, 1929, and 1959 are used, which are however criticized. The 1902 and 1929 treaties were heavily influenced by colonialism
Colonialism is the control of another territory, natural resources and people by a foreign group. Colonizers control the political and tribal power of the colonised territory. While frequently an Imperialism, imperialist project, colonialism c ...
as the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
made African colonies make concessions on Nile waters to the benefit of British Egypt
The history of Egypt under the British lasted from 1882, when it was occupied by British forces during the Anglo-Egyptian War, until 18 June 1956, when the last British forces withdrew in accordance with the Anglo-Egyptian evacuation agreem ...
. With the end of colonialism and the emergence of postcolonialism
Postcolonialism (also post-colonial theory) is the critical academic study of the cultural, political and economic consequences of colonialism and imperialism, focusing on the impact of human control and extractivism, exploitation of colonized pe ...
, these treaties are seen as colonial products, which have lost their validity. The distribution of Nile waters in the treaties also sets the foundation for the alliance of Sudan and Egypt in the Nile Basin. Both states distributed practically all Nile waters between them in the 1959 agreement and still align their politics regarding the Nile waters. After the announcement of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, Sudan and Egypt conducted three military exercises
A military exercise, training exercise, maneuver (manoeuvre), or war game is the employment of military resources in training for military operations. Military exercises are conducted to explore the effects of warfare or test tactics and strat ...
together.
Already before the plans for the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam were published in 2014, several attempts have been made to establish new agreements between the countries sharing the Nile waters. Countries including Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and Kenya have complained about Egyptian domination of its water resources and the 1999 Nile Basin Initiative promoted a peaceful cooperation among those states. On 14 May 2010 at Entebbe
Entebbe is a city in Central Region, Uganda, Central Uganda which is located on Lake Victoria peninsula, approximately southwest of the Ugandan capital city, Kampala. Entebbe was once the seat of government for the Protectorate of Uganda pri ...
, Uganda, Ethiopia, Rwanda, and Tanzania signed a new agreement on sharing the Nile waters even though this agreement raised strong opposition from Egypt and Sudan. Ideally, such international agreements should promote equitable and efficient usage of the Nile basin's water resources. Without a better understanding about the availability of the future water resources of the Nile, it is possible that conflicts could arise between these countries relying on the Nile for their water supply, economic and social developments. The conflicting priorities of the Nile riparian countries according to different domestic factors such as socioeconomic status, level of development, or climatic conditions severely affect the stance of Egypt and Ethiopia in negotiations. In the several rounds of negotiations since 2014 especially the filling and operation of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam in times of water scarcity appeared to be a critical topic where no consensus was found. The talks about the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam are almost exclusively between Egypt, Sudan, and Ethiopia, however some rounds of negotiations were accompanied and led by other actors such as the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
, or the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. The failure of the several rounds of negotiations has led some to argue that the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam dispute might develop into a water war. Especially after the failed negotiations led by the United States, this risk was discussed as president Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
threatened that Egypt might “blow up the dam”. Nevertheless, a water war is thus far considered unlikely, given the serious consequences this would have for the countries involved and the region. Also, given the high protection of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam it is unclear if the Egyptian military would be successful in an attack.
Modern achievements and exploration
White Nile
In 1951, American John Goddard together with two French explorers became the first to successfully navigate the entire Nile from its source in Burundi at the potential headsprings of the Kagera River in Burundi to its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, a journey of approximately . Their 9-month journey is described in the book ''Kayaks down the Nile''. The White Nile Expedition, led by South African national Hendrik Coetzee, navigated the White Nile's entire length of approximately . The expedition began at the White Nile's beginning at Lake Victoria in Uganda, on 17 January 2004 and arrived at the Mediterranean in Rosetta, four and a half months later.Blue Nile
The Blue Nile Expedition, led by geologist Pasquale Scaturro and his partner, kayaker and documentary filmmaker Gordon Brown became the first known people to descend the entire Blue Nile, from Lake Tana in Ethiopia to the beaches of Alexandria on the Mediterranean. Their approximately journey took 114 days, from 25 December 2003 to 28 April 2004. Though their expedition included others, Brown and Scaturro were the only ones to complete the entire journey. Although they descendedwhitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's Stream gradient, gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that foam, froths, making t ...
manually, the team used outboard motor
An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes engine, gearbox and propeller or jet drive, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom. They are the most common motorised method ...
s for much of their journey.
On 29 January 2005, Canadian Les Jickling and New Zealander Mark Tanner completed the first human-powered transit of Ethiopia's Blue Nile. Their journey of over took five months. They recount that they paddled through two war zones, regions notorious for bandits, and were arrested at gunpoint.
Dangers
Inland flood events cause the highest number of casualties among all natural catastrophes - including the devastation of harvest, starvation, sickness and famine in the aftermath of floods. Millions of people have died in consequence of single flood events before. An estimated 2- 4 million people perished in consequence of the Yangtze–Huai River flood of 1931 including famine and epidemics in the following years. A flood in Egypt, caused by overtopping of AHD and the subsequent eroding of the dam, can be 20 times worse than the historic flood in China. Nasser Lake contains a water-volume that defies imagination and it would increase to 209 cubic kilometers during the events described in this study. Moreover, the flood caused by a dam breach is concentrated to plus/minus one day, instead of a seasonal flood distributed over 4 months. The short flood is much more violent. Millions of homes would be destroyed. Nationwide irrigation infrastructure would be covered by a layer of contaminated sediment that becomes hard as stone after a short while. After Nasser lake has disappeared (emptied), agricultural production would fall back to pre-AHD levels causing widespread famine for years. "Nicol-André Berdellé (2024) Breach of Aswan Dam - a realistic worst case scenarioCrossings
Crossings from Khartoum to the Mediterranean Sea
Soba
Soba ( or , "buckwheat") are Japanese noodles made primarily from buckwheat flour, with a small amount of wheat flour mixed in.
It has an ashen brown color, and a slightly grainy texture. The noodles are served either chilled with a dipping sau ...
Bridge
The following bridges cross the White Nile and connect Khartoum to Omdurman:
* White Nile Bridge
* Victory Bridge, also known as El Fitihab Bridge
The following bridges cross from Omdurman to Khartoum North:
* Hafaya Bridge
The following bridges cross to Tuti from Khartoum state's three cities:
* Tuti Bridge
The Tuti Bridge () is a modern suspension bridge linking between Tuti Island and the City of Khartoum in Sudan that was completed in February 2008.
In the past the only approach to Tuti Island was via ferries but thanks to the Tuti-Khartoum Bri ...
(previously known as the Khartoum North-Tuti bridge)
Other bridges:
* Shandi Bridge, Shendi
Shendi or Shandi () is a small city in northern Sudan, situated on the southeastern bank of the Nile River 150 km northeast of Khartoum. Shandi is also about 45 km southwest of the ancient city of Meroë. Located in the River Nile s ...
* Atbarah Bridge, Atbarah
* Merowe Dam, Merowe
* Merowe Bridge, Merowe
* Aswan Bridge, Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the Nile at the first cataract. The modern city ha ...
* Luxor Bridge, Luxor
Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt. Luxor had a population of 263,109 in 2020, with an area of approximately and is the capital of the Luxor Governorate. It is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited c ...
* Suhag Bridge, Suhag
* Assiut Bridge, Assiut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut''. ( ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at , while the ancient city i ...
* Al Minya Bridge, Minya
* Al Marazeek Bridge, Helwan
Helwan ( ', , ) is a suburban district in the Southern Area of Cairo, Egypt. The area of Helwan witnessed prehistoric, ancient Egyptian, Roman and Muslim era activity. More recently it was designated as a city until as late as the 1960s, befor ...
* First Ring Road Bridge (Moneeb Crossing), Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
* Abbas Bridge, Cairo
* University Bridge, Cairo
* Qasr al-Nil Bridge
The Qasr el Nil Bridge (originally named ''Khedive Ismail Bridge'', Egyptian Arabic: Asr el Nil Bridge), is a historic swing bridge structure dating from 1931 which replaced the first bridge to span the Nile River in central Cairo, Egypt. It conne ...
, Cairo
* 6th October Bridge, Cairo
* Abu El Ela Bridge, Cairo (removed in 1998)
* New Abu El Ela Bridge, Cairo
* Imbaba Bridge, Cairo
* Rod Elfarag Bridge, Cairo
* Second Ring Road Bridge, Cairo
* Banha Bridge, Banha
* Samanoud Bridge, Samanoud
* Mansoura 2 Bridges, Mansoura
Mansoura (; ', , rural: ) is a city in Egypt located on the eastern bank of the Damietta branch of the Nile river. The city is the capital of the Dakahlia Governorate and has a population of 621,953 as of 2021.
Etymology
''Mansoura'' in Arabic ...
* Talkha Bridge, Talkha
* Shirbine high Bridge
* Shirbine Bridge
* Kafr Sad – Farscor Bridge
* International Coastal Road Bridge
* Damietta high Bridge, Damietta
Damietta ( ' ) is a harbor, port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt. It is located at the Damietta branch, an eastern distributary of the Nile Delta, from the Mediterranean Sea, and about north of Cairo. It was a Cath ...
* Damietta Bridge, Damietta
Damietta ( ' ) is a harbor, port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt. It is located at the Damietta branch, an eastern distributary of the Nile Delta, from the Mediterranean Sea, and about north of Cairo. It was a Cath ...
* Kafr El Zayat Bridges, Kafr El Zayat
* Zefta Bridge, Zefta
Crossings from Jinja, Uganda to Khartoum
* Source of the Nile Bridge, Jinja, Uganda * River Nile Railway Bridge, Jinja, Uganda * Nalubaale Bridge,Jinja, Uganda
Jinja is a city in the Eastern Region, Uganda, Eastern Region of Uganda, located on the north shore of Lake Victoria.
Location
Jinja is in Jinja District, Busoga sub-region, in the Eastern Region of Uganda. It is approximately east of Kampala, ...
(Formerly Owen Falls Bridge)
* Karuma Bridge, Karuma, Uganda
* Pakwach Bridge, Uganda
See also
* Bujagali Hydroelectric Power Station *Egyptian Public Works
The Egyptian Department of Public Works was established in the early 19th century, and concentrates mainly on public works relating to irrigation and hydraulic engineering. These irrigation projects have constituted the bulk of work performed by th ...
* Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station
* Water politics in the Nile Basin
* Merowe Dam
* Nalubaale Hydroelectric Power Station
* Orders of magnitude
In a ratio scale based on powers of ten, the order of magnitude is a measure of the nearness of two figures. Two numbers are "within an order of magnitude" of each other if their ratio is between 1/10 and 10. In other words, the two numbers are wi ...
* Vid Flumina, a river of liquid methane and ethane on Saturn's moon Titan
* ''The River War
''The River War: An Historical Account of the Reconquest of the Soudan'' (1899), by Winston Churchill, is a history of the conquest of the Sudan between 1896 and 1899 by Anglo-Egyptian forces led by Lord Kitchener. He defeated the Sudanese D ...
'' (1899), Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
's second book, an account of steaming up the Nile to the Battle of Omdurman
The Battle of Omdurman, also known as the Battle of Karary, was fought during the Anglo-Egyptian conquest of Sudan between a British–Egyptian expeditionary force commanded by British Commander-in-Chief (sirdar) major general Horatio Herbert ...
, Sudan, in 1898
Notes and references
;Notes ;References ;Sources *Further reading
* * Jeal, Tim (2011). ''Explorers of the Nile: The Triumph and Tragedy of a Great Victorian Adventure''. * Moorehead, Alan, "The White Nile" (Hamish Hamilton, 1960; revised and illustrated edition, 1971). Abridged illustrated edition, as The Story of the White Nile (Harper & Row, 1967) * Moorehead, Alan, "The Blue Nile" (Hamish Hamilton, 1962; revised and illustrated edition, 1972). Abridged illustrated edition, as The Story of the Blue Nile (Harper & Row, 1966) * Tvedt, Terje, ed. ''The River Nile in the Post-Colonial Age: Conflict and Cooperation Among the Nile Basin Countries'' (I.B. Tauris, 2010) 293 pages; studies of the river's finite resources as shared by multiple nations in the post-colonial era; includes research by scholars from Burundi, Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. * Tvedt, Terje, (2004) "The Nile: An Annotated Bibliography", London/New York,External links
A Struggle Over the Nile
– slideshow by ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
''
Thesis Analyzing Nile River Negotiations
(archived 10 January 2016) *
Old maps of the Nile
from the Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The
National Library of Israel
The National Library of Israel (NLI; ; ), formerly Jewish National and University Library (JNUL; ), is the library dedicated to collecting the cultural treasures of Israel and of Judaism, Jewish Cultural heritage, heritage. The library holds more ...
{{Authority control
International rivers of Africa
*
Rivers of Egypt
Rivers of Sudan
Rivers of South Sudan
Rivers of Uganda
Geography of ancient Egypt
Hebrew Bible rivers
National parks of Egypt
Water transport in Egypt
Articles containing video clips