Niger Delta on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
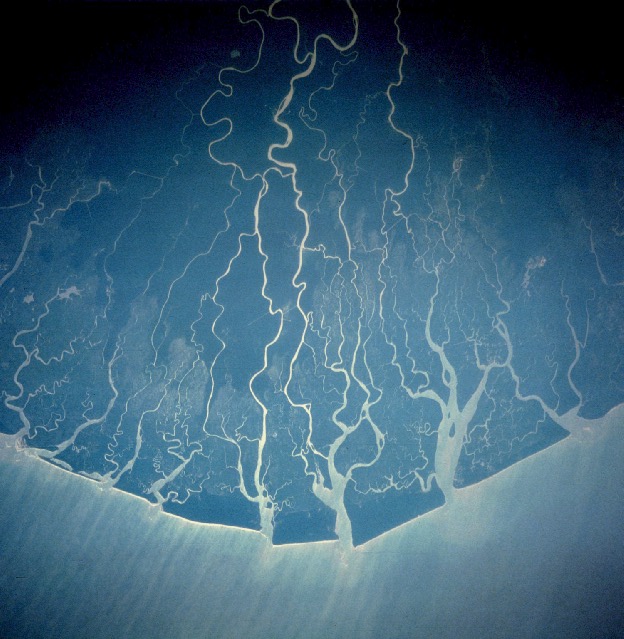 The Niger Delta is the
The Niger Delta is the
World Bank Report
Niger Delta-Archive of News, Interviews, Articles, Analysis from 1999 to Present
* ''Proceedings of the Ibibio Union 1928–1937''. Edited by Monday Efiong Noah. Modern Business Press Ltd, Uyo. * Urhobo Historical Society (4 August 2003). Urhobo Historical Society Responds to Itsekiri Claims on Warri City and Western Niger Delta.
"Nigeria's agony dwarfs the Gulf oil spill. The US and Europe ignore it"
National Geographic Magazine: "Curse of the Black Gold, Hope, and betrayal on the Niger Delta"
— ''February 2007 issue''.
* Niger-Delta Development Commission
Niger Delta: A Brief History
* American Association for the Advancement of Science
Niger Delta
Environmental Rights Action
News on the Niger Delta
{{Authority control *Delta Gulf of Guinea
 The Niger Delta is the
The Niger Delta is the delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
of the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
on the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
in Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South
The South-South is one of the six geopolitical zones of Nigeria. It designates both a geographic and political region of the country's eastern coast. It comprises six States of Nigeria, states – Akwa Ibom, Bayelsa, Cross-River State, Cross Ri ...
geopolitical zone, one state ( Ondo) from South West geopolitical zone and two states ( Abia and Imo) from South East geopolitical zone.
The Niger Delta is a very densely populated region sometimes called the Oil Rivers because it was once a major producer of palm oil. The area was the British Oil Rivers Protectorate from 1885 until 1893, when it was expanded and became the Niger Coast Protectorate.
The delta is a petroleum-rich region and has been the center of international concern over extensive pollution which is often used as an example of ecocide
Ecocide (from Greek 'home' and Latin 'to kill') is the destruction of the natural environment, environment by humans. Ecocide threatens all human populations that are dependent on natural resources for maintaining Ecosystem, ecosystems and ensu ...
. The principal cause is major oil spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into th ...
s by multinational corporation
A multinational corporation (MNC; also called a multinational enterprise (MNE), transnational enterprise (TNE), transnational corporation (TNC), international corporation, or stateless corporation, is a corporate organization that owns and cont ...
s of the petroleum industry.
Geography
The Niger Delta, as now defined officially by the Nigerian government, extends over and makes up 7.5% of Nigeria's land mass. Historically and cartographically, it consists of present-day Bayelsa,Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
, and Rivers State
Rivers is a states of Nigeria, state in the Niger Delta region of southern Nigeria (Old Eastern Region). Formed on 27 May 1967, when it was split from the former Eastern Region, Nigeria, Eastern Region, Rivers State borders include Imo State, Im ...
s. In 2000, however, Obasanjo's regime included Abia, Akwa-Ibom, Cross River State, Edo, Imo and Ondo States in the region.
The Niger Delta and the South-South geopolitical zone (which contains six of the states in the Niger Delta) are two different entities. The Niger Delta separates the Bight of Benin from the Bight of Bonny within the larger Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez i ...
.
Demographics
The political Niger Delta is home to approximately 31 million people from over 40 ethnic groups, including the Ibibio, Urhobo, Annang, Oron, Efik, Ogoni, Bini, Esan, Isoko, and Ijaws—such as the Kalabari, Okrika, Epie-Atissa, Ogbia, Abua, Obolo, Opobo, Ibani, Apoi, Arogbo, Olodiama, Biseni, Akinima, among others—as well as the Igbo. These communities speak around 250 different dialects. The Ijaw are the largest ethnic group in the Niger Delta, with a widespread presence across six states in the region. The major language groups spoken in the Niger Delta include the Ijaw languages, Ibibio and Ibibio-Efik languages, Igbo languages, Urhobo, Isoko, and Edoid languages.History
Colonial period
The area was theBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
Oil Rivers Protectorate from 1885 until 1893 when it was expanded and became the Niger Coast Protectorate. The core Niger Delta later became a part of the eastern region of Nigeria, which came into being in 1951 (one of the three regions, and later one of the four regions). The majority of the people were those from the colonial Calabar and Ogoja divisions, the present-day Ogoja, Annang, Ibibio, Oron, Efik
The Efik are an ethnic group located primarily in southern Nigeria, and western Cameroon. Within Nigeria, the Efik can be found in the present-day Cross River State and Akwa Ibom state. The Efik speak the Efik language which is a member of the ...
, Ijaw and Ogoni people. The National Council of Nigeria and Cameroon (NCNC) was the ruling political party of the region. The NCNC later became the National Convention of Nigerian Citizens, after western Cameroon decided to separate from Nigeria. The ruling party of eastern Nigeria did not seek to preclude the separation and even encouraged it. The then Eastern Region had the third, fourth, and fifth largest indigenous ethnic groups in the country, which are the Igbo, Ibibio and Ijaw.
In 1953, the Old Eastern region had a major crisis when professor Eyo Ita was expelled from office by the majority Igbo tribe of the Old Eastern region. Ita, an Efik
The Efik are an ethnic group located primarily in southern Nigeria, and western Cameroon. Within Nigeria, the Efik can be found in the present-day Cross River State and Akwa Ibom state. The Efik speak the Efik language which is a member of the ...
man from Calabar
Calabar (also referred to as Callabar, Calabari, Calbari, Cali and Kalabar) is the capital city of Cross River State, Nigeria. It was originally named Akwa Akpa, in the Efik language, as the Efik people dominate this area. The city is adjac ...
, was one of the pioneer nationalists for Nigerian independence. The minorities in the region, the Ibibio, Annang, Efik
The Efik are an ethnic group located primarily in southern Nigeria, and western Cameroon. Within Nigeria, the Efik can be found in the present-day Cross River State and Akwa Ibom state. The Efik speak the Efik language which is a member of the ...
, Ijaw and Ogoja, were situated along the southeastern coast and in the delta region and demanded a state of their own, the Calabar-Ogoja-Rivers (COR) state. The struggle for the creation of the COR state continued and was a major issue concerning the status of minorities in Nigeria during debates in Europe on Nigerian independence. As a result of this crisis, Professor Eyo Ita left the NCNC to form a new political party called the National Independence Party which was one of the five Nigerian political parties represented at the conferences on Nigerian Constitution and Independence.
Post-colonial period
In 1961, another major crisis occurred when the then-eastern region of Nigeria allowed present-day southwesternCameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
to separate from Nigeria (from the region of what is now Akwa Ibom and Cross River states) through a plebiscite while the leadership of the Northern Region took the necessary steps to keep northwestern Cameroon in Nigeria, in present-day Adamawa and Taraba states. The aftermath of the 1961 plebiscite has led to a dispute between Cameroon and Nigeria over the small territory of Bakassi.
A new phase of the struggle saw the declaration of an Independent Niger Delta Republic by Isaac Adaka Boro during Nigerian president Ironsi's administration, just before the Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Biafran War, Nigeria-Biafra War, or Biafra War, was fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a Secession, secessionist state which had declared its independen ...
. Also just before the Nigerian civil war, Southeastern State of Nigeria was created (also known as Southeastern Nigeria or Coastal Southeastern Nigeria), which had the colonial Calabar division, and colonial Ogoja division. Rivers State
Rivers is a states of Nigeria, state in the Niger Delta region of southern Nigeria (Old Eastern Region). Formed on 27 May 1967, when it was split from the former Eastern Region, Nigeria, Eastern Region, Rivers State borders include Imo State, Im ...
was also created. Southeastern State and River State became two states for the minorities of the old eastern region, and the majority Igbo of the old eastern region had a state called East Central State. Southeastern State was renamed Cross River State and was later split into Cross River State and Akwa Ibom State. Rivers State was later divided into Rivers State and Bayelsa State.
Nigerian Civil War
Niger Delta people suffered heavily with the great loss of lives and properties, hunger and starvation, and sustained many deaths during 1967–1970Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Biafran War, Nigeria-Biafra War, or Biafra War, was fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a Secession, secessionist state which had declared its independen ...
, also known as the Biafran War, in which the eastern region declared an independent state named Biafra that was eventually defeated. During this period, schools were shut down completely, and gunfire became a daily occurrence.
Non-violent resistance
Following the civil war, local communities increasingly demanded social andenvironmental justice
Environmental justice is a social movement that addresses injustice that occurs when poor or marginalized communities are harmed by hazardous waste, resource extraction, and other land uses from which they do not benefit. The movement has gene ...
from the federal government, with Ken Saro Wiwa and the Ogoni tribe as the lead figures for this phase of the struggle. Cohesive oil protests became most pronounced in 1990 with the publication of the Ogoni Bill of Rights. Indigenous people protested against the lack of economic development, e.g. schools, good roads, and hospitals, in the region, despite all the oil wealth created. They also complained about environmental pollution and the destruction of their land and rivers by foreign oil companies. Ken Saro Wiwa and nine other oil activists from Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People (MOSOP) were arrested and killed under Sani Abacha
Sani Abacha (; (20 September 1943 – 8 June 1998) was a Nigerian military dictator and statesman who ruled Nigeria with an iron fist as military head of state from 1993 following a palace coup d'état until his death in 1998.
Abacha's seiz ...
in 1995.
Recent armed conflict
When long-held concerns about loss of control over resources to the oil companies were voiced by theIjaw people
The Ijaw people, also known as the Izon people, are an ethnic group found in the Niger Delta region in Nigeria, with primary Population, population clusters in Bayelsa State, Bayelsa, Delta State, Delta, and Rivers State, Rivers. They also have ...
in the Kaiama Declaration in 1998, the Nigerian government sent troops to occupy the Bayelsa and Delta states. Soldiers opened fire with rifles, machine guns, and tear gas, killing at least three protesters and arresting twenty-five more. Since then, local Indigenous activity against commercial oil refineries and pipelines in the region has increased in frequency and militancy. Recently foreign employees of Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard outer layer of a marine ani ...
, the primary corporation operating in the region, were taken hostage by local people. Such activities have also resulted in greater governmental intervention in the area and the mobilization of the Nigerian Army and State Security Service into the region, resulting in violence and human rights abuses. In April 2006, a bomb exploded near an oil refinery in the Niger Delta region, a warning against Chinese expansion in the region. The Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND) stated: "We wish to warn the Chinese government and its oil companies to steer well clear of the Niger Delta. The Chinese government, by investing in stolen crude, places its citizens in our line of fire."
Government and private initiatives to develop the Niger Delta region have been introduced recently. These include the Niger Delta Development Commission, a government initiative, and the Development Initiative, a community development non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
based in Port Harcourt
Port Harcourt (Pidgin: ''Po-ta-kot or Pi-ta-kwa)'' is the capital and largest city of Rivers State in Nigeria. It is the fifth most populous city in Nigeria after Lagos, Kano, Ibadan and Benin. It lies along the Bonny River and is locate ...
. Uz and Uz Transnational, a company with a strong commitment to the Niger Delta, has introduced ways of developing the poor in the Niger Delta, especially in Rivers State. In September 2008, MEND released a statement proclaiming that their militants had launched an " oil war" throughout the Niger Delta against both, pipelines and oil-production facilities, and the Nigerian soldiers that protect them. Both MEND and the Nigerian Government claim to have inflicted heavy casualties on one another. In August 2009, the Nigerian government granted amnesty to the militants; many militants subsequently surrendered their weapons in exchange for a presidential pardon, rehabilitation programme, and education.
Sub-regions
Western Niger Delta consists of the western section of coastal South-South Nigeria which includes Delta, and the southernmost parts of Edo, and Ondo States. The western (or Northern) Niger Delta is a heterogeneous society with several ethnic groups including the Urhobo, Ika people, Aniocha People, Isoko, Ijaw (or Izon) and Ukwuani, Itsekiri the Bini, Esan, Auchi, Esako, oral, and Afenmai in Edo State; and the Ilaje Yoruba in Ondo State. Their livelihoods are primarily based on fishing and farming. History has it that the Western Niger was controlled by Kings of the four primary ethnic groups the Urhobo, Isoko, Ijaw, and, Itsekiri with whom the British government had to sign separate "Treaties of Protection" in their formation of "Protectorates" that later became southern Nigeria. Central Niger Delta consists of the central section of coastal South-South Nigeria which includes Bayelsa, Rivers, Abia, and Imo States. The Central Niger Delta region has the Ijaw (including the Nembe-Brass, Ogbia, Kalabari people, Ibani of Opobo & Bonny, Abua, Okrika, Engenni and Andoni clans), the Ogoni people (Khana, Gokana, Tai and Eleme), the Etche, Egbema, Omuma, Ogba, Ikwerre, Ndoni, Ekpeye and Ndoki in Rivers State. Eastern Niger Delta consists of Cross River State and Akwa Ibom State. It has the homogeneous Annang,Efik
The Efik are an ethnic group located primarily in southern Nigeria, and western Cameroon. Within Nigeria, the Efik can be found in the present-day Cross River State and Akwa Ibom state. The Efik speak the Efik language which is a member of the ...
and Ibibio people.
Calabar of Niger Delta
The Niger Delta of Nigeria was a core component of the Southern Protectorate with the seat of government in Calabar before the birth of Nigeria as a country. People ofthen refer to Calabar as the first capital of Nigeria before Lagos and now Abuja. Interestingly, while the oil of the Niger Delta is what finances the nation, the Niger Delta remains the last of everything in the country. While all former district cities in Nigeria such as Enugu, Lagos, Kaduna, Kano, etc have been imortalized as state names, this is not the case of Calabar of Niger Delta. This injustice or oversight needs to be corrected. With the ongoing demand for Ogoja state from the present Cross River State. If and when Ogoja state is created from the northern part of the present Cross River state, the southern part should be called Calabar state.Nigerian oil
Nigeria has becomeWest Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
's biggest producer of petroleum. Some per day are extracted in the Niger Delta, with an estimated 38 billion barrels of reserves. The first oil operations in the region began in the 1950s and were undertaken by multinational corporations, which provided Nigeria with necessary technological and financial resources to extract oil. Since 1975, the region has accounted for more than 75% of Nigeria's export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is a ...
earnings. Together oil and natural gas extraction comprise "97 percent of Nigeria's foreign exchange revenues". More than 70% of the natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
extracted in oil wells in the delta is immediately burned, or flared, into the air at a rate of approximately 70 million m3 per day. This is equivalent to 41% of African natural gas consumption and forms the largest single source of greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
on the planet. In 2003, about 99% of excess gas was flared in the Niger Delta, although this value has fallen to 11% in 2010. (See also gas flaring volumes). The biggest gas flaring company is the Shell Petroleum Development Company of Nigeria Ltd, a joint venture that is majority-owned by the Nigerian government. In Nigeria, "...despite regulations introduced 20 years ago to outlaw the practice, most associated gas is flared, causing local pollution and contributing to climate change." The environmental devastation associated with the industry and the lack of distribution of oil wealth have been the source and/or key aggravating factors of numerous environmental movements and inter-ethnic conflicts in the region, including recent guerrilla activity by MEND.
In September 2012 Eland Oil & Gas purchased a 45% interest in OML 40, with its partner Starcrest Energy Nigeria Limited, from the Shell Group. They intend to recommission the existing infrastructure and restart existing wells to re-commence production at an initial gross rate of of oil per day with a target to grow gross production to of oil per day within four years.
Oil revenue derivation
Oil revenue allocation has been the subject of much contention well before Nigeria gained its independence. Allocations have varied from as much as 50%, owing to the First Republic's high degree of regional autonomy, and as low as 10% during the military dictatorships. ''* State allocations are based on 5 criteria: equality (equal shares per state), population, social development, land mass, and revenue generation. '' ''**The derivation formula refers to the percentage of the revenue oil-producing states retain from taxes on oil and other natural resources produced in the state.'World Bank Report
Media
The documentary film '' Sweet Crude'', which premiered April 2009 at the Full Frame Documentary Film Festival, tells the story of Nigeria's Niger Delta.Environmental issues
The Niger Delta is a region of unparalleled ecological richness, characterized by its intricate network of waterways, lush mangrove forests, and diverse ecosystems. However, the serene beauty of this landscape has been damaged by a persistent environmental menace, oil spills. Over the years, the Niger Delta has experienced a series of devastating oil spills, primarily caused by industrial activities related to the extraction and transportation of oil and gas. Due to this high amount of spills, the Niger Delta is considered one of the most polluted areas on Earth. These spills have inflicted severe and continuous damage on the delicate balance of the region's ecosystems. They impact both the environment and the livelihoods of the communities that depend on its resources. Two spills in 2008 and 2009 have been the largest and most harmful by far, collectively lasting for almost 150 days and causing flora death throughout 393 km2. The extensive network of tidal rivers and mangrove swamps makes it even easier for the oil to spread quickly, and the delta becomes a sink, trapping the oil that is not removed. The spills came from a pipeline operated by Shell Petroleum Development Company. In addition to smaller spills that took place over the years 2006–2019, it is estimated that a total of 92,479,170 liters (or 24430412.139 gallons) of crude oil were released into the studied area. Since then, following spills have continued to exacerbate the ecological damage. The exact impact of spills like these is hard to know because traditional field studies are nearly impossible in this region. However, techniques such as the normalized difference vegetation index have been successful in measuring the impact of oil spills on the river's plant health. Additionally, independently collected field samples have confirmed the presence of hydrocarbon pollutants in high concentrations in the impacted areas. Oil and gas pollution/spills greatly increase the possibility of human exposure to dangerous chemicals. Many components of crude oil are particularly concerning due to their link to the health problems caused by exposure. This includes organic contaminants such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene, as well as heavy metals such as lead, vanadium and cadmium. In fact, according to the Scientific Committee on Health, Environmental and Emerging Risks, more than 1300 different chemicals can be put into the environment as a result of oil and gas exploration. Then, humans come in contact with these harmful substances through eating contaminated food as well as breathing in the air pollution. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are especially concerning because of their persistence in the environment. Even in low amounts, prolonged exposure can cause serious health issues such as cancer and other chronic illnesses. In general, the harmful pollutants emitted from oil spills and other pollution include cancer, metabolic syndrome, miscarriages, stillbirths, and infertility. Less deadly, but still serious, health problems include headache, watery eyes, sore throat, respiratory problems, itchy skin, rashes on face and neck, sneezing, coughing, nausea, dizziness, chest pain, and diarrhea are common issues caused from oil spills. Collectively, more than 1 million people live in the area that has been contaminated by oil/gas pollution. This population is especially vulnerable to chronic illnesses because of their pre-existing low life expectancy and large ratio of young people. Additionally, a 2006 report done by the United Nations Development Programme says “The Niger Delta is a region suffering from administrative neglect, crumbling social infrastructure and services, high unemployment, social deprivation, abject poverty, filth and squalor, and endemic conflict,". These factors make it increasingly harder for the local communities to deal with the negative effects caused by foreign oil exploration. The people affected by oil spills in the Niger Delta are diverse communities residing in the region. Their lives are intricately connected to the natural environment. These communities, often made up of indigenous groups, rely on the Niger Delta's resources for their food, water, livelihoods, and cultural practices. The impact of oil spills on these communities is multi-faceted and extends beyond health problems. Fishing and agriculture are central to the livelihoods of many Niger Delta communities. Oil spills contaminate water sources and farmlands, severely affecting fish stocks and crops. This disruption can lead to food shortages and economic hardship for those dependent on these activities. Another facet of the people's livelihoods is their culture. The Niger Delta's people have strong spiritual and cultural ties to their environment. The harm inflicted on their land and waterways caused by oil spills deeply disrupts sacred sites and interferes with their cultural practices. The loss of these cultural elements contributes to a sense of displacement and identity crisis among the affected groups/communities. Additionally, when communities fight back against the oil industries as an act of protest, violence is often perpetuated. Since the 1990s there has been continuous violence in an effort to give local communities control of the oil in the delta. These acts of violence include the kidnapping of foreign oil workers and holding them for ransom, vandalization, and even the blowing up of oil installations.Notes
References
Niger Delta-Archive of News, Interviews, Articles, Analysis from 1999 to Present
* ''Proceedings of the Ibibio Union 1928–1937''. Edited by Monday Efiong Noah. Modern Business Press Ltd, Uyo. * Urhobo Historical Society (4 August 2003). Urhobo Historical Society Responds to Itsekiri Claims on Warri City and Western Niger Delta.
"Nigeria's agony dwarfs the Gulf oil spill. The US and Europe ignore it"
External links
National Geographic Magazine: "Curse of the Black Gold, Hope, and betrayal on the Niger Delta"
— ''February 2007 issue''.
* Niger-Delta Development Commission
Niger Delta: A Brief History
* American Association for the Advancement of Science
Niger Delta
Environmental Rights Action
News on the Niger Delta
{{Authority control *Delta Gulf of Guinea
Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
Landforms of Nigeria
Freshwater ecoregions of Africa
Ecoregions of Nigeria
Afrotropical ecoregions