Nicolas Hartsoeker on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nicolaas Hartsoeker (26 March 1656 – 10 December 1725) was a Dutch
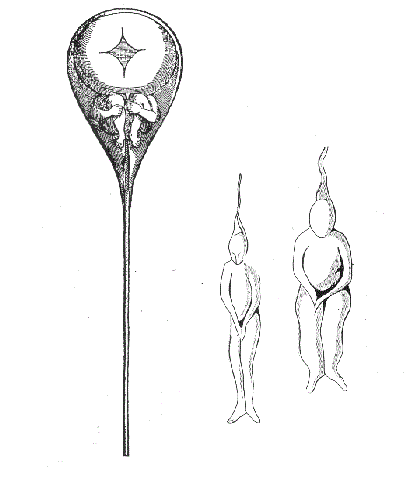 It is often said that in 1694, while observing human sperm through a microscope, Hartsoeker believed that he saw tiny men inside the sperm, which he called
It is often said that in 1694, while observing human sperm through a microscope, Hartsoeker believed that he saw tiny men inside the sperm, which he called
''Essay de dioptrique''
* (1696
''Principes de physique''
* (1706
''Conjectures physiques''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hartsoeker, Nicolaas 1656 births 1725 deaths Dutch biologists 17th-century Dutch inventors 17th-century Dutch mathematicians 18th-century Dutch physicists People from Gouda, South Holland Members of the French Academy of Sciences Members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences Academic staff of Heidelberg University
mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematica ...
and physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
who invented the screw-barrel simple microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
.
Biography
He was the son of Anna van der Meij and Christiaan Hartsoeker (1626–1683), aRemonstrant
The Remonstrants (or the Remonstrant Brotherhood) is a Protestant movement that split from the Dutch Reformed Church in the early 17th century. The early Remonstrants supported Jacobus Arminius, and after his death, continued to maintain his ori ...
minister in Moordrecht
Moordrecht () is a village and a former municipality in the province of South Holland, the Netherlands, situated along the river Hollandse IJssel.
In September 2006, 93% of the population of Moordrecht chose by referendum to pursue a merger with ...
near Gouda. His father took the family to Alkmaar
Alkmaar () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Holland. Alkmaar is well known fo ...
in 1661 and finally to Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , ; ; ) is the second-largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city in the Netherlands after the national capital of Amsterdam. It is in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, part of the North S ...
in 1669. Nicolaas started to make a living as a lens maker in Rotterdam, and was instructed in optics by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch art, science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " ...
. In 1674, he and a fellow student, assisted by Van Leeuwenhoek, were the first to observe semen, a situation that would later lead to a priority dispute between Hartsoeker and Leeuwenhoek over the discovery of spermatozoid
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete that joins with an ovum ...
s.
In 1677, Hartsoeker met Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
and initiated him in the making of lenses. In June 1678, Hartsoeker accompanied, in the role of an assistant, Huygens on a trip to Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, where they made a great impression with their microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
s. However, Huygens failed to mention Hartsoeker even once in a subsequent publication in France, leading to a fall-out between the two.
Hartsoeker returned to Rotterdam, where his parents still lived and where he married Elisabeth Vettekeucken in October 1680. His business as an instrument maker and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
merchant failed and, after the death of his father in August 1683, he moved his family in 1684 to Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, where he made instruments for the Paris observatory
The Paris Observatory (, ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centres in the world. Its historic building is on the Left Ban ...
and the academy. Hartsoeker also came up with contrivances for aiming very large aerial telescope
An aerial telescope is a type of very long focal length refracting telescope, built in the second half of the 17th century, that did not use a tube. Instead, the objective was mounted on a pole, tree, tower, building or other structure on a swive ...
s originally popularized by Huygens. He remained there until 1698.
homunculi
A homunculus ( , , ; "little person", : homunculi , , ) is a small human being. Popularized in 16th-century alchemy and 19th-century fiction, it has historically referred to the creation of a miniature, fully formed human. The concept has root ...
or animalcules
Animalcule (; ) is an archaic term for microscopic organisms that included bacteria, protozoans, and very small animals. The word was invented by 17th-century Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek to refer to the microorganisms he observed i ...
. However, he only postulate
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or f ...
d their existence as part of his spermist theory of conception and never claimed to have seen them. The 1694 "Essay on dioptrics", in which this hypothesis appears, was a highly lauded book, in fact tackling several misconceptions of the time. For example, Hartsoeker disavows the contemporary position (e.g. of Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living ...
) that with refractor telescope
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope d ...
s one soon would be able to see man-sized creatures on the moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, if any in fact existed.
At the end of the century, Hartsoeker had become quite famous. In 1699 he was elected member of the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefron ...
and in 1704 of the Prussian Academy of Sciences
The Royal Prussian Academy of Sciences () was an academy established in Berlin, Germany on 11 July 1700, four years after the Prussian Academy of Arts, or "Arts Academy," to which "Berlin Academy" may also refer. In the 18th century, when Frenc ...
, in both cases as one of the first foreign members. Czar Peter met him in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
and offered him the chair of mathematics in St Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
. Hartsoeker did not accept, but the czar did finance an observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed.
Th ...
for him in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
. Later, in 1704, Hartsoeker accepted the offer of Johann Wilhelm, Elector Palatine
John William, Elector Palatine (''Jan Wellem'' in Low German, English: ''John William''; 19 April 1658 – 8 June 1716) of the Wittelsbach dynasty was Elector Palatine (1690–1716), Duke of Neuburg (1690–1716), Duke of Jülich and Ber ...
to become "first mathematician and honorary professor of philosophy" at the University of Heidelberg
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg (; ), is a public university, public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Founded in 1386 on instruction of Pope Urban VI, Heidelberg is List ...
. The last years of his life were spent in Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The ...
.
Major works
* * * ''Conjectures physiques'', Amsterdam, 1706. * ''Suite des conjectures physiques'', Amsterdam, 1708. * ''Eclaircissements sur les conjectures physiques'', Amsterdam, 1710.Editions
*References
External links
Digitized works by Nicolaas Hartsoeker from theLinda Hall Library
The Linda Hall Library is a privately endowed American library of science, engineering and technology located in Kansas City, Missouri, on the grounds of a urban arboretum. It claims to be the "largest independently funded public library of sc ...
* (1694''Essay de dioptrique''
* (1696
''Principes de physique''
* (1706
''Conjectures physiques''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hartsoeker, Nicolaas 1656 births 1725 deaths Dutch biologists 17th-century Dutch inventors 17th-century Dutch mathematicians 18th-century Dutch physicists People from Gouda, South Holland Members of the French Academy of Sciences Members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences Academic staff of Heidelberg University