New York Central Mohawk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
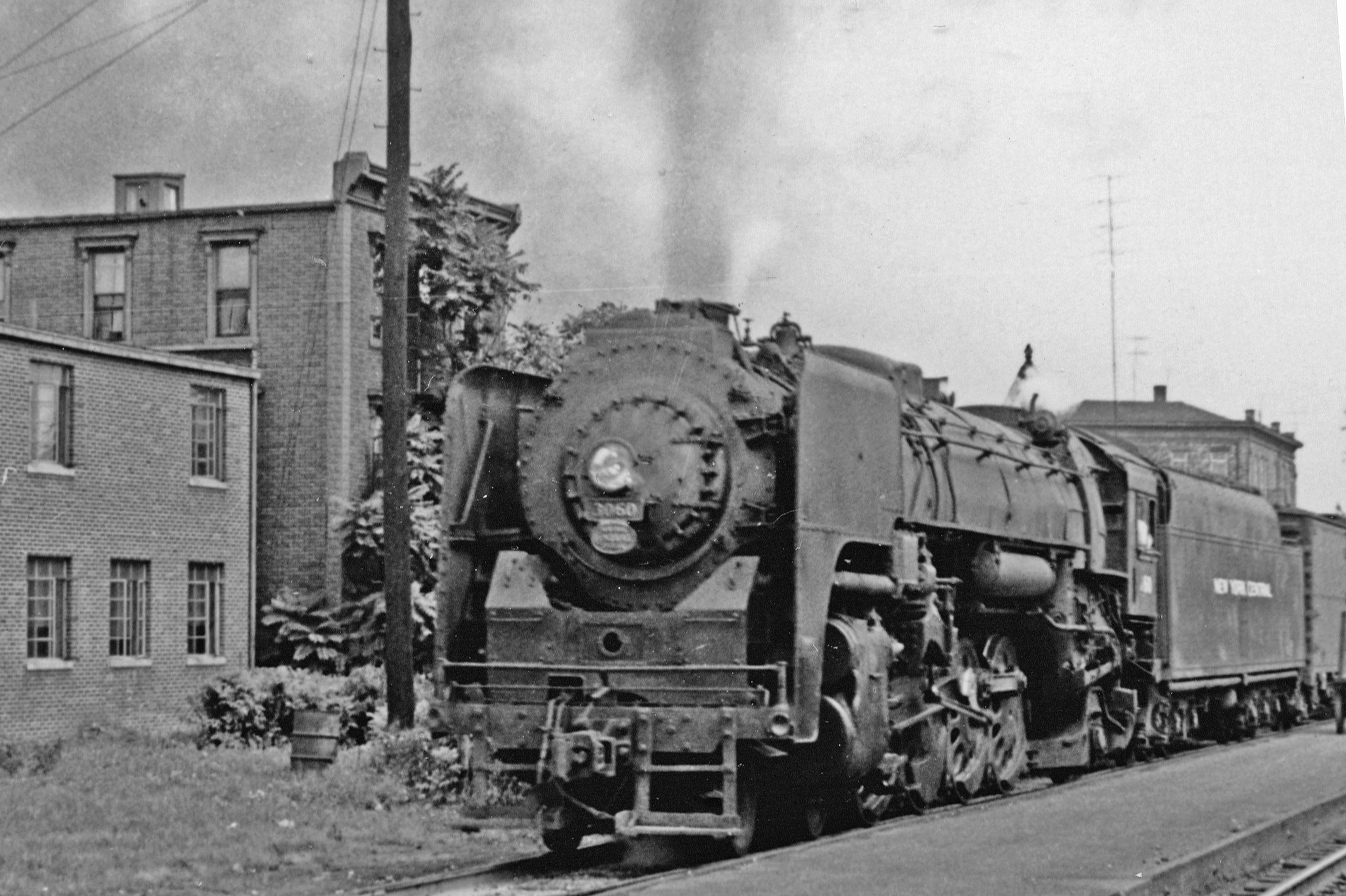 The next development of the Mohawk type was that of the dual-service locomotive, capable of working passenger as well as freight trains. Passenger service required the ability to work at , as opposed to the required of freight. The NYC's fleet of Hudsons, 275 strong though it was, was proving inadequate to handle peak traffic demands, and some dual-purpose power would fix the problem nicely as well as giving the ability to handle express freight and mail services.
Two L-2 locomotives were given modifications for dual service work: higher boiler pressure, smaller cylinders, lightweight reciprocating parts, dynamic counterbalancing of the drivers,
The next development of the Mohawk type was that of the dual-service locomotive, capable of working passenger as well as freight trains. Passenger service required the ability to work at , as opposed to the required of freight. The NYC's fleet of Hudsons, 275 strong though it was, was proving inadequate to handle peak traffic demands, and some dual-purpose power would fix the problem nicely as well as giving the ability to handle express freight and mail services.
Two L-2 locomotives were given modifications for dual service work: higher boiler pressure, smaller cylinders, lightweight reciprocating parts, dynamic counterbalancing of the drivers,
New York Central Railroad
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected New York metropolitan area, gr ...
(NYC) called the 4-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This type of steam locomotive is commonly known as ...
type of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
the Mohawk type. It was known as the ''Mountain'' type on other roads, but the New York Central did not see the name as fitting on its famous Water Level Route
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midw ...
. Instead, it picked the name of one of those rivers its rails followed, the Mohawk River
The Mohawk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 river in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It is the largest tributary of the Hudson R ...
, to name its newest type of locomotive.
The L1s and L2s were unstable at higher speeds due to the lack of effective cross-balancing, making the 4-wheel leading truck simply a better distributor of their weight; the L1s and L2s were consequently limited to , though this issue was resolved for the L3s and L4s using data gathered from two experimental L-2s.
The New York Central became the largest 4-8-2 user in North America, with 600 locomotives of this type built for its service; only the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
came close, with 301 M1's of the type.
The Mohawk type was the pre-eminent freight power of the network, displacing the 2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wh ...
type from first-line service. While other roads obtained much more massive freight power, such as 2-10-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and no trailing wheels. This arrangement was of ...
s and 2-10-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a locomotive has two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a Bissel truck, ten coupled driving wheels on five axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles, usually in a bog ...
types and a multitude of articulated designs, the New York Central, with its practically-grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grading in education, a measurement of a student's performance by educational assessment (e.g. A, pass, etc.)
* A designation for students, classes and curricula indicating the number of the year a student has reach ...
less high-speed riverside lines, needed speed over pulling power.
The 600 Mohawks delivered were divided into four main classes, plus a few experimental and prototypes that were rebuilt between 1922 and 1939.
L-1a, b, c, d
The first Mohawks delivered for the NYC were delivered byALCO
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
in 1916; these were purely freighters, with 69-inch drivers and small four axle tenders, though they would almost universally later be refitted with more six-axle examples. They would be equipped with the appropriate accouterment of the time; kerosene headlights, straight running boards, full pilots, Cole trailing trucks, and in some cases Russia iron
Russia iron or Russian iron refers to a type of sheet iron produced in Russia during the 19th and early 20th century.
This iron sheeting had a smooth, glossy black surface coating, sometimes greenish-tinged, which did not flake upon bending and mad ...
boiler jackets.
Further orders of L-1 subclasses followed in subsequent years, all built by ALCO except the L-1cs, which would be built by the Lima Locomotive Works
Lima Locomotive Works (LLW) was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company's name is derived from the location of its main manufacturing plant in Lima, Ohio ( ). The shops were located be ...
. These engines were built with clean lines and a notable lack of appliances, though they would be modified extensively in the coming years. As with the tenders, the earlier L-1s would later be fitted with feedwater heaters, with the majority sporting Elesco bundle-type and Coffin internal feedwater heaters, though a handful of examples on the subsidiary Peoria & Eastern (as well as one on the NYC proper) had open-cycle Worthington SA type units, and one each were furnished with the Elesco coil type (#2503) and the external Coffin variety. The vast majority of Elesco bundle-type equipped L-1s had them installed protruding forward, as seen universally on the L-2a subclass. However, there is evidence of at least one unit (#2568) having the feedwater heater installed in the semi-sunken fashion seen on some of the Central's H-7e Mikados.
One modification to the L-1s made in the 1920s was the installation of mechanical stokers, mostly of the duplex type, which were fitted universally, easing the job of the firemen. Many L-1s would also see their original fabricated Cole trailing trucks replaced with single-piece cast Deltas. Additionally, those constructed with full pilots would all have them swapped for footboard freight pilots by the 1920s. Some units would be fitted with booster-equipped trailing trucks, an invention of the New York Central's mechanical department.
185 L-1 locomotives were produced. The L-1a's were numbered 2500–2529, the L-1b's were numbered 2530–2584, the L-1c's were numbered 2585-2639 and the L-1d's were numbered 2640–2684. Interestingly, in the 1936 fleet-wide renumbering, the L-1s would remain untouched, retaining their as-built numbers.
When they were introduced in the late 1910's, the L-1s were the preeminent examples of hauling power on the New York Central, and served extensively on the main line from New York to Chicago. Gradually, as the L-2s rolled off ALCO's production line in the 1920s, many of the L-1s were displaced, with most of them stationed on the Central's Pennsylvania Division. As a consequence of the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
and the associated decline in freight traffic, some were retired permanently or put into long-term storage.
By the late 1930s and the introduction of the L-3s, it was a rarity to see an L-1 outside those operating zones, where they served alongside the NE-2s, the NYC's articulated 2-6-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and one pair of trailing wheels. ...
s. An exception would be the few operated by the Peoria and Eastern, which operated in Illinois and Indiana, though again they were largely limited in the scope of their travel. Much like their cousins on the Pennsylvania Division, they would last until the dieselization of the 1950s, and would all be retired by 1957.
Experimental 3-cylindered
The New York Central had two L-1 locomotives, numbered 2518 and 2605, rebuilt by ALCO in 1922 with three cylinders to help determine if the arrangement was worthwhile. They were substantially more powerful than the two-cylinder models, but it was debatable if the additional maintenance requirements of a third, centralcylinder
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite ...
, valve gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing ...
, main rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the crankshaf ...
and crank axle
A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice ...
were worth the performance boost. In 1924, locomotive 2569 was rebuilt by Alco as a Class L-1b-3 Cylinder. The NYC must have come down on the negative side of that question, for no more were built.
L-2a, b, c, d
The next development of the Mohawk type for the New York Central was the L-2, 300 of its various subclasses being built between 1925 and 1930 by theAmerican Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
. These were more modern locomotives than the L-1 class with wide boilers, long tenders, and fitted with feedwater heaters (mostly of the Elesco type and generally mounted in front of the smokebox at the top). Later L-2 subclasses, the L-2b and L-2c, had somewhat smoother lines with recessed feedwater heaters. The later L-2 locomotives, from a front-on view, appeared quite similar to the Central's fleet of Hudson passenger locomotives. The L2a's were numbered 2700–2799, the L2b's were numbered 2900–2924, the L2c's were numbered 2800-2899 and the L2d's were numbered 2925-2949 and 2950–2999. Locomotives 2995 and 2998 were modified for high-speed service in 1939.
L-3a, b, c
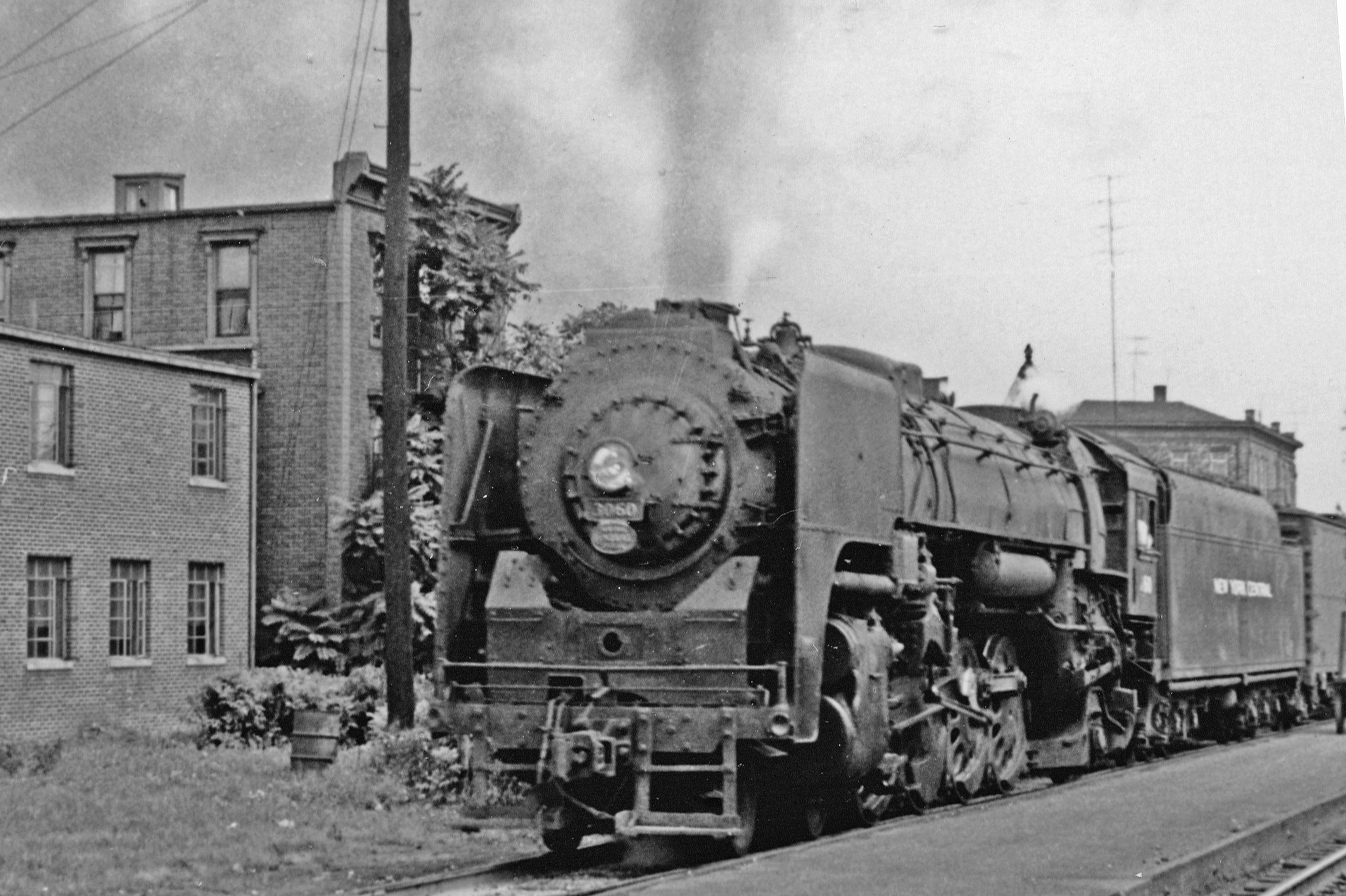 The next development of the Mohawk type was that of the dual-service locomotive, capable of working passenger as well as freight trains. Passenger service required the ability to work at , as opposed to the required of freight. The NYC's fleet of Hudsons, 275 strong though it was, was proving inadequate to handle peak traffic demands, and some dual-purpose power would fix the problem nicely as well as giving the ability to handle express freight and mail services.
Two L-2 locomotives were given modifications for dual service work: higher boiler pressure, smaller cylinders, lightweight reciprocating parts, dynamic counterbalancing of the drivers,
The next development of the Mohawk type was that of the dual-service locomotive, capable of working passenger as well as freight trains. Passenger service required the ability to work at , as opposed to the required of freight. The NYC's fleet of Hudsons, 275 strong though it was, was proving inadequate to handle peak traffic demands, and some dual-purpose power would fix the problem nicely as well as giving the ability to handle express freight and mail services.
Two L-2 locomotives were given modifications for dual service work: higher boiler pressure, smaller cylinders, lightweight reciprocating parts, dynamic counterbalancing of the drivers, roller bearing
In mechanical engineering, a rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing,ISO 15 is a bearing which carries a load by placing rolling elements (such as balls, cylinders, or cones) between two concentric, grooved rings called race ...
s on all axles and so forth. The success of these modifications prompted the construction of 65 units of the L-3 class in 1940, 25 of which were built for dual-service and the remaining 40 for freight-only; as a result, the first 25 were equipped with roller bearings on every axle while the remaining 40 had roller bearings on every axle except for the drivers. Other major difference between L-3as and L-3b/c included footboard pilots and the addition of a trailing truck booster engine used on the L-3b/c. The Class L-3a's were numbered 3000–3024, made by ALCO. The Class L-3b's were numbered 3025–3049, with ALCO producing the first ten (3025-3034) and Lima producing the remaining fifteen (3035-3049). The L-3c's were essentially 15 additional copies of the ALCO made L-3bs, numbered 3050–3064. All had oval NYC emblems under their smokebox engine number placards.
Notably, the Lima made L-3bs had a distinct smokebox front appearance, with a plated-over Elesco feedwater heater giving them their distinct look.
All L-3 locomotives were given axle-spacing that could accommodate 72" drivers, but only one was ever fitted with such. This locomotive, #3000, paved the way for the final class of Mohawks on the New York Central, the L-4. The other 64 engines received 69" drivers.
L-4a, b’s
50 L-4 locomotives were produced by theLima Locomotive Works
Lima Locomotive Works (LLW) was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company's name is derived from the location of its main manufacturing plant in Lima, Ohio ( ). The shops were located be ...
in 1942. None of them had booster engines, although they were built to accommodate them should they ever need to start heavy trains, but were never so modified. The L-4s were versatile locomotives, with 72" drivers, and worked the heaviest freight and passenger trains during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
The L-3 and L-4 classes had large tenders riding on two six-wheel trucks that were almost as long as the locomotives hauling them, and were mostly coal space with a capacity of 43 tons; water was taken en route using the tender scoop from track pan
A water trough (British terminology), or track pan ( American terminology), is a device to enable a steam locomotive to replenish its water supply while in motion. It consists of a long trough filled with water, lying between the rails. When a s ...
s and thus the locomotives did not need to have a large on-board water capacity. Some L-4s had Scullin Disc drivers. The L4a's and L4b's were numbered 3100-3124 and 3125–3149, respectively, and all were equipped with roller bearings on every axle. All L-4a's bore the above-described NYC "passenger" logo plates underneath their front smokebox number plates.
Many L-4 locomotives were fitted with smoke deflectors around 1945/46, after initial delivery in 1942.
Preservation
Only two Mohawks out of the original 600 built are preserved. One of them, No. 2933, is a 1929 ALCO-built L-2d and resides at theNational Museum of Transportation
The National Museum of Transportation (TNMOT) is a private, 42-acre transport museum, transportation museum in the Kirkwood, Missouri, Kirkwood suburb of St. Louis, St. Louis, Missouri. Founded in 1944, it restores, preserves, and displays a wide ...
, Kirkwood, Missouri
Kirkwood is an inner-ring suburb of St. Louis located in western St. Louis County, Missouri. As of the 2020 census, the city's population was 29,461. Founded in 1853, the city is named after James P. Kirkwood, chief engineer of the Pacific Railr ...
. The other Mohawk, No. 3001, is a 1940 ALCO-built L-3a at the National New York Central Railroad Museum in Elkhart, Indiana
Elkhart ( ) is a city in Elkhart County, Indiana, United States. The population was 53,923 at the 2020 census. The city is located east of South Bend, Indiana. It is the most populous city in the Elkhart–Goshen metropolitan area, which in tu ...
and is the largest surviving NYC steam locomotive. In October 2024, the Fort Wayne Railroad Historical Society
The Fort Wayne Railroad Historical Society (FWRHS) is a non-profit group in New Haven, Indiana that is dedicated to the restoration and operation of the ex-NKP 765, Nickel Plate Railroad's steam locomotive no. 765 and other vintage railroad equip ...
announced that they had acquired No. 3001 and made plans to eventually restore it to operating condition.
Two Mohawk tenders also still exist. The tender from 2662, a class L-1d, is currently in use behind Western Maryland Scenic Railroad
The Western Maryland Scenic Railroad (WMSR) is a heritage railway, heritage railroad based in Cumberland, Maryland, that operates passenger excursion trains and occasional freight trains using both Steam locomotive, steam and diesel locomotive, ...
734 (ex-Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad
The Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad , is a Class iii railroad, Class III railroad U.S. railroad offering service from Marquette, Michigan, to nearby locations in Michigan's Upper Peninsula. It began operations in 1896. The LS&I continues to ...
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
34) in Cumberland, Maryland
Cumberland is a city in Allegany County, Maryland, United States, and its county seat. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 19,075. Located on the Potomac River, Cumberland is a regional business and comm ...
. The tender for L-3b 3042 was converted into a canteen
Canteen most often refers to:
* Canteen (bottle), a water container
* Cafeteria, a type of food service location within an institution in which there is little or no waiting staff table service
* A complete set of cutlery comprising knives, forks, ...
and was used with Reading T-1
The Reading T-1 was a class of 4-8-4 "Northern" type steam locomotives owned by the Reading Company. They were rebuilt from thirty "I-10sa" class 2-8-0 "Consolidation" type locomotives between 1945 and 1947. Out of the thirty rebuilt, four survive ...
4-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type wa ...
2101 during its 1976 tour with the American Freedom Train, as well as with the Chessie System Special. It was later damaged in a roundhouse fire in 1979. This water tender is currently behind L3a 3001 at the National New York Central Railroad Museum in Elkhart, Indiana. The tender was sold to the Fort Wayne Railroad Historical Society in September 2023 along with 3001.
See also
*PRR M1
The M1 was a class of steam locomotive of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR). It was a class of heavy mixed-traffic locomotives of the "Mountain" arrangement, which uses four pairs of driving wheels with a four-wheel guiding truck in front for sta ...
, The Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
's version of the Mohawks
*4-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This type of steam locomotive is commonly known as ...
, a dual mode "mountain" type steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
References
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Nyc Mohawk ALCO locomotives Lima locomotives 4-8-2 locomotives New York Central Railroad locomotives Steam locomotives of the United States Railway locomotives introduced in 1916 Standard-gauge locomotives of the United States