Neural arch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an
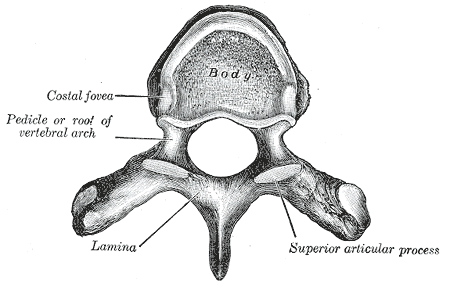
 A typical vertebra has a body (vertebral body), also known as the centrum, which consists of a large anterior middle portion, and a posterior vertebral arch, also called a neural arch. The body is composed of
A typical vertebra has a body (vertebral body), also known as the centrum, which consists of a large anterior middle portion, and a posterior vertebral arch, also called a neural arch. The body is composed of  The vertebral arch is formed by pedicles and laminae. Two pedicles extend from the sides of the vertebral body to join the body to the arch. The pedicles are short thick
The vertebral arch is formed by pedicles and laminae. Two pedicles extend from the sides of the vertebral body to join the body to the arch. The pedicles are short thick
p. 31
/ref> because it corresponds to a rudimentary rib (''costa'') which, as opposed to the thorax, is not developed in the lumbar region. There are superior and inferior
 Vertebrae take their names from the regions of the vertebral column that they occupy. There are usually thirty-three vertebrae in the human vertebral column — seven
Vertebrae take their names from the regions of the vertebral column that they occupy. There are usually thirty-three vertebrae in the human vertebral column — seven
 There are seven
There are seven
 The twelve
The twelve

 The five
The five
p. 19
/ref> The superior, or upper tubercle is the mammillary process which connects with the superior articular process. The
 There are five sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) which are fused in maturity, into one large bone, the
There are five sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) which are fused in maturity, into one large bone, the
Spinal cord direv.svg, The
 In other animals, the vertebrae take the same regional names except for the coccygeal – in animals with tails, the separate vertebrae are usually called the
In other animals, the vertebrae take the same regional names except for the coccygeal – in animals with tails, the separate vertebrae are usually called the  "Procoelous" vertebrae feature a spherical protrusion extending from the caudal end of the centrum of one vertebra that fits into a concave socket on the cranial end of the centrum of an adjacent vertebra. These vertebrae are most often found in
"Procoelous" vertebrae feature a spherical protrusion extending from the caudal end of the centrum of one vertebra that fits into a concave socket on the cranial end of the centrum of an adjacent vertebra. These vertebrae are most often found in
File:Gray303.png, Vertebral arches of three thoracic vertebrae
File:Gray312.png, Costovertebral joints seen from the front
File:Sobo 1909 9.png, Lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae seen from the side
File:Sobo 1909 4.png, Cervical vertebrae seen from the back
File:Vertebrae Anatomy by Jason Christian.webm, Vertebrae anatomy
Vertebra
- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School * *
– University of the Cumberlands {{Authority control Irregular bones Skeletal system Vertebrate anatomy
irregular bone
The irregular bones are bones which, from their peculiar form, cannot be grouped as long, short, flat or sesamoid bones. Irregular bones serve various purposes in the body, such as protection of nervous tissue (such as the vertebrae protect the ...
with a complex structure composed of bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
and some hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has ...
, that make up the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
or spine, of vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.
The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
s. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava
The ligamenta flava (: ligamentum flavum, Latin for ''yellow ligament'') are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring ...
(ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ...
s. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen; the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal
In human anatomy, the spinal canal, vertebral canal or spinal cavity is an elongated body cavity enclosed within the dorsal bony arches of the vertebral column, which contains the spinal cord, spinal roots and dorsal root ganglia. It is a pro ...
, which encloses and protects the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
.
Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.
Structure
In the humanvertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
, the size of the vertebrae varies according to placement in the vertebral column, spinal loading, posture and pathology. Along the length of the spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Spinal column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoology), ...
, the vertebrae change to accommodate different needs related to stress and mobility. Each vertebra is an irregular bone.
cancellous bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
, which is the spongy type of osseous tissue
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provi ...
, whose microanatomy has been specifically studied within the pedicle bones. This cancellous bone is in turn, covered by a thin coating of cortical bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
(or compact bone), the hard and dense type of osseous tissue. The vertebral arch and processes have thicker coverings of cortical bone. The upper and lower surfaces of the body of the vertebra are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
. These surfaces are the vertebral endplates which are in direct contact with the intervertebral discs and form the joint. The endplates are formed from a thickened layer of the cancellous bone of the vertebral body, the top layer being more dense. The endplates function to contain the adjacent discs, to evenly spread the applied loads, and to provide anchorage for the collagen fibers
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body, consisting of around 90% of the body's total collagen in vertebrates. Due to this, it is also the most abundant protein type found in all vertebrates. Type I forms large, eosinoph ...
of the disc. They also act as a semi-permeable interface for the exchange of water and solutes.
process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
es that extend, one from each side, posteriorly, from the junctions of the posteriolateral surfaces of the centrum, on its upper surface.
From each pedicle a broad plate, a lamina, projects backward and medially to join and complete the vertebral arch and form the posterior border of the vertebral foramen, which completes the triangle of the vertebral foramen. The upper surfaces of the laminae are rough to give attachment to the ligamenta flava
The ligamenta flava (: ligamentum flavum, Latin for ''yellow ligament'') are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring ...
. These ligaments connect the laminae of adjacent vertebra along the length of the spine from the level of the second cervical vertebra. Above and below the pedicles are shallow depressions called vertebral notches (''superior'' and ''inferior''). When the vertebrae articulate the notches align with those on adjacent vertebrae and these form the openings of the intervertebral foramina. The foramina allow the entry and exit of the spinal nerves from each vertebra, together with associated blood vessels. The articulating vertebrae provide a strong pillar of support for the body.
Processes
There are seven processes projecting from the vertebra: * one spinous process * two transverse processes * fourarticular processes
The articular process or zygapophysis ( + apophysis) of a vertebra is a projection of the vertebra that serves the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. ...
A major part of a vertebra is a backward extending spinous process (sometimes called the neural spine) which projects centrally. This process points dorsally
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
and caudally
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
from the junction of the laminae. The spinous process serves to attach muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s and ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s.
The two transverse processes, one on each side of the vertebral body, project laterally from either side at the point where the lamina joins the pedicle, between the superior and inferior articular processes. They also serve for the attachment of muscles and ligaments, in particular the intertransverse ligament
The intertransverse ligaments are weak, sheet-like ligaments interconnecting adjacent transverse processes in the thoracic spine, and adjacent accessory processes in the lumbar spine. They act to limit lateral flexion and rotation of the spine.
...
s. There is a facet on each of the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae which articulates with the tubercle of the rib. A facet on each side of the thoracic vertebral body articulates with the head of the rib. The transverse process of a lumbar vertebra
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe the ...
is also sometimes called the costalPlatzer (2004), pp 42–43Latin ''costa'' refers to either a "rib" or "side" of the body. (Diab (1999), p 76) or costiform processTweedie, A. ''The library of medicine'p. 31
/ref> because it corresponds to a rudimentary rib (''costa'') which, as opposed to the thorax, is not developed in the lumbar region. There are superior and inferior
articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two o ...
facet joint
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial joint, synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each functional s ...
s on each side of the vertebra, which serve to restrict the range of movement possible. These facets are joined by a thin portion of the vertebral arch called the pars interarticularis.
Regional variation
cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
, twelve thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
, five lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
, five fused sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
forming the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
and four coccygeal vertebrae
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other ...
, forming the coccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
. Excluding rare deviations, the total number of vertebrae ranges from 32 to 35. In about 10% of people, both the total number of pre-sacral vertebrae and the number of vertebrae in individual parts of the spine can vary. The most frequent deviations are eleven (rarely thirteen) thoracic vertebrae, four or six lumbar vertebrae and three or five coccygeal vertebrae (rarely up to seven).
The regional vertebrae increase in size as they progress downward but become smaller in the coccyx.
Cervical
 There are seven
There are seven cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
(but eight cervical spinal nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ...
s), designated C1 through C7. These bones are, in general, small and delicate. Their spinous processes are short (with the exception of C2 and C7, which have palpable spinous processes). C1 is also called the atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
, and C2 is also called the axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
. The structure of these vertebrae is the reason why the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
and head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
have a large range of motion. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
to move up and down, while the atlanto-axial joint allows the upper neck to twist left and right. The axis also sits upon the first intervertebral disc of the spinal column.
Cervical vertebrae possess transverse foramina to allow for the vertebral arteries to pass through on their way to the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
to end in the circle of Willis
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including huma ...
. These are the smallest, lightest vertebrae and the vertebral foramina are triangular in shape. The spinous processes are short and often bifurcated (the spinous process of C7 is not bifurcated, and is substantially longer than that of the other cervical spinous processes).
The atlas differs from the other vertebrae in that it has no body and no spinous process. It has instead a ring-like form, having an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. At the outside centre points of both arches there is a tubercle, an anterior tubercle and a posterior tubercle, for the attachment of muscles. The front surface of the anterior arch is convex and its anterior tubercle gives attachment to the longus colli muscle. The posterior tubercle is a rudimentary spinous process and gives attachment to the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
The rectus capitis posterior minor (or rectus capitis posticus minor) is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the posterior arch of atlas; its superior attachment is on ...
. The spinous process is small so as not to interfere with the movement between the atlas and the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. On the under surface is a facet for articulation with the dens of the axis.
Specific to the cervical vertebra is the transverse foramen (also known as ''foramen transversarium''). This is an opening on each of the transverse processes which gives passage to the vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major artery, arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, m ...
and vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
and a sympathetic nerve plexus. On the cervical vertebrae other than the atlas, the anterior and posterior tubercles are on either side of the transverse foramen on each transverse process. The anterior tubercle on the sixth cervical vertebra is called the carotid tubercle because it separates the carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of ...
from the vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major artery, arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, m ...
.
There is a hook-shaped uncinate process on the side edges of the top surface of the bodies of the third to the seventh cervical vertebrae and of the first thoracic vertebra. Together with the vertebral disc, this uncinate process prevents a vertebra from sliding backward off the vertebra below it and limits lateral flexion (side-bending). Luschka's joints involve the vertebral uncinate processes.
The spinous process on C7 is distinctively long and gives the name vertebra prominens to this vertebra. Also a cervical rib Cervical ribs are the ribs of the neck in many tetrapods. In most mammals, including humans, cervical ribs are not normally present as separate structures. They can, however, occur as a pathology. In humans, pathological cervical ribs are usually no ...
can develop from C7 as an anatomical variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with Morphology (biology), morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomica ...
.
The term cervicothoracic is often used to refer to the cervical and thoracic vertebrae together, and sometimes also their surrounding areas.
Thoracic
 The twelve
The twelve thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
and their transverse processes have surfaces that articulate with the rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s. Some rotation can occur between the thoracic vertebrae, but their connection with the rib cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great ve ...
prevents much ''flexion'' or other movement. They may also be known as "dorsal vertebrae" in the human context.
The vertebral bodies are roughly heart-shaped and are about as wide anterio-posteriorly as they are in the transverse dimension. Vertebral foramina are roughly circular in shape.
The top surface of the first thoracic vertebra has a hook-shaped uncinate process, just like the cervical vertebrae.
The thoracolumbar spine or thoracolumbar division refers to the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae together, and sometimes also their surrounding areas.
The thoracic vertebrae attach to ribs and so have articular facets specific to them; these are the superior, transverse
Transverse may refer to:
*Transverse engine, an engine in which the crankshaft is oriented side-to-side relative to the wheels of the vehicle
*Transverse flute, a flute that is held horizontally
* Transverse force (or ''Euler force''), the tangen ...
and inferior costal facet
The inferior costal facet (or inferior costal fovea) is a site where a rib forms a joint with the inferior aspect of the body of a thoracic vertebra.
In the adjacent picture, the arrow points to an inferior costal facet. The facets are named for ...
s. As the vertebrae progress down the spine they increase in size to match up with the adjoining lumbar section.
Lumbar

 The five
The five lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
are the largest of the vertebrae, their robust construction being necessary for supporting greater weight than the other vertebrae. They allow significant ''flexion'', ''extension'' and moderate lateral flexion (side-bending). The discs between these vertebrae create a natural lumbar
In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.
Naming and location
The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lowe ...
lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical vertebrae, cervical regio ...
(a spinal curvature that is concave posteriorly). This is due to the difference in thickness between the front and back parts of the intervertebral discs.
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the ribcage and the pelvis and are the largest of the vertebrae. The pedicles are strong, as are the laminae, and the spinous process is thick and broad. The vertebral foramen is large and triangular. The transverse processes are long and narrow and three tubercles can be seen on them. These are a lateral costiform process, a mammillary process and an accessory process.Postacchini, Franco (1999) ''Lumbar Disc Herniation'p. 19
/ref> The superior, or upper tubercle is the mammillary process which connects with the superior articular process. The
multifidus muscle
The multifidus (multifidus spinae; : ''multifidi'') muscle consists of a number of fleshy and tendinous fasciculi, which fill up the groove on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, from the sacrum to the axis. While very thin, ...
attaches to the mammillary process and this muscle extends through the length of the vertebral column, giving support. The inferior, or lower tubercle is the accessory process and this is found at the back part of the base of the transverse process. The term lumbosacral is often used to refer to the lumbar and sacral vertebrae together, and sometimes includes their surrounding areas.
Sacral
 There are five sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) which are fused in maturity, into one large bone, the
There are five sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) which are fused in maturity, into one large bone, the sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
, with no intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
s. The sacrum with the ilium forms a sacroiliac joint
The sacroiliac joint or SI joint (SIJ) is the joint between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis, which are connected by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side. The ...
on each side of the pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
, which articulates with the hips
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint ...
.
Coccygeal
The last three to five coccygeal vertebrae (but usually four) (Co1–Co5) make up the tailbone orcoccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
. There are no intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
s.
Development

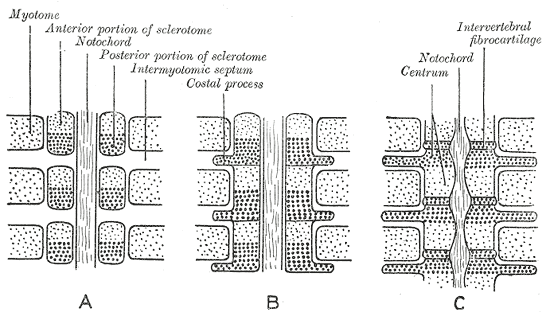
Somite
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryogenesis, embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmentation (biology), segmented animals. ...
s form in the early embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
and some of these develop into sclerotomes. The sclerotomes form the vertebrae as well as the rib cartilage and part of the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
. From their initial location within the somite, the sclerotome cells migrate medially toward the notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb ...
. These cells meet the sclerotome cells from the other side of the paraxial mesoderm
Paraxial mesoderm, also known as presomitic or somitic mesoderm, is the area of mesoderm in the neurulating embryo that flanks and forms simultaneously with the neural tube. The cells of this region give rise to somites, blocks of tissue running ...
. The lower half of one sclerotome fuses with the upper half of the adjacent one to form each vertebral body.
Walker, Warren F., Jr. (1987) ''Functional Anatomy of the Vertebrate'' San Francisco: Saunders College Publishing. From this vertebral body, sclerotome cells move dorsally and surround the developing spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, forming the vertebral arch
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
. Other cells move distally to the costal processes of thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
to form the ribs.
Function
Functions of vertebrae include: #Support of the vertebrae function in the skeletomuscular system by forming the vertebral column to support the body #Protection. Vertebrae contain avertebral foramen
In a typical vertebra, the vertebral foramen is the foramen (opening) of a vertebra bounded ventrally/anteriorly by the body of the vertebra, and the dorsally/posteriorly by the vertebral arch.
In the articulated spine, the successive vertebral ...
for the passage of the spinal canal and its enclosed spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
and covering meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
. They also afford sturdy protection for the spinal cord. The upper and lower surfaces of the centrum are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs.
#Movement. The vertebrae also provide the openings, the intervertebral foramina which allow the entry and exit of the spinal nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into ...
. Similarly to the surfaces of the centrum, the upper and lower surfaces of the fronts of the laminae are flattened and rough to give attachment to the ligamenta flava
The ligamenta flava (: ligamentum flavum, Latin for ''yellow ligament'') are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring ...
. Working together in the vertebral column their sections provide controlled movement and flexibility.
#Feeding of the intervertebral discs through the reflex (hyaline ligament) plate that separates the cancellous bone of the vertebral body from each disk
spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
nested in the vertebral column.
Gray298.png, Vertebral joint
Gray313.png, Costovertebral joint
The costovertebral joints are the joints that connect the ribs to the vertebral column.
* The articulation of head of rib, articulation of the head of rib connects the rib, head of the rib and the Vertebra, bodies of thoracic vertebra, vertebrae. ...
Gray90.png, A facet joint
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial joint, synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each functional s ...
between the superior and inferior articular processes (labeled at top and bottom).
Clinical significance
There are a number of congenital vertebral anomalies, mostly involving variations in the shape or number of vertebrae, and many of which are unproblematic. Others though can cause compression of the spinal cord. Wedge-shaped vertebrae, called ''hemivertebrae'' can cause an angle to form in the spine which can result in the spinal curvature diseases ofkyphosis
Kyphosis () is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the Spinal column, spine as it occurs in the Thoracic spine, thoracic and sacrum, sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the Cervical spine, cervical and Lumba ...
, scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
and lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical vertebrae, cervical regio ...
. Severe cases can cause spinal cord compression. Block vertebrae where some vertebrae have become fused can cause problems. Spina bifida
Spina bifida (SB; ; Latin for 'split spine') is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the vertebral column, spine and the meninges, membranes around the spinal cord during embryonic development, early development in pregnancy. T ...
can result from the incomplete formation of the vertebral arch.
Spondylolysis
Spondylolysis also known as a pars defect or pars fracture, is a defect or stress fracture in the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch. The vast majority of cases occur in the lower lumbar vertebrae (L5), but spondylolysis may also occur ...
is a defect in the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch. In most cases this occurs in the lowest of the lumbar vertebrae (L5), but may also occur in the other lumbar vertebrae, as well as in the thoracic vertebrae.
Spinal disc herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
, more commonly called a ''slipped disc'', is the result of a tear in the outer ring ( anulus fibrosus) of the intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
, which lets some of the soft gel-like material, the nucleus pulposus, bulge out in a hernia
A hernia (: hernias or herniae, from Latin, meaning 'rupture') is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. The term is also used for the normal Devel ...
. This may be treated by a minimally-invasive endoscopic procedure called Tessys method.
A laminectomy
A laminectomy is a surgical procedure that removes a portion of a vertebra called the Lamina of the vertebral arch, lamina, which is the roof of the spinal canal. It is a major spine operation with residual scar tissue and may result in postla ...
is a surgical operation to remove the laminae in order to access the spinal canal. The removal of just part of a lamina is called a laminotomy
A laminotomy is an orthopaedic neurosurgery, neurosurgical procedure that removes part of the lamina of the vertebral arch, lamina of a vertebral arch in order to relieve pressure in the vertebral canal. A laminotomy is less invasive than conve ...
.
A pinched nerve
Radiculopathy (; ), also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain ( radicular pain), weakness, altered s ...
caused by pressure from a disc, vertebra or scar tissue might be remedied by a foraminotomy to broaden the intervertebral foramina and relieve pressure. It can also be caused by a foramina stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
, a narrowing of the nerve opening, as a result of arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
.
Another condition is spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is when one spinal vertebra slips out of place compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it (o ...
when one vertebra slips forward onto another. The reverse of this condition is retrolisthesis
A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to the subjacent vertebra to a degree less than a luxation (dislocation). Retrolistheses are most easily diagnosed on lateral x-ray views of the spine. Views where ...
where one vertebra slips backward onto another.
The vertebral pedicle is often used as a radiographic marker and entry point in vertebroplasty
Vertebral augmentation, including vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, refers to similar percutaneous spinal procedures in which bone cement is injected through a small hole in the skin into a fractured vertebra in order to relieve back pain caused b ...
, kyphoplasty, and spinal fusion
Spinal fusion, also called spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a surgery performed by Orthopedic surgery#Practice, orthopaedic surgeons or neurosurgeons that joins two or more vertebrae. This procedure can be performed at any level in the spine ...
procedures.
The arcuate foramen is a common anatomical variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with Morphology (biology), morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomica ...
more frequently seen in females. It is a bony ''bridge'' found on the first cervical vertebra, the atlas where it covers the groove for the vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major artery, arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, m ...
.
Degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the vertebral column, spine. DDD can take ...
is a condition usually associated with ageing in which one or more discs degenerate. This can often be a painfree condition but can also be very painful.
Other animals
caudal vertebrae
Caudal vertebrae are the vertebrae of the tail in many vertebrates. In birds, the last few caudal vertebrae fuse into the pygostyle, and in apes, including humans, the caudal vertebrae are fused into the coccyx.
In many reptiles, some of the caud ...
. Because of the different types of locomotion and support needed between the aquatic and other vertebrates, the vertebrae between them show the most variation, though basic features are shared. The spinous processes which are backward extending are directed upward in animals without an erect stance. These processes can be very large in the larger animals since they attach to the muscles and ligaments of the body. In the elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
, the vertebrae are connected by tight joints, which limit the backbone's flexibility. Spinous processes are exaggerated in some animals, such as the extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
''Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ; ) is an extinct genus of sphenacodontid synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian) Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian period, around 295–272 million years ago. With most species measuring long and ...
'' and ''Spinosaurus
''Spinosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of large spinosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in what now is North Africa during the Cenomanian faunal stage, stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 100 to 94 annum, million year ...
'', where they form a sailback or finback.
Vertebrae with saddle-shaped articular surfaces on their bodies, called "heterocoelous", allow vertebrae to flex both vertically and horizontally while preventing twisting motions. Such vertebrae are found in the necks of birds and some turtles.
 "Procoelous" vertebrae feature a spherical protrusion extending from the caudal end of the centrum of one vertebra that fits into a concave socket on the cranial end of the centrum of an adjacent vertebra. These vertebrae are most often found in
"Procoelous" vertebrae feature a spherical protrusion extending from the caudal end of the centrum of one vertebra that fits into a concave socket on the cranial end of the centrum of an adjacent vertebra. These vertebrae are most often found in reptiles
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
, but are found in some amphibians
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
such as frogs. The vertebrae fit together in a ball-and-socket articulation, in which the convex articular feature of an anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
vertebra acts as the ball to the socket of a caudal vertebra. This type of connection permits a wide range of motion in most directions, while still protecting the underlying nerve cord. The central point of rotation is located at the midline of each centrum, and therefore flexion of the muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
surrounding the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
does not lead to an opening between vertebrae.
In many species, though not in mammals, the cervical vertebrae bear ribs. In many groups, such as lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s and saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithi ...
n dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The transverse processes
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the ...
. In the whale, the cervical vertebrae are typically fused, an adaptation trading flexibility for stability during swimming. All mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s except manatee
Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing t ...
s and sloth
Sloths are a Neotropical realm, Neotropical group of xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant Arboreal locomotion, arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of move ...
s have seven cervical vertebrae, whatever the length of the neck. This includes seemingly unlikely animals such as the giraffe, the camel, and the blue whale, for example. Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
usually have more cervical vertebrae with most having a highly flexible neck consisting of 13–25 vertebrae.
In all mammals, the thoracic vertebrae are connected to rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s and their bodies differ from the other regional vertebrae due to the presence of facets. Each vertebra has a facet on each side of the vertebral body, which articulates with the head of a rib. There is also a facet on each of the transverse processes which articulates with the tubercle of a rib. The number of thoracic vertebrae varies considerably across the species. Most marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s have thirteen, but koala
The koala (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), sometimes inaccurately called the koala bear, is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only Extant taxon, extant representative of the Family (biology), family ''Phascolar ...
s only have eleven. The usual number is twelve to fifteen in mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, (twelve in the human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
), though there are from eighteen to twenty in the horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
, tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a Suidae, pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk (proboscis). Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South America, South and Centr ...
, rhinoceros
A rhinoceros ( ; ; ; : rhinoceros or rhinoceroses), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls) in the family (biology), famil ...
and elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
. In certain sloths, there is an extreme number of twenty-five and at the other end only nine in the cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
.
There are fewer lumbar vertebrae in chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close rel ...
s and gorilla
Gorillas are primarily herbivorous, terrestrial great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five su ...
s, which have three in contrast to the five in the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
''. This reduction in number gives an inability of the lumbar spine to lordose but gives an anatomy that favours vertical climbing, and hanging ability more suited to feeding locations in high-canopied regions. The bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee (less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee), is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus ''Pan (genus), Pan'' (the other bei ...
differs by having four lumbar vertebrae.
Caudal vertebrae are the bones that make up the tails of vertebrates. They range in number from a few to fifty, depending on the length of the animal's tail.
In humans and other tailless primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s, they are called the coccygeal vertebrae
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other ...
, number from three to five and are fused into the coccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
.
Additional images
See also
* Limbus vertebra * Functional spinal unit *Pott disease
Pott's disease, or Pott disease, named for British surgeon Percivall Pott who first described the symptoms in 1799, is tuberculosis of the vertebral column, spine, usually due to haematogenous spread from other sites, often the lungs. The lowe ...
* Scheuermann's disease
Scheuermann's disease is a skeletal disorder. It describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the sig ...
References
External links
* – Axis & Atlas Articulated, Posterior View * * * *Vertebra
- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School * *
– University of the Cumberlands {{Authority control Irregular bones Skeletal system Vertebrate anatomy