neolithisation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many

 One of the world's most important crops,
One of the world's most important crops,
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
 West Asia was the source for many animals that could be domesticated, such as sheep, goats and pigs. This area was also the first region to
West Asia was the source for many animals that could be domesticated, such as sheep, goats and pigs. This area was also the first region to

 The millet and rice-farming cultures also first came into contact with each other at around 9,000 to 7,000 BP, resulting in a corridor between the millet and rice cultivation centres where both rice and millet were cultivated. At around 5,500 to 4,000 BP, there was increasing migration into
The millet and rice-farming cultures also first came into contact with each other at around 9,000 to 7,000 BP, resulting in a corridor between the millet and rice cultivation centres where both rice and millet were cultivated. At around 5,500 to 4,000 BP, there was increasing migration into

File:Map of the spread of Neolithic farming cultures in Europe.jpg, Map of the spread of Neolithic farming cultures from the Near-East to Europe, with dates in year BCE.
File:Modern distribution of the haplotypes of PPNB farmers.jpg, Modern distribution of the haplotypes of PPNB farmers
File:Genetic distance between PPNB farmers and modern populations.jpg, Genetic distance between PPNB farmers and modern populations
 Andrew Sherratt has argued that following upon the Neolithic Revolution was a second phase of discovery that he refers to as the secondary products revolution. Animals, it appears, were first domesticated purely as a source of meat. The Secondary Products Revolution occurred when it was recognised that animals also provided a number of other useful products. These included:
* History of hide materials, hides and skins (from undomesticated animals)
* manure for soil conditioning (from all domesticated animals)
* wool (from sheep, llamas, alpacas, and Angora goats)
* milk (from goats, cattle, yaks, sheep, horses, and camels)
* Working animal, traction (from oxen, onagers, donkeys, horses, camels, and dogs)
* guarding and herding assistance (dogs)
Sherratt argued that this phase in agricultural development enabled humans to make use of the energy possibilities of their animals in new ways, and permitted permanent intensive subsistence farming and crop production, and the opening up of heavier soils for farming. It also made possible nomadic pastoralism in semi arid areas, along the margins of deserts, and eventually led to the domestication of both the
Andrew Sherratt has argued that following upon the Neolithic Revolution was a second phase of discovery that he refers to as the secondary products revolution. Animals, it appears, were first domesticated purely as a source of meat. The Secondary Products Revolution occurred when it was recognised that animals also provided a number of other useful products. These included:
* History of hide materials, hides and skins (from undomesticated animals)
* manure for soil conditioning (from all domesticated animals)
* wool (from sheep, llamas, alpacas, and Angora goats)
* milk (from goats, cattle, yaks, sheep, horses, and camels)
* Working animal, traction (from oxen, onagers, donkeys, horses, camels, and dogs)
* guarding and herding assistance (dogs)
Sherratt argued that this phase in agricultural development enabled humans to make use of the energy possibilities of their animals in new ways, and permitted permanent intensive subsistence farming and crop production, and the opening up of heavier soils for farming. It also made possible nomadic pastoralism in semi arid areas, along the margins of deserts, and eventually led to the domestication of both the
Agriculture, plant physiology, and human population growth: past, present, and future." Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology 25 (2013): 167–181
Hort 306 - READING 3-1
* Wright, Gary A. (1971). "Origins of Food Production in Southwestern Asia: A Survey of Ideas" Current Anthropology, Vol. 12, No. 4/5 (Oct.–Dec. 1971), pp. 447–477 * Kuijt, Ian; Finlayson, Bill. (2009)
"Evidence for food storage and predomestication granaries 11,000 years ago in the Jordan Valley"
PNAS, Vol. 106, No. 27, pp. 10966–10970. {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Prehistoric agriculture History of technology Neolithic, Revolution Agricultural revolutions Stages of history Historical eras
 The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
s during the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period in Afro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia (also Afroeurasia and Eurafrasia) is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The terms are compound (linguistics), compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Afro-Eurasia has also been called th ...
from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
and settlement, making an increasingly large population possible. These settled communities permitted humans to observe and experiment with plants, learning how they grew and developed. This new knowledge led to the domestication of plants into crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. In other words, a crop is a plant or plant product that is grown for a specific purpose such as food, Fiber, fibre, or fuel.
When plants of the same spe ...
s.
Archaeological data indicate that the domestication
Domestication is a multi-generational Mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a st ...
of various types of plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s and animals happened in separate locations worldwide, starting in the geological epoch of the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
11,700 years ago, after the end of the last Ice Age. It was humankind's first historically verifiable transition to agriculture. The Neolithic Revolution greatly narrowed the diversity of foods available, resulting in a decrease in the quality of human nutrition compared with that obtained previously from foraging
Foraging is searching for wild food resources. It affects an animal's fitness because it plays an important role in an animal's ability to survive and reproduce. Foraging theory is a branch of behavioral ecology that studies the foraging behavi ...
. However, because food production became more efficient, it released humans to invest their efforts in other activities and was thus "ultimately necessary to the rise of modern civilization by creating the foundation for the later process of industrialization and sustained economic growth".
The Neolithic Revolution involved much more than the adoption of a limited set of food-producing techniques. During the next millennia, it transformed the small and mobile groups of hunter-gatherers that had hitherto dominated human prehistory into sedentary (non-nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic) societies
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
based in built-up villages and towns. These societies radically modified their natural environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all life, biotic and abiotic component, abiotic things occurring nature, naturally, meaning in this case not artificiality, artificial. The term is most often applied to Earth or some parts ...
by means of specialized food-crop cultivation, with activities such as irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
and deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
which allowed the production of surplus food. Other developments that are found very widely during this era are the domestication of animals
The domestication of vertebrates is the mutual relationship between vertebrate animals, including birds and mammals, and the humans who influence their care and reproduction.
Charles Darwin recognized a small number of traits that made domestica ...
, pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
, polished stone tools, and rectangular houses. In many regions, the adoption of agriculture by prehistoric societies caused episodes of rapid population growth, a phenomenon known as the Neolithic demographic transition
The Neolithic demographic transition was a period of rapid population growth following the adoption of agriculture by prehistoric societies (the Neolithic Revolution). It was a demographic transition caused by an abrupt increase in birth rates due ...
.
These developments, sometimes called the Neolithic package, provided the basis for centralized administrations and political structures, hierarchical ideologies
An ideology is a set of beliefs or values attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely about belief in certain knowledge, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones". Form ...
, depersonalized systems of knowledge (e.g. writing
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ...
), densely populated
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ...
settlements, specialization and division of labour
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise ( specialisation). Individuals, organisations, and nations are endowed with or acquire specialised capabilities, a ...
, more trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
, the development of non-portable art
Art is a diverse range of cultural activity centered around ''works'' utilizing creative or imaginative talents, which are expected to evoke a worthwhile experience, generally through an expression of emotional power, conceptual ideas, tec ...
and architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, and greater property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ...
ownership. The earliest known civilization developed in Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
in southern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
(); its emergence also heralded the beginning of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
.
The relationship of the aforementioned Neolithic characteristics to the onset of agriculture, their sequence of emergence, and their empirical relation to each other at various Neolithic sites remains the subject of academic debate. It is usually understood to vary from place to place, rather than being the outcome of universal laws of social evolution.
Background
Prehistorichunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s had different subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing and shelter) rather than to the market.
Definition
"Subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself and family at a minimum level. Basic subsiste ...
requirements and lifestyles from agriculturalists. Hunter-gatherers were often highly mobile and migratory, living in temporary shelters and in small tribal groups, and having limited contact with outsiders. Their diet was well-balanced though heavily dependent on what the environment could provide each season. In contrast, because the surplus and plannable supply of food provided by agriculture made it possible to support larger population groups, agriculturalists lived in more permanent dwellings in more densely populated settlements than what could be supported by a hunter-gatherer lifestyle. The agricultural communities' seasonal need to plan and coordinate resource
''Resource'' refers to all the materials available in our environment which are Technology, technologically accessible, Economics, economically feasible and Culture, culturally Sustainability, sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and want ...
and manpower
Human resources (HR) is the set of people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, industry, or economy. A narrower concept is human capital, the knowledge and skills which the individuals command. Similar terms include ...
encouraged division of labour
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise ( specialisation). Individuals, organisations, and nations are endowed with or acquire specialised capabilities, a ...
, which gradually led to specialization of labourers and complex societies. The subsequent development of trading networks to exchange surplus commodities and services brought agriculturalists into contact with outside groups, which promoted cultural exchange
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, attitudes, and habits of the individuals in these ...
s that led to the rise of civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyon ...
s and technological evolutions.
However, higher population and food abundance did not necessarily correlate with improved health. Reliance on a very limited variety of staple crop
A staple food, food staple, or simply staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs an ...
s can adversely affect health even while making it possible to feed more people. As an example from the Americas, maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
is deficient in certain essential amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
(lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
and tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
) and is a poor source of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
. The phytic acid
Phytic acid is a six-fold dihydrogenphosphate ester of inositol (specifically, of the ''myo'' isomer), also called inositol hexaphosphate, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) or inositol polyphosphate. At physiological pH, the phosphates are partia ...
it contains may inhibit nutrient absorption. Other factors that likely affected the health of early agriculturalists and their domesticated livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
would have been increased numbers of parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
and disease-bearing pests associated with human waste and contaminated food and water supplies. Fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
may have increased crop yields but also would have promoted proliferation of insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s and bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
in the local environment while grain storage attracted additional insects and rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
.
Agricultural transition
The term 'neolithic revolution' was invented by V. Gordon Childe in his book ''Man Makes Himself'' (1936). Childe introduced it as the first in a series of agricultural revolutions inMiddle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
ern history, calling it a "revolution" to denote its significance, the degree of change to communities adopting and refining agricultural practices.
The beginning of this process in different regions has been dated from 10,000 to 8,000 BCE in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
,Thissen, L. "Appendix I, The CANeW 14C databases, Anatolia 10,000–5000 cal. BC." in: F. Gérard and L. Thissen (eds.), '' The Neolithic of Central Anatolia. Internal developments and external relations during the 9th–6th millennia cal BC'', Proc. Int. CANeW Round Table, Istanbul 23–24 November 2001, (2002) and perhaps 8000 BCE in the Kuk Early Agricultural Site of Papua New Guinea in Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanu ...
. Everywhere, this transition is associated with a change from a largely nomadic
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
way of life to a more settled
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among the first settli ...
, agrarian one, with the domestication
Domestication is a multi-generational Mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a st ...
of various plant and animal species – depending on the species locally available, and influenced by local culture. Archaeological research in 2003 suggests that in some regions, such as the Southeast Asian peninsula, the transition from hunter-gatherer to agriculturalist was not linear, but region-specific.
*
Domestication
Crops
Once agriculture started gaining momentum, around 9000 BP, human activity resulted in theselective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
of cereal grasses (beginning with emmer
Emmer is a hybrid species of wheat, producing edible seeds that have been used as food since ancient times. The domesticated types are ''Triticum turgidum'' subsp. ''dicoccum'' and ''T. t. ''conv.'' durum''. The wild plant is called ''T. t.'' s ...
, einkorn and barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
), and not simply of those that favoured greater caloric returns through larger seeds. Plants with traits such as small seeds or bitter taste were seen as undesirable. Plants that rapidly shed their seeds on maturity tended not to be gathered at harvest, therefore not stored and not seeded the following season; successive years of harvesting spontaneously selected for strains that retained their edible seeds longer.

Daniel Zohary
Daniel (Dani) Zohary (; 24 April 1926 - 16 December 2016) was an Israeli plant geneticist, agronomist, and professor at the Hebrew University. He was the co-author of a comprehensive review of the origin and spread of domesticated plants in southw ...
identified several plant species as "pioneer crops" or Neolithic founder crops
The founder crops or primary domesticates are a group of flowering plants that were Domestication, domesticated by early farming communities in Southwest Asia and went on to form the basis of agriculture, agricultural economies across Eurasia. As ...
. He highlighted the importance of wheat, barley and rye, and suggested that domestication of flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
, pea
Pea (''pisum'' in Latin) is a pulse or fodder crop, but the word often refers to the seed or sometimes the pod of this flowering plant species. Peas are eaten as a vegetable. Carl Linnaeus gave the species the scientific name ''Pisum sativum' ...
s, chickpea
The chickpea or chick pea (''Cicer arietinum'') is an annual plant, annual legume of the family (biology), family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, cultivated for its edible seeds. Its different types are variously known as gram," Bengal gram, ga ...
s, bitter vetch and lentil
The lentil (''Vicia lens'' or ''Lens culinaris'') is an annual plant, annual legume grown for its Lens (geometry), lens-shaped edible seeds or ''pulses'', also called ''lentils''. It is about tall, and the seeds grow in Legume, pods, usually w ...
s came a little later. Based on analysis of the gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s of domesticated plants, he preferred theories of a single, or at most a very small number of domestication events for each taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
that spread in an arc from the Levantine corridor around the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
and later into Europe. Gordon Hillman and Stuart Davies carried out experiments with varieties of wild wheat to show that the process of domestication would have occurred over a relatively short period of between 20 and 200 years.
Some of the pioneering attempts failed at first and crops were abandoned, sometimes to be taken up again and successfully domesticated thousands of years later: rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
, tried and abandoned in Neolithic Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, made its way to Europe as weed seeds and was successfully domesticated in Europe, thousands of years after the earliest agriculture. Wild lentils presented a different problem: most of the wild seeds do not germinate in the first year; the first evidence of lentil domestication, breaking dormancy in their first year, appears in the early Neolithic at Jerf el Ahmar (in modern Syria), and lentils quickly spread south to the Netiv HaGdud
Netiv HaGdud () is an Israeli settlement organized as a moshav in the West Bank.Netiv HaGdud
Bik'at HaYarden R ...
site in the Jordan Valley. The process of domestication allowed the founder crops to adapt and eventually become larger, more easily harvested, more dependable in storage and more useful to the human population.
Selectively propagated Bik'at HaYarden R ...
figs
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Moraceae, native to the Mediterranean region, together with western and southern Asia. It has been cultivated since ancient times and i ...
, wild barley and wild oats were cultivated at the early Neolithic site of Gilgal I, where in 2006 archaeologists found caches of seeds of each in quantities too large to be accounted for even by intensive gathering, at strata datable to 11,000 years ago. Some of the plants tried and then abandoned during the Neolithic period in the Ancient Near East, at sites like Gilgal, were later successfully domesticated in other parts of the world.
Once early farmers perfected their agricultural techniques like irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
(traced as far back as the 6th millennium BCE in Khuzistan
Khuzestan province () is one of the 31 Provinces of Iran. Located in the southwest of the country, the province borders Iraq and the Persian Gulf, covering an area of . Its capital is the city of Ahvaz. Since 2014, it has been part of Iran's ...
), their crops yielded surpluses that needed storage. Most hunter-gatherers could not easily store food for long due to their migratory lifestyle, whereas those with a sedentary dwelling could store their surplus grain. Eventually granaries were developed that allowed villages to store their seeds longer. So with more food, the population expanded and communities developed specialized workers and more advanced tools.
The process was not as linear as was once thought, but a more complicated effort, which was undertaken by different human populations in different regions in many different ways.
 One of the world's most important crops,
One of the world's most important crops, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
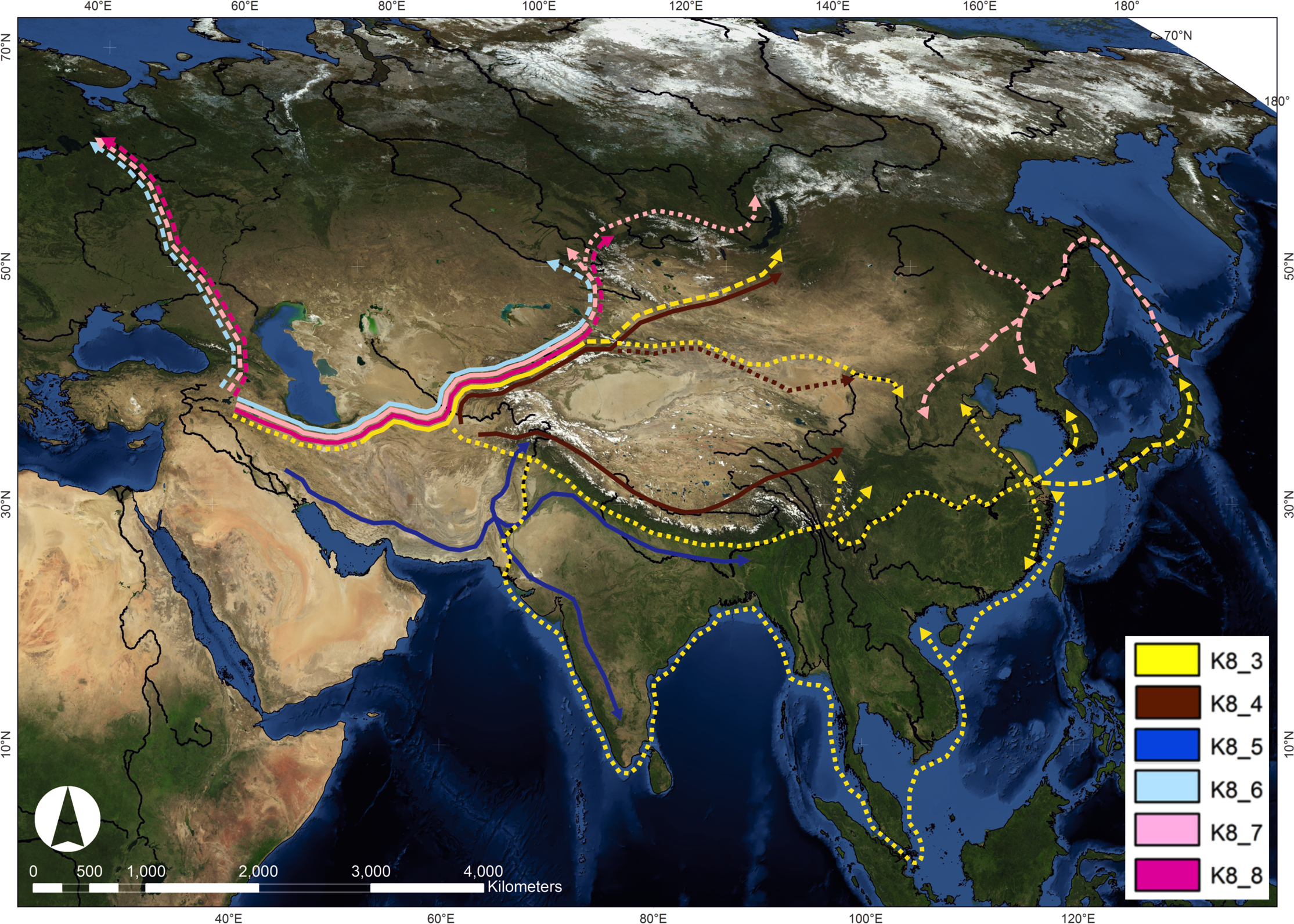
, was domesticated in the Near East around 11,000 years ago (). Barley is a highly resilient crop, able to grow in varied and marginal environments, such as in regions of high altitude and latitude. Archaeobotanical evidence shows that barley had spread throughout Eurasia by 2,000 BCE. To further elucidate the routes by which barley cultivation was spread through Eurasia, genetic analysis was used to determine genetic diversity and population structure in extant barley taxa. Genetic analysis shows that cultivated barley spread through Eurasia via several different routes, which were most likely separated in both time and space. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Livestock
When hunter-gathering began to be replaced by sedentary food production it became more efficient to keep animals close at hand. Therefore, it became necessary to bring animals permanently to their settlements, although in many cases there was a distinction between relatively sedentary farmers and nomadic herders. The animals' size, temperament, diet, mating patterns, and life span were factors in the desire and success in domesticating animals. Animals that provided milk, such as cows and goats, offered a source of protein that was renewable and therefore quite valuable. The animal's ability as a worker (for example ploughing or towing), as well as a food source, also had to be taken into account. Besides being a direct source of food, certain animals could provide leather, wool, hides, and fertilizer. Some of the earliest domesticated animals includeddogs
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers ...
(East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
, about 15,000 years ago), sheep, goats, cows, and pigs. West Asia was the source for many animals that could be domesticated, such as sheep, goats and pigs. This area was also the first region to
West Asia was the source for many animals that could be domesticated, such as sheep, goats and pigs. This area was also the first region to domesticate
Domestication is a multi-generational mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a steady supply of resou ...
the dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius''), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel and one-humped camel, is a large camel of the genus '' Camelus'' with one hump on its back. It is the tallest of the three camel species; adult males sta ...
. Henri Fleisch discovered and termed the Shepherd Neolithic
Shepherd Neolithic is a name given by archaeologists to a style (or industry) of small flint tools from the Hermel plains in the north Beqaa Valley, Lebanon.Fleisch, Henri., Les industries lithiques récentes de la Békaa, République Libana ...
flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
industry from the Bekaa Valley in Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and suggested that it could have been used by the earliest nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic shepherd
A shepherd is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations; it exists in many parts of the globe, and it is an important part of Pastoralism, pastoralist animal husbandry. ...
s. He dated this industry to the Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
or Pre-Pottery Neolithic
The Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) represents the early Neolithic in the Near East, dating to years ago, (10000 – 6500 BCE).Richard, Suzanne ''Near Eastern archaeology'' Eisenbrauns; illustrated edition (1 Aug 2004) p.24/ref> It succeeds the ...
as it is evidently not Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
, Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
or even Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
.
The presence of these animals gave the region a large advantage in cultural and economic development. As the climate in the Middle East changed and became drier, many of the farmers were forced to leave, taking their domesticated animals with them. It was this massive emigration from the Middle East that later helped distribute these animals to the rest of Afroeurasia. This emigration was mainly on an east–west axis of similar climates, as crops usually have a narrow optimal climatic range outside of which they cannot grow for reasons of light or rain changes. For instance, wheat does not normally grow in tropical climates, just like tropical crops such as bananas do not grow in colder climates. Some authors, like Jared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond (born September 10, 1937) is an American scientist, historian, and author. In 1985 he received a MacArthur Genius Grant, and he has written hundreds of scientific and popular articles and books. His best known is '' Guns, G ...
, have postulated that this east–west axis is the main reason why plant and animal domestication spread so quickly from the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
to the rest of Eurasia and North Africa, while it did not reach through the north–south axis of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
to reach the Mediterranean climates of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, where temperate crops were successfully imported by ships in the last 500 years. Similarly, the African Zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus''), also known as indicine cattle and humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of Bos taurus, domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump ...
of central Africa and the domesticated bovines of the fertile-crescent – separated by the dry sahara desert – were not introduced into each other's region.
Centers of agricultural origin
West Asia

Use-wear analysis
Use-wear analysis is a method in archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture ...
of five glossed flint blades found at Ohalo II
Ohalo II is an archaeological site in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District, Israel, near Kinneret (archaeological site), Kinneret, on the southwest shore of the Sea of Galilee. It is one of the best preserved hunter-gatherer archaeol ...
, a 23,000-years-old fisher-hunter-gatherers' camp on the shore of the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth ...
, Northern Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, provides the earliest evidence for the use of composite cereal harvesting tools. Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The Ohalo site is at the junction of the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
and the Early Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
, and has been attributed to both periods.
The wear traces indicate that tools were used for harvesting near-ripe semi-green wild cereals, shortly before grains are ripe and disperse naturally. The studied tools were not used intensively, and they reflect two harvesting modes: flint knives held by hand and inserts hafted in a handle. The finds shed new light on cereal harvesting techniques some 8,000 years before the Natufian
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even befor ...
and 12,000 years before the establishment of sedentary farming communities in the Near East. Furthermore, the new finds accord well with evidence for the earliest ever cereal cultivation at the site and the use of stone-made grinding implements.
Agriculture appeared first in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
about 2,000 years later, around 10,000–9,000 years ago. The region was the centre of domestication for three cereals (einkorn wheat, emmer wheat and barley), four legumes (lentil, pea, bitter vetch and chickpea), and flax. Domestication was a slow process that unfolded across multiple regions, and was preceded by centuries if not millennia
A millennium () is a period of one thousand years, one hundred decades, or ten centuries, sometimes called a kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting p ...
of pre-domestication cultivation.
Finds of large quantities of seeds and a grinding stone at the Epipalaeolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
site of Ohalo II
Ohalo II is an archaeological site in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District, Israel, near Kinneret (archaeological site), Kinneret, on the southwest shore of the Sea of Galilee. It is one of the best preserved hunter-gatherer archaeol ...
, dating to around 19,400 BP, has shown some of the earliest evidence for advanced planning of plants for food consumption and suggests that humans at Ohalo II processed the grain before consumption.Compiled largely with reference to: Tell Aswad is the oldest site of agriculture, with domesticated emmer
Emmer is a hybrid species of wheat, producing edible seeds that have been used as food since ancient times. The domesticated types are ''Triticum turgidum'' subsp. ''dicoccum'' and ''T. t. ''conv.'' durum''. The wild plant is called ''T. t.'' s ...
wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
dated to 10,800 BP. Soon after came hulled, two-row barley – found domesticated earliest at Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017.
F ...
in the Jordan valley and at Iraq ed-Dubb in Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
.
Other sites in the Levantine corridor that show early evidence of agriculture include Wadi Faynan 16 and Netiv Hagdud
Netiv HaGdud () is an Israeli settlement organized as a moshav in the West Bank.Netiv HaGdud
Bik'at HaYarden R ...
. Jacques Cauvin noted that the settlers of Aswad did not domesticate on site, but ''"arrived, perhaps from the neighbouring Anti-Lebanon, already equipped with the seed for planting"''. In the Eastern Fertile Crescent, evidence of cultivation of wild plants has been found in Choga Gholan in Bik'at HaYarden R ...
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
dated to 12,000 BP, with domesticated emmer wheat appearing in 9,800 BP, suggesting there may have been multiple regions in the Fertile Crescent where cereal domestication evolved roughly contemporaneously. The Heavy Neolithic Qaraoun culture has been identified at around fifty sites in Lebanon around the source springs of the River Jordan, but never reliably dated.
In his 1997 book ''Guns, Germs, and Steel
''Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies'' (subtitled ''A Short History of Everybody for the Last 13,000 Years'' in Britain) is a 1997 transdisciplinary nonfiction book by the American author Jared Diamond. The book attempts to ...
'', Jared Diamond argues that the vast continuous east–west stretch of temperate climatic zones of Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
and North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
gave peoples living there a highly advantageous geographical location that afforded them a head start in the Neolithic Revolution. Both shared the temperate climate ideal for the first agricultural settings, and both were near a number of easily domesticable plant and animal species. In areas where continents aligned north–south such as the Americas and Africa, crops—and later domesticated animals—could not spread across tropical zones.
East Asia
Agriculture inNeolithic China
This is a list of Neolithic cultures of China that have been unearthed by archaeologists. They are sorted in chronological order from earliest to latest and are followed by a schematic visualization of these cultures.
It would seem that the defi ...
can be separated into two broad regions, Northern China and Southern China.
The agricultural centre in northern China is believed to be the homelands of the early Sino-Tibetan-speakers, associated with the Houli, Peiligang, Cishan, and Xinglongwa cultures
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, clustered around the Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
basin. It was the domestication centre for foxtail millet
Foxtail millet, scientific name ''Setaria italica'' (synonym ''Panicum italicum'' L.), is an annual grass grown for human food. It is the second-most widely planted species of millet, and the most grown millet species in Asia. The oldest evidenc ...
(''Setaria italica'') and broomcorn millet (''Panicum miliaceum''), with early evidence of domestication approximately 8,000 years ago, and widespread cultivation 7,500 years ago. (Soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
was also domesticated in northern China 4,500 years ago. Orange and peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
also originated in China, being cultivated .)
The agricultural centres in southern China are clustered around the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
basin. Rice was domesticated in this region, together with the development of paddy field cultivation, between 13,500 and 8,200 years ago.
There are two possible centres of domestication for rice. The first is in the lower Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
, believed to be the homelands of pre-Austronesians and associated with the Kauhuqiao, Hemudu, Majiabang, and Songze cultures
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
. It is characterized by typical pre-Austronesian features, including stilt houses, jade carving, and boat technologies. Their diet were also supplemented by acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s, water chestnuts, foxnuts, and pig domestication. The second is in the middle Yangtze River, believed to be the homelands of the early Hmong-Mien-speakers and associated with the Pengtoushan
The Pengtoushan culture was a Neolithic culture located around the central Yangtze River region in northwestern Hunan province, China. It dates to around 7500–6100 BC, and was roughly contemporaneous with the Peiligang culture to the north. It ...
and Daxi cultures
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
. Both of these regions were heavily populated and had regular trade contacts with each other, as well as with early Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ...
speakers to the west, and early Kra-Dai speakers to the south, facilitating the spread of rice cultivation throughout southern China.
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
from the early Austronesian Dapenkeng culture, bringing rice and millet cultivation technology with them. During this period, there is evidence of large settlements and intensive rice cultivation in Taiwan and the Penghu Islands
The Penghu ( , Hokkien POJ: ''Phîⁿ-ô͘'' or ''Phêⁿ-ô͘'' ) or Pescadores Islands are an archipelago of 90 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait, about west of the main island of Taiwan across the Penghu Channel, cove ...
, which may have resulted in overexploitation
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to ...
. Bellwood (2011) proposes that this may have been the impetus of the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
which started with the migration of the Austronesian-speakers from Taiwan to the Philippines at around 5,000 BP.
Austronesians carried rice cultivation technology to Island Southeast Asia along with other domesticated species. The new tropical island environments also had new food plants that they exploited. They carried useful plants and animals during each colonization voyage, resulting in the rapid introduction of domesticated and semi-domesticated species throughout Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
. They also came into contact with the early agricultural centres of Papuan-speaking populations of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
as well as the Dravidian-speaking regions of South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
by around 3,500 BP. They acquired further cultivated food plants like bananas and pepper from them, and in turn introduced Austronesian technologies like wetland cultivation and outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull (watercraft), hull. They can range from small dugout (boat), dugout canoes to large ...
s. During the 1st millennium CE, they also colonized Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
and the Comoros
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an archipelagic country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni, ...
, bringing Southeast Asian food plants, including rice, to East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
.
Africa
On the African continent, three areas have been identified as independently developing agriculture: theEthiopian highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
, the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
and West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
. By contrast, Agriculture in the Nile River Valley is thought be related to migration of populations and to have developed from the original Neolithic Revolution in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
.
Many grinding stones are found with the early Egyptian Sebilian and Mechian cultures and evidence has been found of a Neolithic domesticated crop-based economy dating around 7,000 BP.
Unlike the Middle East, this evidence appears as a "false dawn" to agriculture, as the sites were later abandoned, and permanent farming then was delayed until 6,500 BP with the Tasian culture and Badarian culture and the arrival of crops and animals from the Near East.
Bananas
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – berry (botany), botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called pla ...
and Plantain (cooking), plantains, which were first domesticated in Southeast Asia, most likely Papua New Guinea, were re-domesticated in Africa possibly as early as 5,000 years ago. Asian yams and taro were also cultivated in Africa.
The most famous crop domesticated in the Ethiopian highlands is coffee. In addition, khat, ensete, noog, teff and finger millet were also domesticated in the Ethiopian highlands. Crops domesticated in the Sahel region include sorghum and pearl millet. The kola nut was first domesticated in West Africa. Other crops domesticated in West Africa include African rice, Yam (vegetable), yams and the oil palm.
Agriculture spread to Central and Southern Africa in the Bantu expansion during the 1st millennium BCE to 1st millennium CE.
Americas
The term "Neolithic" is not customarily used in describing cultures in the Americas. However, a broad similarity exists between Eastern Hemisphere cultures of the Neolithic and cultures in the Americas. Maize (corn), beans and Squash (plant), squash were among the earliest crops domesticated in Mesoamerica: squash as early as 6000 BCE, beans no later than 4000 BCE, and maize beginning about 7000 BCE. Potatoes and manioc were domesticated in South America. In what is now the eastern United States, Native Americans domesticated sunflower, sumpweed and goosefoot . In the highlands of central Mexico, sedentary village life based on farming did not develop until the "formative period" in the second millennium BCE.New Guinea
Evidence of drainage ditches at Kuk Swamp on the borders of the Western Highlands Province, Western and Southern Highlands Province, Southern Highlands of Papua New Guinea indicates cultivation of taro and a variety of other crops, dating back to 11,000 BP. Two potentially significant economic species, taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') and yam (vegetable), yam (''Dioscorea'' sp.), have been identified dating at least to 10,200 calibrated years before present (cal BP). Further evidence of bananas and sugarcane dates to 6,950 to 6,440 BCE. This was at the altitudinal limits of these crops, and it has been suggested that cultivation in more favourable ranges in the lowlands may have been even earlier. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, CSIRO has found evidence that taro was introduced into the Solomon Islands (archipelago), Solomon Islands for human use, from 28,000 years ago, making taro the earliest cultivated crop in the world. It seems to have resulted in the spread of the Trans–New Guinea languages from New Guinea east into the Solomon Islands and west into Timor and adjacent areas of Indonesia. This seems to confirm the theories of Carl O. Sauer, Carl Sauer who, in "Agricultural Origins and Dispersals", suggested as early as 1952 that this region was a centre of early agriculture.Spread of agriculture
Europe
Archaeologists trace the emergence of food-producing societies in the Levantine region of southwest Asia at the close of the last glacial period around 12,000 BCE, and developed into a number of regionally distinctive cultures by the eighth millennium BCE. Remains of food-producing societies in the Aegean civilization, Aegean have been carbon-dated to at Knossos, Franchthi Cave, and a number of mainland sites in Thessaly. Neolithic groups appear soon afterwards in the Balkans and south-central Europe. The Neolithic cultures of southeastern Europe (the Balkans and the Aegean civilization, Aegean) show some continuity with groups in southwest Asia andAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
(e.g., Çatalhöyük).
Current evidence suggests that Neolithic material culture was introduced to Europe via western Anatolia. All Neolithic sites in Europe contain pottery, ceramics, and contain the plants and animals domesticated in Southwest Asia: einkorn, emmer
Emmer is a hybrid species of wheat, producing edible seeds that have been used as food since ancient times. The domesticated types are ''Triticum turgidum'' subsp. ''dicoccum'' and ''T. t. ''conv.'' durum''. The wild plant is called ''T. t.'' s ...
, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, lentil
The lentil (''Vicia lens'' or ''Lens culinaris'') is an annual plant, annual legume grown for its Lens (geometry), lens-shaped edible seeds or ''pulses'', also called ''lentils''. It is about tall, and the seeds grow in Legume, pods, usually w ...
s, pigs, goats, sheep, and cattle. Genetic data suggest that no independent domestication of animals took place in Neolithic Europe, and that all domesticated animals were originally domesticated in Southwest Asia. The only domesticate not from Southwest Asia was broomcorn millet, domesticated in East Asia.The earliest evidence of cheese-making dates to 5500 BCE in Kujawy, Poland.
The diffusion across Europe, from the Aegean to Britain, took about 2,500 years (8500–6000 BP). The Baltic region was penetrated a bit later, around 5500 BP, and there was also a delay in settling the Pannonian plain. In general, colonization shows a "saltatory" pattern, as the Neolithic advanced from one patch of fertile alluvial soil to another, bypassing mountainous areas. Analysis of radiocarbon dates show clearly that Mesolithic and Neolithic populations lived side by side for as much as a millennium in many parts of Europe, especially in the Iberian peninsula and along the Atlantic coast.
Carbon 14 evidence
The spread of the Neolithic from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, Near East Neolithic to Europe was first studied quantitatively in the 1970s, when a sufficient number of Carbon 14 age determinations for early Neolithic sites had become available.Original text published under Creative Commons license CC BY 4.0: Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License In 1973, Ammerman and Cavalli-Sforza discovered a linear relationship between the age of an Early Neolithic site and its distance from the conventional source in the Near East (Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017.
F ...
), demonstrating that the Neolithic spread at an average speed of about 1 km/yr. More recent studies (2005) confirm these results and yield the speed of 0.6–1.3 km/yr (at 95% confidence level).
Analysis of mitochondrial DNA
Since the original human Recent African origin of modern humans, expansions out of Africa 200,000 years ago, different prehistoric and historic migration events have taken place in Europe. Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Considering that the movement of the people implies a consequent movement of their genes, it is possible to estimate the impact of these migrations through the genetic analysis of human populations. Agricultural and husbandry practices originated 10,000 years ago in a region of the Near East known as the Fertile Crescent. According to the archaeological record this phenomenon, known as "Neolithic", rapidly expanded from these territories into Europe. However, whether this diffusion was accompanied or not by human migrations is greatly debated. Mitochondrial DNA – a type of maternally inherited DNA located in the cell cytoplasm – was recovered from the remains of Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) farmers in the Near East and then compared to available data from other Neolithic populations in Europe and also to modern populations from South Eastern Europe and the Near East. The obtained results show that substantial human migrations were involved in the Neolithic spread and suggest that the first Neolithic farmers entered Europe following a maritime route through Cyprus and the Aegean Islands.South Asia
The earliest Neolithic site in South Asia is Mehrgarh, dated to between 6500 and 5500 BCE, in the Kacchi Plain, Kachi plain of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan, Pakistan; the site has evidence of farming (wheat and barley) and herding (cattle, sheep and goats). There is strong evidence for causal connections between the Near-Eastern Neolithic and that further east, up to the Indus Valley. Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License There are several lines of evidence that support the idea of connection between the Neolithic in the Near East and in the Indian subcontinent. The prehistoric site of Mehrgarh in Baluchistan (modern Pakistan) is the earliest Neolithic site in the north-west Indian subcontinent, dated as early as 8500 BCE. Neolithic domesticated crops in Mehrgarh include more than 90% barley and a small amount of wheat. There is good evidence for the local domestication of barley and the zebu cattle at Mehrgarh, but the wheat varieties are suggested to be of Near-Eastern origin, as the modern distribution of wild varieties of wheat is limited to Northern Levant and Southern Turkey. A detailed satellite map study of a few archaeological sites in the Baluchistan and Khybar Pakhtunkhwa regions also suggests similarities in early phases of farming with sites in Western Asia. Pottery prepared by sequential slab construction, circular fire pits filled with burnt pebbles, and large granaries are common to both Mehrgarh and many Mesopotamian sites. The postures of the skeletal remains in graves at Mehrgarh bear strong resemblance to those at Ali Kosh in the Zagros Mountains of southern Iran. Despite their scarcity, the Carbon-14 and archaeological age determinations for early Neolithic sites in Southern Asia exhibit remarkable continuity across the vast region from the Near East to the Indian Subcontinent, consistent with a systematic eastward spread at a speed of about 0.65 km/yr.Causes
The most prominent of several theories (not mutually exclusive) as to factors that caused populations to develop agriculture include: * The Oasis Theory, originally proposed by Raphael Pumpelly in 1908, popularized by V. Gordon Childe in 1928 and summarised in Childe's book ''Man Makes Himself''. This theory maintains that as the climate got drier due to the Atlantic depressions shifting northward, communities contracted to oases where they were forced into close association with animals, which were then domesticated together with planting of seeds. However, this theory now has little support amongst archaeologists because subsequent climate data suggests that the region was getting wetter rather than drier. * The Hilly Flanks hypothesis, proposed by Robert John Braidwood in 1948, suggests that agriculture began in the hilly flanks of the Taurus Mountains, Taurus and Zagros Mountains, where the climate was not drier as Childe had believed, and fertile land supported a variety of plants and animals amenable to domestication. * The Feasting model by Brian Hayden suggests that agriculture was driven by ostentatious displays of power, such as giving feasts, to exert dominance. This required assembling large quantities of food, which drove agricultural technology. * The Demographic theories proposed by Carl Sauer and adapted by Lewis Binford and Kent Flannery posit an increasingly sedentary population that expanded up to the carrying capacity of the local environment and required more food than could be gathered. Various social and economic factors helped drive the need for food. * The evolutionary/intentionality theory, developed by David Rindos and others, considers agriculture as an evolutionary adaptation of plants and humans. Starting with domestication by protection of wild plants, it resulted specialization of location and then complete domestication. * Peter Richerson, Robert Boyd (anthropologist), Robert Boyd, and Robert Bettinger make a case for the development of agriculture coinciding with an increasingly stable climate at the beginning of theHolocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
. Ronald Wright's book and Massey Lecture Series ''A Short History of Progress'' popularized this hypothesis.
* Leonid Grinin argues that whatever plants were cultivated, the independent invention of agriculture always occurred in special natural environments (e.g., South-East Asia). It is supposed that the cultivation of cereals started somewhere in the Near East: in the hills of Israel or Egypt. So Grinin dates the beginning of the agricultural revolution within the interval 12,000 to 9,000 BP, though in some cases the first cultivated plants or domesticated animals' bones are even of a more ancient age of 14–15 thousand years ago.
* Andrew M. T. Moore, Andrew Moore suggested that the Neolithic Revolution originated over long periods of development in the Levant, possibly beginning during the Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
. In ''"A Reassessment of the Neolithic Revolution"'', Frank Hole further expanded the relationship between plant and animal domestication. He suggested the events could have occurred independently during different periods of time, in as yet unexplored locations. He noted that no transition site had been found documenting the shift from what he termed immediate and delayed return social systems. He noted that the full range of domesticated animals (goats, sheep, cattle and pigs) were not found until the sixth millennium BCE at Tell Ramad. Hole concluded that "close attention should be paid in future investigations to the western margins of the Euphrates basin, perhaps as far south as the Arabian Peninsula, especially where wadis carrying Pleistocene rainfall runoff flowed."
Consequences
Social change
Despite the significant technological advance and advancements in knowledge, arts and trade, the Neolithic revolution did not lead immediately to a rapid growth of population. Its benefits appear to have been offset by various adverse effects, mostly diseases and warfare. The introduction of agriculture has not necessarily led to unequivocal progress. The nutritional standards of the growing Neolithic populations were inferior to that of hunter-gatherers. Several ethnological and archaeological studies conclude that the transition to cereal-based diets caused a reduction in life expectancy and stature, an increase in infant mortality and infectious diseases, the development of chronic, inflammatory or degenerative diseases (such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases) and multiple nutritional deficiencies, including vitamin deficiencies, iron deficiency anemia and mineral disorders affecting bones (such as osteoporosis and rickets) and teeth. Average height for Europeans went down from for men and for women to respectively, and it took until the twentieth century for average height for Europeans to return to the pre-Neolithic Revolution levels. The traditional view is that agricultural food production supported a denser population, which in turn supported larger sedentary communities, the accumulation of goods and tools, and specialization in diverse forms of new labor. Food surpluses made possible the development of a social elite who were not otherwise engaged in agriculture, industry or commerce, but dominated their communities by other means and monopolized decision-making. Nonetheless, larger societies made it more feasible for people to adopt diverse decision making and governance models. Jared Diamond (in ''The World Until Yesterday'') identifies the availability of milk and cereal grains as permitting mothers to raise both an older (e.g. 3 or 4 year old) and a younger child concurrently. The result is that a population can increase more rapidly. Diamond, in agreement with feminist scholars such as V. Spike Peterson, points out that agriculture brought about deep social divisions and encouraged gender inequality. This social reshuffle is traced by historical theorists, like Veronica Strang, through developments in theological depictions. Strang supports her theory through a comparison of aquatic deities before and after the Neolithic Agricultural Revolution, most notably the Venus of Lespugue and the Greco-Roman deities such as Circe or Charybdis: the former venerated and respected, the latter dominated and conquered. The theory, supplemented by the widely accepted assumption from Parsons that "society is always the object of religious veneration", argues that with the centralization of government and the dawn of the Anthropocene, roles within society became more restrictive and were rationalized through the conditioning effect of religion; a process that is crystallized in the progression from polytheism to monotheism.Subsequent revolutions
 Andrew Sherratt has argued that following upon the Neolithic Revolution was a second phase of discovery that he refers to as the secondary products revolution. Animals, it appears, were first domesticated purely as a source of meat. The Secondary Products Revolution occurred when it was recognised that animals also provided a number of other useful products. These included:
* History of hide materials, hides and skins (from undomesticated animals)
* manure for soil conditioning (from all domesticated animals)
* wool (from sheep, llamas, alpacas, and Angora goats)
* milk (from goats, cattle, yaks, sheep, horses, and camels)
* Working animal, traction (from oxen, onagers, donkeys, horses, camels, and dogs)
* guarding and herding assistance (dogs)
Sherratt argued that this phase in agricultural development enabled humans to make use of the energy possibilities of their animals in new ways, and permitted permanent intensive subsistence farming and crop production, and the opening up of heavier soils for farming. It also made possible nomadic pastoralism in semi arid areas, along the margins of deserts, and eventually led to the domestication of both the
Andrew Sherratt has argued that following upon the Neolithic Revolution was a second phase of discovery that he refers to as the secondary products revolution. Animals, it appears, were first domesticated purely as a source of meat. The Secondary Products Revolution occurred when it was recognised that animals also provided a number of other useful products. These included:
* History of hide materials, hides and skins (from undomesticated animals)
* manure for soil conditioning (from all domesticated animals)
* wool (from sheep, llamas, alpacas, and Angora goats)
* milk (from goats, cattle, yaks, sheep, horses, and camels)
* Working animal, traction (from oxen, onagers, donkeys, horses, camels, and dogs)
* guarding and herding assistance (dogs)
Sherratt argued that this phase in agricultural development enabled humans to make use of the energy possibilities of their animals in new ways, and permitted permanent intensive subsistence farming and crop production, and the opening up of heavier soils for farming. It also made possible nomadic pastoralism in semi arid areas, along the margins of deserts, and eventually led to the domestication of both the dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius''), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel and one-humped camel, is a large camel of the genus '' Camelus'' with one hump on its back. It is the tallest of the three camel species; adult males sta ...
and Bactrian camel. Overgrazing of these areas, particularly by herds of goats, greatly extended the areal extent of deserts.
Diet and health
Compared to foragers, Neolithic farmers' diets were higher in carbohydrates but lower in Dietary fiber, fibre, micronutrients, and protein. This led to an increase in the frequency of Tooth decay, carious teeth and slower growth in childhood , and studies have consistently found that populations around the world became shorter after the transition to agriculture. This trend may have been exacerbated by the greater seasonality of farming diets and with it the increased risk of famine due to crop failure. Throughout the development of sedentary societies, disease spread more rapidly than it had during the time in which hunter-gatherer societies existed. Inadequate sanitary practices and the domestication of animals may explain the rise in deaths and sickness following the Neolithic Revolution, as diseases jumped from the animal to the human population. Some examples of infectious diseases spread from animals to humans are influenza, smallpox, and measles. Ancient microbial genomics has shown that progenitors to human-adapted strains of ''Salmonella enterica'' infected up to 5,500 year old agro-pastoralists throughout Western Eurasia, providing molecular evidence for the hypothesis that the Neolithization process facilitated the emergence of Salmonella entericia. In concordance with a process of natural selection, the humans who first domesticated the big mammals quickly built up immunities to the diseases as within each generation the individuals with better immunities had better chances of survival. In their approximately 10,000 years of shared proximity with animals, such as cows, Eurasians and Africans became more resistant to those diseases compared with the indigenous populations encountered outsideEurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. For instance, the population of most Caribbean and several Pacific Islands have been completely wiped out by diseases. 90% or more of many populations of the Americas were Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas, wiped out by European and African diseases before recorded contact with European explorers or colonists. Some cultures like the Inca Empire did have a large domestic mammal, the llama, but llama milk was not drunk, nor did llamas live in a closed space with humans, so the risk of contagion was limited. According to bioarchaeological research, the effects of agriculture on dental health in Southeast Asian rice farming societies from 4000 to 1500 BP was not detrimental to the same extent as in other world regions.
Jonathan C. K. Wells and Jay T. Stock have argued that the dietary changes and increased pathogen exposure associated with agriculture profoundly altered human biology and Life history theory, life history, creating conditions where natural selection favoured the allocation of resources towards reproduction over somatic effort.
Comparative chronology
See also
* Upper Paleolithic revolution * Broad spectrum revolution * Secondary products revolution * Urban revolution * Industrial revolution * Green RevolutionFurther reading
* Taiz, Lincoln.Agriculture, plant physiology, and human population growth: past, present, and future." Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology 25 (2013): 167–181
References
Bibliography
* Bailey, Douglass. (2001). ''Balkan Prehistory: Exclusions, Incorporation and Identity.'' Routledge Publishers. . * Bailey, Douglass. (2005). ''Prehistoric Figurines: Representation and Corporeality in the Neolithic.'' Routledge Publishers. . * Balter, Michael (2005). ''The Goddess and the Bull: Catalhoyuk, An Archaeological Journey to the Dawn of Civilization.'' New York: Free Press. . * * Bocquet-Appel, Jean-Pierre, editor and Ofer Bar-Yosef, editor, ''The Neolithic Demographic Transition and its Consequences'', Springer (21 October 2008), hardcover, 544 pages, , trade paperback and Kindle editions are also available. * Cohen, Mark Nathan (1977)''The Food Crisis in Prehistory: Overpopulation and the Origins of Agriculture.'' New Haven and London: Yale University Press. . * Diamond, Jared (2002). "Evolution, Consequences and Future of Plant and Animal Domestication". ''Nature'', Vol 418. * Harlan, Jack R. (1992). ''Crops & Man: Views on Agricultural Origins'' ASA, CSA, Madison, WIHort 306 - READING 3-1
* Wright, Gary A. (1971). "Origins of Food Production in Southwestern Asia: A Survey of Ideas" Current Anthropology, Vol. 12, No. 4/5 (Oct.–Dec. 1971), pp. 447–477 * Kuijt, Ian; Finlayson, Bill. (2009)
"Evidence for food storage and predomestication granaries 11,000 years ago in the Jordan Valley"
PNAS, Vol. 106, No. 27, pp. 10966–10970. {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Prehistoric agriculture History of technology Neolithic, Revolution Agricultural revolutions Stages of history Historical eras