Nationality Issues on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nationality is the
''Nationality and Statelessness in International Law''
. BRILL; 1979 ited 19 August 2012 . p. 29–61. and are often complemented by
 Conceptually
Conceptually
 In the context of former
In the context of former
Handbook of Citizenship Studies
''. SAGEs; 2003-01-29. . p. 278–279. This might occur, for example, if a person's parents are nationals of separate countries, and the mother's country claims all offspring of the mother's as their own nationals, but the father's country claims all offspring of the father's. Nationality, with its historical origins in
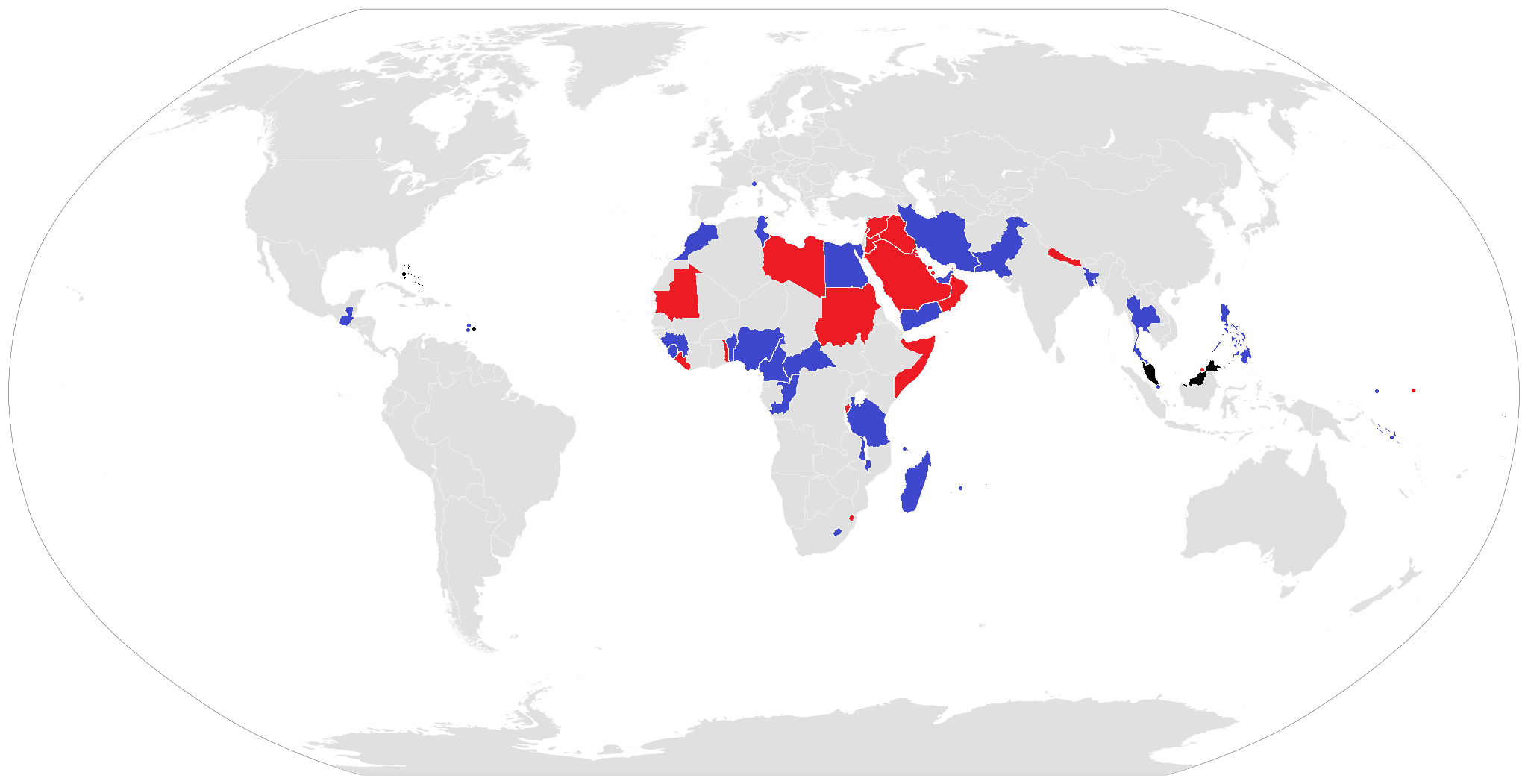 The following list includes states in which parents are able to confer nationality on their children or spouses.
The following list includes states in which parents are able to confer nationality on their children or spouses.
What is a nationality?
", based on "Globalization and the Mythology of the Nation State", in A.G.Hopkins, ed. ''Global History: Interactions Between the Universal and the Local'' Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 257–284 * Grossman, Andrew
''Gender and National Inclusion''
(1862) {{Authority control Conflict of laws Human migration Rights
legal
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Socia ...
status of belonging to a particular nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
, defined as a group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic iden ...
of people organized in one country, under one legal jurisdiction, or as a group of people who are united on the basis of culture.
In international law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generall ...
, nationality is a legal identification establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
. It affords the state jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' and 'speech' or 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, the concept of jurisdiction applies at multiple level ...
over the person and affords the person the protection of the state against other states. The rights and duties of nationals vary from state to state,Weis, Paul''Nationality and Statelessness in International Law''
. BRILL; 1979 ited 19 August 2012 . p. 29–61. and are often complemented by
citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
law, in some contexts to the point where citizenship is synonymous with nationality. However, nationality differs technically and legally from citizenship, which is a different legal relationship between a person and a country. The noun "national" can include both citizens and non-citizens. The most common distinguishing feature of citizenship is that citizens have the right to participate in the political life of the state, such as by voting
Voting is the process of choosing officials or policies by casting a ballot, a document used by people to formally express their preferences. Republics and representative democracies are governments where the population chooses representative ...
or standing for election. However, in most modern countries all nationals are citizens of the state, and full citizens are always nationals of the state.
In international law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generall ...
, a "stateless person
Stateless may refer to:
Society
* Anarchism, a political philosophy opposed to the institution of the state
* Stateless communism, which Karl Marx predicted would be the final phase of communism
* Stateless nation, a group of people without a ...
" is someone who is "not considered as a national by any state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
under the operation of its law". To address this, Article 15 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
states that "Everyone has the right to a nationality", and "No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his nationality nor denied the right to change his nationality", even though, by international custom
Custom, customary, or consuetudinary may refer to:
Traditions, laws, and religion
* Convention (norm), a set of agreed, stipulated or generally accepted rules, norms, standards or criteria, often taking the form of a custom
* Mores, what is wid ...
and conventions, it is the right of each state to determine who its nationals are. Such determinations are part of nationality law
Nationality law is the law of a sovereign state, and of each of its jurisdictions, that defines the legal manner in which a national identity is acquired and how it may be lost. In international law, the legal means to acquire nationality and for ...
. In some cases, determinations of nationality are also governed by public international law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generall ...
—for example, by treaties
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention ...
on statelessness
In international law, a stateless person is someone who is "not considered as a national by any state under the operation of its law". Some stateless people are also refugees. However, not all refugees are stateless, and many people who are s ...
or the European Convention on Nationality
The European Convention on Nationality (European Treaty Series, E.T.S. No. 166) was signed in Strasbourg on 6 November 1997. It is a comprehensive convention of the Council of Europe dealing with the law of nationality. The convention is open ...
. For when a person lacks nationality, globally only 23 countries have established dedicated statelessness determination procedures. Even where such procedures exist, they still have shortcomings in accessibility and functionality, preventing stateless people from accessing rights connected to being determined stateless.
The general process of acquiring nationality is called naturalization
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the ...
. Each state determines in its nationality law
Nationality law is the law of a sovereign state, and of each of its jurisdictions, that defines the legal manner in which a national identity is acquired and how it may be lost. In international law, the legal means to acquire nationality and for ...
the conditions (statute
A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wil ...
) under which it will recognize persons as its nationals, and the conditions under which that status will be withdrawn. Some countries permit their nationals to have multiple nationalities, while others insist on exclusive allegiance
An allegiance is a duty of fidelity said to be owed, or freely committed, by the people, subjects or citizens to their state or sovereign.
Etymology
The word ''allegiance'' comes from Middle English ' (see Medieval Latin ', "a liegance"). The ...
.
Due to the etymology of nationality, in older texts or other languages the word "nationality", rather than "ethnicity", is often used to refer to an ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
(a group of people who share a common ethnic identity, language, culture, lineage, history, and so forth). Individuals may also be considered nationals of groups with autonomous status that have ceded some power to a larger sovereign state.
Nationality is also employed as a term for national identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language".
National identity ...
, with some cases of identity politics
Identity politics is politics based on a particular identity, such as ethnicity, Race (human categorization), race, nationality, religion, Religious denomination, denomination, gender, sexual orientation, Socioeconomic status, social background ...
and nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
conflating the legal nationality as well as ethnicity with a national identity.
International law
Nationality is the status that allows a nation to grant rights to the subject and to impose obligations upon the subject. In most cases, no rights or obligations are automatically attached to this status, although the status is a necessary precondition for any rights and obligations created by the state. In European law, nationality is the status or relationship that gives the nation the right to protect a person from other nations.Diplomatic
Diplomatics (in American English, and in most anglophone countries), or diplomatic (in British English), is a scholarly discipline centred on the critical analysis of documents, especially historical documents. It focuses on the conventions, pr ...
and consular protection are dependent upon this relationship between the person and the state. A person's status as being the national of a country is used to resolve the conflict of laws
Conflict of laws (also called private international law) is the set of rules or laws a jurisdiction applies to a Legal case, case, Transactional law, transaction, or other occurrence that has connections to more than one jurisdiction."Conflict o ...
.
Within the broad limits imposed by a few treaties and international law, states may freely define who are and are not their nationals. However, since the ''Nottebohm'' case, other states are only required to respect the claim(s) by a state to protect an alleged national if the nationality is based on a true social bond. In the case of dual nationality, the states may determine the most effective nationality for the person, to determine which state's laws are the most relevant. There are also limits on removing a person's status as a national. Article 15 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
states that "Everyone has the right to a nationality," and "No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his nationality nor denied the right to change his nationality."
Determining factors
A person can be recognized or granted nationality on a number of bases. Usually, nationality based on circumstances of birth is automatic, but an application may be required. * Nationality by family (''jus sanguinis
( or , ), meaning 'right of blood', is a principle of nationality law by which nationality is determined or acquired by the nationality of one or both parents. Children at birth may be nationals of a particular state if either or both of thei ...
''). If one or both of a person's parents are citizens of a given state, then the person may have the right to be a citizen of that state as well. Formerly this might only have applied through the paternal line, but sex equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality, gender egalitarianism, or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making, an ...
became common since the late twentieth century. Citizenship is granted based on ancestry or ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
and is related to the concept of a nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
common in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. Where ''jus sanguinis'' holds, a person born outside a country, one or both of whose parents are citizens of the country, is also a citizen. Some states (United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
) limit the right to citizenship by descent to a certain number of generations born outside the state; others (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
) grant citizenship only if each new generation is registered with the relevant foreign mission within a specified deadline; while others (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, for example) have no limitation on the number of generations born abroad who can claim citizenship of their ancestors' country. This form of citizenship is common in civil law countries.
* Nationality by birth (''jus soli
''Jus soli'' ( or , ), meaning 'right of soil', is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship. ''Jus soli'' was part of the English common law, in contrast to ''jus sanguinis'' ('right of blood') ass ...
''). Some people are automatically nationals of the state in which they are born. This form of citizenship originated in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, where those who were born within the realm were subjects of the monarch (a concept pre-dating that of citizenship in England) and is common in common law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on prece ...
countries. Most countries in the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.'' Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sin ...
grant unconditional ''jus soli'' citizenship, while it has been limited or abolished in almost all other countries.
** In many cases, both ''jus soli'' and ''jus sanguinis'' hold citizenship either by place or parentage (or both).
* Nationality by marriage (''jus matrimonii
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the ...
''). Many countries fast-track naturalization based on the marriage of a person to a citizen. Countries that are destinations for such immigration often have regulations to try to detect sham marriage
A sham marriage or fake marriage is a marriage of convenience entered into without intending to create a real marital relationship. This is usually for the purpose of gaining an advantage from the marriage.
Definitions of sham marriage vary b ...
s, where a citizen marries a non-citizen typically for payment, without them having the intention of living together. Many countries (United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
) allow citizenship by marriage only if the foreign spouse is a permanent resident of the country in which citizenship is sought; others (Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
) allow foreign spouses of expatriate citizens to obtain citizenship after a certain period of marriage, and sometimes also subject to language skills and proof of cultural integration (e.g. regular visits to the spouse's country of citizenship).
* Naturalization
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the ...
. States normally grant nationality to people who have entered the country legally and been granted a permit to stay, or been granted political asylum
The right of asylum, sometimes called right of political asylum (''asylum'' ), is a juridical concept, under which people persecuted by their own rulers might be protected by another sovereignty, sovereign authority, such as a second country or ...
, and also lived there for a specified period. In some countries, naturalization is subject to conditions which may include passing a test demonstrating reasonable knowledge of the language or way of life of the host country, good conduct (no serious criminal record), and moral character (such as drunkenness, or gambling, or an understanding of the nature of drunkenness, or gambling) vowing allegiance to their new state or its ruler and renouncing their prior citizenship. Some states allow dual citizenship
Multiple citizenship (or multiple nationality) is a person's legal status in which a person is at the same time recognized by more than one sovereign state, country under its nationality law, nationality and citizenship law as a national or cit ...
and do not require naturalized citizens to formally renounce any other citizenship.
* Nationality by investment or economic citizenship. Wealthy people invest money in property or businesses, buy government bonds or simply donate cash directly, in exchange for citizenship and a passport. Whilst legitimate and usually limited in quota, the schemes are controversial. Costs for citizenship by investment range from as little as $100,000 (£74,900) to as much as €2.5m (£2.19m)
Legal protections
The following instruments address the right to a nationality: *Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees
The Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees, also known as the 1951 Refugee Convention or the Geneva Convention of 28 July 1951 is a United Nations multilateral treaty that defines who a refugee is and sets out the rights of individuals ...
*Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees
The Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees is a key treaty in international refugee law. It entered into force on 4 October 1967, and 146 countries are parties.
The 1951 United Nations Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees restrict ...
* Convention Relating to the Status of Stateless Persons
The Convention Relating to the Status of Stateless Persons is a 1954 United Nations multilateral treaty that aims to protect statelessness, stateless individuals.
Surrounding events
The United Nations Charter and Universal Declaration of Human ...
* Convention on the Reduction of Statelessness
The Convention on the Reduction of Statelessness is a 1961 United Nations multilateral treaty whereby sovereign states agree to reduce the incidence of statelessness. The convention was originally intended as a Protocol to the Convention Rel ...
* European Convention on Nationality
The European Convention on Nationality (European Treaty Series, E.T.S. No. 166) was signed in Strasbourg on 6 November 1997. It is a comprehensive convention of the Council of Europe dealing with the law of nationality. The convention is open ...
* African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child The African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child (also called the ACRWC or Children's Charter) was adopted by the Organisation of African Unity (OAU) in 1990 (in 2001, the OAU legally became the African Union) and was entered into force i ...
(art. 6)
* American Convention on Human Rights
The American Convention on Human Rights (ACHR), also known as the Pact of San José or by its Spanish name used in most of the signatory nations, ''Convención Americana sobre Derechos Humanos'', is an international human rights instrument. It was ...
(art. 20)
* American Declaration of the Rights and Duties of Man
The American Declaration of the Rights and Duties of Man, also known as the Bogota Declaration, was the world's first international human rights instrument of a general nature, predating the Universal Declaration of Human Rights by less than a y ...
(art. 19)
* Arab Charter on Human Rights
The Arab Charter on Human Rights (ACHR), adopted by the Council of the League of Arab States on 22 May 2004, affirms the principles contained in the UN Charter, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Covenants on Human Righ ...
(art. 24)
* Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women
The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly.
Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted ...
(art. 9)
* International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination
The International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (ICERD) is a United Nations convention. A third-generation human rights instrument, the Convention commits its members to the elimination of racial discri ...
(art. 5(d)(iii))
* Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights instrument, international human rights multilateral treaty, treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with Disabil ...
(art. 18)
* Convention on the Rights of the Child
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (commonly abbreviated as the CRC or UNCRC) is an international international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of ch ...
(arts. 7 and 8)
* Council of Europe Convention on the Avoidance of Statelessness in Relation to State Succession
The Council of Europe Convention on the Avoidance of Statelessness in Relation to State Succession is a treaty that aims to ensure that people are not left without a nationality when one or more states replace their state of nationality. Suc ...
* International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom ...
(art. 24(3))
* Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights on the Rights of Women in Africa (Maputo Protocol
The Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights on the Rights of Women in Africa, better known as the Maputo Protocol, is an international human rights instrument established by the African Union that went into effect in 2005. ...
) (art. 6(g) and (h))
* Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
(art. 15)
National law
Nationals normally have the right to enter or return to the country they belong to.Passports
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that certifies a person's identity and nationality for international travel. A passport allows its bearer to enter and temporarily reside in a foreign country, access local aid ...
are issued to nationals of a state, rather than only to citizens, because a passport is a travel document used to enter the country. However, nationals may not have the right of abode
The right of abode is an individual's freedom from immigration control in a particular country. A person who has the right of abode in a country does not need permission from the government to enter the country and can live and work there witho ...
(the right to live permanently) in the countries that granted them passports.
Nationality versus citizenship
 Conceptually
Conceptually citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
and nationality are different dimensions of state membership. Citizenship is focused on the internal political life of the state and nationality is the dimension of state membership in international law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generall ...
. Article 15 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
states that everyone has the right to nationality. As such nationality in international law can be called and understood as citizenship, or more generally as subject or belonging to a sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
, and not as ethnicity. This notwithstanding, around 10 million people are stateless.
Today, the concept of full citizenship encompasses not only active political rights, but full civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' political freedom, freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and ...
and social rights
Economic, social and cultural rights (ESCR) are socio-economic human rights, such as the right to education, right to housing, right to an adequate standard of living, right to health, victims' rights and the right to science and culture. Econo ...
.
Historically, the most significant difference between a national and a citizen is that the citizen has the right to vote for elected officials, and the right to be elected. This distinction between full citizenship and other, lesser relationships goes back to antiquity. Until the 19th and 20th centuries, it was typical for only a certain percentage of people who belonged to the state to be considered as full citizens. In the past, a number of people were excluded from citizenship on the basis of sex, socioeconomic class, ethnicity, religion, and other factors. However, they held a legal relationship with their government akin to the modern concept of nationality.
Nationality in context
United States nationality law
United States nationality law details the conditions in which a person holds United States nationality. In the United States, nationality is typically obtained through provisions in the U.S. Constitution, various laws, and international agre ...
defines some persons born in some of the US outlying possessions as US nationals but not citizens. British nationality law
The primary law governing nationality in the United Kingdom is the British Nationality Act 1981, which came into force on 1 January 1983. Regulations apply to the British Islands, which include the UK itself (England, Wales, Scotland, and Nor ...
defines six classes of British national, among which "British citizen" is one class (having the right of abode
The right of abode is an individual's freedom from immigration control in a particular country. A person who has the right of abode in a country does not need permission from the government to enter the country and can live and work there witho ...
in the United Kingdom, along with some "British subject
The term "British subject" has several different meanings depending on the time period. Before 1949, it referred to almost all subjects of the British Empire (including the United Kingdom, Dominions, and colonies, but excluding protectorates ...
s"). Similarly, in the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, commonly known as Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, the status of national without household registration applies to people who have the Republic of China nationality, but do not have an automatic entitlement to enter or reside in the Taiwan Area
The Taiwan Area, also called the Taiwan Area of the Republic of China, the free area of the Republic of China, and the "Tai-Min Area (Taiwan and Fuchien)" , is a term used to refer to the territories under the effective control of the Rep ...
, and do not qualify for civic rights and duties there. Under the nationality laws of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
, Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
, and some other Latin American countries, nationals do not become citizens until they turn the age of majority.
List of nationalities which do not have full citizenship rights
Even if the nationality law classifies people with the same nationality on paper (''de jure''), the right conferred can be different according to the place of birth or residence, creating different ''de facto'' classes of nationality, sometimes with different passports as well. For example, although Chinese nationality law
Chinese nationality law details the conditions by which a person holds nationality of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The primary law governing these requirements is the Nationality Law of the People's Republic of China, which came int ...
operates uniformly in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, including Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
and Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by p ...
SARs, with all Chinese nationals classified the same under the nationality law, in reality local laws, in mainland and also in the SARs, govern the right of Chinese nationals in their respective territories which give vastly different rights, including different passports, to Chinese nationals according to their birthplace or residence place, effectively making a distinction between Chinese national of mainland China, Hong Kong or Macau, both domestically and internationally. The United Kingdom had a similar distinction as well before 1983, where all nationals with a connection to the UK or one of the colonies were classified as ''Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies'', but their rights were different depending on the connection under different laws, which was formalised into different classes of nationalities under the British Nationality Act 1981
The British Nationality Act 1981 (c. 61) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom concerning British nationality since 1 January 1983.
History
In the mid-1970s the British Government decided to update the nationality code, which ha ...
.
Nationality versus ethnicity
Nationality is sometimes used simply as an alternative word forethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
or national origin, just as some people assume that citizenship and nationality are identical. In some countries, the cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language.
Because language change can have radical effects on both the s ...
word for ''nationality'' in local language may be understood as a synonym of ethnicity or as an identifier of cultural and family-based self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
, rather than on relations with a state or current government. For example, some Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
say that they have Kurdish nationality, even though there is no Kurdish sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
at this time in history.
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (commonly abbreviated as SFRY or SFR Yugoslavia), known from 1945 to 1963 as the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as Socialist Yugoslavia or simply Yugoslavia, was a country ...
, "nationality" is often used as translation of the Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
''nacional'nost' '' and Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually i ...
''narodnost'', which were the terms used in those countries for ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
s and local affiliations within the member states of the federation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
. In the Soviet Union, more than 100 such groups were formally recognized. Membership in these groups was identified on Soviet internal passport
An internal or domestic passport is a type of identity document issued in a passport-like booklet format. Internal passports may have a variety of uses including:
# An ordinary identity document produced in a passport format (such as the modern ...
s, and recorded in census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
es in both the USSR and Yugoslavia. In the early years of the Soviet Union's existence, ethnicity was usually determined by the person's native language, and sometimes through religion or cultural factors, such as clothing.Slezkine, Yuri (Summer 1994) "The USSR as a Communal Apartment, or How a Socialist State Promoted Ethnic Particularism" ''Slavic Review'' Vol. 53, No. 2, pp. 414-452 Children born after the revolution were categorized according to their parents' recorded ethnicities. Many of these ethnic groups are still recognized by modern Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and other countries.
Similarly, the term ''nationalities of China
The Han people are the largest ethnic group in mainland China. In 2010, 91.51% of the population were classified as Han (~1.2 billion). Besides the Han Chinese majority, 55 other ethnic (minority) groups are categorized in present-day China, n ...
'' refers to ethnic and cultural groups in China. Spain is one nation, made up of nationalities
Nationality is the legal status of belonging to a particular nation, defined as a group of people organized in one country, under one legal jurisdiction, or as a group of people who are united on the basis of culture.
In international law, nat ...
, which are not politically recognized as nations (state), but can be considered smaller nations within the Spanish nation. Spanish law recognizes the autonomous communities of Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomou ...
, Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
, Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, ...
, Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situate ...
, Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
, Galicia and the Basque Country as "nationalities
Nationality is the legal status of belonging to a particular nation, defined as a group of people organized in one country, under one legal jurisdiction, or as a group of people who are united on the basis of culture.
In international law, nat ...
" (''nacionalidades'').
In 2013, the Supreme Court of Israel
The Supreme Court of Israel (, Hebrew acronym Bagatz; ) is the Supreme court, highest court in Israel. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all other courts, and in some cases original jurisdiction.
The Supreme Court consists of 15 jud ...
unanimously affirmed the position that "citizenship" (e.g. Israeli) is separate from ''le'om'' (; "nationality" or "ethnic affiliation"; e.g. Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
, Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
, Circassian), and that the existence of a unique "Israeli" ''le'om'' has not been proven. Israel recognizes more than 130 ''le'umim'' in total.
The older ethnicity meaning of "nationality" is not defined by political borders or passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that certifies a person's identity and nationality for international travel. A passport allows its bearer to enter and temporarily reside in a foreign country, access local aid ...
ownership and includes nations that lack an independent state
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a ...
(such as the Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
, Scots, Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, of or about Wales
* Welsh language, spoken in Wales
* Welsh people, an ethnic group native to Wales
Places
* Welsh, Arkansas, U.S.
* Welsh, Louisiana, U.S.
* Welsh, Ohio, U.S.
* Welsh Basin, during t ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
, Andalusians
The Andalusians () are the people of Andalusia, an autonomous community in southern Spain. Andalusia's statute of autonomy defines Andalusians as the Spanish citizens who reside in any of the municipalities of Andalusia, as well as those Spani ...
, Basques
The Basques ( or ; ; ; ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a Basque culture, common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous peoples, ...
, Catalans
Catalans ( Catalan, French and Occitan: ''catalans''; ; ; or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to Catalonia, who speak Catalan. The current official category of "Catalans" is that of the citizens of Catalonia, a nationality and autono ...
, Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
, Punjabis
The Punjabis (Punjabi language, Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Pañjābī) are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region, comprising areas of northwestern India and eastern Paki ...
, Kabyles
The Kabyle people (, or ''Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', , ) are a Berber ethnic group indigenous to Kabylia in the north of Algeria, spread across the Atlas Mountains, east of Algiers. They represent the largest Berber population of Algeria a ...
, Baluchs, Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ;), also known as Pakhtuns, or Pathans, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group primarily residing in southern and eastern Afghanistan and northwestern Pakistan. They were historically also referred to as Afghan (ethnon ...
, Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
, Bosniaks
The Bosniaks (, Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia (region), Bosnia, today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and who sha ...
, Palestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
, Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related ...
, Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
, Copts
Copts (; ) are a Christians, Christian ethnoreligious group, ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptians, Egyptian population, des ...
, Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
, Wakhis
The Wakhi people (, , ; ; ), also locally referred to as the Wokhik (), are an Iranian ethnic group native to Central and South Asia. They are found in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Pakistan, and China—primarily situated in and around Afghanistan' ...
, Xhosas and Zulus
Zulu people (; ) are a native people of Southern Africa of the Nguni. The Zulu people are the largest ethnic group and nation in South Africa, living mainly in the province of KwaZulu-Natal.
They originated from Nguni communities who took p ...
, among others).
Nationality versus national identity
National identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language".
National identity ...
is person's subjective sense of belonging to one state or to one nation. A person may be a national of a state, in the sense of being its citizen
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality ...
, without subjectively or emotionally feeling a part of that state, for example a migrant may identify with their ancestral and/or religious background rather than with the state of which they are citizens. Conversely, a person may feel that he belongs to one state without having any legal relationship to it. For example, children who were brought to the US illegally when quite young and grew up there while having little contact with their native country and their culture often have a national identity of feeling American, despite legally being nationals of a different country.
Dual nationality
Dual nationality
Multiple citizenship (or multiple nationality) is a person's legal status in which a person is at the same time recognized by more than one country under its nationality and citizenship law as a national or citizen of that country. There is no ...
is when a single person has a formal relationship with two separate, sovereign states.Turner, Bryan S; Isin, Engin F. Handbook of Citizenship Studies
''. SAGEs; 2003-01-29. . p. 278–279. This might occur, for example, if a person's parents are nationals of separate countries, and the mother's country claims all offspring of the mother's as their own nationals, but the father's country claims all offspring of the father's. Nationality, with its historical origins in
allegiance
An allegiance is a duty of fidelity said to be owed, or freely committed, by the people, subjects or citizens to their state or sovereign.
Etymology
The word ''allegiance'' comes from Middle English ' (see Medieval Latin ', "a liegance"). The ...
to a sovereign monarch, was seen originally as a permanent, inherent, unchangeable condition, and later, when a change of allegiance was permitted, as a strictly exclusive relationship, so that becoming a national of one state required rejecting the previous state.
Dual nationality was considered a problem that caused a conflict between states and sometimes imposed mutually exclusive requirements on affected people, such as simultaneously serving in two countries' military forces. Through the middle of the 20th century, many international agreements were focused on reducing the possibility of dual nationality. Since then, many accords recognizing and regulating dual nationality have been formed.
Statelessness
Statelessness
In international law, a stateless person is someone who is "not considered as a national by any state under the operation of its law". Some stateless people are also refugees. However, not all refugees are stateless, and many people who are s ...
is the condition in which an individual has no formal or protective relationship with any state. There are various reasons why a person can become stateless. This might occur, for example, if a person's parents are nationals of separate countries, and the mother's country rejects all offspring of mothers married to foreign fathers, but the father's country rejects all offspring born to foreign mothers. People in this situation may not legally be the national of any state despite possession of an emotional national identity.
Another stateless situation arises when a person holds a travel document (passport) which recognizes the bearer as having the nationality of a "state" which is not internationally recognized, has no entry into the International Organization for Standardization's country list, is not a member of the United Nations, etc. In the current era, persons native to Taiwan who hold passports of Republic of China are one example.
Some countries (like Kuwait, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia) can also remove one's citizenship; the reasons for removal can be fraud and/or security issues. There are also people who are abandoned at birth and the parents' whereabouts are not known.
''De jure'' vs ''de facto'' statelessness
Nationality law defines nationality and statelessness. Nationality is awarded based on two well-known principles: ''jus sanguinis
( or , ), meaning 'right of blood', is a principle of nationality law by which nationality is determined or acquired by the nationality of one or both parents. Children at birth may be nationals of a particular state if either or both of thei ...
'' and ''jus soli
''Jus soli'' ( or , ), meaning 'right of soil', is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship. ''Jus soli'' was part of the English common law, in contrast to ''jus sanguinis'' ('right of blood') ass ...
''. ''Jus sanguinis'' translated from Latin means "right of blood". According to this principle, nationality is awarded if the parent(s) of the person are nationals of that country. ''Jus soli'' is referred to as "birthright citizenship". It means, anyone born in the territory of the country is awarded nationality of that country.
Statelessness is defined thus in the 1954 Statelessness Convention: "For the purpose of this Convention, the term 'stateless person' means a person who is not considered as a national by any State under the operation of
its law." A person can become stateless because of administrative reasons. For example, "A person may be at risk of statelessness if she is born in a State that applies ''jus sanguinis'' while her parents were born in a State that applies ''jus soli'', leaving the person ineligible for citizenship in both States due to conflicting laws." Moreover, there are countries in which if a person does not reside for a specified period of time, they can automatically lose their nationality. To protect those individuals from being deemed "stateless", the 1961 Statelessness Convention places limitations on nationality laws.
Conferment of nationality
 The following list includes states in which parents are able to confer nationality on their children or spouses.
The following list includes states in which parents are able to confer nationality on their children or spouses.
Africa
America
Asia
Europe
Oceania
See also
*Blood quantum laws
Blood quantum laws or Indian blood laws are laws that define Native Americans in the United States status by fractions of Native American ancestry. These laws were enacted by the federal government and state governments as a way to establish ...
* Demonym
A demonym (; ) or 'gentilic' () is a word that identifies a group of people ( inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place ( hamlet, village, town, city, region, ...
* Discrimination based on nationality
* Imagined communities
''Imagined Communities: Reflections on the Origin and Spread of Nationalism'' is a book by Benedict Anderson about the development of national feeling in different eras and throughout different geographies across the world. It introduced the ter ...
* Intersectionality
Intersectionality is an analytical framework for understanding how groups' and individuals' social and political identities result in unique combinations of discrimination and privilege. Examples of these intersecting and overlapping factor ...
* ''jus sanguinis
( or , ), meaning 'right of blood', is a principle of nationality law by which nationality is determined or acquired by the nationality of one or both parents. Children at birth may be nationals of a particular state if either or both of thei ...
''
* ''jus soli
''Jus soli'' ( or , ), meaning 'right of soil', is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship. ''Jus soli'' was part of the English common law, in contrast to ''jus sanguinis'' ('right of blood') ass ...
''
* List of adjectival and demonymic forms for countries and nations
The following is a list of adjectival and demonymic forms of countries and nations in English (language), English and their demonymic equivalents. A country adjective describes something as being from that country, for example, "Italian cuisine" is ...
* Nottebohm (Liechtenstein v. Guatemala), a 1955 case that is cited for its definitions of nationality
* Second-class citizen
A second-class citizen is a person who is systematically and actively discriminated against within a state or other political jurisdiction, despite their nominal status as a citizen or a legal resident there. While not necessarily slaves, ou ...
* People
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. I ...
* Volk
The German noun ''Volk'' () translates to :wikt:people, people,
both uncountable in the sense of ''people'' as in a crowd, and countable (plural ''Völker'') in the sense of ''People, a people'' as in an ethnic group or nation (compare the E ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* White, Philip L. (2006).What is a nationality?
", based on "Globalization and the Mythology of the Nation State", in A.G.Hopkins, ed. ''Global History: Interactions Between the Universal and the Local'' Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 257–284 * Grossman, Andrew
''Gender and National Inclusion''
(1862) {{Authority control Conflict of laws Human migration Rights