Nanoindenter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
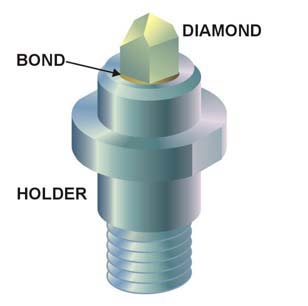 A nanoindenter is the main component for indentation
A nanoindenter is the main component for indentation


 There are many types of nanoindenters in current use differing mainly on their tip geometry. Among the numerous available geometries are three and four sided
There are many types of nanoindenters in current use differing mainly on their tip geometry. Among the numerous available geometries are three and four sided
 A nanoindenter is the main component for indentation
A nanoindenter is the main component for indentation hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
tests used in nanoindentation. Since the mid-1970s nanoindentation has become the primary method for measuring and testing very small volumes of mechanical properties. Nanoindentation, also called ''depth sensing indentation'' or ''instrumented indentation'', gained popularity with the development of machines that could record small load and displacement with high accuracy and precision. The load displacement data can be used to determine modulus of elasticity, hardness, yield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress–strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and w ...
, fracture toughness
In materials science, fracture toughness is the critical stress intensity factor of a sharp Fracture, crack where propagation of the crack suddenly becomes rapid and unlimited. It is a material property that quantifies its ability to resist crac ...
, scratch hardness
Scratch hardness refers to the hardness of a material in terms of resistance to scratches and abrasion by a harder material forcefully drawn over its surface. Scratch hardness test or scratch test refers to any of a number of methods of measuring s ...
and wear properties.
Types


 There are many types of nanoindenters in current use differing mainly on their tip geometry. Among the numerous available geometries are three and four sided
There are many types of nanoindenters in current use differing mainly on their tip geometry. Among the numerous available geometries are three and four sided pyramids
A pyramid () is a Nonbuilding structure, structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a Pyramid (geometry), pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid ca ...
, wedges, cones
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the ''apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, ...
, cylinders
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite ...
, filaments, and sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three ...
s. Several geometries have become a well established common standard due to their extended use and well known properties; such as Berkovich, cube corner, Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 18 ...
, and Knoop nanoindenters. To meet the high precision required, nanoindenters must be made following the definitions of ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
14577-2, and be inspected and measured with equipment and standards traceable to the National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of p ...
(NIST). The tip end of the indenter can be made sharp, flat, or rounded to a cylindrical or spherical shape. The material for most nanoindenters is diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
and sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire ...
, although other hard materials can be used such as quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
, tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: ) is a carbide containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes through sintering for use in in ...
and almost any other hard metal or ceramic material. Diamond is the most commonly used material for nanoindentation due to its properties of hardness, thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low ...
, and chemical inertness. In some cases electrically conductive
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity in ...
diamond may be needed for special applications and is also available.
Holders
Nanoindenters are mounted on holders which could be the standard design from a manufacturer of nanoindenting equipment, or custom design. The holder material can be steel,titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, machinable ceramic, other metals or rigid materials. In most cases the indenter is attached to the holder using a rigid metal bonding process. The metal forms a molecular bond with both material be it diamond-steel, diamond-ceramic, etc.
Angular measurements
Nanoindenter dimensions are very small, some less than , and made with precise angular geometry in order to achieve the highly accurate readings required for nanoindentation. Instruments that measure angles on larger objects such asprotractor
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry derives from two Greek words, γωνία (''gōnía'') 'angle' and μέτρον (''métron'') ' me ...
s or comparators are neither practical nor precise enough to measure nanoindenter angles even with help of microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
s. For precise measurements a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
goniometer
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry derives from two Greek words, γωνία (''gōnía'') 'angle' and μέτρον (''métron'') ' me ...
is used to measure diamond nanoindenter angles. Nanoindenter faces are highly polished and reflective which is the basis for the laser goniometer measurements. The laser goniometer can measure within a thousandth of a degree to specified or requested angles.
References
{{Reflist Hardness tests Nanotechnology