Mycoreovirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mycoreovirus'' is a genus of

 Viruses in genus ''Mycoreovirus'' are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries. The outer
Viruses in genus ''Mycoreovirus'' are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries. The outer
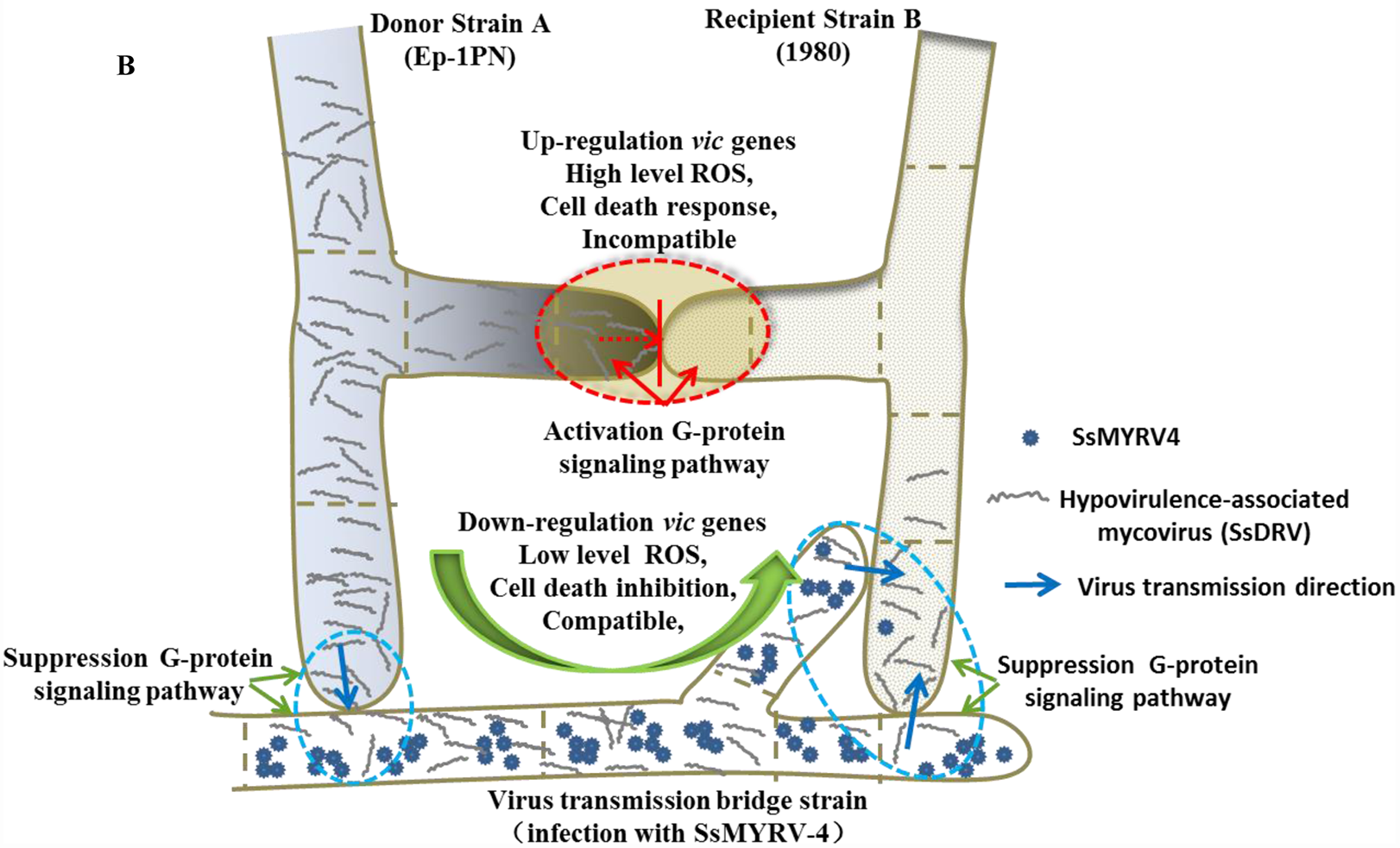 Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by cell to cell movement, and monopartite non-tubule guided viral movement. Fungi serve as the natural host.
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by cell to cell movement, and monopartite non-tubule guided viral movement. Fungi serve as the natural host.
Viralzone: Mycoreovirus
ICTV
{{Taxonbar, from=Q18822295 Virus genera Spinareovirinae
double-stranded RNA viruses
Double-stranded RNA viruses (dsRNA viruses) are a polyphyletic group of viruses that have double-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The double-stranded genome is used as a template by the viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to ...
in the order ''Reovirales
''Reovirales'' is an Order (biology), order of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses, called reoviruses, have a wide Host (biology), host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid Viral envelop ...
'' and family ''Spinareoviridae
''Spinareoviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses in the order ''Reovirales''. Viruses in this group are distinguished by the presence of a turreted protein on the inner capsid. (''Spina'' = spiny or thorny in Latin.)
Taxonomy
The ...
''. Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include: hypovirulence of the fungal host. The name of the group derives from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
''myco'' which means fungus. There are three species in this genus.
Structure

 Viruses in genus ''Mycoreovirus'' are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries. The outer
Viruses in genus ''Mycoreovirus'' are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries. The outer capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
has T=13 symmetry and the inner capsid has T=2 symmetry. The diameter is around 80 nm. Genomes are linear and segmented, and around 23 kbp in total length. The genome codes for 12 proteins.
Life cycle
 Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by cell to cell movement, and monopartite non-tubule guided viral movement. Fungi serve as the natural host.
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by cell to cell movement, and monopartite non-tubule guided viral movement. Fungi serve as the natural host.
Taxonomy
There are three species in this genus: * ''Mycoreovirus alcryphonectriae'' * ''Mycoreovirus becryphonectriae'' * ''Mycoreovirus roselliniae''References
External links
Viralzone: Mycoreovirus
ICTV
{{Taxonbar, from=Q18822295 Virus genera Spinareovirinae