Musical Theory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of
 Pitch is the lowness or highness of a
Pitch is the lowness or highness of a
 Notes can be arranged in a variety of scales and
Notes can be arranged in a variety of scales and
 Rhythm is produced by the sequential arrangement of sounds and silences in time.
Rhythm is produced by the sequential arrangement of sounds and silences in time.
 A
A
 A chord, in music, is any
A chord, in music, is any
 In music, " dynamics" normally refers to variations of intensity or volume, as may be measured by physicists and audio engineers in
In music, " dynamics" normally refers to variations of intensity or volume, as may be measured by physicists and audio engineers in
 Articulation is the way the performer sounds notes. For example, ''
Articulation is the way the performer sounds notes. For example, ''
 The term musical form (or musical architecture) refers to the overall structure or plan of a piece of music, and it describes the layout of a composition as divided into sections. In the tenth edition of '' The Oxford Companion to Music'',
The term musical form (or musical architecture) refers to the overall structure or plan of a piece of music, and it describes the layout of a composition as divided into sections. In the tenth edition of '' The Oxford Companion to Music'',
 Musical expression is the art of playing or singing music with emotional communication. The elements of music that comprise expression include dynamic indications, such as forte or piano, phrasing, differing qualities of timbre and articulation, color, intensity, energy and excitement. All of these devices can be incorporated by the performer. A performer aims to elicit responses of sympathetic feeling in the audience, and to excite, calm or otherwise sway the audience's physical and emotional responses. Musical expression is sometimes thought to be produced by a combination of other parameters, and sometimes described as a transcendent quality that is more than the sum of measurable quantities such as pitch or duration.
Expression on instruments can be closely related to the role of the breath in singing, and the voice's natural ability to express feelings, sentiment and deep emotions. Whether these can somehow be categorized is perhaps the realm of academics, who view expression as an element of musical performance that embodies a consistently recognizable
Musical expression is the art of playing or singing music with emotional communication. The elements of music that comprise expression include dynamic indications, such as forte or piano, phrasing, differing qualities of timbre and articulation, color, intensity, energy and excitement. All of these devices can be incorporated by the performer. A performer aims to elicit responses of sympathetic feeling in the audience, and to excite, calm or otherwise sway the audience's physical and emotional responses. Musical expression is sometimes thought to be produced by a combination of other parameters, and sometimes described as a transcendent quality that is more than the sum of measurable quantities such as pitch or duration.
Expression on instruments can be closely related to the role of the breath in singing, and the voice's natural ability to express feelings, sentiment and deep emotions. Whether these can somehow be categorized is perhaps the realm of academics, who view expression as an element of musical performance that embodies a consistently recognizable
 Musical notation is the written or symbolized representation of music. This is most often achieved by the use of commonly understood graphic symbols and written verbal instructions and their abbreviations. There are many systems of music notation from different cultures and different ages. Traditional Western notation evolved during the Middle Ages and remains an area of experimentation and innovation. In the 2000s, computer
Musical notation is the written or symbolized representation of music. This is most often achieved by the use of commonly understood graphic symbols and written verbal instructions and their abbreviations. There are many systems of music notation from different cultures and different ages. Traditional Western notation evolved during the Middle Ages and remains an area of experimentation and innovation. In the 2000s, computer
 Musical analysis is the attempt to answer the question ''how does this music work?'' The method employed to answer this question, and indeed exactly what is meant by the question, differs from analyst to analyst, and according to the purpose of the analysis. According to Ian Bent, "analysis, as a pursuit in its own right, came to be established only in the late 19th century; its emergence as an approach and method can be traced back to the 1750s. However, it existed as a scholarly tool, albeit an auxiliary one, from the
Musical analysis is the attempt to answer the question ''how does this music work?'' The method employed to answer this question, and indeed exactly what is meant by the question, differs from analyst to analyst, and according to the purpose of the analysis. According to Ian Bent, "analysis, as a pursuit in its own right, came to be established only in the late 19th century; its emergence as an approach and method can be traced back to the 1750s. However, it existed as a scholarly tool, albeit an auxiliary one, from the
 In the modern era, musical
In the modern era, musical
 Music semiology (
Music semiology (
 Music theory in the practical sense has been a part of education at conservatories and music schools for centuries, but the status music theory currently has within academic institutions is relatively recent. In the 1970s, few universities had dedicated music theory programs, many music theorists had been trained as composers or historians, and there was a belief among theorists that the teaching of music theory was inadequate and that the subject was not properly recognised as a scholarly discipline in its own right. A growing number of scholars began promoting the idea that music theory should be taught by theorists, rather than composers, performers or music historians. This led to the founding of the
Music theory in the practical sense has been a part of education at conservatories and music schools for centuries, but the status music theory currently has within academic institutions is relatively recent. In the 1970s, few universities had dedicated music theory programs, many music theorists had been trained as composers or historians, and there was a belief among theorists that the teaching of music theory was inadequate and that the subject was not properly recognised as a scholarly discipline in its own right. A growing number of scholars began promoting the idea that music theory should be taught by theorists, rather than composers, performers or music historians. This led to the founding of the
EuroT&AM
As part of their initial training, music theorists will typically complete a B.Mus or a
Archaeological Evidence for the Emergence of Language, Symbolism, and Music – An Alternative Multidisciplinary Perspective
. ''Journal of World Prehistory'' 17, no. 1 (March): 1–70. * Despopoulos, Agamemnon, and Stefan Silbernagl (2003). ''Color Atlas of Physiology'', fifth edition. New York and Stuttgart: Thieme. . * * Dunbar, Brian (2010). ''Practical Music Theory: A Guide to Music as Art, Language, and Life''. Rochester, MN: Factum Musicae. . * * * Harnsberger, Lindsey C. (1997). "Articulation". ''Essential Dictionary of Music: Definitions, Composers, Theory, Instrument and Vocal Ranges'', second edition. The Essential Dictionary Series. Los Angeles: Alfred Publishing. . * * * Huang, Xiang-peng (黄翔鹏) (1989). "Wuyang Jiahu gudi de ceyin yanjiu (舞阳贾湖骨笛的测音研究)" [Pitch Measurement Studies of Bone Flutes from Jiahu of Wuyang County]. ''Wenwu'' (文物) [Cultural Relics], no. 1:15–17. Reprinted in 黄翔鹏文存 [Collected Essays of Huang Xiang-Peng], 2 vols, edited by Zhongguo Yishu Yanjiuyuan Yinyue Yanjiusuo (中国艺术研究院音乐研究所), 557–560. Ji'nan, China: Shandong Wenyi Chubanshe, 2007. . * Hung, Eric (2012).
Western University, Don Wright Faculty of Music: Tenure-Track Appointment in Music Theory
. Toronto: MusCan. * * Josephs, Jess L. (1967). ''The Physics of Musical Sound''. Princeton, Toronto, and London: D. Van Nostrand Company. * Stefan Kostka, Kostka, Stefan, and Dorothy Payne (2004). ''Tonal Harmony'', fifth edition. New York: McGraw-Hill. * Gerhard Kubik, Kubik, Gerhard (1998). ''Kalimba—Nsansi—Mbira. Lamellophone in Afrika''. Berlin: Museum fur Volkerkunde. . * Emmanuel Laroche, Laroche, Emmanuel (1955). ''Le palais royal d' Ugarit 3: Textes accadiens et hourrites des archives est, ouest et centrales''. Paris: C. Klincksieck * Lawn, Richard J., and Jeffrey L. Hellmer (1996). ''Jazz Theory and Practice''. [n.p.]: Alfred Publishing Co. . * Lee, Yuan-Yuan, and Sin-Yan Shen (1999). ''Chinese Musical Instruments''. Chinese Music Monograph Series. Chicago: Chinese Music Society of North America Press. . * Fred Lerdahl, Lerdahl, Fred (2001). ''Tonal Pitch Space''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. * Lloyd, Llewellyn S., and Hugh Boyle (1978). ''Intervals, Scales and Temperaments''. New York: St. Martin's Press. . * Lu, Liancheng (2005). "The Eastern Zhou and the Growth of Regionalism". In ''The Formation of Chinese Civilization'', edited by Sarah Allan, 203–248. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. . * Alfred Mann (musicologist), Mann, Alfred, J. Kenneth Wilson, and Peter Urquhart. n.d. "Canon (i)." ''Grove Music Online''. Oxford Music Online (Accessed 2 January 2011) . * * * *
Text at archive.org
* Miguel, Roig-Francoli (2011). ''Harmony in Context'', Second edition, McGraw-Hill Higher Education. . * * Nave, R. (n.d.).
, Hyperphysics website, Georgia State University (accessed 5 December 2014). * Steve Olson, Olson, Steve (2011).
A Grand Unified Theory of Music
. ''Princeton Alumni Weekly'' 111, no. 7 (9 February) (Online edition accessed 25 September 2012). * * Owen, Harold (2000). ''Music Theory Resource Book''. Oxford University Press. . * Ptolemy (1999). ''Harmonics'', translation and commentary by Jon Solomon. Mnemosyne, bibliotheca classica Batava: Supplementum 203. Leiden and Boston: Brill Academic Publications. . * Don Michael Randel, Randel, Don Michael (ed.) (2003). ''The Harvard Dictionary of Music'', fourth edition, 260–262. Cambridge: The Belknap Press for Harvard University Press. * * * Carl Seashore, Seashore, Carl (1933). ''Approaches to the Science of Music and Speech''. Iowa City: The university. * * * Sorce, Richard (1995). ''Music Theory for the Music Professional''. [N.p.]: Ardsley House. . * Stevens, S. S., J. Volkmann, and E. B. Newman (1937). "A Scale for the Measurement of the Psychological Magnitude Pitch". ''Journal of the Acoustical Society of America'' 8, no. 3:185–190. * Richard Taruskin, Taruskin, Richard (2009). ''Music from the Earliest Notations to the Sixteenth Century: The Oxford History of Western Music.'' Oxford University Press . * Taylor, Eric (1989). ''AB Guide to Music Theory, Part 1''. London: Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music. . * Taylor, Eric (1991). ''AB Guide to Music Theory, Part 2''. London: Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music. . * Thrasher, Alan (2000). ''Chinese Musical Instruments''. London and New York: Oxford University Press. . * Hugh Tracey, Tracey, Hugh (1969). "The Mbira Class of African Instruments in Rhodesia". ''African Music Society Journal'' 4, no. 3:78–95. * Dmitri Tymoczko, Tymoczko, Dmitri (2011). ''A Geometry of Music: Harmony and Counterpoint in the Extended Common Practice''. Oxford Studies in Music Theory. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. . * Martin Litchfield West, West, Martin Litchfield (1994). "The Babylonian Musical Notation and the Hurrian Melodic Texts". ''Music & Letters'' 75, no. 2 (May): 161–179 * Wu, Zhao (吴钊) (1991). "Jiahu guiling gudi yu Zhongguo yinyue wenming zhi yuan (贾湖龟铃骨笛与中国音乐文明之源)" [The relation of Jiahu bone flutes and turtle shell shakers to the origin of Chinese music]. ''Wenwu'' (文物) [Cultural Relics], no. 3: 50–55. * Wu, Zhongzian, and Karin Taylor Wu (2014). ''Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches: Tian Gan Dizhi, The Heart of Chinese Wisdom Traditions''. London and Philadelphia: Singing Dragon (Jessica Kingsley Publishers). * Yamaguchi, Masaya (2006). ''The Complete Thesaurus of Musical Scales'', revised edition. New York: Masaya Music Services. . * * *
Outline of basic music theory
(2011) {{DEFAULTSORT:Music Theory Music theory, Music history Musicology
 Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
. '' The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "rudiments
In ''rudimental drumming'', a form of percussion music, a drum rudiment is one of a number of relatively small patterns which form the foundation for more extended and complex drumming patterns. The term "drum rudiment" is most closely associa ...
", that are needed to understand music notation
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The proces ...
(key signature
In Western musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp (), flat (), or rarely, natural () symbols placed on the staff at the beginning of a section of music. The initial key signature in a piece is placed immediately after the cl ...
s, time signature
A time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, and measure signature) is an indication in music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type fit into each measure ( bar). The time signature indicates th ...
s, and rhythmic notation); the second is learning scholars' views on music from antiquity to the present; the third is a sub-topic of musicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
that "seeks to define processes and general principles in music". The musicological approach to theory differs from music analysis "in that it takes as its starting-point not the individual work or performance but the fundamental materials from which it is built."
Music theory is frequently concerned with describing how musicians and composers make music, including tuning systems and composition methods among other topics. Because of the ever-expanding conception of what constitutes music, a more inclusive definition could be the consideration of any sonic phenomena, including silence. This is not an absolute guideline, however; for example, the study of "music" in the ''Quadrivium
From the time of Plato through the Middle Ages, the ''quadrivium'' (plural: quadrivia) was a grouping of four subjects or arts—arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy—that formed a second curricular stage following preparatory work in th ...
'' liberal arts university
A liberal arts college or liberal arts institution of higher education is a college with an emphasis on undergraduate study in the liberal arts of humanities and science. Such colleges aim to impart a broad general knowledge and develop general in ...
curriculum, that was common in medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
, was an abstract system of proportions that was carefully studied at a distance from actual musical practice. But this medieval discipline became the basis for tuning systems in later centuries and is generally included in modern scholarship on the history of music theory.
Music theory as a practical discipline encompasses the methods and concepts that composers and other musicians use in creating and performing music. The development, preservation, and transmission of music theory in this sense may be found in oral and written music-making traditions, musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
s, and other artifacts. For example, ancient instruments from prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
sites around the world reveal details about the music they produced and potentially something of the musical theory that might have been used by their makers. In ancient and living cultures around the world, the deep and long roots of music theory are visible in instruments, oral traditions, and current music-making. Many cultures have also considered music theory in more formal ways such as written treatise
A treatise is a Formality, formal and systematic written discourse on some subject concerned with investigating or exposing the main principles of the subject and its conclusions."mwod:treatise, Treatise." Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Acc ...
s and music notation
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The proces ...
. Practical and scholarly traditions overlap, as many practical treatises about music place themselves within a tradition of other treatises, which are cited regularly just as scholarly writing
Academic writing or scholarly writing refers primarily to nonfiction writing that is produced as part of academic work in accordance with the standards of a particular academic subject or discipline, including:
* reports on empirical fieldwork o ...
cites earlier research.
In modern academia, music theory is a subfield of musicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
, the wider study of musical cultures and history. Guido Adler, however, in one of the texts that founded musicology in the late 19th century, wrote that "the science of music originated at the same time as the art of sounds", where "the science of music" (''Musikwissenschaft'') obviously meant "music theory". Adler added that music only could exist when one began measuring pitches and comparing them to each other. He concluded that "all people for which one can speak of an art of sounds also have a science of sounds". One must deduce that music theory exists in all musical cultures of the world.
Music theory is often concerned with abstract musical aspects such as tuning and tonal systems, scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
, consonance and dissonance
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness, unple ...
, and rhythmic relationships. There is also a body of theory concerning practical aspects, such as the creation or the performance of music, orchestration
Orchestration is the study or practice of writing music for an orchestra (or, more loosely, for any musical ensemble, such as a concert band) or of adapting music composed for another medium for an orchestra. Also called "instrumentation", orch ...
, ornamentation
An ornament is something used for decoration.
Ornament may also refer to:
Decoration
* Ornament (art), any purely decorative element in architecture and the decorative arts
* Ornamental turning
* Biological ornament, a characteristic of animals ...
, improvisation, and electronic sound
''Electronic Sound'' is the second studio album by the English rock musician George Harrison. Released in May 1969, it was the last of two LPs issued on the Beatles' short-lived Zapple Records, Zapple record label, a subsidiary of Apple Records t ...
production. A person who researches or teaches music theory is a music theorist. University study, typically to the MA or PhD
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, DPhil; or ) is a terminal degree that usually denotes the highest level of academic achievement in a given discipline and is awarded following a course of graduate study and original research. The name of the deg ...
level, is required to teach as a tenure-track music theorist in a US or Canadian university. Methods of analysis include mathematics, graphic analysis, and especially analysis enabled by western music notation. Comparative, descriptive, statistical, and other methods are also used. Music theory textbook
A textbook is a book containing a comprehensive compilation of content in a branch of study with the intention of explaining it. Textbooks are produced to meet the needs of educators, usually at educational institutions, but also of learners ( ...
s, especially in the United States of America, often include elements of musical acoustics
Musical acoustics or music acoustics is a multidisciplinary field that combines knowledge from physics, psychophysics, organology (classification of the instruments), physiology, music theory, ethnomusicology, signal processing and instrument buil ...
, considerations of musical notation
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The proce ...
, and techniques of tonal composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
* Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include ...
(harmony
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harm ...
and counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ...
), among other topics.
History
Antiquity
Mesopotamia
Several surviving Sumerian and Akkadianclay tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian language, Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age.
Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay t ...
s include musical information of a theoretical nature, mainly lists of intervals and tunings. The scholar Sam Mirelman reports that the earliest of these texts dates from before 1500 BCE, a millennium earlier than surviving evidence from any other culture of comparable musical thought. Further, "All the Mesopotamian texts bout musicare united by the use of a terminology for music that, according to the approximate dating of the texts, was in use for over 1,000 years."
China
Much of Chinese music history and theory remains unclear. Chinese theory starts from numbers, the main musical numbers being twelve, five and eight. Twelve refers to the number of pitches on which the scales can be constructed, Five refers to the Pentatonic Scale (primarily uses a 5-note scale), And Eight refers to the eight categories of Chinese Music Instruments; classified by the material they are made from: (Metal, Stone, Silk, Bamboo, Gourd, Clay, Leather, and Wood). TheLüshi chunqiu
The ''Lüshi Chunqiu'' (), also known in English as ''Master Lü's Spring and Autumn Annals'', is an encyclopedic Chinese classic text compiled around 239BC under the patronage of late pre-imperial Qin Chancellor Lü Buwei. In the evaluati ...
from about 238 BCE recalls the legend of Ling Lun. On order of the Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch, or Huangdi ( zh, t=黃帝, s=黄帝, first=t) in Chinese, is a mythical Chinese sovereign and culture hero included among the legendary Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors. He is revered as ...
, Ling Lun collected twelve bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of mostly evergreen perennial plant, perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily (biology), subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family, in th ...
lengths with thick and even nodes. Blowing on one of these like a pipe, he found its sound agreeable and named it ''huangzhong'', the "Yellow Bell." He then heard phoenixes singing. The male and female phoenix each sang six tones. Ling Lun cut his bamboo pipes to match the pitches of the phoenixes, producing twelve pitch pipes in two sets: six from the male phoenix and six from the female: these were called the ''lülü'' or later the ''shierlü''.
Apart from technical and structural aspects, ancient Chinese music theory also discusses topics such as the nature and functions of music. The '' Yueji'' ("Record of music", c1st and 2nd centuries BCE), for example, manifestsConfucian Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, religion, theory of government, or way of life. Founded by Confucius ...moral theories of understanding music in its social context. Studied and implemented by Confucian scholar-officials .. these theories helped form a musical Confucianism that overshadowed but did not erase rival approaches. These include the assertion ofMozi Mozi, personal name Mo Di, was a Chinese philosopher, logician, and founder of the Mohist school of thought, making him one of the most important figures of the Warring States period (221 BCE). Alongside Confucianism, Mohism became the ...(c. 468 – c. 376 BCE) that music wasted human and material resources, andLaozi Laozi (), also romanized as Lao Tzu #Name, among other ways, was a semi-legendary Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher and author of the ''Tao Te Ching'' (''Laozi''), one of the foundational texts of Taoism alongside the ''Zhuangzi (book) ...'s claim that the greatest music had no sounds. ..Even the music of the ''qin'' zither, a genre closely affiliated with Confucian scholar-officials, includes many works withDaoist Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', ' ...references, such as ''Tianfeng huanpei'' ("Heavenly Breeze and Sounds of Jade Pendants").
India
TheSamaveda
The ''Samaveda'' (, , from '' सामन्'', "song" and ''वेद'', "knowledge"), is the Veda of melodies and chants. It is an ancient Vedic Sanskrit text, and is one of the sacred scriptures in Hinduism. One of the four Vedas, it is a l ...
and Yajurveda
The ''Yajurveda'' (, , from यजुस्, "worship", and वेद, "knowledge") is the Veda primarily of prose mantras for worship rituals.Michael Witzel (2003), "Vedas and Upaniṣads", in ''The Blackwell Companion to Hinduism'' (Edito ...
(c. 1200 – 1000 BCE) are among the earliest testimonies of Indian music, but properly speaking, they contain no theory. The Natya Shastra
The ''Nāṭya Shāstra'' (, ''Nāṭyaśāstra'') is a Sanskrit treatise on the performing arts. The text is attributed to sage Bharata, and its first complete compilation is dated to between 200 BCE and 200 CE, but estimates vary b ...
, written between 200 BCE to 200 CE, discusses intervals ('' Śrutis''), scales (''Grāmas''), consonances and dissonances, classes of melodic structure (''Mūrchanās'', modes?), melodic types (''Jātis''), instruments, etc.
Greece
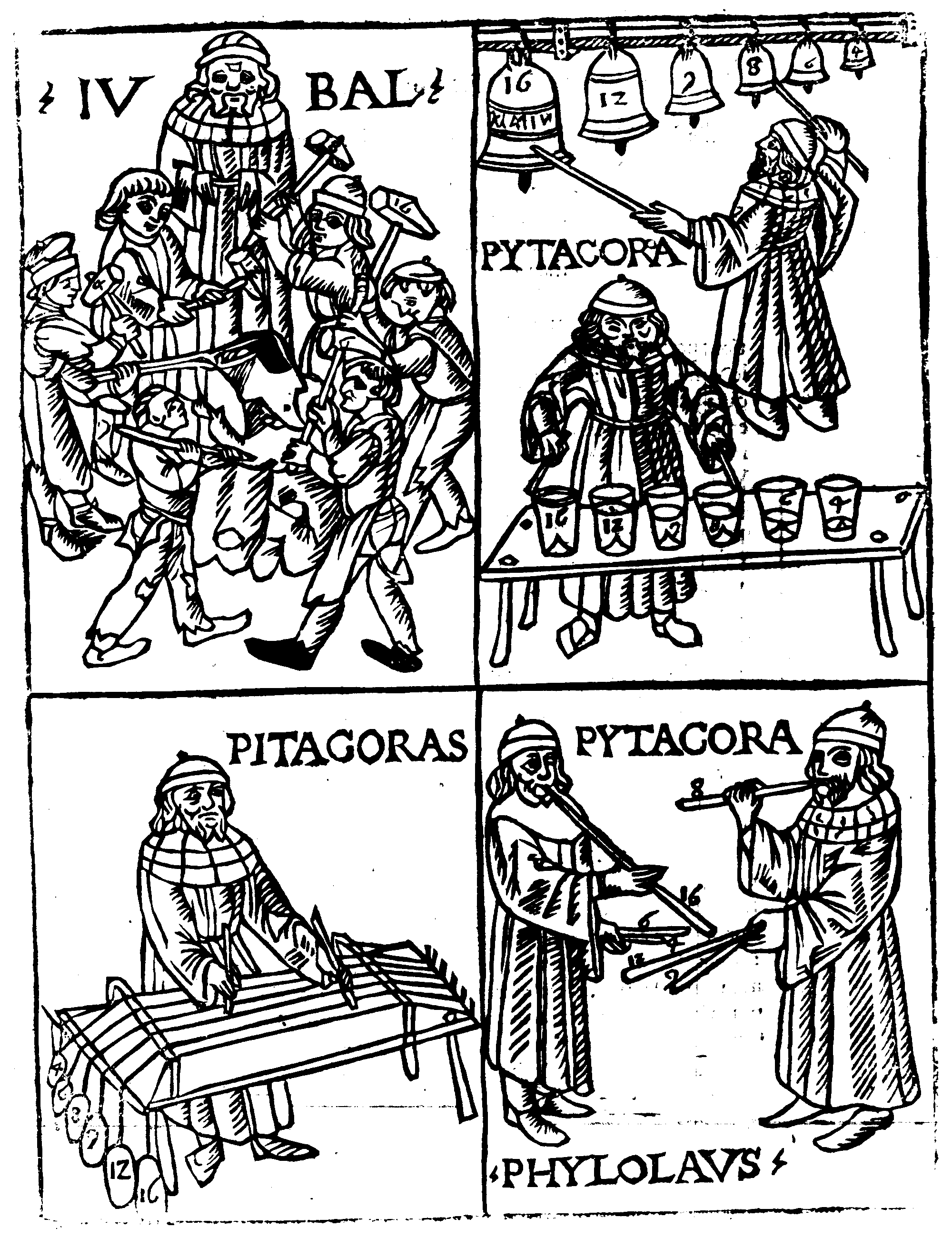
Early preserved Greek writings on music theory include two types of works: * technical manuals describing the Greek musical system including notation, scales, consonance and dissonance, rhythm, and types of musical compositions; * treatises on the way in which music reveals universal patterns of order leading to the highest levels of knowledge and understanding. Several names of theorists are known before these works, includingPythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of P ...
( ~ ), Philolaus
Philolaus (; , ''Philólaos''; )
was a Greek Pythagorean and pre-Socratic philosopher. He was born in a Greek colony in Italy and migrated to Greece. Philolaus has been called one of three most prominent figures in the Pythagorean tradition and ...
(), and others.
Works of the first type (technical manuals) include
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
More philosophical treatises of the second type include
*
*
*
*
Post-classical or Medieval Period
China
Thepipa
The pipa, pípá, or p'i-p'a () is a traditional Chinese musical instrument belonging to the plucked category of instruments. Sometimes called the "Chinese lute", the instrument has a pear-shaped wooden body with a varying number of frets rangi ...
instrument carried with it a theory of musical modes that subsequently led to the Sui and Tang theory of 84 musical modes.
Arabic countries / Persian countries
Medieval Arabic music theorists include: * Abū Yūsuf Ya'qūbal-Kindi
Abū Yūsuf Yaʻqūb ibn ʼIsḥāq aṣ-Ṣabbāḥ al-Kindī (; ; ; ) was an Arab Muslim polymath active as a philosopher, mathematician, physician, and music theorist
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understandin ...
(Bagdad, 873 CE), who uses the first twelve letters of the alphabet to describe the twelve frets on five strings of the oud
The oud ( ; , ) is a Middle Eastern short-neck lute-type, pear-shaped, fretless stringed instrument (a chordophone in the Hornbostel–Sachs classification of instruments), usually with 11 strings grouped in six courses, but some models have ...
, producing a chromatic scale of 25 degrees.
* aḥyā ibnal- Munajjim (Baghdad, 856–912), author of ''Risāla fī al-mūsīqī'' ("Treatise on music", MS GB-Lbl Oriental 2361) which describes a Pythagorean tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are determined by choosing a sequence of fifthsBruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh editi ...
of the oud
The oud ( ; , ) is a Middle Eastern short-neck lute-type, pear-shaped, fretless stringed instrument (a chordophone in the Hornbostel–Sachs classification of instruments), usually with 11 strings grouped in six courses, but some models have ...
and a system of eight modes perhaps inspired by Ishaq al-Mawsili
Ishaq al-Mawsili (; 767/772 – March 850) was an Arab musician of Persian origin active as a composer, singer and music theorist. The leading musician of his time in the Abbasid Caliphate, he served under six successive Abbasid caliphs: Haru ...
(767–850).
* Abū n-Nașr Muḥammad al-Fārābi (Persia, 872? – Damas, 950 or 951 CE), author of '' Kitab al-Musiqa al-Kabir'' ("The Great Book of Music").
* 'Ali ibn al-Husayn ul-Isfahānī (897–967), known as Abu al-Faraj al-Isfahani
Ali ibn al-Husayn al-Iṣfahānī (), also known as Abul-Faraj, (full form: Abū al-Faraj ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥusayn ibn Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn al-Ḥaytham al-Umawī al-Iṣfahānī) (897–967Common Era, CE / 284–356Islamic calendar, AH) w ...
, author of ''Kitāb al-Aghānī'' ("The Book of Songs").
* Abū 'Alī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd-Allāh ibn Sīnā, known as Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
(c. 980 – 1037), whose contribution to music theory consists mainly in Chapter 12 of the section on mathematics of his ''Kitab Al-Shifa'' ("The Book of Healing
''The Book of Healing'' (; ; also known as ) is a scientific and philosophical encyclopedia written by Abu Ali ibn Sīna (also known as Avicenna). He most likely began to compose the book in 1014, completed it around 1020, and published it in ...
").
* al-Ḥasan ibn Aḥmad ibn 'Ali al-Kātib, author of Kamāl adab al Ghinā' ("The Perfection of Musical Knowledge"), copied in 1225 (Istanbul, Topkapi Museum, Ms 1727).
* Safi al-Din al-Urmawi
Safi al-Din al-Urmawi al-Baghdadi () or Safi al-Din Abd al-Mu'min ibn Yusuf ibn al-Fakhir al-Urmawi al-Baghdadi (born c. 1216 AD in Urmia, died in 1294 AD in Baghdad) was a musician and writer on the theory of music.
Background and life
Safi ...
(1216–1294 CE), author of the ''Kitabu al-Adwār'' ("Treatise of musical cycles") and ''ar-Risālah aš-Šarafiyyah'' ("Epistle to Šaraf").
* Mubārak Šāh, commentator of Safi al-Din's ''Kitāb al-Adwār'' (British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
, Ms 823).
* Anon. LXI, Anonymous commentary on Safi al-Din's ''Kitāb al-Adwār''.
* Shams al-dῑn al-Saydᾱwῑ Al-Dhahabῑ (14th century CE (?)), music theorist. Author of ''Urjῡza fi'l-mῡsῑqᾱ'' ("A Didactic Poem on Music").
Europe
The Latin treatise ''De institutione musica'' by the Roman philosopherBoethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known simply as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480–524 AD), was a Roman Roman Senate, senator, Roman consul, consul, ''magister officiorum'', polymath, historian, and philosopher of the Early Middl ...
(written c. 500, translated as ''Fundamentals of Music'') was a touchstone for other writings on music in medieval Europe. Boethius represented Classical authority on music during the Middle Ages, as the Greek writings on which he based his work were not read or translated by later Europeans until the 15th century. This treatise carefully maintains distance from the actual practice of music, focusing mostly on the mathematical proportions involved in tuning systems and on the moral character of particular modes. Several centuries later, treatises began to appear which dealt with the actual composition of pieces of music in the plainchant
Plainsong or plainchant (calque from the French ; ) is a body of chants used in the liturgies of the Western Church. When referring to the term plainsong, it is those sacred pieces that are composed in Latin text. Plainsong was the exclusive for ...
tradition. At the end of the ninth century, Hucbald
Hucbald ( – 20 June 930; also Hucbaldus or Hubaldus) was a Benedictine monk active as a music theorist, poet, composer, teacher, and hagiographer. He was long associated with Saint-Amand Abbey, so is often known as Hucbald of St Amand. Deeply i ...
worked towards more precise pitch notation for the neume
A neume (; sometimes spelled neum) is the basic element of Western and some Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff (music), staff notation.
The earliest neumes were inflective marks that indicated the gener ...
s used to record plainchant.
Guido d'Arezzo
Guido of Arezzo (; – after 1033) was an Italian music theorist and pedagogue of High medieval music. A Benedictine monk, he is regarded as the inventor—or by some, developer—of the modern staff notation that had a massive influence on ...
wrote a letter to Michael of Pomposa in 1028, entitled ''Epistola de ignoto cantu'', in which he introduced the practice of using syllables to describe notes and intervals. This was the source of the hexachordal solmization
Solmization is a mnemonic system in which a distinct syllable is attributed to each note of a musical scale. Various forms of solmization are in use and have been used throughout the world, but solfège is the most common convention in countries ...
that was to be used until the end of the Middle Ages. Guido also wrote about emotional qualities of the modes, the phrase structure of plainchant, the temporal meaning of the neumes, etc.; his chapters on polyphony "come closer to describing and illustrating real music than any previous account" in the Western tradition.
During the thirteenth century, a new rhythm system called mensural notation
Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphony, polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measur ...
grew out of an earlier, more limited method of notating rhythms in terms of fixed repetitive patterns, the so-called rhythmic modes, which were developed in France around 1200. An early form of mensural notation was first described and codified in the treatise ''Ars cantus mensurabilis'' ("The art of measured chant") by Franco of Cologne
Franco of Cologne (; also Franco of Paris) was a German music theorist and possibly a composer. He was one of the most influential theorists of the Late Middle Ages, and was the first to propose an idea which was to transform musical notation per ...
(c. 1280). Mensural notation used different note shapes to specify different durations, allowing scribes to capture rhythms which varied instead of repeating the same fixed pattern; it is a proportional notation, in the sense that each note value is equal to two or three times the shorter value, or half or a third of the longer value. This same notation, transformed through various extensions and improvements during the Renaissance, forms the basis for rhythmic notation in European classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
today.
Modern
Middle Eastern and Central Asian countries
* Bāqiyā Nāyinῑ (Uzbekistan, 17th century CE), Uzbek author and music theorist. Author of ''Zamzama e wahdat-i-mῡsῑqῑ'' The Chanting of Unity in Music" * Baron Francois Rodolphe d'Erlanger (Tunis, Tunisia, 1910–1932 CE), French musicologist. Author of ''La musique arabe'' and ''Ta'rῑkh al-mῡsῑqᾱ al-arabiyya wa-usῡluha wa-tatawwurᾱtuha'' A History of Arabian Music, its principles and its Development" D'Erlanger divulges that the Arabic music scale is derived from the Greek music scale, and that Arabic music is connected to certain features of Arabic culture, such as astrology.Europe
* Renaissance * Baroque * 1750–1900 ** As Western musical influence spread throughout the world in the 1800s, musicians adopted Western theory as an international standard—but other theoretical traditions in both textual and oral traditions remain in use. For example, the long and rich musical traditions unique to ancient and current cultures of Africa are primarily oral, but describe specific forms, genres, performance practices, tunings, and other aspects of music theory. **Sacred harp
Sacred Harp singing is a tradition of sacred choral music which developed in New England and perpetuated in the American South. The name is derived from ''The Sacred Harp'', a historically important shape notes, shape-note tunebook printed in ...
music uses a different kind of scale and theory in practice. The music focuses on the solfege "fa, sol, la" on the music scale. Sacred Harp also employs a different notation involving "shape notes", or notes that are shaped to correspond to a certain solfege syllable on the music scale. Sacred Harp music and its music theory originated with Reverend Thomas Symmes in 1720, where he developed a system for "singing by note" to help his church members with note accuracy.
Contemporary
Fundamentals of music
Music is composed ofaural
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory s ...
phenomena; "music theory" considers how those phenomena apply in music. Music theory considers melody, rhythm, counterpoint, harmony, form, tonal systems, scales, tuning, intervals, consonance, dissonance, durational proportions, the acoustics of pitch systems, composition, performance, orchestration, ornamentation, improvisation, electronic sound production, etc.
Pitch
 Pitch is the lowness or highness of a
Pitch is the lowness or highness of a tone
Tone may refer to:
Visual arts and color-related
* Tone (color theory), a mix of tint and shade, in painting and color theory
* Tone (color), the lightness or brightness (as well as darkness) of a color
* Toning (coin), color change in coins
* ...
, for example the difference between middle C
C or Do is the first note of the C major scale, the third note of the A minor scale (the relative minor of C major), and the fourth note (G, A, B, C) of the Guidonian hand, commonly pitched around 261.63 Hz. The actual frequency has d ...
and a higher C. The frequency of the sound waves producing a pitch can be measured precisely, but the perception of pitch is more complex because single notes from natural sources are usually a complex mix of many frequencies. Accordingly, theorists often describe pitch as a subjective sensation rather than an objective measurement of sound.
Specific frequencies are often assigned letter names. Today most orchestras assign concert A
Concert pitch is the pitch reference to which a group of musical instruments are tuned for a performance. Concert pitch may vary from ensemble to ensemble, and has varied widely over time. The ISO defines international standard pitch as A440, ...
(the A above middle C
C or Do is the first note of the C major scale, the third note of the A minor scale (the relative minor of C major), and the fourth note (G, A, B, C) of the Guidonian hand, commonly pitched around 261.63 Hz. The actual frequency has d ...
on the piano) to the frequency of 440 Hz. This assignment is somewhat arbitrary; for example, in 1859 France, the same A was tuned to 435 Hz. Such differences can have a noticeable effect on the timbre of instruments and other phenomena. Thus, in historically informed performance
Historically informed performance (also referred to as period performance, authentic performance, or HIP) is an approach to the performance of Western classical music, classical music which aims to be faithful to the approach, manner and style of ...
of older music, tuning is often set to match the tuning used in the period when it was written. Additionally, many cultures do not attempt to standardize pitch, often considering that it should be allowed to vary depending on genre, style, mood, etc.
The difference in pitch between two notes is called an interval. The most basic interval is the unison
Unison (stylised as UNISON) is a Great Britain, British trade union. Along with Unite the Union, Unite, Unison is one of the two largest trade unions in the United Kingdom, with over 1.2 million members who work predominantly in public servic ...
, which is simply two notes of the same pitch. The octave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
interval is two pitches that are either double or half the frequency of one another. The unique characteristics of octaves gave rise to the concept of pitch class
In music, a pitch class (p.c. or pc) is a set of all pitches that are a whole number of octaves apart; for example, the pitch class C consists of the Cs in all octaves. "The pitch class C stands for all possible Cs, in whatever octave positio ...
: pitches of the same letter name that occur in different octaves may be grouped into a single "class" by ignoring the difference in octave. For example, a high C and a low C are members of the same pitch class—the class that contains all C's.
Musical tuning
In music, there are two common meanings for tuning:
* #Tuning practice, Tuning practice, the act of tuning an instrument or voice.
* #Tuning systems, Tuning systems, the various systems of Pitch (music), pitches used to tune an instrument, and ...
systems, or temperaments, determine the precise size of intervals. Tuning systems vary widely within and between world cultures. In Western culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
, there have long been several competing tuning systems, all with different qualities. Internationally, the system known as equal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencie ...
is most commonly used today because it is considered the most satisfactory compromise that allows instruments of fixed tuning (e.g. the piano) to sound acceptably in tune in all keys.
Scales and modes
 Notes can be arranged in a variety of scales and
Notes can be arranged in a variety of scales and modes
Mode ( meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* MO''D''E (magazine), a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is the setting fo ...
. Western music theory generally divides the octave into a series of twelve pitches, called a chromatic scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the ...
, within which the interval between adjacent tones is called a semitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between ...
, or half step. Selecting tones from this set of 12 and arranging them in patterns of semitones and whole tones creates other scales.
The most commonly encountered scales are the seven-toned major
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in musi ...
, the harmonic minor
The harmonic minor scale (or Aeolian ♮7 scale) is a musical scale derived from the natural minor scale, with the minor seventh degree raised by one semitone to a major seventh, creating an augmented second between the sixth and seventh degree ...
, the melodic minor
In Classical_music, Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three Scale (music), scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending).
...
, and the natural minor
In Classical_music, Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three Scale (music), scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending).
...
. Other examples of scales are the octatonic scale
An octatonic scale is any eight-note musical scale. However, the term most often refers to the ancohemitonic symmetric scale composed of alternating whole and half steps, as shown at right. In classical theory (in contrast to jazz theory), ...
and the pentatonic
A pentatonic scale is a Scale (music), musical scale with five Musical note, notes per octave, in contrast to heptatonic scales, which have seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale).
Pentatonic scales were developed inde ...
or five-tone scale, which is common in folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes #Traditional folk music, traditional folk music and the Contemporary folk music, contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be ca ...
and blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
. Non-Western cultures often use scales that do not correspond with an equally divided twelve-tone division of the octave. For example, classical Ottoman, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
musical systems often make use of multiples of quarter tones (half the size of a semitone, as the name indicates), for instance in 'neutral' seconds (three quarter tones) or 'neutral' thirds (seven quarter tones)—they do not normally use the quarter tone itself as a direct interval.
In traditional Western notation, the scale used for a composition is usually indicated by a key signature
In Western musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp (), flat (), or rarely, natural () symbols placed on the staff at the beginning of a section of music. The initial key signature in a piece is placed immediately after the cl ...
at the beginning to designate the pitches that make up that scale. As the music progresses, the pitches used may change and introduce a different scale. Music can be transposed
In linear algebra, the transpose of a matrix is an operator which flips a matrix over its diagonal;
that is, it switches the row and column indices of the matrix by producing another matrix, often denoted by (among other notations).
The tra ...
from one scale to another for various purposes, often to accommodate the range of a vocalist. Such transposition raises or lowers the overall pitch range, but preserves the intervallic relationships of the original scale. For example, transposition from the key of C major to D major raises all pitches of the scale of C major equally by a whole tone
In Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (). A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more deta ...
. Since the interval relationships remain unchanged, transposition may be unnoticed by a listener, however other qualities may change noticeably because transposition changes the relationship of the overall pitch range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
compared to the range of the instruments or voices that perform the music. This often affects the music's overall sound, as well as having technical implications for the performers.
The interrelationship of the keys most commonly used in Western tonal music is conveniently shown by the circle of fifths
In music theory, the circle of fifths (sometimes also cycle of fifths) is a way of organizing pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. Starting on a C, and using the standard system of tuning for Western music (12-tone equal temperament), the se ...
. Unique key signatures are also sometimes devised for a particular composition. During the Baroque period, emotional associations with specific keys, known as the doctrine of the affections
The doctrine of the affections, also known as the ''doctrine of affects'', ''doctrine of the passions'', ''theory of the affects'', or by the German term Affektenlehre (after the German ''Affekt''; plural ''Affekte'') was a theory in the aestheti ...
, were an important topic in music theory, but the unique tonal colorings of keys that gave rise to that doctrine were largely erased with the adoption of equal temperament. However, many musicians continue to feel that certain keys are more appropriate to certain emotions than others. Indian classical music
Indian classical music is the art music, classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It is generally described using terms like ''Shastriya Sangeet'' and ''Marg Sangeet''. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music known as ...
theory continues to strongly associate keys with emotional states, times of day, and other extra-musical concepts and notably, does not employ equal temperament.
Consonance and dissonance
Consonance and dissonance
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness, unple ...
are subjective qualities of the sonority of intervals that vary widely in different cultures and over the ages. Consonance (or concord) is the quality of an interval or chord that seems stable and complete in itself. Dissonance (or discord) is the opposite in that it feels incomplete and "wants to" resolve to a consonant interval. Dissonant intervals seem to clash. Consonant intervals seem to sound comfortable together. Commonly, perfect fourths, fifths, and octaves and all major and minor thirds and sixths are considered consonant. All others are dissonant to a greater or lesser degree.
Context and many other aspects can affect apparent dissonance and consonance. For example, in a Debussy prelude, a major second may sound stable and consonant, while the same interval may sound dissonant in a Bach fugue. In the Common practice era, the perfect fourth is considered dissonant when not supported by a lower third or fifth. Since the early 20th century, Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian and American composer, music theorist, teacher and writer. He was among the first Modernism (music), modernists who transformed the practice of harmony in 20th-centu ...
's concept of "emancipated" dissonance, in which traditionally dissonant intervals can be treated as "higher," more remote consonances, has become more widely accepted.
Rhythm
Meter
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
measures music in regular pulse groupings, called measures or bars. The time signature
A time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, and measure signature) is an indication in music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type fit into each measure ( bar). The time signature indicates th ...
or meter signature specifies how many beats are in a measure, and which value of written note is counted or felt as a single beat.
Through increased stress, or variations in duration or articulation, particular tones may be accented. There are conventions in most musical traditions for regular and hierarchical accentuation of beats to reinforce a given meter. Syncopated
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat (music), off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of ...
rhythms contradict those conventions by accenting unexpected parts of the beat. Playing simultaneous rhythms in more than one time signature is called polyrhythm
Polyrhythm () is the simultaneous use of two or more rhythms that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic layers may be the basis of an entire piece of music (cross-rh ...
.
In recent years, rhythm and meter have become an important area of research among music scholars. The most highly cited of these recent scholars are Maury Yeston
Maury Yeston (born October 23, 1945) is an American composer, lyricist and music theorist.
Yeston has written the music and lyrics for several Broadway musicals and is also a classical orchestral and ballet composer. Among his Broadway music ...
, Fred Lerdahl
Alfred Whitford (Fred) Lerdahl (born March 10, 1943) is an American music theorist and composer. Best known for his work on musical grammar, Music cognition, cognition, Rhythm, rhythmic theory, and pitch space, he and the linguist Ray Jackendoff d ...
and Ray Jackendoff
Ray Jackendoff (born January 23, 1945) is an American linguist. He is professor of philosophy, Seth Merrin Chair in the Humanities and, with Daniel Dennett, co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies at Tufts University. He has always str ...
, Jonathan Kramer
Jonathan Donald Kramer (December 7, 1942, Hartford, Connecticut – June 3, 2004, New York City) was an American composer and music theorist.
Biography
Kramer received his B.A. magna cum laude from Harvard University (1965) and his MA and ...
, and Justin London.
Melody
melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figurativel ...
is a group of musical sounds in agreeable succession or arrangement. Because melody is such a prominent aspect in so much music, its construction and other qualities are a primary interest of music theory.
The basic elements of melody are pitch, duration, rhythm, and tempo. The tones of a melody are usually drawn from pitch systems such as scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
or modes
Mode ( meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* MO''D''E (magazine), a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is the setting fo ...
. Melody may consist, to increasing degree, of the figure, motive, semi-phrase, antecedent and consequent phrase, and period or sentence. The period may be considered the complete melody, however some examples combine two periods, or use other combinations of constituents to create larger form melodies.
Chord
harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
set of three or more note
Note, notes, or NOTE may refer to:
Music and entertainment
* Musical note, a pitched sound (or a symbol for a sound) in music
* ''Notes'' (album), a 1987 album by Paul Bley and Paul Motian
* ''Notes'', a common (yet unofficial) shortened versi ...
s that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggio
An arpeggio () is a type of Chord (music), chord in which the Musical note, notes that compose a chord are individually sounded in a progressive rising or descending order. Arpeggios on keyboard instruments may be called rolled chords.
Arpe ...
s and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African, and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.
The most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give seventh chord
A seventh chord is a chord (music), chord consisting of a triad (music), triad plus a note forming an interval (music), interval of a Interval (music), seventh above the chord's root (chord), root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" ...
s, extended chord
In music, extended chords are certain Chord (music), chords (built from third (chord), thirds) or triad (music), triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh (chord), seventh. Ninth chord, Ninth, Eleventh chord, eleventh, and T ...
s, or added tone chord
An added tone chord, or added note chord, is a non-tertian chord (music), chord composed of a Triad (music), triad and an extra "added" note (music), note. Any tone that is not a Seventh (chord), seventh factor is commonly categorized as an adde ...
s. The most common chords are the ''major
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in musi ...
'' and ''minor
Minor may refer to:
Common meanings
* Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities.
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Mathematics
* Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to an ...
triads'' and then the ''augmented
Augment or augmentation may refer to:
Language
*Augment (Indo-European), a syllable added to the beginning of the word in certain Indo-European languages
* Augment (Bantu languages), a morpheme that is prefixed to the noun class prefix of nouns ...
'' and '' diminished triads''. The descriptions ''major'', ''minor'', ''augmented'', and ''diminished'' are sometimes referred to collectively as chordal ''quality''. Chords are also commonly classed by their root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
note—so, for instance, the chord C major may be described as a triad of major quality built on the note C. Chords may also be classified by inversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ''Inversions'' (novel) by Iain M. Bank ...
, the order in which the notes are stacked.
A series of chords is called a chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from ...
. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, chords are numbered, using Roman numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
(upward from the key-note), per their diatonic function
In music, function (also referred to as harmonic function) is a term used to denote the relationship of a chord"Function", unsigned article, ''Grove Music Online'', . or a scale degree to a tonal centre. Two main theories of tonal functions exist ...
. Common ways of notating or representing chords in western music other than conventional include Roman numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
, figured bass
Figured bass is musical notation in which numerals and symbols appear above or below (or next to) a bass note. The numerals and symbols (often accidental (music), accidentals) indicate interval (music), intervals, chord (music), chords, and non- ...
(much used in the Baroque era
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from the early 17th century until the 1750s. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (i ...
), chord letter
Musicians use various kinds of chord names and symbols in different contexts to represent musical chords. In most genres of popular music, including jazz, pop, and rock, a chord name and its corresponding symbol typically indicate one or more ...
s (sometimes used in modern musicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
), and various systems of chord chart
A chord chart (or chart) is a form of musical notation that describes the basic harmonic and rhythmic information for a song or tune. It is the most common form of notation used by professional session musicians playing jazz or popular music. It ...
s typically found in the lead sheet
A lead sheet or fake sheet is a form of musical notation that specifies the essential elements of a popular song: the melody, lyrics and harmony. The melody is written in modern Western music notation, the lyric is written as text below the s ...
s used in popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
to lay out the sequence of chords so that the musician may play accompaniment chords or improvise a solo.
Harmony
In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches ( tones,notes
Note, notes, or NOTE may refer to:
Music and entertainment
* Musical note, a pitched sound (or a symbol for a sound) in music
* ''Notes'' (album), a 1987 album by Paul Bley and Paul Motian
* ''Notes'', a common (yet unofficial) shortened versi ...
), or chords
Chord or chords may refer to:
Art and music
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord, a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* The Chords (British band), 1970s British mod ...
. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from ...
s and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the "vertical" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term ca ...
, or the "horizontal" aspect. Counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ...
, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice ( monophony) or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chord ...
, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, is thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.
In popular and jazz harmony
Jazz harmony is the theory and practice of how chords are used in jazz music. Jazz bears certain similarities to other practices in the tradition of Western harmony, such as many chord progressions, and the incorporation of the major and minor s ...
, chords are named by their root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. For example, a lead sheet
A lead sheet or fake sheet is a form of musical notation that specifies the essential elements of a popular song: the melody, lyrics and harmony. The melody is written in modern Western music notation, the lyric is written as text below the s ...
may indicate chords such as C major, D minor, and G dominant seventh. In many types of music, notably Baroque, Romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with "tensions". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. It is part of a chord, but is not one of the chord tones (1 3 5 7). Typically, in the classical common practice period
In Western classical music, the common practice period (CPP) was the period of about 250 years during which the tonal system was regarded as the only basis for composition. It began when composers' use of the tonal system had clearly supersede ...
a dissonant chord (chord with tension) "resolves" to a consonant chord. Harmonization
In music, harmonization is the chordal accompaniment to a line or melody: "Using chords and melodies together, making harmony by stacking scale tones as triads".
A harmonized scale can be created by using each note of a musical scale as a r ...
usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between "tense" and "relaxed" moments.
Timbre
Timbre, sometimes called "color", or "tone color," is the principal phenomenon that allows us to distinguish one instrument from another when both play at the same pitch and volume, a quality of a voice or instrument often described in terms like bright, dull, shrill, etc. It is of considerable interest in music theory, especially because it is one component of music that has as yet, no standardized nomenclature. It has been called "... the psychoacoustician's multidimensional waste-basket category for everything that cannot be labeled pitch or loudness," but can be accurately described and analyzed byFourier analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph Fo ...
and other methods because it results from the combination of all sound frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
, attack and release envelopes, and other qualities that a tone comprises.
Timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
is principally determined by two things: (1) the relative balance of overtones
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental i ...
produced by a given instrument due its construction (e.g. shape, material), and (2) the envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
of the sound (including changes in the overtone structure over time). Timbre varies widely between different instruments, voices, and to lesser degree, between instruments of the same type due to variations in their construction, and significantly, the performer's technique. The timbre of most instruments can be changed by employing different techniques while playing. For example, the timbre of a trumpet changes when a mute is inserted into the bell, the player changes their embouchure, or volume.
A voice can change its timbre by the way the performer manipulates their vocal apparatus, (e.g. the shape of the vocal cavity or mouth). Musical notation frequently specifies alteration in timbre by changes in sounding technique, volume, accent, and other means. These are indicated variously by symbolic and verbal instruction. For example, the word ''dolce'' (sweetly) indicates a non-specific, but commonly understood soft and "sweet" timbre. ''Sul tasto'' instructs a string player to bow near or over the fingerboard to produce a less brilliant sound. ''Cuivre'' instructs a brass player to produce a forced and stridently brassy sound. Accent symbols like ''marcato'' (^) and dynamic indications (''pp'') can also indicate changes in timbre.
Dynamics
decibels
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a ...
or phon
The phon is a logarithmic unit of loudness level for tones and complex sounds. Loudness is measured in sones, a linear unit. Human sensitivity to sound is variable across different frequencies; therefore, although two different tones may pres ...
s. In music notation, however, dynamics are not treated as absolute values, but as relative ones. Because they are usually measured subjectively, there are factors besides amplitude that affect the performance or perception of intensity, such as timbre, vibrato, and articulation.
The conventional indications of dynamics are abbreviations for Italian words like ''forte'' (''f'') for loud and ''piano'' (''p'') for soft. These two basic notations are modified by indications including ''mezzo piano'' (''mp'') for moderately soft (literally "half soft") and ''mezzo forte'' (''mf'') for moderately loud, ''sforzando'' or ''sforzato'' (''sfz'') for a surging or "pushed" attack, or ''fortepiano'' (''fp'') for a loud attack with a sudden decrease to a soft level. The full span of these markings usually range from a nearly inaudible ''pianissississimo'' (''pppp'') to a loud-as-possible ''fortissississimo'' (''ffff'').
Greater extremes of ''pppppp'' and ''fffff'' and nuances such as ''p+'' or ''più piano'' are sometimes found. Other systems of indicating volume are also used in both notation and analysis: dB (decibels), numerical scales, colored or different sized notes, words in languages other than Italian, and symbols such as those for progressively increasing volume (''crescendo'') or decreasing volume (''diminuendo'' or ''decrescendo''), often called " hairpins" when indicated with diverging or converging lines as shown in the graphic above.
Articulation
 Articulation is the way the performer sounds notes. For example, ''
Articulation is the way the performer sounds notes. For example, ''staccato
Staccato (; Italian for "detached") is a form of Articulation (music), musical articulation. In modern notation, it signifies a note of shortened duration, separated from the note that may follow by silence. It has been described by theorists and ...
'' is the shortening of duration compared to the written note value, ''legato
In music performance and notation, legato (; Italian for "tied together"; French ''lié''; German ''gebunden'') indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly, such that the transition from note to note is made with no intervening si ...
'' performs the notes in a smoothly joined sequence with no separation. Articulation is often described rather than quantified, therefore there is room to interpret how to execute precisely each articulation.
For example, ''staccato'' is often referred to as "separated" or "detached" rather than having a defined or numbered amount by which to reduce the notated duration. Violin players use a variety of techniques to perform different qualities of ''staccato.'' The manner in which a performer decides to execute a given articulation is usually based on the context of the piece or phrase, but many articulation symbols and verbal instructions depend on the instrument and musical period (e.g. viol, wind; classical, baroque; etc.).
There is a set of articulations that most instruments and voices perform in common. They are—from long to short: ''legato'' (smooth, connected); ''tenuto
In musical notation, ''tenuto'' ( Italian, past participle of ''tenere'', "to hold"), written as a horizontal bar above or below a note, is a direction for the performer to hold or sustain a note for its full length.
Its precise interpretation ...
'' (pressed or played to full notated duration); ''marcato
''Marcato'' (short form: Marc.; Italian for ''marked'') is a musical instruction indicating a note, chord, or passage is to be played louder or more forcefully than the surrounding music. The instruction may involve the word ''marcato'' itself w ...
'' (accented and detached); ''staccato'' ("separated", "detached"); '' martelé'' (heavily accented or "hammered"). Many of these can be combined to create certain "in-between" articulations. For example, ''portato
Portato (; Italian past participle of ''portare'', "to carry"), also mezzo-staccato, French notes portées, in music denotes a smooth, pulsing articulation and is often notated by adding dots under slur markings.
Portato is also known as ar ...
'' is the combination of ''tenuto'' and ''staccato''. Some instruments have unique methods by which to produce sounds, such as ''spiccato
''Spiccato'' is a bowing technique for string instruments in which the bow appears to bounce lightly upon the string. The term comes from the past participle of the Italian verb ''spiccare'', meaning "to separate". The terms '' martelé'', '' sa ...
'' for bowed strings, where the bow bounces off the string.
Texture
In music, texture is how themelodic
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term c ...
, rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular r ...
ic, and harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
materials are combined in a composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
* Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include ...
, thus determining the overall quality of the sound in a piece. Texture is often described in regard to the density, or thickness, and range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
, or width, between lowest and highest pitches, in relative terms as well as more specifically distinguished according to the number of voices, or parts, and the relationship between these voices. For example, a thick texture contains many "layers" of instruments. One of these layers could be a string section, or another brass.
The thickness also is affected by the number and the richness of the instruments playing the piece. The thickness varies from light to thick. A lightly textured piece will have light, sparse scoring. A thickly or heavily textured piece will be scored for many instruments. A piece's texture may be affected by the number and character of parts playing at once, the timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
of the instruments or voices playing these parts and the harmony, tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition ...
, and rhythms used. The types categorized by number and relationship of parts are analyzed and determined through the labeling of primary textural elements: primary melody, secondary melody, parallel supporting melody, static support, harmonic support, rhythmic support, and harmonic and rhythmic support.
Common types included monophonic
Monaural sound or monophonic sound (often shortened to mono) is sound intended to be heard as if it were emanating from one position. This contrasts with stereophonic sound or ''stereo'', which uses two separate audio channels to reproduce sou ...
texture (a single melodic voice, such as a piece for solo soprano or solo flute), biphonic texture (two melodic voices, such as a duo for bassoon and flute in which the bassoon plays a drone note and the flute plays the melody), polyphonic
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice ( monophony) or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords ...
texture and homophonic
Homophony and Homophonic are from the Greek language, Greek ὁμόφωνος (''homóphōnos''), literally 'same sounding,' from ὁμός (''homós''), "same" and φωνή (''phōnē''), "sound". It may refer to:
*Homophones − words with the s ...
texture (chords accompanying a melody).
Form or structure
 The term musical form (or musical architecture) refers to the overall structure or plan of a piece of music, and it describes the layout of a composition as divided into sections. In the tenth edition of '' The Oxford Companion to Music'',
The term musical form (or musical architecture) refers to the overall structure or plan of a piece of music, and it describes the layout of a composition as divided into sections. In the tenth edition of '' The Oxford Companion to Music'', Percy Scholes
Percy Alfred Scholes (pronounced ''skolz''; 24 July 1877 – 31 July 1958) was an English musician, journalist, vegetarianism activist and prolific writer, whose best-known achievement was his compilation of the first edition of the '' Oxford Co ...
defines musical form as "a series of strategies designed to find a successful mean between the opposite extremes of unrelieved repetition and unrelieved alteration." According to Richard Middleton, musical form is "the shape or structure of the work." He describes it through difference: the distance moved from a repeat
Repeat may refer to:
* Rerun, a rebroadcast of an episode of a radio or television program
* Repeated sequence (DNA), a pattern of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) that occurs in multiple copies throughout the genome
** CRISPR
* The smallest rectangle th ...
; the latter being the smallest difference. Difference is quantitative and qualitative: ''how far'', and ''of what type'', different. In many cases, form depends on statement and restatement, unity and variety, and contrast
Contrast may refer to:
Science
* Contrast (vision), the contradiction in form, colour and light between parts of an image
* Contrast (statistics), a combination of averages whose coefficients add up to zero, or the difference between two means
* ...
and connection.
Expression
 Musical expression is the art of playing or singing music with emotional communication. The elements of music that comprise expression include dynamic indications, such as forte or piano, phrasing, differing qualities of timbre and articulation, color, intensity, energy and excitement. All of these devices can be incorporated by the performer. A performer aims to elicit responses of sympathetic feeling in the audience, and to excite, calm or otherwise sway the audience's physical and emotional responses. Musical expression is sometimes thought to be produced by a combination of other parameters, and sometimes described as a transcendent quality that is more than the sum of measurable quantities such as pitch or duration.
Expression on instruments can be closely related to the role of the breath in singing, and the voice's natural ability to express feelings, sentiment and deep emotions. Whether these can somehow be categorized is perhaps the realm of academics, who view expression as an element of musical performance that embodies a consistently recognizable
Musical expression is the art of playing or singing music with emotional communication. The elements of music that comprise expression include dynamic indications, such as forte or piano, phrasing, differing qualities of timbre and articulation, color, intensity, energy and excitement. All of these devices can be incorporated by the performer. A performer aims to elicit responses of sympathetic feeling in the audience, and to excite, calm or otherwise sway the audience's physical and emotional responses. Musical expression is sometimes thought to be produced by a combination of other parameters, and sometimes described as a transcendent quality that is more than the sum of measurable quantities such as pitch or duration.
Expression on instruments can be closely related to the role of the breath in singing, and the voice's natural ability to express feelings, sentiment and deep emotions. Whether these can somehow be categorized is perhaps the realm of academics, who view expression as an element of musical performance that embodies a consistently recognizable emotion
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is ...
, ideally causing a sympathetic emotional response in its listeners. The emotional content of musical expression is distinct from the emotional content of specific sounds (e.g., a startlingly-loud 'bang') and of learned associations (e.g., a national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and European ...
), but can rarely be completely separated from its context.
The components of musical expression continue to be the subject of extensive and unresolved dispute.
Notation
 Musical notation is the written or symbolized representation of music. This is most often achieved by the use of commonly understood graphic symbols and written verbal instructions and their abbreviations. There are many systems of music notation from different cultures and different ages. Traditional Western notation evolved during the Middle Ages and remains an area of experimentation and innovation. In the 2000s, computer
Musical notation is the written or symbolized representation of music. This is most often achieved by the use of commonly understood graphic symbols and written verbal instructions and their abbreviations. There are many systems of music notation from different cultures and different ages. Traditional Western notation evolved during the Middle Ages and remains an area of experimentation and innovation. In the 2000s, computer file formats
A file format is a Computer standard, standard way that information is encoded for storage in a computer file. It specifies how bits are used to encode information in a digital storage medium. File formats may be either proprietary format, pr ...
have become important as well. Spoken language and hand signs are also used to symbolically represent music, primarily in teaching.
In standard Western music notation, tones are represented graphically by symbols (notes) placed on a staff or staves, the vertical axis corresponding to pitch and the horizontal axis corresponding to time. Note head shapes, stems, flags, ties and dots are used to indicate duration. Additional symbols indicate keys, dynamics, accents, rests, etc. Verbal instructions from the conductor are often used to indicate tempo, technique, and other aspects.
In Western music, a range of different music notation systems are used. In Western Classical music, conductors use printed scores that show all of the instruments' parts and orchestra members read parts with their musical lines written out. In popular styles of music, much less of the music may be notated. A rock band may go into a recording session with just a handwritten chord chart
A chord chart (or chart) is a form of musical notation that describes the basic harmonic and rhythmic information for a song or tune. It is the most common form of notation used by professional session musicians playing jazz or popular music. It ...
indicating the song's chord progression
In a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural, or simply changes) is a succession of chords. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in Western musical tradition from ...
using chord names (e.g., C major, D minor, G7, etc.). All of the chord voicings, rhythms and accompaniment figures are improvised by the band members.
As academic discipline
The scholarly study of music theory in the twentieth century has a number of different subfields, each of which takes a different perspective on what are the primary phenomenon of interest and the most useful methods for investigation.Analysis
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
onwards." Adolf Bernhard Marx
Friedrich Heinrich Adolf Bernhard Marx . B. Marx(15 May 1795, Halle, Saxony-Anhalt, Halle – 17 May 1866, Berlin) was a German people, German Music theory, music theorist, Music criticism, critic, and musicologist.
Life
Marx was the son of ...
was influential in formalising concepts about composition and music understanding towards the second half of the 19th century. The principle of analysis has been variously criticized, especially by composers, such as Edgard Varèse
Edgard Victor Achille Charles Varèse (; also spelled Edgar; December 22, 1883 – November 6, 1965) was a French and American composer who spent the greater part of his career in the United States. Varèse's music emphasizes timbre and rhythm; h ...
's claim that, "to explain by means of nalysisis to decompose, to mutilate the spirit of a work".
Schenkerian analysis
Schenkerian analysis is a method of musical analysis, analyzing tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker (1868–1935). The goal is to demonstrate the organic coherence of the work by showing how the "foreground" (all notes in the sco ...
is a method of musical analysis of tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker
Heinrich Schenker (19 June 1868 – 14 January 1935) was an Austrian music theory, music theorist #Theoretical writings, whose writings have had a profound influence on subsequent musical analysis. His approach, now termed Schenkerian analysis ...
(1868–1935). The goal of a Schenkerian analysis is to interpret the underlying structure of a tonal work and to help reading the score according to that structure. The theory's basic tenets can be viewed as a way of defining tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitch (music), pitches and / or chord (music), chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived ''relations'', ''stabilities'', ''attractions'', and ''directionality''.
In this hierarchy, the single pitch or ...
in music. A Schenkerian analysis of a passage of music shows hierarchical relationships among its pitches, and draws conclusions about the structure of the passage from this hierarchy. The analysis makes use of a specialized symbolic form of musical notation that Schenker devised to demonstrate various techniques of elaboration. The most fundamental concept of Schenker's theory of tonality may be that of ''tonal space''. The intervals between the notes of the tonic triad form a ''tonal space'' that is filled with passing and neighbour notes, producing new triads and new tonal spaces, open for further elaborations until the surface of the work (the score) is reached.
Although Schenker himself usually presents his analyses in the generative direction, starting from the fundamental structure
In Schenkerian analysis#Ursatz, Schenkerian analysis, the fundamental structure () describes the structure of a tonal music, tonal work as it occurs at the most remote (or "Background (Schenker), background") structural level, level and in the mo ...
(''Ursatz'') to reach the score, the practice of Schenkerian analysis more often is reductive, starting from the score and showing how it can be reduced to its fundamental structure. The graph of the ''Ursatz'' is arrhythmic, as is a strict-counterpoint cantus firmus exercise. Even at intermediate levels of the reduction, rhythmic notation (open and closed noteheads, beams and flags) shows not rhythm but the hierarchical relationships between the pitch-events. Schenkerian analysis is ''subjective''. There is no mechanical procedure involved and the analysis reflects the musical intuitions of the analyst. The analysis represents a way of hearing (and reading) a piece of music.
Transformational theory is a branch of music theory developed by David Lewin
David Benjamin Lewin (July 2, 1933 – May 5, 2003) was an American music theorist, music critic and composer. Called "the most original and far-ranging theorist of his generation", he did his most influential theoretical work on the development ...
in the 1980s, and formally introduced in his 1987 work, ''Generalized Musical Intervals and Transformations''. The theory, which models musical transformations as elements of a mathematical group, can be used to analyze both tonal and atonal music
Atonality in its broadest sense is music that lacks a tonal center, or key. ''Atonality'', in this sense, usually describes compositions written from about the early 20th-century to the present day, where a hierarchy of harmonies focusing on a ...
. The goal of transformational theory is to change the focus from musical objects—such as the "C major chord
In music theory, a major chord is a chord (music), chord that has a root (chord), root, a major third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a major Triad (music), triad. For example, the major triad bui ...
" or "G major chord"—to relations between objects. Thus, instead of saying that a C major chord is followed by G major, a transformational theorist might say that the first chord has been "transformed" into the second by the " Dominant operation." (Symbolically, one might write "Dominant(C major) = G major.") While traditional musical set theory
Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Howard Hanson first elaborated many of the concepts for analyzing tonality, tonal music. Other theorists, such as Allen Forte, further devel ...
focuses on the makeup of musical objects, transformational theory focuses on the intervals
Interval may refer to:
Mathematics and physics
* Interval (mathematics), a range of numbers
** Partially ordered set#Intervals, its generalization from numbers to arbitrary partially ordered sets
* A statistical level of measurement
* Interval es ...
or types of musical motion that can occur. According to Lewin's description of this change in emphasis, " he transformationalattitude does not ask for some observed measure of extension between reified 'points'; rather it asks: 'If I am ''at'' s and wish to get to t, what characteristic ''gesture'' should I perform in order to arrive there?'"
Music perception and cognition
Music psychology or the psychology of music may be regarded as a branch of bothpsychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
and musicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
. It aims to explain and understand musical behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
and experience
Experience refers to Consciousness, conscious events in general, more specifically to perceptions, or to the practical knowledge and familiarity that is produced by these processes. Understood as a conscious event in the widest sense, experience i ...
, including the processes through which music is perceived, created, responded to, and incorporated into everyday life. Modern music psychology is primarily empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how t ...
; its knowledge tends to advance on the basis of interpretations of data collected by systematic observation
Observation in the natural sciences is an act or instance of noticing or perceiving and the acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the percep ...
of and interaction with human participants. Music psychology is a field of research with practical relevance for many areas, including music performance
A performance is an act or process of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Performance has evolved glo ...
, composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
* Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include ...
, education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
, criticism
Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative or positive qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. , ''the act of giving your opinion or judgment about the ...
, and therapy
A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, ''treatment'' and ''therapy'', are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx.
As a rule, each therapy has indications a ...
, as well as investigations of human aptitude
An aptitude is a component of a competence to do a certain kind of work at a certain level. Outstanding aptitude can be considered "talent", or "skill". Aptitude is inborn potential to perform certain kinds of activities, whether physical or ...
, skill, intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
, creativity, and social behavior
Social behavior is behavior among two or more organisms within the same species, it encompasses any behavior in which one member affects another. Social behavior can be seen as similar to an exchange of goods, with the expectation that when you ...
.
Music psychology can shed light on non-psychological aspects of musicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
and musical practice. For example, it contributes to music theory through investigations of the perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
and computational modelling
Computer simulation is the running of a mathematical model on a computer, the model being designed to represent the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determin ...
of musical structures such as melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figurativel ...
, harmony
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harm ...
, tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitch (music), pitches and / or chord (music), chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived ''relations'', ''stabilities'', ''attractions'', and ''directionality''.
In this hierarchy, the single pitch or ...
, rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular r ...
, meter
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
, and form
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form may also refer to:
*Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter dat ...
. Research in music history
Music history, sometimes called historical musicology, is a highly diverse subfield of the broader discipline of musicology that studies music from a historical point of view. In theory, "music history" could refer to the study of the history of ...
can benefit from systematic study of the history of musical syntax When analysing the regularities and structure of music as well as the processing of music in the brain, certain findings lead to the question of whether music is based on a syntax that could be compared with linguistic syntax. To get closer to this ...
, or from psychological analyses of composers and compositions in relation to perceptual, affective, and social responses to their music.
Genre and technique
A music genre is a conventional category that identifies some pieces of music as belonging to a shared tradition or set of conventions. It is to be distinguished from ''musical form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or musical improvisation, performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a ...
'' and ''musical style'', although in practice these terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
Music can be divided into different genres
Genre () is any style or form of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other form ...
in many different ways. The artistic nature of music means that these classifications are often subjective and controversial, and some genres may overlap. There are even varying academic definitions of the term ''genre ''itself. In his book ''Form in Tonal Music'', Douglass M. Green distinguishes between genre and form
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form may also refer to:
*Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter dat ...
. He lists madrigal
A madrigal is a form of secular vocal music most typical of the Renaissance (15th–16th centuries) and early Baroque (1580–1650) periods, although revisited by some later European composers. The polyphonic madrigal is unaccompanied, and the ...
, motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the preeminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to the Eng ...
, canzona
The canzona, also known as the canzon or canzone, is an Italian musical form derived from the Franco-Flemish and Parisian '' chansons''.
Background
The canzona is an instrumental musical form that differs from the similar forms of ricercare ...
, ricercar
A ricercar ( , ) or ricercare ( , ) is a type of late Renaissance and mostly early Baroque instrumental composition. The term ''ricercar'' derives from the Italian verb , which means "to search out; to seek"; many ricercars serve a preludial func ...
, and dance as examples of genres from the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
period. To further clarify the meaning of ''genre'', Green writes, "Beethoven's Op. 61 and Mendelssohn's Op. 64 are identical in genre—both are violin concertos—but different in form. However, Mozart's Rondo for Piano, K. 511, and the ''Agnus Dei'' from his Mass, K. 317 are quite different in genre but happen to be similar in form." Some, like Peter van der Merwe, treat the terms ''genre'' and ''style'' as the same, saying that ''genre'' should be defined as pieces of music that came from the same style or "basic musical language."
Others, such as Allan F. Moore, state that ''genre'' and ''style'' are two separate terms, and that secondary characteristics such as subject matter can also differentiate between genres. A music genre or subgenre may also be defined by the musical technique
Musical technique is the ability of musical instrument, instrumental and Human voice, vocal musicians to exert optimal control of their instruments or vocal cords in order to produce the precise musical effects they desire. Improving one's tech ...
s, the style, the cultural context, and the content and spirit of the themes. Geographical origin is sometimes used to identify a music genre, though a single geographical category will often include a wide variety of subgenres. Timothy Laurie argues that "since the early 1980s, genre has graduated from being a subset of popular music studies to being an almost ubiquitous framework for constituting and evaluating musical research objects".
Musical technique is the ability of instrumental
An instrumental or instrumental song is music without any vocals, although it might include some inarticulate vocals, such as shouted backup vocals in a big band setting. Through Semantic change, semantic widening, a broader sense of the word s ...
and vocal musicians to exert optimal control of their instruments or vocal cords
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
to produce precise musical effects. Improving technique generally entails practicing exercises that improve muscular sensitivity and agility. To improve technique, musicians often practice fundamental patterns of notes such as the natural
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part ...
, minor
Minor may refer to:
Common meanings
* Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities.
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Mathematics
* Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to an ...
, major
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in musi ...
, and chromatic scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the ...
s, minor
Minor may refer to:
Common meanings
* Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities.
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Mathematics
* Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to an ...
and major triad
In music theory, a major chord is a chord that has a root, a major third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a major triad. For example, the major triad built on C, called a C major triad, has pitch ...
s, dominant and diminished seventh
In classical music from Western culture, a diminished seventh () is an interval (music), interval produced by Diminution, narrowing a minor seventh by a chromatic semitone,Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. ...
s, formula patterns and arpeggio
An arpeggio () is a type of Chord (music), chord in which the Musical note, notes that compose a chord are individually sounded in a progressive rising or descending order. Arpeggios on keyboard instruments may be called rolled chords.
Arpe ...
s. For example, triads and sevenths teach how to play chords with accuracy and speed. Scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
teach how to move quickly and gracefully from one note to another (usually by step). Arpeggios teach how to play broken chord
In Western music theory, a chord is a group of notes played together for their harmonic consonance or dissonance. The most basic type of chord is a triad, so called because it consists of three distinct notes: the root note along with interv ...
s over larger intervals. Many of these components of music are found in compositions, for example, a scale is a very common element of classical and romantic era compositions.
Heinrich Schenker
Heinrich Schenker (19 June 1868 – 14 January 1935) was an Austrian music theory, music theorist #Theoretical writings, whose writings have had a profound influence on subsequent musical analysis. His approach, now termed Schenkerian analysis ...
argued that musical technique's "most striking and distinctive characteristic" is repetition
Repetition may refer to:
*Repetition (rhetorical device), repeating a word within a short space of words
*Repetition (bodybuilding), a single cycle of lifting and lowering a weight in strength training
*Working title for the 1985 slasher film '' ...
. Works known as étude
An étude (; ) or study is an instrumental musical composition, designed to provide practice material for perfecting a particular musical skill. The tradition of writing études emerged in the early 19th century with the rapidly growing popu ...
s (meaning "study") are also frequently used for the improvement of technique.
Mathematics
Music theorists sometimes use mathematics to understand music, and although music has noaxiomatic
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or fi ...
foundation in modern mathematics, mathematics is "the basis of sound" and sound itself "in its musical aspects... exhibits a remarkable array of number properties", simply because nature itself "is amazingly mathematical". The attempt to structure and communicate new ways of composing and hearing music has led to musical applications of set theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies Set (mathematics), sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory – as a branch of mathema ...
, abstract algebra
In mathematics, more specifically algebra, abstract algebra or modern algebra is the study of algebraic structures, which are set (mathematics), sets with specific operation (mathematics), operations acting on their elements. Algebraic structur ...
and number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects constructed from integers (for example ...
. Some composers have incorporated the golden ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their summation, sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities and with , is in a golden ratio to if
\fr ...
and Fibonacci numbers
In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each element is the sum of the two elements that precede it. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted . Many writers begin the s ...
into their work. There is a long history of examining the relationships between music and mathematics. Though ancient Chinese, Egyptians and Mesopotamians are known to have studied the mathematical principles of sound, the Pythagoreans
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek co ...
(in particular Philolaus
Philolaus (; , ''Philólaos''; )
was a Greek Pythagorean and pre-Socratic philosopher. He was born in a Greek colony in Italy and migrated to Greece. Philolaus has been called one of three most prominent figures in the Pythagorean tradition and ...
and Archytas
Archytas (; ; 435/410–360/350 BC) was an Ancient Greek mathematician, music theorist, statesman, and strategist from the ancient city of Taras (Tarentum) in Southern Italy. He was a scientist and philosopher affiliated with the Pythagorean ...
) of ancient Greece were the first researchers known to have investigated the expression of musical scale
In music theory, a scale is "any consecutive series of notes that form a progression between one note and its octave", typically by order of pitch or fundamental frequency.
The word "scale" originates from the Latin ''scala'', which literal ...
s in terms of numerical ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
s.
set theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies Set (mathematics), sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory – as a branch of mathema ...
uses the language of mathematical set theory in an elementary way to organize musical objects and describe their relationships. To analyze the structure of a piece of (typically atonal) music using musical set theory, one usually starts with a set of tones, which could form motives or chords. By applying simple operations such as transposition and inversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ''Inversions'' (novel) by Iain M. Bank ...
, one can discover deep structures in the music. Operations such as transposition and inversion are called isometries
In mathematics, an isometry (or congruence, or congruent transformation) is a distance-preserving transformation between metric spaces, usually assumed to be bijective. The word isometry is derived from the Ancient Greek: ἴσος ''isos'' mea ...
because they preserve the intervals between tones in a set. Expanding on the methods of musical set theory, some theorists have used abstract algebra to analyze music. For example, the pitch classes in an equally tempered octave form an abelian group
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is commu ...
with 12 elements. It is possible to describe just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in thi ...
in terms of a free abelian group
In mathematics, a free abelian group is an abelian group with a Free module, basis. Being an abelian group means that it is a Set (mathematics), set with an addition operation (mathematics), operation that is associative, commutative, and inverti ...
.
Serial composition and set theory
In music theory, serialism is a method or technique ofcomposition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
* Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include ...
that uses a series of values to manipulate different musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian and American composer, music theorist, teacher and writer. He was among the first Modernism (music), modernists who transformed the practice of harmony in 20th-centu ...
's twelve-tone technique
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition. The technique is a means of ensuring that all 12 notes of the chromatic scale ...
, though his contemporaries were also working to establish serialism as one example of post-tonal
Atonality in its broadest sense is music that lacks a tonal center, or key. ''Atonality'', in this sense, usually describes compositions written from about the early 20th-century to the present day, where a hierarchy of harmonies focusing on a ...
thinking. Twelve-tone technique orders the twelve notes of the chromatic scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the ...
, forming a row
Row or ROW may refer to:
Exercise
* Rowing, or a form of aquatic movement using oars
* Row (weight-lifting), a form of weight-lifting exercise
Mathematics and informatics
* Row vector, a 1 × ''n'' matrix in linear algebra
* Row(s) in a table ( ...
or series and providing a unifying basis for a composition's melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figurativel ...
, harmony
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harm ...
, structural progressions, and variations
Variation or Variations may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Variation (astronomy), any perturbation of the mean motion or orbit of a planet or satellite, particularly of the moon
* Genetic variation, the difference in DNA among individual ...
. Other types of serialism also work with sets, collections of objects, but not necessarily with fixed-order series, and extend the technique to other musical dimensions (often called "parameters
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...
"), such as duration, dynamics, and timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
. The idea of serialism is also applied in various ways in the visual arts, design, and architecture;
"Integral serialism" or "total serialism" is the use of series for aspects such as duration, dynamics, and register as well as pitch. Other terms, used especially in Europe to distinguish post-World War II serial music from twelve-tone music and its American extensions, are "general serialism" and "multiple serialism".
Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Many of the notions were first elaborated by Howard Hanson
Howard Harold Hanson (October 28, 1896 – February 26, 1981)''The New York Times'' – Obituaries. Harold C. Schonberg. February 28, 1981 p. 1011/ref> was an American composer, conductor, educator and music theorist. As director for forty year ...
(1960) in connection with tonal music, and then mostly developed in connection with atonal music by theorists such as Allen Forte
Allen Forte (December 23, 1926 – October 16, 2014) was an American music theorist and musicologist. He was Battell Professor Emeritus of the Theory of Music at Yale University and specialized in 20th-century atonal music and music analysis.
...
(1973), drawing on the work in twelve-tone theory of Milton Babbitt. The concepts of set theory are very general and can be applied to tonal and atonal styles in any equally tempered tuning system, and to some extent more generally than that.
One branch of musical set theory deals with collections (sets and permutations) of pitches and pitch classes (pitch-class set theory), which may be ordered or unordered, and can be related by musical operations such as transposition, inversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ''Inversions'' (novel) by Iain M. Bank ...
, and complementation. The methods of musical set theory are sometimes applied to the analysis of rhythm as well.
Musical semiotics
 Music semiology (
Music semiology (semiotics
Semiotics ( ) is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter.
Semiosis is a ...
) is the study of signs as they pertain to music on a variety of levels. Following Roman Jakobson
Roman Osipovich Jakobson (, ; 18 July 1982) was a Russian linguist and literary theorist. A pioneer of structural linguistics, Jakobson was one of the most celebrated and influential linguists of the twentieth century. With Nikolai Trubetzk ...
, Kofi Agawu adopts the idea of musical semiosis being introversive or extroversive—that is, musical signs within a text and without. "Topics", or various musical conventions (such as horn calls, dance forms, and styles), have been treated suggestively by Agawu, among others. The notion of gesture
A gesture is a form of nonverbal communication or non-vocal communication in which visible bodily actions communicate particular messages, either in place of, or in conjunction with, speech. Gestures include movement of the hands, face, or othe ...
is beginning to play a large role in musico-semiotic enquiry.
:"There are strong arguments that music inhabits a semiological realm which, on both ontogenetic
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the stu ...
and phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
levels, has developmental priority over verbal language."
Writers on music semiology include Kofi Agawu (on topical theory, Heinrich Schenker
Heinrich Schenker (19 June 1868 – 14 January 1935) was an Austrian music theory, music theorist #Theoretical writings, whose writings have had a profound influence on subsequent musical analysis. His approach, now termed Schenkerian analysis ...
, Robert Hatten (on topic, gesture), Raymond Monelle
Raymond Monelle (19 August 1937 in Bristol, England – 12 March 2010 in Edinburgh, Scotland). was a music theorist, teacher, music critic, composer and jazz pianist. Monelle wrote three books, dozens of articles on music, and many music cr ...
(on topic, musical meaning), Jean-Jacques Nattiez
Jean-Jacques Nattiez (; born December 30, 1945) is a French musicologist and ethnomusicologist active in Canada, who is seminal figure in music semiology. Professor of musicology at the Université de Montréal since 1972,. he studied semio ...
(on introversive taxonomic analysis and ethnomusicological applications), Anthony Newcomb (on narrativity), and Eero Tarasti
Eero Aarne Pekka Tarasti (born 27 September 1948 in Helsinki) is a Finnish musicologist and semiotician, currently serving as Professor Emeritus of Musicology at the University of Helsinki. He has contributed significantly to the semiotics of ...
.
Roland Barthes
Roland Gérard Barthes (; ; 12 November 1915 – 25 March 1980) was a French literary theorist, essayist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. His work engaged in the analysis of a variety of sign systems, mainly derived from Western popu ...
, himself a semiotician and skilled amateur pianist, wrote about music in ''Image-Music-Text,'' ''The Responsibilities of Form,'' and ''Eiffel Tower,'' though he did not consider music to be a semiotic system.
Signs, meanings in music, happen essentially through the connotations of sounds, and through the social construction, appropriation and amplification of certain meanings associated with these connotations. The work of Philip Tagg
Philip Tagg (22 February 1944 – 9 May 2024) was a British musicologist, writer and educator. He was co-founder of the International Association for the Study of Popular Music (IASPM) and author of several influential books on popular music and ...
(''Ten Little Tunes'', ''Fernando the Flute'', ''Music's Meanings'') provides one of the most complete and systematic analysis of the relation between musical structures and connotations in western and especially popular, television and film music. The work of Leonard B. Meyer
Leonard B. Meyer (January 12, 1918 – December 30, 2007) was a composer, author, and philosopher. He contributed major works in the fields of aesthetic theory in music, and of compositional analysis.
Career
Meyer studied at Columbia Univ ...
in ''Style and Music'' theorizes the relationship between ideologies and musical structures and the phenomena of style change, and focuses on romanticism as a case study.
Education and careers
Society for Music Theory
The Society for Music Theory (SMT) is an American organization devoted to the promotion, development and engagement of music theory as a scholarly and pedagogical discipline. Founded in 1977 by a group of distinguished theorists, among them Alle ...
in the United States in 1977. In Europe, the French ''Société d'Analyse musicale'' was founded in 1985. It called the First European Conference of Music Analysis for 1989, which resulted in the foundation of the ''Société belge d'Analyse musicale'' in Belgium and the ''Gruppo analisi e teoria musicale'' in Italy the same year, the ''Society for Music Analysis'' in the UK in 1991, the ''Vereniging voor Muziektheorie'' in the Netherlands in 1999 and the ''Gesellschaft für Musiktheorie'' in Germany in 2000. They were later followed by the Russian Society for Music Theory in 2013, the Polish Society for Music Analysis in 2015 and the ''Sociedad de Análisis y Teoría Musical'' in Spain in 2020, and others are in construction. These societies coordinate the publication of music theory scholarship and support the professional development of music theory researchers. They formed in 2018 a network of European societies for Theory and/or Analysis of Music, thEuroT&AM
As part of their initial training, music theorists will typically complete a B.Mus or a
B.A.
A Bachelor of Arts (abbreviated B.A., BA, A.B. or AB; from the Latin ', ', or ') is the holder of a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate program in the liberal arts, or, in some cases, other disciplines. A Bachelor of Arts degree ...
in music (or a related field) and in many cases an M.A. in music theory. Some individuals apply directly from a bachelor's degree to a PhD, and in these cases, they may not receive an M.A. In the 2010s, given the increasingly interdisciplinary nature of university graduate programs, some applicants for music theory PhD programs may have academic training both in music and outside of music (e.g., a student may apply with a B.Mus. and a Masters in Music Composition or Philosophy of Music).
Most music theorists work as instructors, lecturers or professors in colleges, universities or conservatories. The job market for tenure-track professor positions is very competitive: with an average of around 25 tenure-track positions advertised per year in the past decade, 80–100 PhD graduates are produced each year (according to the Survey of Earned Doctorates) who compete not only with each other for those positions but with job seekers that received PhD's in previous years who are still searching for a tenure-track job. Applicants must hold a completed PhD or the equivalent degree (or expect to receive one within a year of being hired—called an "ABD", for " All But Dissertation" stage) and (for more senior positions) have a strong record of publishing in peer-reviewed journals. Some PhD-holding music theorists are only able to find insecure positions as sessional lecturer
Sessional lecturer or sessional instructor are contract faculty who hold full- or part-time teaching positions and may perform administrative duties but have no research responsibilities. Sessionals hold short-term contracts, typically running ...
s. The job tasks of a music theorist are the same as those of a professor in any other humanities discipline: teaching undergraduate and/or graduate classes in this area of specialization and, in many cases some general courses (such as Music appreciation
Music appreciation is a division of musicology that is designed to teach students how to understand and describe the contexts and creative processes involved in music composition.
The concept of music appreciation is often taught as a subset of ...
or Introduction to Music Theory), conducting research in this area of expertise, publishing research articles in peer-reviewed journals, authoring book chapters, books or textbooks, traveling to conferences to present papers and learn about research in the field, and, if the program includes a graduate school, supervising M.A. and PhD students and giving them guidance on the preparation of their theses and dissertations. Some music theory professors may take on senior administrative positions in their institution, such as Dean
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
* Dean Sw ...
or Chair of the School of Music.
See also
*List of music theorists
Music theory has existed since the advent of writing in ancient times. The earliest known practitioners include primarily Greek and some Chinese scholars. A few Indian sages such as Bharata Muni (''Natya Shastra'') are also credited with impor ...
* Music psychology
The psychology of music, or music psychology, is a branch of psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and/or musicology. It aims to explain and understand musical behaviour and experience, including the processes through which music is pe ...
* Musicology
Musicology is the academic, research-based study of music, as opposed to musical composition or performance. Musicology research combines and intersects with many fields, including psychology, sociology, acoustics, neurology, natural sciences, ...
* Theory of painting
The idea of founding a theory of painting after the model of music theory was suggested by Goethe in 1807 and gained much regard among the avant-garde artists of the 1920s, the Weimar culture period, like Paul Klee.
From Goethe to Klee
Goethe famo ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* *Aristoxenus
Aristoxenus of Tarentum (; born 375, fl. 335 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek Peripatetic school, Peripatetic philosopher, and a pupil of Aristotle. Most of his writings, which dealt with philosophy, ethics and music, have been lost, but one musi ...
(1902). ''Aristoxenou Harmonika stoicheia: The Harmonics of Aristoxenus'', Greek text edited with an English translation and notes by Henry Marcam. Oxford: The Clarendon Press.
*
* Bakshi, Haresh (2005). ''101 Raga-s for the 21st Century and Beyond: A Music Lover's Guide to Hindustani Music''. Victoria, British Columbia: Trafford. (ebook).
* Baur, John (2014). ''Practical Music Theory''. Dubuque: Kendall-Hunt Publishing Company.
* Benade, Arthur H. (1960). ''Horns, Strings, and Harmony''. Science Study Series S 11. Garden City, New York: Doubleday
* Ian Bent, Bent, Ian D., and Anthony Pople (2001). "Analysis." ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (musicologist), John Tyrrell. London: Macmillan.
* Benward, Bruce, Barbara Garvey Jackson, and Bruce R. Jackson. (2000). ''Practical Beginning Theory: A Fundamentals Worktext'', 8th edition, Boston: McGraw-Hill. . [First edition 1963]
* Benward, Bruce, and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice'', eighth edition, vol. 2. Boston: McGraw-Hill. .
* Billmeier, Uschi (1999). ''Mamady Keïta: A Life for the Djembé – Traditional Rhythms of the Malinké'', fourth edition. Kirchhasel-Uhlstädt: Arun-Verlag. .
* Benjamin Boretz, Boretz, Benjamin (1995). ''Meta-Variations: Studies in the Foundations of Musical Thought''. Red Hook, New York: Open Space.
* Both, Arnd Adje (2009). "Music Archaeology: Some Methodological and Theoretical Considerations". ''Yearbook for Traditional Music'' 41:1–11.
* Albert Bregman, Bregman, Albert (1994). ''Auditory Scene Analysis: The Perceptual Organization of Sound''. Cambridge: MIT Press. .
* Mark Brill, Brill, Mark (2012). "Music of the Ancient Maya: New Venues of Research". Paper presented at AMS-SW Conference Fall 2012. Texas State University
* Brown, James Murray (1967). ''A Handbook of Musical Knowledge'', 2 vols. London: Trinity College of Music.
* (Accessed 1 May 2010)
*
* Cheong, Kong F. (2012). "A Description of the Ceramic Musical Instruments Excavated from the North Group of Pacbitun, Belize". In ''Pacbitun Regional Archaeological Project, Report on the 2011 Field Season'', edited by Terry G. Powis, 15–29. Belmopan, Belize: Institute of Archaeology.
* Chernoff, John (1981). ''African Rhythm and African Sensibility: Aesthetics and Social Action in African Musical Idioms''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. .
* Civil, Miguel (2010). "The Lexical Texts in the Schøyen Collection". ''Cornell University Studies in Assyriology and Sumerology'' 12:203–214.
* Confucius (1999). ''The Analects of Confucius'', edited by Roger T. Ames and Henry Rosemont Jr. Ballantine Books. .
* Conrad, Nicholas J., Maria Malina, and Susanne C. Münzel (2009). "New Flutes Document the Earliest Musical Tradition in Southwestern Germany". ''Nature (journal), Nature'' 460, no. 7256 (6 August): 737–740.
* Robert P. Crease, Crease, Robert P. (2011). ''World in the Balance: The Historic Quest for an Absolute System of Measurement''. New York, London: W. W. Norton.
*
* Chase, Wayne (2006). ''How Music REALLY Works!'', second edition. Vancouver, Canada: Roedy Black Publishing. (book).
* Francesco d'Errico, d'Errico, Francesco, Christopher Henshilwood, Graeme Lawson, Marian Vanhaeren, Anne-Marie Tillier, Marie Soressi, Frederique Bresson, Bruno Maureille, April Nowell, Joseba Lakarra, Lucinda Backwell, Michele Julien (2003).Archaeological Evidence for the Emergence of Language, Symbolism, and Music – An Alternative Multidisciplinary Perspective
. ''Journal of World Prehistory'' 17, no. 1 (March): 1–70. * Despopoulos, Agamemnon, and Stefan Silbernagl (2003). ''Color Atlas of Physiology'', fifth edition. New York and Stuttgart: Thieme. . * * Dunbar, Brian (2010). ''Practical Music Theory: A Guide to Music as Art, Language, and Life''. Rochester, MN: Factum Musicae. . * * * Harnsberger, Lindsey C. (1997). "Articulation". ''Essential Dictionary of Music: Definitions, Composers, Theory, Instrument and Vocal Ranges'', second edition. The Essential Dictionary Series. Los Angeles: Alfred Publishing. . * * * Huang, Xiang-peng (黄翔鹏) (1989). "Wuyang Jiahu gudi de ceyin yanjiu (舞阳贾湖骨笛的测音研究)" [Pitch Measurement Studies of Bone Flutes from Jiahu of Wuyang County]. ''Wenwu'' (文物) [Cultural Relics], no. 1:15–17. Reprinted in 黄翔鹏文存 [Collected Essays of Huang Xiang-Peng], 2 vols, edited by Zhongguo Yishu Yanjiuyuan Yinyue Yanjiusuo (中国艺术研究院音乐研究所), 557–560. Ji'nan, China: Shandong Wenyi Chubanshe, 2007. . * Hung, Eric (2012).
Western University, Don Wright Faculty of Music: Tenure-Track Appointment in Music Theory
. Toronto: MusCan. * * Josephs, Jess L. (1967). ''The Physics of Musical Sound''. Princeton, Toronto, and London: D. Van Nostrand Company. * Stefan Kostka, Kostka, Stefan, and Dorothy Payne (2004). ''Tonal Harmony'', fifth edition. New York: McGraw-Hill. * Gerhard Kubik, Kubik, Gerhard (1998). ''Kalimba—Nsansi—Mbira. Lamellophone in Afrika''. Berlin: Museum fur Volkerkunde. . * Emmanuel Laroche, Laroche, Emmanuel (1955). ''Le palais royal d' Ugarit 3: Textes accadiens et hourrites des archives est, ouest et centrales''. Paris: C. Klincksieck * Lawn, Richard J., and Jeffrey L. Hellmer (1996). ''Jazz Theory and Practice''. [n.p.]: Alfred Publishing Co. . * Lee, Yuan-Yuan, and Sin-Yan Shen (1999). ''Chinese Musical Instruments''. Chinese Music Monograph Series. Chicago: Chinese Music Society of North America Press. . * Fred Lerdahl, Lerdahl, Fred (2001). ''Tonal Pitch Space''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. * Lloyd, Llewellyn S., and Hugh Boyle (1978). ''Intervals, Scales and Temperaments''. New York: St. Martin's Press. . * Lu, Liancheng (2005). "The Eastern Zhou and the Growth of Regionalism". In ''The Formation of Chinese Civilization'', edited by Sarah Allan, 203–248. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. . * Alfred Mann (musicologist), Mann, Alfred, J. Kenneth Wilson, and Peter Urquhart. n.d. "Canon (i)." ''Grove Music Online''. Oxford Music Online (Accessed 2 January 2011) . * * * *
Text at archive.org
* Miguel, Roig-Francoli (2011). ''Harmony in Context'', Second edition, McGraw-Hill Higher Education. . * * Nave, R. (n.d.).
, Hyperphysics website, Georgia State University (accessed 5 December 2014). * Steve Olson, Olson, Steve (2011).
A Grand Unified Theory of Music
. ''Princeton Alumni Weekly'' 111, no. 7 (9 February) (Online edition accessed 25 September 2012). * * Owen, Harold (2000). ''Music Theory Resource Book''. Oxford University Press. . * Ptolemy (1999). ''Harmonics'', translation and commentary by Jon Solomon. Mnemosyne, bibliotheca classica Batava: Supplementum 203. Leiden and Boston: Brill Academic Publications. . * Don Michael Randel, Randel, Don Michael (ed.) (2003). ''The Harvard Dictionary of Music'', fourth edition, 260–262. Cambridge: The Belknap Press for Harvard University Press. * * * Carl Seashore, Seashore, Carl (1933). ''Approaches to the Science of Music and Speech''. Iowa City: The university. * * * Sorce, Richard (1995). ''Music Theory for the Music Professional''. [N.p.]: Ardsley House. . * Stevens, S. S., J. Volkmann, and E. B. Newman (1937). "A Scale for the Measurement of the Psychological Magnitude Pitch". ''Journal of the Acoustical Society of America'' 8, no. 3:185–190. * Richard Taruskin, Taruskin, Richard (2009). ''Music from the Earliest Notations to the Sixteenth Century: The Oxford History of Western Music.'' Oxford University Press . * Taylor, Eric (1989). ''AB Guide to Music Theory, Part 1''. London: Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music. . * Taylor, Eric (1991). ''AB Guide to Music Theory, Part 2''. London: Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music. . * Thrasher, Alan (2000). ''Chinese Musical Instruments''. London and New York: Oxford University Press. . * Hugh Tracey, Tracey, Hugh (1969). "The Mbira Class of African Instruments in Rhodesia". ''African Music Society Journal'' 4, no. 3:78–95. * Dmitri Tymoczko, Tymoczko, Dmitri (2011). ''A Geometry of Music: Harmony and Counterpoint in the Extended Common Practice''. Oxford Studies in Music Theory. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. . * Martin Litchfield West, West, Martin Litchfield (1994). "The Babylonian Musical Notation and the Hurrian Melodic Texts". ''Music & Letters'' 75, no. 2 (May): 161–179 * Wu, Zhao (吴钊) (1991). "Jiahu guiling gudi yu Zhongguo yinyue wenming zhi yuan (贾湖龟铃骨笛与中国音乐文明之源)" [The relation of Jiahu bone flutes and turtle shell shakers to the origin of Chinese music]. ''Wenwu'' (文物) [Cultural Relics], no. 3: 50–55. * Wu, Zhongzian, and Karin Taylor Wu (2014). ''Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches: Tian Gan Dizhi, The Heart of Chinese Wisdom Traditions''. London and Philadelphia: Singing Dragon (Jessica Kingsley Publishers). * Yamaguchi, Masaya (2006). ''The Complete Thesaurus of Musical Scales'', revised edition. New York: Masaya Music Services. . * * *
External links
* Oscar van Dillen, Dillen, Oscar vanOutline of basic music theory
(2011) {{DEFAULTSORT:Music Theory Music theory, Music history Musicology