|
Transformation (music)
In music, a transformation consists of any operation or process that may apply to a musical variable (usually a set or tone row in twelve tone music, or a melody or chord progression in tonal music), or rhythm in composition, performance, or analysis. Transformations include multiplication, rotation, permutation (i.e. transposition, inversion, and retrograde), prolation ( augmentation, diminution) and combinations thereof. Transformations may also be applied to simpler or more complex variables such as interval and spectrum or timbre. See also * Developing variation * Identity (music) * Operation (music) * Permutation (music) * Transformational theory Transformational theory is a branch of music theory developed by David Lewin in the 1980s, and formally introduced in his 1987 work ''Generalized Musical Intervals and Transformations''. The theory—which models Transformation (music), musical t ... References Musical techniques {{Music-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition Example From Koch
Transposition may refer to: Logic and mathematics * Transposition (mathematics), a permutation which exchanges two elements and keeps all others fixed * Transposition, producing the transpose of a matrix ''A''T, which is computed by swapping columns for rows in the matrix ''A'' * Transpose of a linear map * Transposition (logic), a rule of replacement in philosophical logic * Transpose relation, another name for converse relation Games * Transposition (chess), different moves or a different move order leading to the same position, especially during the openings * Transposition table, used in computer games to speed up the search of the game tree Biology * Transposition (birth defect), a group of congenital defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of Tissue (biology), tissue or Organ (anatomy), organ ** Transposition of the great vessels, cardiac transposition, a congenital heart defect with malformation of any of the major vessels ** Transposition of teeth ** Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
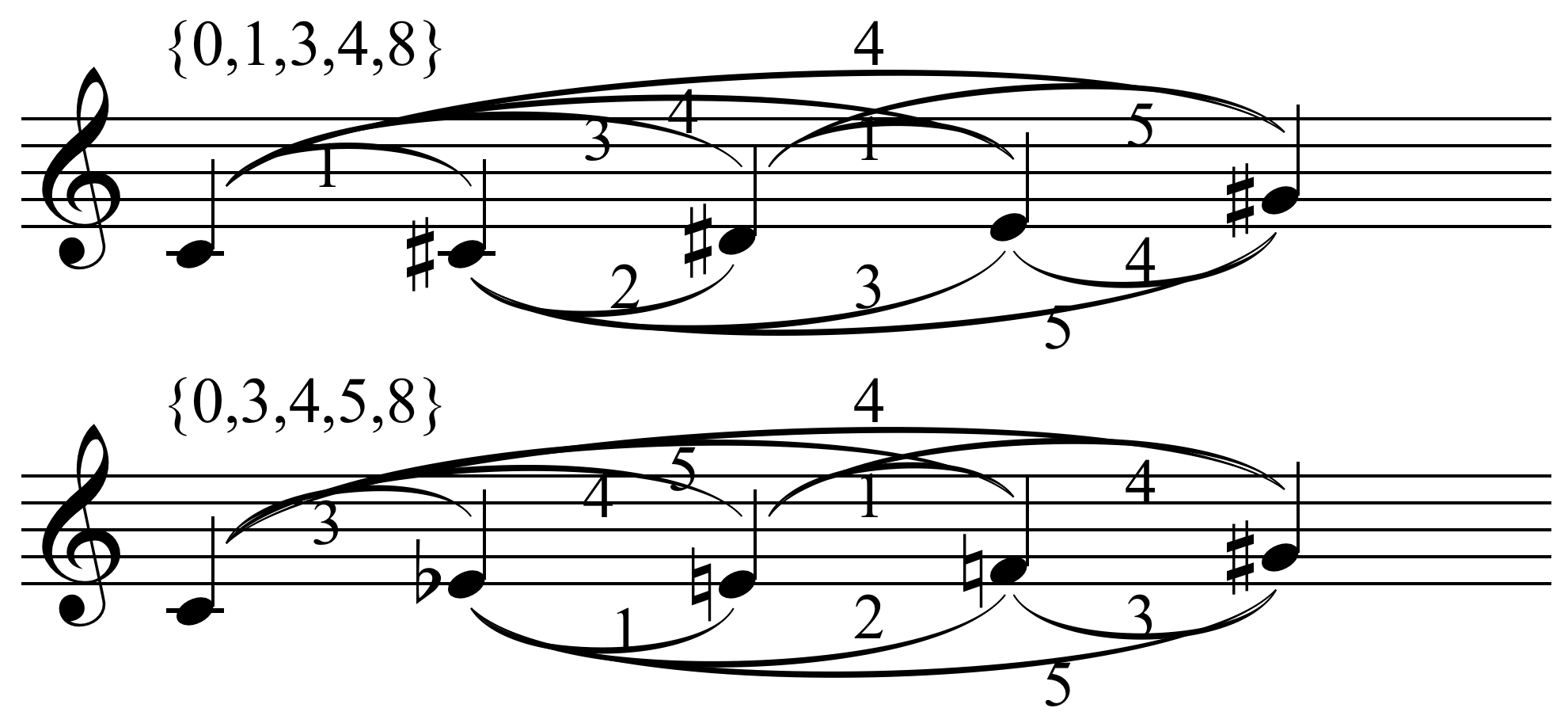
Transposition (music)
In music, transposition refers to the process or operation of moving a collection of notes ( pitches or pitch classes) up or down in pitch by a constant interval. For example, a music transposer might transpose an entire piece of music into another key. Similarly, one might transpose a tone row or an unordered collection of pitches such as a chord so that it begins on another pitch. The transposition of a set ''A'' by ''n'' semitones is designated by ''T''''n''(''A''), representing the addition ( mod 12) of an integer ''n'' to each of the pitch class integers of the set ''A''. Thus the set (''A'') consisting of 0–1–2 transposed by 5 semitones is 5–6–7 (''T''5(''A'')) since , , and . Scalar transpositions In scalar transposition, every pitch in a collection is shifted up or down a fixed number of scale steps within some scale. The pitches remain in the same scale before and after the shift. This term covers both chromatic and diatonic transpositions as follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation (music)
Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Howard Hanson first elaborated many of the concepts for analyzing tonal music. Other theorists, such as Allen Forte, further developed the theory for analyzing atonal music, drawing on the twelve-tone theory of Milton Babbitt. The concepts of musical set theory are very general and can be applied to tonal and atonal styles in any equal temperament tuning system, and to some extent more generally than that. One branch of musical set theory deals with collections ( sets and permutations) of pitches and pitch classes (pitch-class set theory), which may be ordered or unordered, and can be related by musical operations such as transposition, melodic inversion, and complementation. Some theorists apply the methods of musical set theory to the analysis of rhythm as well. Comparison with mathematical set theory Although musical set theory is often thought to involve the applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity (music)
In post-tonal music theory, identity is similar to identity in universal algebra. An identity function is a permutation or transformation which transforms a pitch or pitch class set into itself. Generally this requires symmetry. For instance, inverting an augmented triad or C4 interval cycle, 048, produces itself. Performing a retrograde operation upon the tone row 01210 produces 01210. Doubling the length of a rhythm while doubling the tempo produces a rhythm of the same durations as the original. In addition to being a property of a specific set, identity is, by extension, the "family" of sets or set forms which satisfy a possible identity. These families are defined by symmetry, which means that an object is invariant to any of various transformations; including reflection and rotation. George Perle George Perle (6 May 1915 – 23 January 2009) was an American composer and music theory, music theorist. As a composer, his music was largely atonality, atonal, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Variation
In musical composition, developing variation is a formal technique in which the variations are produced through the development of existing material. The term was coined by Arnold Schoenberg, twentieth-century composer and inventor of the twelve-tone technique, who believed it was one of the most important compositional principles since around 1750:Haimo, Ethan. 1990. ''Schoenberg's Serial Odyssey: The Evolution of his Twelve-Tone Method, 1914–1928'', p. 73, n8. Oxford ngland: Clarendon Press ; New York : Oxford University Press . The technique has also become associated with Johannes Brahms, whom Schoenberg believed to have used it in its "most advanced state". Schoenberg distinguished this from the "unravelling" procedures of contrapuntal tonal music, but developing variation may be related to other textures and to Schoenberg's own freely atonal pieces which employ a "method of atonal developing variation each chord, line, and harmony results from the subtle alteration a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe and a clarinet, both woodwinds). In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctive with its own unique tone color. Musicians distinguish instruments based on their varied timbres, even instruments playing notes at the same pitch and volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Series (music)
The harmonic series (also overtone series) is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a ''fundamental frequency''. Definite pitch, Pitched musical instruments are often based on an Acoustics, acoustic resonator such as a String (music), string or a column of air, which Oscillation, oscillates at numerous Normal mode, modes simultaneously. As waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, they reinforce and cancel one another to form standing waves. Interaction with the surrounding air produces audible sound waves, which travel away from the instrument. These frequencies are generally integer multiples, or harmonics, of the Fundamental frequency, fundamental and such multiples form the Harmonic series (mathematics), harmonic series. The fundamental, which is usually perceived as the lowest #Partial, partial present, is generally perceived as the Pitch (music), pitch of a musical tone. The musical timbre of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (music)
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord. In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. Intervals between successive notes of a scale are also known as scale steps. The smallest of these intervals is a semitone. Intervals smaller than a semitone are called microtones. They can be formed using the notes of various kinds of non-diatonic scales. Some of the very smallest ones are called commas, and describe small discrepancies, observed in some tuning systems, between enharmonically equivalent notes such as C and D. Intervals can be arbitrarily small, and even imperceptible to the human ear. In physical terms, an interval is the ratio between two sonic fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminution
In Western culture, Western music and music theory, diminution (from Medieval Latin ''diminutio'', alteration of Latin ''deminutio'', decrease) has four distinct meanings. Diminution may be a form of embellishment (music), embellishment in which a long Musical note, note is divided into a series of shorter, usually melodic, values (also called "Color (medieval music)#Coloration (ornamentation), coloration"; Ger. ''Kolorieren''). Diminution may also be the compositional device where a melody, theme (music), theme or motif (music), motif is presented in shorter note-values than were previously used. Diminution is also the term for the proportional shortening of the note value, value of individual note-shapes in mensural notation, either by color (medieval music), coloration or by a Mensural notation#Proportions and colorations, sign of proportion. A minor or perfect interval (music), interval that is narrowed by a chromatic semitone is a diminished interval, and the process may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmentation (music)
In Western music and music theory, augmentation (from Late Latin ''augmentare'', to increase) is the lengthening of a note or the widening of an interval. Augmentation is a compositional device where a melody, theme or motif is presented in longer note-values than were previously used. Augmentation is also the term for the proportional lengthening of the value of individual note-shapes in older notation by coloration, by use of a sign of proportion, or by a notational symbol such as the modern dot. A major or perfect interval that is widened by a chromatic semitone is an augmented interval, and the process may be called augmentation. Augmentation in composition A melody or series of notes is ''augmented'' if the lengths of the notes are prolonged; augmentation is thus the opposite of diminution, where note values are shortened. A melody originally consisting of four quavers (eighth notes) for example, is augmented if it later appears with four crotchets ( quarter notes) instead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolation Canon
In music, a prolation canon (also called a mensuration canon or proportional canon) is a type of canon, a musical composition wherein the main melody is accompanied by one or more imitations of that melody in other voices. Not only do the voices sing or play the same melody, they do so at different speeds (or ''prolations'', a mensuration term that dates to the medieval and Renaissance eras). Accompanying voices may enter either simultaneously or successively. If voices extend the rhythmic values of the leader (for example, by doubling all note values), a procedure known as augmentation, the resulting canon can be called an augmentation canon or canon by augmentation (''canon per augmentationem'') or sloth canon (recalling the slow movement of the sloth). Conversely, if they reduce the note values in diminution, it can be called a diminution canon or canon by diminution (''canon per diminutionem''). Examples Prolation canons are among the most difficult canons to write, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrograde (music)
A melodic line that is the reverse of a previously or simultaneously stated line is said to be its retrograde or cancrizans ( "walking backward", medieval Latin, from ''cancer'' "crab"). An exact retrograde includes both the pitches and rhythms in reverse. An even more exact retrograde reverses the physical contour of the notes themselves, though this is possible only in electronic music. Some composers choose to subject just the pitches of a musical line to retrograde, or just the rhythms. In twelve-tone music, reversal of the pitch classes alone—regardless of the melodic contour created by their registral placement—is regarded as a retrograde. In modal and tonal music In treatises Retrograde was not mentioned in theoretical treatises prior to 1500.Newes, p. 218. Nicola Vicentino (1555) discussed the difficulty in finding canonic imitation: "At times, the fugue or canon cannot be discovered through the systems mentioned above, either because of the impediment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |