Muisca on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



 The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are
The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are
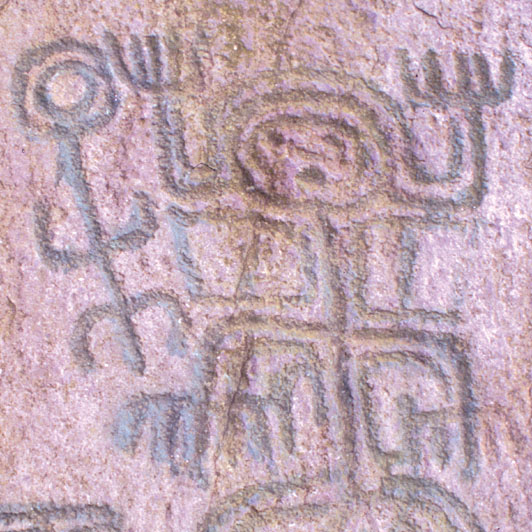
‚Äď Museo del Oro ‚Äď Biblioteca Lu√≠s √Āngel Arango The tribes were divided into ''Capitan√≠as'' (ruled by a capitan). There were two kinds: ''Great Capitania'' (''sybyn'') and ''Minor Capitania'' (''uta''). The status of ''Capitan'' was inherited by maternal lineage. :Confederation (''zipa'' or ''zaque'') ::‚Üí Priests ( Iraca) :::‚Üí Chiefdoms (Cacique) ::::‚Üí ''Capitan√≠a'' (Capitan) :::::‚Üí Sybyn ::::::‚Üí Uta * Territories of the ''zipa'': # Bacat√° rule: Teusaquillo, Tenjo, Subachoque, Facatativ√°, Tabio, Cota, Ch√≠a,
 ''Chibcha'', also known as ''muysca'', ''mosca'', or ''muysca cubun'', belongs to the
''Chibcha'', also known as ''muysca'', ''mosca'', or ''muysca cubun'', belongs to the
 The Muisca had an economy and society considered to have been one of the most powerful of the American Post-Classic stage, mainly because of the precious resources of the area: gold and emeralds. When the Spaniards arrived in Muisca territory, they found a prosperous state, with the Muisca Confederation controlling the mining of the following products:
*
The Muisca had an economy and society considered to have been one of the most powerful of the American Post-Classic stage, mainly because of the precious resources of the area: gold and emeralds. When the Spaniards arrived in Muisca territory, they found a prosperous state, with the Muisca Confederation controlling the mining of the following products:
* 




‚Äď accessed 05-05-2016Official website Guatavita
‚Äď accessed 05-05-2016 The remaining Muisca people in central Colombia also have their own seal.
The Origin of the Legend of El Dorado
/ref> This marks the earliest recorded use of the phrase, occurring just before his meeting with Jiménez de Quesada and the Muisca. In 1550, over ten years after the conquest, Jiménez de Quesada described the continued quest for El Dorado: "All the reports ... which set everyone's feet marching from the North Sea so excitedly ... later appeared to be the same thing, namely this kingdom of New Granada." Other Spanish references speak of El Dorado not as a golden land, but rather to chief whose body was anointed in gold powder as part of a ritual. The ''zipa'' offered gold and other treasures to the Guatavita goddess. To do so, the ''zipa'' covered himself with gold dust and washed it off in the lake while tossing gold trinkets into the waters. This tradition was well known outside the Confederation, as far as the


 When the Muisca structure disappeared under the Spanish Conquest, the territory of the Confederations of the ''zaque'' and ''zipa'' were included in a new political division within the Spanish colonies in America. The territory of the Muisca, located in a fertile plain of the Colombian Andes that contributed to make one of the most advanced South American civilizations, became part of the colonial region named Nuevo Reino de Granada. Much information about the Muisca culture was gathered by the Spanish administration and by authors such as Pedro de Aguado and Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita. The viceregal era contributed to the importance of Bogot√°, and people from the area would play an important role in the fights for independence and republican consolidation.
When the Muisca structure disappeared under the Spanish Conquest, the territory of the Confederations of the ''zaque'' and ''zipa'' were included in a new political division within the Spanish colonies in America. The territory of the Muisca, located in a fertile plain of the Colombian Andes that contributed to make one of the most advanced South American civilizations, became part of the colonial region named Nuevo Reino de Granada. Much information about the Muisca culture was gathered by the Spanish administration and by authors such as Pedro de Aguado and Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita. The viceregal era contributed to the importance of Bogot√°, and people from the area would play an important role in the fights for independence and republican consolidation.
 Writings on the Muisca have a long tradition, dating from the conquest era with Spanish chronicles, colonial-era Spanish religious and civil administrative records, the findings of modern archeologists and anthropologists, and revised interpretations by scholars in recent years. Unlike the Indigenous peoples of
Writings on the Muisca have a long tradition, dating from the conquest era with Spanish chronicles, colonial-era Spanish religious and civil administrative records, the findings of modern archeologists and anthropologists, and revised interpretations by scholars in recent years. Unlike the Indigenous peoples of
History of the Investigation of the Rock Art in Colombia
/ref> Recent archaeological work has also concentrated on the creation and composition of Muisca goldwork, with this data being made available for wider research.
The Art of Pre-Columbian Gold: The Jan Mitchell Collection
‚Äď The Metropolitan Museum of Art exhibition catalog ‚Äď available online as PDF * Muisca Indigenous Heritage ‚Äď development cooperation story of the Wikibook Development Cooperation Handbook
Development Cooperation Handbook
Muisca: "Chibchan Indians"
‚Äď
Books on the Muisca
‚Äď Ibero-American Institute ‚Äď
Nicely animated video about the Muisca and their religious origin
*
Animated video about the Spanish conquest of the Muisca ‚Äď Tisquesusa, Quemuenchatocha and Aquiminzaque
* * {{Authority control Pre-Columbian cultures Indigenous culture of the Americas Ethnic groups in Colombia Indigenous peoples in Colombia Prehistory of Colombia Articles containing video clips



 The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are
The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are indigenous peoples in Colombia
Indigenous Colombians (), also known as Native Colombians (), are the ethnic groups who have inhabited Colombia before the Spanish colonization of Colombia, in the early 16th century.
Estimates on the percentage of Colombians who are indigenou ...
and were a Pre-Columbian culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense that formed the Muisca Confederation
The Muisca Confederation was a loose confederation of different Muisca rulers (''zaques'', ''zipas'', ''iraca'', and ''tundama'') in the central Andes, Andean highlands of what is today Colombia before the Spanish conquest of the Americas, Spanis ...
before the Spanish colonization of the Americas
The Spanish colonization of the Americas began in 1493 on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (now Haiti and the Dominican Republic) after the initial 1492 voyage of Genoa, Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus under license from Queen Isabella ...
. The Muisca speak Muysccubun, a language of the Chibchan language family, also called ''Muysca'' and ''Mosca''. The first known contact with Europeans in the region was in 1537 during the Spanish conquest of New Granada.
In New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
, Spanish clerics and civil officials had a major impact on the Muisca, attempting to Christianize and incorporate them into the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
as subjects.
Postconquest Muisca culture underwent significant changes due to the establishment of the New Kingdom of Granada. Sources for the Muisca are far less abundant than for the Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire, also known as the Triple Alliance (, Help:IPA/Nahuatl, ÔŅĹj√©ňź ÉkaňźnŐ• tÕ°…¨a Ētoňźňąl√≥ňźjaňźnŐ• or the Tenochca Empire, was an alliance of three Nahuas, Nahua altepetl, city-states: , , and . These three city-states rul ...
of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
or the Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
and their incorporation to the Spanish Empire during the colonial era. In the New Kingdom of Granada and into the colonial era, the Muisca became "the official 'tribe' of the Colombian nation" and "a local version of the Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the ...
and Incas". Recent scholarship on the Muisca by archeologists, anthropologists, and historians is revising the understanding of the Muiscas' prehispanic and colonial era past.
History of the Muisca
Subgroupings were identified chiefly by their allegiances to three great Muisca rulers: the ''hoa'' in Hunza, ruling a territory roughly covering modern southern and northeastern Boyac√° and southern Santander; the ''psihipqua'' in Muyquyt√° and encompassing most of modern Cundinamarca, the westernLlanos
The Llanos ( Spanish ''Los Llanos'', "The Plains"; ) is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grasslands, ...
; and the ''iraca'', religious ruler of Suamox and modern northeastern Boyac√° and southwestern Santander.
The territory of the Muisca spanned an area of around from the north of Boyac√° to the Sumapaz P√°ramo and from the summits to the western portion of the Eastern Ranges. Their territory bordered the lands of the Panche in the west, the Muzo
Muzo () is a town and municipality in the Western Boyac√° Province, part of the department of Boyac√°, Colombia. It is widely known as the world capital of emeralds for the mines containing the world's highest quality gems of this type. Muzo ...
in the northwest, the Guane in the north, the Lache in the northeast, the Achagua in the east, and the Sutagao in the south.
At the time of the Spaniard invasion, the area had a large population, although the precise number of inhabitants is not known. Estimates vary from 1 million to over 3 million inhabitants. Their economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
was based on agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
mining, trading
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market (economics), market.
Traders generally negotiate throu ...
, metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
, and manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
.
Due to Spanish colonization, the population of the Muisca drastically decreased and assimilated into the general population. The descendants of the Muisca are often found in rural municipalities including Cota, Chía, Tenjo, Suba, Engativá
Engativ√° is the 10th locality of Bogot√°. It is located in the west of the city. This district is mostly inhabited by lower middle and working class residents.
Etymology
Engativ√° is either derived from ''Ingativ√°''; ''cacique'' Inga; "Land ...
, Tocancipá, Gachancipá, and Ubaté. A census by the Ministry of Interior Affairs in 2005 reports a total of 14,051 Muisca people in Colombia.
Much of the historical knowledge about the Muisca comes from the testimony of conquisadores and colonists: Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada
Gonzalo Jim√©nez de Quesada y Rivera, also spelled as Xim√©nez and De Quezada, (; 1509 ‚Äď 16 February 1579) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador in northern South America, territories currently known as Colombia. He explored the territory n ...
; Spanish poet, soldier, and Catholic priest Juan de Castellanos (16th century); Bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita; and the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
Pedro Simón (17th century).
More recently, Javier Ocampo López and Gonzalo Correal Urrego have contributed notable scholarship.
Knowledge of events up until 1450 is mainly derived from mythological contexts. Thanks to the ''Chronicles of the West Indies,'' we have descriptions of the final period of Muisca's history before the Spanish arrival.
Archeology
Excavations in the Altiplano Cundiboyacense (the highlands of Cundinamarca and Boyac√° departments) show evidence of human activity since the Archaic Period at the beginning of theHolocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
. Colombia has one of the most ancient archaeological sites of the Americas: El Abra, which is estimated to be approximately 13,000 years old. Other archaeological traces in the region of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense have led scholars to talk about an El Abra Culture: In Tibitó, tools and other lithic artifacts date to 9740 BCE; on the Bogotá savanna, especially at Tequendama Falls, other lithic tools dated a millennium later were found that belonged to specialized hunters. Human skeletons were found dating back to 5000 BCE, and an analysis demonstrated that the people were members of the El Abra culture.
Muisca era
Scholars agree that the group identified as Muisca migrated to the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in the Formative stage (between 1000 BCE and 500 CE), as shown by evidence found at Aguazuque and Soacha. Like the other formative-era cultures of America, the Muiscas were transitioning between being hunter-gatherers and becoming sedentary farmers. Around 1500 BCE, groups of agrarians with ceramic traditions came to the region from the lowlands. They had permanent housing and stationary camps, and worked the salty water to extract salt. In Zipacón, there is evidence of agriculture and ceramics; the oldest settlement of the highlands dates to 1270 BCE. Between 800 BCE and 500 BCE, a second wave of migrants came to the highlands. Their presence is identified by multicolor ceramics, housing, and farms. These groups were still in residence upon the arrival of the Spanish invaders. They left abundant traces of their occupation that have been studied since the 16th century, allowing scientists to reconstruct their way of life. The Muisca may have integrated with more ancient inhabitants, but the Muisca were the ones who molded the cultural profile and the social and political organization. Their language, a dialect ofChibcha
The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are indigenous peoples in Colombia and were a Pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia, Pre-Columbian culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense that formed the Muisca Confederation before the Spanish colonizati ...
, was very similar to those peoples of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta
The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta (English: ''Snow-Covered Mountain Range of Saint Martha'') is an isolated mountain range in northern Colombia, separate from the Andes range that runs through the north of the country. Reaching an elevation of ...
( Kogi, Ijka, Wiwa, and Kankuamo) and the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy ( U'wa).
Wars
''Zipa''Saguamanchica
Saguamanchica (died Chocont√°, 1490) was the second ruler (''zipa'') of Muyquyt√°, as of 1470. His '' zaque'' enemy ruling over the northern area of the Muisca territory was Michu√°.
Alternative spellings of his name are Sacuan Machica, Sagua ...
(ruled 1470 to 1490) was in a constant war against aggressive tribes such as the Sutagao, and especially the Panche, who would also make difficulties for his successors, Nemequene
Nemequene or Nemeguene (died 1514) was the third ruler (''zipa'') of Bacat√° as of 1490. His '' zaque'' counterpart ruling over the northern area of the Muisca territory was Quemuenchatocha.
Etymology
Nemequene in the Chibcha language of t ...
and Tisquesusa
Tisquesusa, also spelled Thisquesuza, Thysquesuca or Thisquesusha (referred to in the earliest sources as Bogot√°, the Elder) (died Facatativ√°, 1537) was the fourth and last independent ruler ('' psihipqua'') of Muyquyt√°, main settlement of t ...
. Kalina Caribs were also a permanent threat as rivals of the ''zaque'' of Hunza, especially for the possession of the salt mines of Zipaquirá, Nemocón and Tausa.
Political and administrative organization
The Muisca people were organized in aconfederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
that was a loose union of polities that each retained sovereignty. The confederation was not a kingdom, as there was no absolute monarch, nor was it an empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
, because it did not dominate other ethnic groups or peoples. It is hard to compare the Muisca Confederation with other American civilizations, such as the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
or the Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
empires as it was more similar to a confederation of states, such as the Achaean League
The Achaean League () was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era confederation of polis, Greek city-states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea (ancient region), Achaea in the northwestern Pelopon ...
. The Muisca Confederation was one of the biggest and best-organized confederations of tribes on the South American continent.
Every tribe within the confederation was ruled by a chief or a cacique
A cacique, sometimes spelled as cazique (; ; feminine form: ), was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, who were the Indigenous inhabitants of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles at the time of European cont ...
. Most of the tribes were part of the Muisca ethnic group, sharing the same language and culture and forming relations through trade. They united in the face of a common enemy. The army was the responsibility of the ''zipa'' or ''zaque''. G√ľeches, the traditional ancient warriors of the Muisca, made up the military.
The Muisca Confederation existed as the union of two lesser confederations. The southern confederation, headed by the ''zipa
When the Spain, Spanish arrived in the central Colombian highlands, the region was organized into the Muisca Confederation, which had two rulers; the ''Zipa'' was the ruler of the southern part and based in Funza, Muyquyt√°. The ''Zaque'' was the ...
'', had its capital at Bacat√° (now Bogot√°
Bogot√° (, also , , ), officially Bogot√°, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogot√°, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogot√° (; ) during the Spanish Imperial period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city, capital and largest city ...
). This southern polity included most of the Muisca population and held greater economic power.
The northern territory was ruled by the ''zaque'', and had its capital in Hunza, known today as Tunja. Although both areas had common political relations and affinities and belonged to the same tribal nation, rivalries still existed between them. Among the territories there were four chiefdoms: Bacat√°, Hunza, Duitama, and Sogamoso. The chiefdom was composed by localities.The place of religion in the Muisca social organization‚Äď Museo del Oro ‚Äď Biblioteca Lu√≠s √Āngel Arango The tribes were divided into ''Capitan√≠as'' (ruled by a capitan). There were two kinds: ''Great Capitania'' (''sybyn'') and ''Minor Capitania'' (''uta''). The status of ''Capitan'' was inherited by maternal lineage. :Confederation (''zipa'' or ''zaque'') ::‚Üí Priests ( Iraca) :::‚Üí Chiefdoms (Cacique) ::::‚Üí ''Capitan√≠a'' (Capitan) :::::‚Üí Sybyn ::::::‚Üí Uta * Territories of the ''zipa'': # Bacat√° rule: Teusaquillo, Tenjo, Subachoque, Facatativ√°, Tabio, Cota, Ch√≠a,
Engativ√°
Engativ√° is the 10th locality of Bogot√°. It is located in the west of the city. This district is mostly inhabited by lower middle and working class residents.
Etymology
Engativ√° is either derived from ''Ingativ√°''; ''cacique'' Inga; "Land ...
, Usme, Zipaquirá, Nemocón and Zipacón
# Fusagasug√° District: Fusagasug√°, Pasca and Tibacuy
# Ubaté District: Ubaté, Cucunubá, Simijaca, Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
# Guatavita District: Gachetá, Guatavita and Suesca, Chocontá, Teusacá, Sesquilé, Guasca, Sopó, Usaquén, Tuna, Suba
* Territories of the ''zaque'':
** Hunza rule: Soracá, Ramiriquí, Samacá, Machetá, Tenza, Tibiritá, Lenguazaque and Turmequé
* Territory of Tundama: Cerinza, Oicat√°, Onzaga, Sativanorte, Sativasur, Soat√°, Paipa, Tobasia
* Territory of Sugamuxi: Busbanz√°, Toca
TOCA, formally trading as BARC (TOCA) Ltd, is an organiser of motorsport events in the United Kingdom. The company organises and administers the British Touring Car Championship (BTCC) and the support series to the BTCC, sometimes known as the ...
, Pesca, Pisba, Tópaga
* Autonomous chiefdoms: Charal√°, Chipat√°, Tinjac√°, Saboy√°, Tacasquir√°
Muisca legislation was customary law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law".
Customary law (also, consuetudinary or unofficial law) exists wher ...
; that is, their rule of law was determined by long-extant customs with the approval of the ''zip'' or ''zaque''. This kind of legislation was suitable for a well-organized confederation system. Natural resources could not be privatized: woods, lakes, plateaus, rivers, and other natural resources were common goods.
Language
Chibchan languages
The Chibchan languages (also known as Chibchano) make up a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of these countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa R ...
. At the height of its expanse, the language was spoken across several regions of Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
and the north of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. The Tairona
Tairona or Tayrona was a Pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia, Pre-Columbian culture of Colombia, which consisted in a group of chiefdoms in the region of Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in present-day Cesar Department, Cesar, Magdalena Department, Mag ...
culture and the U'wa, related to the Muisca culture, speak similar languages, which encouraged trade. The Muisca used a form of hieroglyph
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters. ...
s for numbers.
Many Chibcha words were absorbed or "loaned" into Colombian Spanish:
* Geography: Many names of localities and regions were kept. In some cases, the Spanish named cities with a combination of Chibcha and Spanish words, such as Santa Fe de Bogot√° (Chibcha: "Bacat√°"). Most of the municipalities of the Boyac√° and Cundinamarca departments are derived from Chibcha names: Chocont√°, Sogamoso, Zipaquir√°, and many others.
* Fruits, such as curuba and uchuva.
* Relations: the youngest child is called ''cuba'', or ''china'' for a girl; ''muysca'' means people.
Economy
 The Muisca had an economy and society considered to have been one of the most powerful of the American Post-Classic stage, mainly because of the precious resources of the area: gold and emeralds. When the Spaniards arrived in Muisca territory, they found a prosperous state, with the Muisca Confederation controlling the mining of the following products:
*
The Muisca had an economy and society considered to have been one of the most powerful of the American Post-Classic stage, mainly because of the precious resources of the area: gold and emeralds. When the Spaniards arrived in Muisca territory, they found a prosperous state, with the Muisca Confederation controlling the mining of the following products:
* emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York ...
s: Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
is the primary producer of emeralds in the world
* copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
* coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
: the coal mines still operate today at Zipaquir√° and other sites. Colombia has some of the world's most significant coal reserves.
* salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
: there were mines in production at Nemocón, Zipaquirá, and Tausa
* gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
: gold was imported from other regions but was so abundant that it became a preferred material for Muisca handicrafts. The many handicraft works in gold and the ''zipa'' tradition of offering gold to the goddess Guatavita contributed to the legend of '' El Dorado''.
The Muisca traded their goods at local and regional markets with a system of barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''bareter'') is a system of exchange (economics), exchange in which participants in a financial transaction, transaction directly exchange good (economics), goods or service (economics), services for other goods ...
. Items traded ranged from basic necessities to luxury goods. The abundance of salt, emeralds, and coal brought these commodities to '' de facto'' currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
status.
Having developed an agrarian society, the people used terrace farming and irrigation in the highlands. Main products were fruits
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
, coca, quinoa
Quinoa (''Chenopodium quinoa''; , from Quechuan languages, Quechua ' or ') is a flowering plant in the Amaranthaceae, amaranth family. It is a herbaceous annual plant grown as a crop primarily for its edible seeds; the seeds are high in prote ...
, yuca and potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es.
Another major economic activity was weaving. The people made a wide variety of complex textiles. Scholar Paul Bahn said, "The Andean cultures mastered almost every method of textile weaving or decoration now known, and their products were often finer than those of today."




Culture
The Muisca were an agrarian and ceramic society of theAndes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
of the north of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. Their political and administrative organization enabled them to form a compact cultural unity with great discipline.
The contributions of the Muisca culture to the Colombian national identity have been many.
Heraldry
Pre-Columbian Muisca patterns appear in various seals of modern municipalities located on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, for instance Sop√≥ and Guatavita, Cundinamarca.Official website Sop√≥‚Äď accessed 05-05-2016Official website Guatavita
‚Äď accessed 05-05-2016 The remaining Muisca people in central Colombia also have their own seal.
Sports
The Muisca culture had certain sports which were part of their rituals. The ''turmequé'' game, also known as tejo, has survived and became a popular sport of Colombia. Also important were matches ofwrestling
Wrestling is a martial art, combat sport, and form of entertainment that involves grappling with an opponent and striving to obtain a position of advantage through different throws or techniques, within a given ruleset. Wrestling involves di ...
. The winner received a finely woven cotton blanket from the chief and was qualified as a guecha warrior.
Religion
Recent scholarship on the Muisca contends that Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita's 1688 ''Historia general'' of New Granada, has unduly shaped understandings of Muisca religion, saying that it was "full of confident assertions concerning a Muisca 'religion' with a pantheon of deities, creation stories, and visions of the afterlife, led from great temples by high priests -- some of whom were pictured, at great expense, in three richly illustrated pages that accompanied his book." Muisca priests were educated from childhood and led the main religious ceremonies. Only the priests could enter the temples. Besides the religious activities, the priests had much influence in the lives of the people, giving counsel in matters of farming or war. The religion originally includedhuman sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
, but the practice may have been extinct by the time of the Spanish conquest, as there are no first-hand Spanish accounts.
Oral tradition suggests that every family gave up a child for sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving.
Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Gree ...
, that the children were regarded as sacred and cared for until the age of 15, when their lives were then offered to the Sun-god, Sué.
Deities
* Sué, Suá, Zuhé or Xué (The Sun god): he is the father of the Muisca. Histemple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
was in Suamox, the sacred city of the Sun. He was the most venerated god, especially by the Confederation of the ''zaque'', who was considered his descendant. "was "full of confident assertions and visions of the afterlife, led from great temples by high priest --some of whom were pictured, at great expensse, in three richly illustrated title pages that accompied his book"
* Chía (The Moon-goddess): her temple was in what is today the municipality of Chía. She was widely worshipped by the Confederation of the ''zipa'', who was considered her son.
* Bochica: though not properly a god, he enjoyed the same status as one. He was a chief or hero eternized in the oral tradition. The land was flooded by a goddess
A goddess is a female deity. In some faiths, a sacred female figure holds a central place in religious prayer and worship. For example, Shaktism (one of the three major Hinduism, Hindu sects), holds that the ultimate deity, the source of all re ...
, a beautiful and sometimes mean woman, or by Chibchacum, protector of the farmers. Bochica listened to the complaints of the Muisca about floods. With his stick, he broke two rocks at the edge of the Tequendama Falls and all the water came out, forming a waterfall. Bochica punished Huitaca and Chibchacum: He made Huitaca an owl and made her hold up the sky. Chibchacum was tasked with holding up the Earth.
* Bachué: the mother of the Muisca people. It was said that a beautiful woman with a baby came out of Lake Iguaque. Bachué sat down at the bank of the lake and waited for the child to grow up. When he was old enough, they married and had many children, who were the Muisca. Bachué taught them to hunt, to farm, to respect the laws, and to worship the gods. Bachué was so good and loved that the Muisca referred to her as ''Furachoque'' (Good woman in Chibcha
The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are indigenous peoples in Colombia and were a Pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia, Pre-Columbian culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense that formed the Muisca Confederation before the Spanish colonizati ...
). When they became old, Bachué and her husband decided to go back to the deep of the lagoon. That day the Muisca were so sad, but at the same time very happy because they knew their mother was very happy. Other versions of the legend say that after stepping into the lagoon of Iguaque, Bachué ascended to the sky and became Chía; in other versions Chia and Bachué are two different figures.
Astronomy
The cult of the Muisca centered on two main deities; Sué for the Sun and Chía for the Moon. They developed a vigesimal (based on 20)calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
and knew exactly the timing of the summer solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest peri ...
(June 21), which they considered the Day of ''Sué'', the Sun god. The Sué temple was in Sogamoso, the sacred city of the Sun and the seat of the Iraca (priest). The Muisca name of the city, ''Suamox'' or ''Sugamuxi'', means "City of the Sun". On the solstice
A solstice is the time when the Sun reaches its most northerly or southerly sun path, excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around 20‚Äď22 June and 20‚Äď22 December. In many countries ...
, the ''zaque'' went to Suamox for a major festival where ritual offerings were made. It was the only day of the year when the ''zaque'' showed his face, as he was considered a descendant of the Sun god.
Mythology
The Muisca mythology is well documented. Many of the writers who contributed to the ''Chronicles of the West Indies'' were based in Bogot√°. They recorded many of the myths as they were interested in the traditions and culture of the conquered people. The Muisca territory became the seat of the colonial administration for the New Kingdom of Granada (Spanish: ''Nuevo Reino de Granada'').El Dorado
The origin of the legend of ''El Dorado'' (Spanish for "The Golden") in the early 16th century may originate with theMuisca Confederation
The Muisca Confederation was a loose confederation of different Muisca rulers (''zaques'', ''zipas'', ''iraca'', and ''tundama'') in the central Andes, Andean highlands of what is today Colombia before the Spanish conquest of the Americas, Spanis ...
. In 1539, Sebasti√°n de Belalc√°zar's treasurer, Gonzalo de la Pe√Īa, wrote that the expedition left Popay√°n towards Bogot√° "in search of a land called El Dorado".Trupp, T. L.The Origin of the Legend of El Dorado
/ref> This marks the earliest recorded use of the phrase, occurring just before his meeting with Jiménez de Quesada and the Muisca. In 1550, over ten years after the conquest, Jiménez de Quesada described the continued quest for El Dorado: "All the reports ... which set everyone's feet marching from the North Sea so excitedly ... later appeared to be the same thing, namely this kingdom of New Granada." Other Spanish references speak of El Dorado not as a golden land, but rather to chief whose body was anointed in gold powder as part of a ritual. The ''zipa'' offered gold and other treasures to the Guatavita goddess. To do so, the ''zipa'' covered himself with gold dust and washed it off in the lake while tossing gold trinkets into the waters. This tradition was well known outside the Confederation, as far as the
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
. Two small golden rafts were discovered in 1856 and 1969 that seem to confirm this ritual. Each was in the Muisca style of gold work, with a primary central chief surrounded by attendants. The first of these artifacts was destroyed in a fire, while the surviving raft can be seen in Bogot√°'s Museo del Oro (Museum of Gold).
The Spaniards were attracted by stories of a "city of gold" that did not exist. Indigenous people sometimes got rid of the avaricious Spaniards in that way, pointing them in the direction of other peoples. Lake Guatavita was explored by conquistadors who were looking for gold offerings from the ''zipa'' to the goddess. The legend grew until the term became a metaphor for any place where great wealth may be found or made.
Architecture
The Muisca did not construct large stone structures. They didn't use the abundant rock to leave monumental ruins as has happened with other American cultures. Their houses were built with clay, canes, and wood. The houses had a conical form, most of them to the point thatGonzalo Jiménez de Quesada
Gonzalo Jim√©nez de Quesada y Rivera, also spelled as Xim√©nez and De Quezada, (; 1509 ‚Äď 16 February 1579) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador in northern South America, territories currently known as Colombia. He explored the territory n ...
, founder of Bogot√°
Bogot√° (, also , , ), officially Bogot√°, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogot√°, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogot√° (; ) during the Spanish Imperial period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city, capital and largest city ...
, gave the area the name ''Valle de los Alc√°zares'' ("Valley of the Palaces"). The houses had small doors and windows, and the dwellings of the higher rank citizens were different. The Muisca used little furniture as they would typically sit on the floor.


The Spanish conquest
The conquest of the Muisca began with Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada's 1536 expedition up the Magdalena River into the Colombian highlands. There his men encountered the thriving expanse of rich villages spread across a lush plateau. The conquistadors proceeded to loot the Muisca's temples and capture their leaders, holding them for ransom to extract their whereabouts of their gold. Rivalries between the '' zaque'' and the ''zipa
When the Spain, Spanish arrived in the central Colombian highlands, the region was organized into the Muisca Confederation, which had two rulers; the ''Zipa'' was the ruler of the southern part and based in Funza, Muyquyt√°. The ''Zaque'' was the ...
'' were taken advantage of by the Spaniards as they conquered the heart of what would be Colombia. The presence of the Spaniards gave hope to both sovereigns that, were they to make one Confederation, they could prevail in a war against the Spaniards. But the Spaniards prevailed. The reaction of the chief leaders and the people did little to change the destiny of the Confederations. The Spanish executed the last Muisca sovereigns, Sagipa and Aquiminzaque, in 1539 and 1540 respectively.
In 1539, two other expeditions converged on the territory of the Muisca, led by Sebastián de Belalcázar and Nicolás de Federman, who were also searching for lands rich in gold. Despite Jiménez's early arrival, each tried to lay claim to the region. The three leaders traveled back to Spain together to have the dispute adjudicated in court.
In 1542 Gonzalo Suárez Rendón finally put down the last resistance. The territories of the Confederations were distributed as encomiendas among the soldiers of Belalcazar, Federmann, and Jiménez De Quesada. Later the Spanish Crown would elect Jiménez as the mayor of Bogotá, with the title ''adelantado de los cabildos de Santa Fe y Tunja''. Bogotá would later become the capital of the Spaniard's New Kingdom of Granada.
Last Muisca sovereigns
Under the colonial regime
 When the Muisca structure disappeared under the Spanish Conquest, the territory of the Confederations of the ''zaque'' and ''zipa'' were included in a new political division within the Spanish colonies in America. The territory of the Muisca, located in a fertile plain of the Colombian Andes that contributed to make one of the most advanced South American civilizations, became part of the colonial region named Nuevo Reino de Granada. Much information about the Muisca culture was gathered by the Spanish administration and by authors such as Pedro de Aguado and Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita. The viceregal era contributed to the importance of Bogot√°, and people from the area would play an important role in the fights for independence and republican consolidation.
When the Muisca structure disappeared under the Spanish Conquest, the territory of the Confederations of the ''zaque'' and ''zipa'' were included in a new political division within the Spanish colonies in America. The territory of the Muisca, located in a fertile plain of the Colombian Andes that contributed to make one of the most advanced South American civilizations, became part of the colonial region named Nuevo Reino de Granada. Much information about the Muisca culture was gathered by the Spanish administration and by authors such as Pedro de Aguado and Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita. The viceregal era contributed to the importance of Bogot√°, and people from the area would play an important role in the fights for independence and republican consolidation.
Independent Colombia
20th century
After independence in 1810, the new state dissolved many of the Indigenous reservations. The one in Tocancipá was dissolved in 1940. The one in Sesquilé was reduced to 10% of its original size. Tenjo was reduced to 54% of its original size after 1934, and the Indigenous lands in Suba, a northern region in modern-day Bogotá, which had been recognized and protected by the crown, were taken away by the republican governments following a strategy of suppression of the native culture and ethnic presence in the country's largest urban centres. The Reservation of Cota was re-established on land bought by the community in 1916, and then recognized by the 1991 constitution; the recognition was withdrawn in 1998 by the state and restored in 2006. In 1948 the state forbade the production ofchicha
''Chicha'' is a Fermentation, fermented (alcoholic) or non-fermented beverage of Latin America, emerging from the Andes and Amazonia regions. In both the pre- and post-Spanish conquest of Peru, Spanish conquest periods, corn beer (''chicha de jo ...
, a corn-based alcoholic drink. This was a blow to the culture and economy of the Muisca. The ban remained until 1991. Since then, the "Festival of the chicha, maize, life, and joy" is celebrated every year in Barrio La Perseverancia, a neighborhood in Bogot√° where most of the chicha is produced.
21st century
Since 1989, there has been a process of reconstruction of the Indigenous councils by the surviving members of the Muisca culture. Muisca Councils currently working are Suba, Bosa, Cota, Ch√≠a, and Sesquil√©. The councils had an Assembly in Bosa on 20‚Äď22 September 2002, called the ''First General Congress of the Muisca People''. In that congress, they founded the Cabildo Mayor del Pueblo Muisca, affiliated to the National Indigenous Organization of Colombia (ONIC). They proposed linguistic and cultural recuperation, defense of the territories nowadays occupied by others, and proposed urban and tourist plans. They support the communities of Ubat√©, Tocancip√°, Soacha, R√°quira, and Tenjo in their efforts to recover their organizational and human rights. The Muisca people of Suba opposed the drying up of the Tibabuyeswetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
and wanted to recover the Juan Amarillo wetland. They defended the natural reserves like ''La Conejera'', part of the Suba Hills that is considered by the Shelter's Council to be communal land. ''Suati'' Magazine (''The Song of the Sun'') is a publication of poetry, literature, and essays about Muisca culture.
The community of Bosa made important achievements in its project of natural medicine in association with the Paul VI Hospital and the District Secretary of Health of Bogot√°. The community of Cota has reintroduced the growing of quinua, and regularly barter their products at market.
Toward the end of 2006 there was a report on the Muisca population:
* Three Muisca councils: Cota, Chía, and Sesquilé, with a population of 2,318 persons
* in the Capital District 5,186 people are registered as belonging to the Muisca ethnic group
* in the localities of Suba and Bosa, 1,573 people are registered
* the report does not include the number of people of the Muisca ethnic group in the entire territory of the ancient Muisca Confederation or outside that territory. It does not include Muisca Creole persons, it is to say, those of mixed Muisca ancestry.
Sources on the Muisca and scholarly research
 Writings on the Muisca have a long tradition, dating from the conquest era with Spanish chronicles, colonial-era Spanish religious and civil administrative records, the findings of modern archeologists and anthropologists, and revised interpretations by scholars in recent years. Unlike the Indigenous peoples of
Writings on the Muisca have a long tradition, dating from the conquest era with Spanish chronicles, colonial-era Spanish religious and civil administrative records, the findings of modern archeologists and anthropologists, and revised interpretations by scholars in recent years. Unlike the Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
, the Muisca did not have a system of writing before the Spanish invasion in the sixteenth century and during the colonial era, so that the understanding of Muisca history and culture has largely been based non-native sources. A Spanish document named ‚ÄúEp√≠tome de la Conquista Del Nueva Rieno de Granada‚ÄĚ (Summary of the Conquest of the New Kingdom of Granada) provides what is considered the most complete description of Muisca culture. The author is unknown but is believed to be Gonzalo Jim√©nez de Quesada.
Spanish cleric Lucas Fern√°ndez de Piedrahita authored a major work the New Kingdom of Granada, the ''Historia general de las conquistas de; Nuevo Reyno de Granada, a la S.C.R.M. de D. Carlos Segundo'', 1688, which has shaped colonial era and, until recently, modern understandings of the Muisca. This work creates an image of the Precolombian Muisca, with powerful political structures and a unified religion and priestly hierarchy. Recent scholarship has re-examined early published writings and sought new sources in a variety of archives to posit a different understanding of the Muisca. The Muisca have been integral to the formation of national identity in Colombia, with Colombian scholar Carl Henrik Langebaek describing them as "the official 'tribe' of the Colombian nation" and "a local version of the Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the ...
and Incas". The interpretation of the sixt,eenth-century Spanish invasion has received new attention which departs from a Eurocentric, triumphalist narrative.
Since independence in the early nineteenth century, investigations into Muisca culture as part of national identity formation began. In 1849 president Tom√°s Cipriano de Mosquera invited Italian cartographer Agust√≠n Codazzi, who led the Geography Commission with Manuel Anc√≠zar and did descriptive studies of the national territory and an inventory of the archaeological sites. The result of the expedition was published in Bogot√° in 1889 as ''Peregrinaci√≥n Alfa''. Arg√ľello Garc√≠a pointed out that the goal of that expedition in the context of the new nation was to underline the pre-Hispanic societies and in that sense, they centered on the Muisca culture as the main model. A similar tendency can be found in the works of Ezequiel Uricoechea. An objection to that point of view came from Vicente Restrepo: his work ''Los chibchas antes de la conquista espa√Īola'' showed them as barbarians.
Miguel Triana, in his work ''La Civilizaci√≥n Chibcha'' suggested that the rock art symbols were writing. Wenceslao Cabrera Ort√≠z was the one who concluded that the Muisca were migrants to the highlands; in 1969 he published on this and reported about excavations at the El Abra archaeological site. Those publications opened a new era in the studies of the pre-Hispanic cultures in Colombia.Arg√ľello G., Pedro Mar√≠aHistory of the Investigation of the Rock Art in Colombia
/ref> Recent archaeological work has also concentrated on the creation and composition of Muisca goldwork, with this data being made available for wider research.
Named after the Muisca and their culture
Several (fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
) flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
and fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
found in Colombia in the area of the Muisca have been named after the people. Two volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
es on Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
's moon Io have been named after the Muisca religion and mythology.
Timeline of inhabitation of the Muisca area
See also
* Spanish conquest *Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
, Maya
Maya may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Mayan languages, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (East Africa), a p ...
, Muzo
Muzo () is a town and municipality in the Western Boyac√° Province, part of the department of Boyac√°, Colombia. It is widely known as the world capital of emeralds for the mines containing the world's highest quality gems of this type. Muzo ...
* New Kingdom of Granada, Indigenous peoples in Colombia
Indigenous Colombians (), also known as Native Colombians (), are the ethnic groups who have inhabited Colombia before the Spanish colonization of Colombia, in the early 16th century.
Estimates on the percentage of Colombians who are indigenou ...
:* Panche, Achagua, Guane, Guayupe, Lache, Tegua
*Tunjo
A ''tunjo'' (from Chibcha language, Muysccubun: ''chunso'') is a small anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic or zoomorphism, zoomorphic figure elaborated by the Muisca people, Muisca as part of their Muisca art, art. ''Tunjos'' were made of gol ...
References
Bibliography
* * * Université de Montréal. *Further reading
* *Boada Rivas, Ana María. 1999. "Organización social y económica en la aldea muisca de El Venado (Valle de Samacá, Boyacá)". ''Revista Colombiana de Antropología'' 25, 118-145. *Boada Rivas, Ana María. 2007. ''The Evolution of Social Hierarchy in a Muisca Chiefdom of the Northern Andes of Colombia/La evolución de jerarquía social en un cacicazgo muisca de los Andes septentrionales de Colombia''. Pittshburgh: Department of Anthropology, University of Pittsburgh; Bogotá: Instituto Colombiano de Antropología e Historia. * * * Cobo Betancourt, Juan F. (2024). '' The Coming of the Kingdom: The Muisca, Catholic Reform, and Spanish Colonialism in the New Kingdom of Granada''. Open access. Cambridge University Press. *Cousins, Karen. "Shapes of Love in the Miracle Testimonies of the Virgin of Chiquinquirá, New Kingdom of Granada, 1587 to 1694". ''Colonial Latin American Review'' 28, no. 3, (2019): 396-423. *Deardorff, Max. "The Politics of Devotion: Indigenous Spirituality and the Virgin of Chiquinquirá in the New Kingdom of Granada". ''Ethnohistory
Ethnohistory is the study of cultures and indigenous peoples customs by examining historical records as well as other sources of information on their lives and history. It is also the study of the history of various ethnic groups that may or may ...
'' 65, no. 3.(2018): 465-88.
*Francis, J. Michael. 2007. ''Invading Colombia: Accounts of the Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada Expedition of Conquest''. University Park: Penn State University Press.
*Frassani, Alessia. "La Virgen de Chiquinquirá y la religión muisca". ''Historia y sociedad'' no. 35 (2028) 61-86.
* Friede, Juan 1961: ''Los chibchas bajo la dominaci√≥n espa√Īola'' (tr.en. ''The Chibcha People under the Spaniard Rule''). Bogot√°: La Carreta
* Gamboa Mendoza, Jorge. 2004. "Caciques, encomenderos y sanctuarios en el Nuevo Reino de Granada: Reflexiones metodológicas sobre la ficción en los archivos: el proceso del cacique de Tota, 1574-1575". ''Colonial Latin American Review'' 13 (no. 2), 113-145.
* Gamboa Mendoza, Jorge. ''El cacicazgo muisca en los a√Īos posteriores a la Conquista : del sihipkua al cacique colonial, 1537-1575''. Bogot√°: Instituto Colombiano de Antropolog√≠a e Historia 2010
* Gamboa Mendoza, Jorge. ''Los muiscas y su incorporación a la monarquía castellana en el siglo XVI: Nuevas lecturas desde la Nueva Historia de la Conquista''. Tunja: Universidad Pedagógica y Tecnológica de Colombia 2016.
*
* González de Pérez, María Stella 1987: ''Diccionario y Gramática Chibcha (''Chibchan Dictionary and Grammar''). Manuscrito anónimo de la Biblioteca Nacional de Colombia''. Bogotá: Instituto Caro y Cuervo
* Enciclopedia de Colombia a su alcance Espasa Siglo (''Colombian Encyclopedia within reach ‚Äď Espasa Century''). Tomo 1 Bogot√°, Colombia 2003
* Hern√°ndez Rodr√≠guez Guillermo 1949: ''De los Chibchas a la Colonia y la Rep√ļblica'' (tr.en. ''From the Chibcha People to the Colony to the Republic''). Bogot√°: Ediciones Paraninfo, 1991
* Historia de Colombia (tr.en. ''History of Colombia''). Tomo 1 Zamora Editores, Bogot√°, Colombia 2003
* Gran Enciclopedia de Colombia Tematica. Tomos 1 y 11 Círculo de Lectores, Bogotá, Colombia 1994
* Fundación Misión Colombia: Historia de Bogota, Conquista y Colonia. Tomo 1 Salvat-Villegas editores, Bogotá, Colombia 1989
*
* Langebaek, Carl Henrik"Buscando Sacerdotes y encontrando chuques: sobre la organización religiosa de los cacicazgos muiscas". ''Revista de Antropología y Arqueología'' 6, 1990. no. 1.
* Langebaek, Carl Henrik. ''Los herederos del pasado : indígenas y pensamiento criollo en Colombia y Venezuela''. Bogotá: Universidad de los Andes: Ediciones Uniandes 2009
* Londo√Īo, Eduardo 1998: ''Los muiscas: una rese√Īa hist√≥rica con base en las primeras descripciones''. Bogot√°: Museo del Oro
* Llano Restrepo, María Clara y Marcela Campuzano 1994: ''La Chicha, una bebida fermentada a través de la historia''. Bogotá: Instituto Colombiano de Antropología
*
* Lleras P√©rez, Roberto. "Los Muiscas en la literatura hist√≥rica y antropolg√≠a: Qui√©n interpreta a qui√©n?" ''Bolet√≠n de Historia y Antig√ľedades ''. 92, no. 829 (2005), 307-338.
* Mu√Īoz Arbel√°ez, Santiago. ''Costumbres en disputa: Los muiscas y el Imperio espa√Īol en Ubaque, siglo XVI''. Bogot√°: Universidad de los Andes, Facultad de Ciencias Sociales, Departamento de Historia 2015.
* Mu√Īoz Arbel√°ez, Santiago. "The New Kingdom of Granada: The Making an Unmaking of Spain's Atlantic Empire, 1530-1620". PhD dissertation, Yale University 2018.
*
* Restrepo, Luis Fernando. ''El estado impostor: Apropiaciones literarias y culturales de la memoria de los muiscas y la América indígena''. Medellín: Editorial Universidad de Antioquia, 2013.
*
*
* Tovar Pinzón, Hermes 1980: ''La formación social chibcha''. Bogotá. CIEC
External links
The Art of Pre-Columbian Gold: The Jan Mitchell Collection
‚Äď The Metropolitan Museum of Art exhibition catalog ‚Äď available online as PDF * Muisca Indigenous Heritage ‚Äď development cooperation story of the Wikibook
Muisca: "Chibchan Indians"
‚Äď
Online Books Page
The Online Books Page is an index of e-text books available on the Internet. It is edited by John Mark Ockerbloom and is hosted by the library of the University of Pennsylvania. The Online Books Page lists over 2 million books and has several fe ...
Books on the Muisca
‚Äď Ibero-American Institute ‚Äď
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
*Nicely animated video about the Muisca and their religious origin
*
Animated video about the Spanish conquest of the Muisca ‚Äď Tisquesusa, Quemuenchatocha and Aquiminzaque
* * {{Authority control Pre-Columbian cultures Indigenous culture of the Americas Ethnic groups in Colombia Indigenous peoples in Colombia Prehistory of Colombia Articles containing video clips