Muhammad Bin Tughluq on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 – 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his
 Three days after the death of his father Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq, Muhammad bin Tughlaq ascended the throne of Tughlaq dynasty of
Three days after the death of his father Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq, Muhammad bin Tughlaq ascended the throne of Tughlaq dynasty of
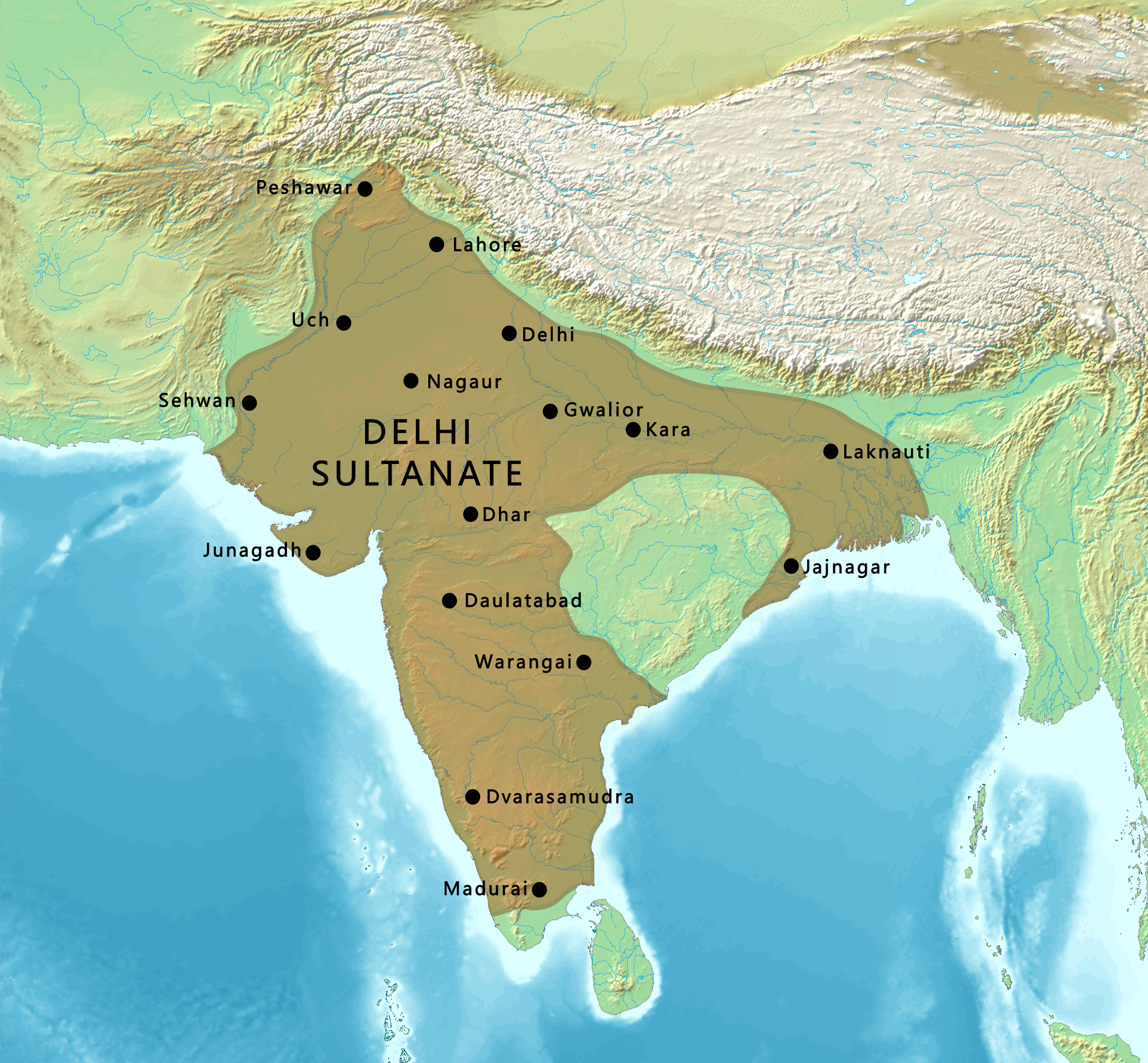 In 1327, Tughluq ordered to move his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad (also known as Devagiri) (in present-day
In 1327, Tughluq ordered to move his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad (also known as Devagiri) (in present-day
Muhammad ibn Tughluq
–
epithets
An epithet (, ), also a byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) commonly accompanying or occurring in place of the name of a real or fictitious person, place, or thing. It is usually literally descriptive, as in Alfred the Great, Suleima ...
, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February 1325 until his death in 1351. The sultan was the eldest son of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, founder of the Tughlaq dynasty. In 1321, the young Muhammad was sent by his father to the Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound ...
to fight a military campaign against the Kakatiya dynasty
The Kakatiya dynasty (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: Kākatīya) was a Andhras, Telugu dynasty that ruled most of eastern Deccan Plateau, Deccan region in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their ter ...
. In 1323, the future sultan successfully laid siege upon the Kakatiya capital in Warangal
Warangal () is a city in the Indian state of Telangana and the district headquarters of Warangal district. It is the second largest city in Telangana with a population of 811,844 per 2011 Census of India, and spreading over an .
Warangal serv ...
. This victory over King Prataparudra
Pratāparudra (r. c. 1289–1323) was the last monarch of the Kakatiya dynasty of India. He ruled the eastern part of Deccan Plateau, Deccan, with his capital at Warangal.
Prataparudra succeeded his grandmother Rudramadevi, Rudrama as the Kakat ...
ended the Kakatiya dynasty
The Kakatiya dynasty (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: Kākatīya) was a Andhras, Telugu dynasty that ruled most of eastern Deccan Plateau, Deccan region in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their ter ...
.
Muhammad ascended to the Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
throne upon his father's death in 1325. Muhammad bin Tughluq had an interest in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
. He was also skilled in several languages: Persian, Hindavi, Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
and Turkic. Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
, the famous traveler and jurist from Morocco, wrote in his book about his time at the Sultan's court.
Early life
Muhammad bin Tughluq was born to Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, who founded the Tughlaq dynasty after taking control of theDelhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.
. He is also known as Prince Fakhr Malik Jauna Khan, Juna Khan or Ulugh Khan. Jauna Khan remarked that he was "bound to all Indians by ties of blood and relation."
Ascension
 Three days after the death of his father Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq, Muhammad bin Tughlaq ascended the throne of Tughlaq dynasty of
Three days after the death of his father Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq, Muhammad bin Tughlaq ascended the throne of Tughlaq dynasty of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
on 4 February 1325. In his reign, he conquered Warangal
Warangal () is a city in the Indian state of Telangana and the district headquarters of Warangal district. It is the second largest city in Telangana with a population of 811,844 per 2011 Census of India, and spreading over an .
Warangal serv ...
(in present-day Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
, India), Ma'abar ( Kayalpatnam) and Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is ...
(Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
, India), and areas up to the modern day southern tip of the Indian state of Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
. In the conquered territories, Tughluq created a new set of revenue officials to assess the financial aspects of the area. Their accounts helped the audit in the office of the '' wazir''.
Muhammad bin Tughluq was also known for his tolerance for other religions. Several historians mention that the Sultan honored the Jain monk Jinaprabha Suri during the year 1328. Peter Jackson mentions that Muhammad was the only Sultan who participated in Hindu festivities.
Moving of the capital
 In 1327, Tughluq ordered to move his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad (also known as Devagiri) (in present-day
In 1327, Tughluq ordered to move his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad (also known as Devagiri) (in present-day Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
) in the Deccan region of India. Muhammad bin Tughlaq himself had spent a number of years as a prince on campaign in the southern states during the reign of his father. Daulatabad was also situated at a central place so the administration of both the north and the south could be possible. These elite colonists from Delhi were Urdu-speakers, who carried the Urdu language
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
to the Deccan. These immigrants included Hasan Gangu, a celebrated general who would later found the Bahmanid Empire.
A broad road was constructed for convenience. Shady trees were planted on both sides of the road; he set up halting stations at an interval of two miles. Provisions for food and water were also made available at the stations but most of the people died during the shifting as the ruler was not able to provide them with enough food and water for their survival. Tughluq established a khanqah at each of the stations where at least one sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
saint was stationed. A regular postal service was established between Delhi and Daulatabad. In 1329, his mother also went to Daulatabad, accompanied by the nobles. By around the same year, Tughluq summoned all the slaves, nobles, servants, ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
, sufis to the new capital. The new capital was divided into wards called ''mohalla'' with separate quarters for different people like soldiers, poets, judges, and nobles Grants were also given by Tughluq to the immigrants. Even though the citizens migrated, they showed dissent. According to Ibn Batuta's accounts, the reason for the transfer of capital was that Tughluq shifted the capital for protection from Mongol and Afghan Invasion which was later confirmed by Historian Garner Brown. In the process, many died on the road due to hunger and exhaustion as there were not enough resources. Moreover, coins minted in Daulatabad around 1333, showed that Daulatabad was "the second capital".
In 1334, there was a rebellion in Mabar, led by the North Indian Muslim soldier, Jalaluddin Ahsan Khan Kaithali, a native of Kaithal in North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
, who founded the Madurai Sultanate. While on his way to suppress the rebellion, there was an outbreak of bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of Plague (disease), plague caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and ...
at Bidar
Bidar ( ) is a city and headquarters of the Bidar district in Karnataka state of India. Bidar is a prominent place on the archaeological map of India, it is well known for architectural, historical religious and rich heritage sites. Pictures ...
due to which Tughluq himself became ill, and many of his soldiers died. While he retreated back to Daulatabad, Mabar and Dwarsamudra broke away from Tughluq's control. This was followed by a revolt in Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
. Fearing that the sultanate's northern borders were exposed to attacks, in 1335, he decided to shift the capital back to Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, forcing the citizens to return to their previous city. This caused many more deaths.
Impact
While most of the Medieval historians, including Barani and Ibn Battuta, tend to have implied that Delhi was entirely emptied (as is famously mentioned by Barani that not a dog or cat was left), it is generally believed that this is an exaggeration. Such exaggerated accounts simply imply thatDelhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
suffered a downfall in its stature and trade. Besides, it is believed that only the powerful and nobility suffered hardships if any. Two Sanskrit inscriptions dated 1327 and 1328 C.E. confirm this view and establish the prosperity of the Hindus of Delhi and its vicinity at that time.
Although this decision was unpopular among the Muslim elite, one impact of this decision was that Islamic rule in Deccan lasted centuries longer than Delhi's own unstable authority over the south. If not for Tughlaq's creation of a Muslim elite at Daulatabad, there would have been no stable Muslim power like the Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellio ...
to check the rising power of the Hindu Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
.
Expeditions
After the death ofGenghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
, one line of his descendants, the Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the l ...
, ruled over Turkistan and Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
and another branch of Hulagu Khan conquered present day Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
. However, at the time of Tughlaq, both of the dynasties were on the downfall, with conditions in Transoxiana unstable after the death of Tarmashirin. He was ambitious of annexing these kingdoms. He invited nobles and leaders from these regions and gave them grants. At that time many Afghan rulers gained independence and posed a significant threat to the Tughluq empire.
Tughluq raised an army of possibly up to 370,000 soldiers in 1329. Barani has written that Tughluq took no step to check the ability of the soldiers or the brand of horses. They were paid in one year advance, and after being kept idle for one year, Tughluq found it difficult to pay them. Therefore, he decided to disperse and dissolve the soldiers in 1329.
In 1333, Muhammad Bin Tughlaq led the Qarachil expedition to the kumaon region of modern-day Uttrakhand in India. Historians like Badauni and Ferishta wrote that Tughluq originally wanted to cross the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
and invade China. However, he faced local resistance in Kumaon. Dharm Chand is Pahadi Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
from kingdom of Kumaon ( ''including garhwal and some part of himachal'' ) defeated the army of Muhammad Bin Tughlaq which was not able to fight in the hills. Nearly all his 100,000 soldiers perished and were forced to retreat.
Death and ensuing collapse of the empire
Muhammad Bin Tughlaq died in 1351 on his way to Thatta,Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
, while he was campaigning in Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
against Taghi, a Turkic slave tribe. It was during his reign that the Sultanate of Delhi collapsed by twofold resistance. One was from Rajputs led by Hammir Singh of Mewar.
and the other from Harihara and Bukka of South India. While Rana Hammir Singh liberated the strategic Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
following the victory in Battle of Singoli in 1336, Harihara and Bukka established a new empire called Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
, by initially defeating and later ending Madurai Sultanate that was ruling the city of Madurai and its environs of South India on behalf of Delhi Sultanate. Several other south Indian rulers like Musunuri Kaapaaneedu, etc. also contributed to the downfall of the Islamic Sultanate of Delhi. To add to Tughluq's woes, his own generals rebelled against him. One of his generals, an Afghan or Turk Muslim named Hasan Gangu, would go on to form the Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellio ...
in the Deccan during the Rebellion of Ismail Mukh.
Token currency
Historian Ishwari Prasad writes that different coins of different shapes and sizes were produced by his mints which lacked the artistic perfection of design and finish. In 1330, after his failed expedition to Deogiri, he issued token currency; that iscoins
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
of brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. I ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
were minted whose value was equal to that of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
coins. Historian Ziauddin Barani felt that this step was taken by Tughluq as he wanted to annex all the inhabited areas of the world for which a treasury was required to pay the army. Barani had also written that the sultan's treasury had been exhausted by his action of giving rewards and gifts in gold. In the rural areas, officials like the '' muqaddams'' paid the revenue in brass and copper coins and also used the same coins to purchase arms and horses. As a result, the value of coins decreased, and, in the words of Satish Chandra, the coins became "''as worthless as stones''". This also disrupted trade and commerce. The token currency had inscriptions in Persian and Arabic marking the use of new coins instead of the royal seal and so the citizens could not distinguish between the official and the forged coins. Records show that the use of token currency had stopped by 1333 as Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
who came to Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
in 1334, wrote a journal which made no mention of this currency.
Religious policy
There are conflicting views expressed by historians on his religious tolerance. While visitors Ibn Battuta, Nunez and Firistha mention that Muhammed Bin Tughlaq showed intolerance to other religions, on the contrary, Peter Jackson mentions that Muhammed was the only Sultan who participated in Hindu festivities. Ibn Battuta mentions that the king of China (the Yuan Emperor) had sent an embassy to Muhammad for reconstruction of a sacked temple atSambhal
Sambhal (pronounced Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, sə̃bʰəl) is a city located in the Sambhal district of Uttar Pradesh, India. The city lies approximately 158 km (98 mi) east of New Delhi and 355 km (220 mi) north-west of the state capit ...
. The envoys were however denied with the statement that only those living in a Muslim territory who paid the ''jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
'' could be permitted to restore a temple. Firuz Shah Tughlaq had claimed that before his rule, idol-temples had been permitted to be rebuilt contrary to the Sharia.
The contemporaneous Jain authorities attests Muhammad cordial relations with the Jains and further showing favour to the Jain scholars.
Personality
Tughluq was a strict Muslim, maintaining his five prayers during a day, used to fast in Ramadan. According to 19th century CEBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
historian Stanley Lane-Poole, apparently courtesans had hailed Tughluq as a "man of knowledge" and had an interest in subjects like philosophy, medicine, mathematics, religion, Persian and Urdu/Hindustani poetry. In his "''Medieval India''", "He was perfect in the humanities of his day, a keen student of Persian poetry... a master of style, supremely eloquent in an age of rhetoric, a philosopher trained in Logic and Greek metaphysics, with whom scholars feared to argue, a mathematician and lover of science." Barani has written that Tughluq wanted the traditions of the '' nubuwwah'' to be followed in his kingdom. Even though he did not believe in mysticism, Chandra states that he respected the Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
saints, which is evident from the fact of his building of the mausoleum of the saint Nizamuddin Auliya at Nizamuddin Dargah. Critics have called him hasty in nature, owing to most of his experiments failing due to lack of preparation. Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
has also written that he depended on his own judgment and rarely took advice from others and has also criticized him for his giving of excessive gifts and "harsh punishments". He was famous because whenever a gift was bestowed upon him, he would give gifts worth three times the value to show his stature.
In popular culture
* A ''Tughlaqi Firman'' is a term regularly used in the Politics of the Indian Sub-continent. It is generally used to criticize laws, acts or orders passed by the local, State or National Government of the day by comparing it to a Royal diktat. * ''Tughlaq'', aKannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
play about his life was written by Indian writer Girish Karnad
Girish Karnad (19 May 1938 – 10 June 2019) was an Indian playwright, actor, film director, Kannada writer, and a Jnanpith awardee, who predominantly worked in Kannada, Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam and Marathi films. His rise as a playwr ...
in 1968.
* ''Muhammad bin Tughluq'' is a 1968 Indian Tamil-language political satire play written by Cho Ramaswamy (who also played the titular role).
* ''Muhammad bin Tughluq'' (1971) is an Indian satirical film in Tamil based on the play by Ramaswamy.
* ''Mohammad Bin Tuglaq'', an Indian Telugu-language film by B. V. Prasad released in 1972. It was a remake of the Tamil film.
* '' Thuglak'' is an Indian weekly news magazine published in Tamil. It was started by Cho Ramaswamy in 1970 and was named after the emperor (who also serves as its mascot).
* Doordarshan
Doordarshan (), abbreviated as DD, is India's State-owned enterprise, state-owned public broadcasting, public television broadcaster. Established by the Government of India on 15 September 1959, it is owned by the Ministry of Information and B ...
presented an episode with Muhammad bin Tughluq as a character in its series, '' Upanishad Ganga''.
* Tughlaq is a term still used in contemporary times to tease someone when they do something illogical or counter-intuitive.
* Indian historical fiction author Anuja Chandramouli wrote '' Muhammad Bin Tughlaq: Tale of a Tyrant'' on Tughlaq which was published by Penguin Random House
Penguin Random House Limited is a British-American multinational corporation, multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate publishing company formed on July 1, 2013, with the merger of Penguin Books and Random House. Penguin Books was or ...
.
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
* *Muhammad ibn Tughluq
–
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tughluq, Muhammad Bin
Muhammad Bin
1290s births
1351 deaths
14th-century Indian Muslims
People from Thatta District
14th-century Indian monarchs