Mughal Royal Family on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mughal dynasty () or the House of Babur (), was a Central Asian dynasty of
 Around 1700, the dynasty was ruling the wealthiest empire in the world, with also the largest military on earth. Mughals had approximately 24 percent share of the world's economy and a military of one million soldiers. At that time the Mughals ruled almost the whole of South Asia with over 150 million subjects, approximately one-quarter of the global population. The Dynasty's power rapidly dwindled during the 18th century with internal dynastic conflicts, incompatible monarchs, foreign invasions from Persians and Afghans, as well as revolts from Marathas, Sikh, Rajputs and regional Nawabs. The power of the last emperor was limited only to the Walled city of Delhi.
Around 1700, the dynasty was ruling the wealthiest empire in the world, with also the largest military on earth. Mughals had approximately 24 percent share of the world's economy and a military of one million soldiers. At that time the Mughals ruled almost the whole of South Asia with over 150 million subjects, approximately one-quarter of the global population. The Dynasty's power rapidly dwindled during the 18th century with internal dynastic conflicts, incompatible monarchs, foreign invasions from Persians and Afghans, as well as revolts from Marathas, Sikh, Rajputs and regional Nawabs. The power of the last emperor was limited only to the Walled city of Delhi.
Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these khanates eventually ass ...
origin that ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from the early 16th to the 19th century. The dynasty was a cadet branch of the Timurid dynasty
The Timurid dynasty, self-designated as Gurkani (), was the ruling dynasty of the Timurid Empire (1370–1507). It was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty or Barlās clan of Turco-Mongol originB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of I ...
, which had ruled in parts of Central Asia and Iran in the 14th and 15th centuries.
The Mughals originated as a branch of the Central Asian Timurid Dynasty
The Timurid dynasty, self-designated as Gurkani (), was the ruling dynasty of the Timurid Empire (1370–1507). It was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty or Barlās clan of Turco-Mongol originB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of I ...
which belonged to the Barlas tribe, which was a branch of the Borjigin
A Borjigin is a member of the Mongol sub-clan that started with Bodonchar Munkhag of the Kiyat clan. Yesugei's descendants were thus said to be Kiyat-Borjigin. The senior Borjigids provided ruling princes for Mongolia and Inner Mongolia u ...
Clan. Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
(1483–1530), the founder of the Mughal dynasty, was a direct descendant of the Asian conqueror Timur (Tamerlane)
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeated ...
through his father and Mongol emperor Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
through his mother. Many of the later Mughal emperors had significant Indian and Persian ancestry through marriage alliances.
During much of the Empire's history, the emperor functioned as the absolute Head of State, Head of government and Head of the military, while during its declining era much of the power shifted to the office of the Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
and the empire became divided into many regional kingdoms and princely states. However, even in the declining era, the Mughal Emperor continued to be the highest manifestation of sovereignty on the Indian subcontinent. Not only the Muslim gentry, but the Maratha
The Marathi people (; Marathi: , ''Marāṭhī lōk'') or Marathis (Marathi: मराठी, ''Marāṭhī'') are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are native to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-A ...
, Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
, and Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
leaders took part in ceremonial acknowledgements of the Emperor as the sovereign of India.
After the Indian Rebellion
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form ...
of 1857, the last Mughal emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar
Bahadur Shah II, (Abu Zafar Siraj-ud-din Muhammad; 24 October 1775 – 7 November 1862), usually referred to by his poetic title Bahadur Shah ''Zafar'' (; ''Zafar'' ), was the twentieth and last List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Mughal emp ...
was arrested by the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
and put on trial for treason. He was then deposed and exiled to Rangoon
Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ...
in Burma, where he spent the last days of his life, marking the formal abolishment of the Mughal Empire on 21 September 1857.
The British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
declared the establishment of the British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
the following year.
Name
History
The Mughal dynasty was founded in 1526 byBabur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
, a Timurid prince from Andijan
Andijan ( ), also spelt Andijon () and formerly romanized as Andizhan ( ), is a city in Uzbekistan. It is the administrative, economic, and cultural center of Andijan Region. Andijan is a district-level city with an area of . Andijan is the most ...
in the Fergana
Fergana ( uz-Latn-Cyrl, Fargʻona, Фарғона, ), () or Ferghana, also Farghana is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 320 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km southwest of A ...
Valley (present-day Uzbekistan), After losing his ancestral domains in Central Asia, Babur first established himself in Kabul and ultimately moved towards the Indian subcontinent. Mughal rule was interrupted for 16 years when Babur's son, Humayun
Nasir al-Din Muhammad (6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), commonly known by his regnal name Humayun (), was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from ...
briefly lost control of the empire to Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri (born Farid al-Din Khan; 1472 or 1486 – 22 May 1545), also known by his title Sultan Adil (), was the ruler of Bihar from 1530 to 1540, and Sultan of Hindustan from 1540 until his death in 1545. He defeated the Mughal Empire, ...
but later reclaimed it in 1555.
The Mughal imperial structure was founded by Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
the Great around the 1580s which lasted until the 1740s, until shortly after the Battle of Karnal. During the reigns of Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
and Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
, the dynasty reached its zenith in terms of geographical extent, economy, military and cultural influence.
 Around 1700, the dynasty was ruling the wealthiest empire in the world, with also the largest military on earth. Mughals had approximately 24 percent share of the world's economy and a military of one million soldiers. At that time the Mughals ruled almost the whole of South Asia with over 150 million subjects, approximately one-quarter of the global population. The Dynasty's power rapidly dwindled during the 18th century with internal dynastic conflicts, incompatible monarchs, foreign invasions from Persians and Afghans, as well as revolts from Marathas, Sikh, Rajputs and regional Nawabs. The power of the last emperor was limited only to the Walled city of Delhi.
Around 1700, the dynasty was ruling the wealthiest empire in the world, with also the largest military on earth. Mughals had approximately 24 percent share of the world's economy and a military of one million soldiers. At that time the Mughals ruled almost the whole of South Asia with over 150 million subjects, approximately one-quarter of the global population. The Dynasty's power rapidly dwindled during the 18th century with internal dynastic conflicts, incompatible monarchs, foreign invasions from Persians and Afghans, as well as revolts from Marathas, Sikh, Rajputs and regional Nawabs. The power of the last emperor was limited only to the Walled city of Delhi.
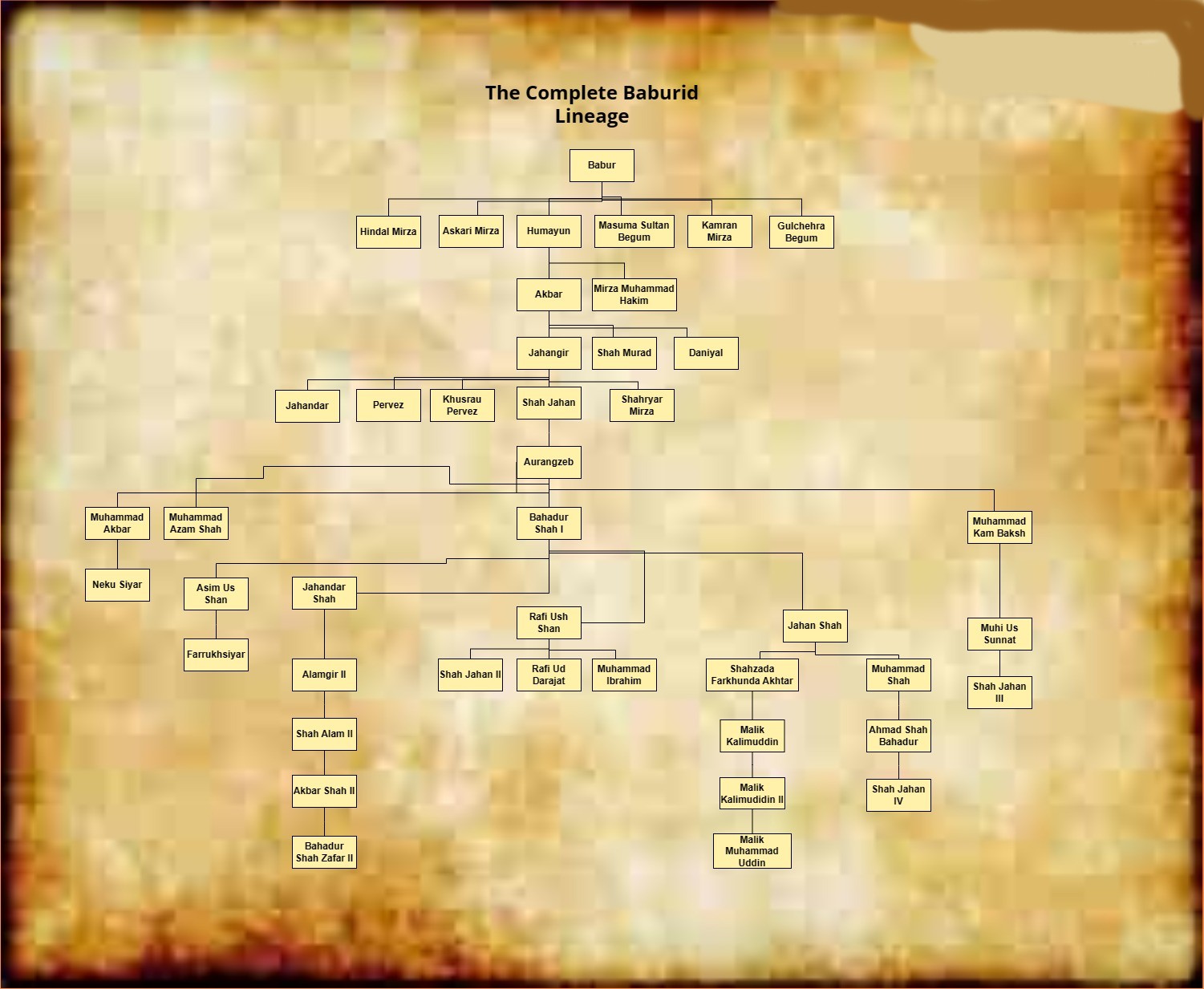
Dynastic Succession
The Mughals followed theTurco-Mongol tradition
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these khanates eventually as ...
of not following a strict rule of primogeniture
Primogeniture () is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn Legitimacy (family law), legitimate child to inheritance, inherit all or most of their parent's estate (law), estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some childre ...
, instead the throne was open to contest by any male member of the dynasty, even though an heir apparent was appointed several times in dynastic history. This led to internal struggles, civil wars and even fratricide
Fratricide (; – the assimilated root of 'to kill, cut down') is the act of killing one's own brother.
It can either be done directly or via the use of either a hired or an indoctrinated intermediary (an assassin). The victim need not be ...
between the princes who wanted to win the Peacock Throne
The Peacock Throne ( Hindustani: ''Mayūrāsana'', Sanskrit: मयूरासन, Urdu: تخت طاؤس, , ''Takht-i Tāvūs'') was the imperial throne of Hindustan. The throne is named after the dancing peacocks at its rear and was the seat ...
. To go into greater detail about these processes, the history of succession between Emperors can be divided into two eras: Era of Imperial successions (1526–1713) and Era of Regent successions (1713–1857).
Disputed claimants to the dynasty
After the fall of Delhi in 1857 and the exile of Bahadur Shah Zafar II to Rangoon, the Mughal dynasty effectively ceased to exist as a ruling power. With the formal abolition of the Mughal Empire by the British in 1858, members of the imperial family were either imprisoned, exiled, or scattered across the subcontinent. The Mughal Emperors practiced polygamy. Besides their wives, they also had several concubines in their harem, who produced children. This makes it difficult to identify all the offspring of each emperor. A man in India named Habeebuddin Tucy claims to be a descendant of Bahadur Shah II, but his claim is not universally believed. Another woman named Sultana Begum who lives in the slums of Kolkata has claimed that her late husband, Mirza Mohammad Bedar Bakht was the great-grandson of Bahadur Shah II. After 1858, the British did not agree on restoring any sort of Mughal authority. However a few descendants were recognized as the Representatives of the Mughal Dynasty, gaining pensions and symbolic recognition, although they held no actual political power. In the years since, various individuals have claimed Mughal descent, occasionally gaining Media attention, but these claims are disputed and mostly incorrect without legal or official standing. Nevertheless, certain branches of the family were recognized by the British and the Governments of India and Pakistan, and some descendants to this day are regarded as the symbolical and ceremonial heirs of the Mughal Empire.Heads of the Mughal Dynasty (Since 1857)
References
Further reading
* {{cite book , last=Asher , first=Catherine Ella Blanshard , year=2003 , orig-year=First published 1992 , title=Architecture of Mughal India , series=The New Cambridge History of India
''The New Cambridge History of India'' is a major multi-volume work of historical scholarship published by Cambridge University Press. It replaced '' The Cambridge History of India'' published between 1922 and 1937.
The new history is being publi ...
, volume=I:4 , publisher=Cambridge University Press , page=368 , isbn=978-0-521-26728-1
Emperors of the Mughal Empire
Mughal nobility
Maturidis
Dynasties of India