Mouse embryonic fibroblast on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

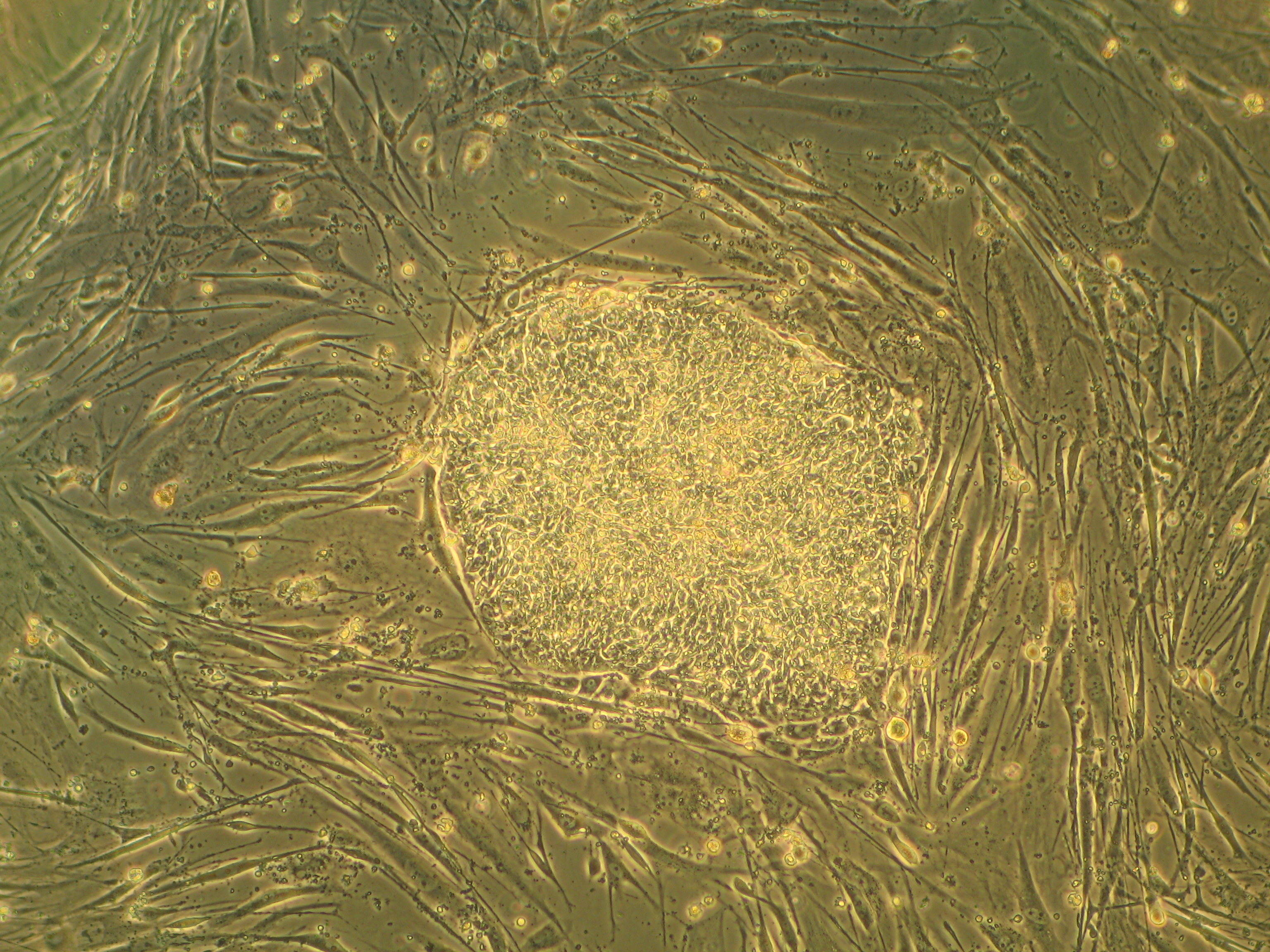 Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) are a type of
Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) are a type of

fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and ...
prepared from mouse embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
. MEFs show a spindle shape when cultured ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'', a typical feature of fibroblasts.
The MEF is a limited cell line. After several transmissions, MEFs will senesce and finally die off. Nevertheless, researchers can use several strategies, like virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
infection or repeated transmission to immortalize MEF cells, which can let MEFs grown indefinitely in spite of some changes in characters.
MEFs are widely used in life science researches, especially in stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
biology.
Preparation and culture
To prepare MEFs, pregnant female mice are needed. After killing the female mouse, the researcher should incise its stomach and then detach the embryo from theplacenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
in a Biosafety Cabinet. Then the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and head should be taken out. Finally digest the remains by enzymes to obtain single isolated cells and culture the cells in a tissue culture
Tissue culture is the growth of tissue (biology), tissues or cell (biology), cells in an artificial medium separate from the parent organism. This technique is also called micropropagation. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-s ...
dishes. MEF cells can be cultured ''in vitro'' in DMEM medium with 10% FBS. To transmit MEFs, researches should use trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
to digest the cells (making them detach from the surface) and transmit 1/5 cells digested into a new dish.
Application in biology
In 1962, George Todaro and Howard Green, two researchers inNew York University
New York University (NYU) is a private university, private research university in New York City, New York, United States. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded in 1832 by Albert Gallatin as a Nondenominational ...
, immortalized MEFs by repeated transmission. These cells developed into the commonly used cell line NIH 3T3.
MEFs treated by mitomycin or gamma rays (such treatment makes MEF stop mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
) are widely used as feeder in embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4� ...
culture because they can mimic the microenvironment in embryo.
In 2006, Shinya Yamanaka reprogrammed MEFs into iPSCs by introducing 4 factors, which is remarkable in the development of stem cell biology.
See also
*Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and ...
*Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4� ...
References
{{reflist, 2 Rodent cell lines