Mood Swing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of mood. Such changes can play a positive or a disruptive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as part of a mental illness, such as
A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of mood. Such changes can play a positive or a disruptive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as part of a mental illness, such as
Measurement innovation: studies on smartphone-based ecological momentary assessment in depression
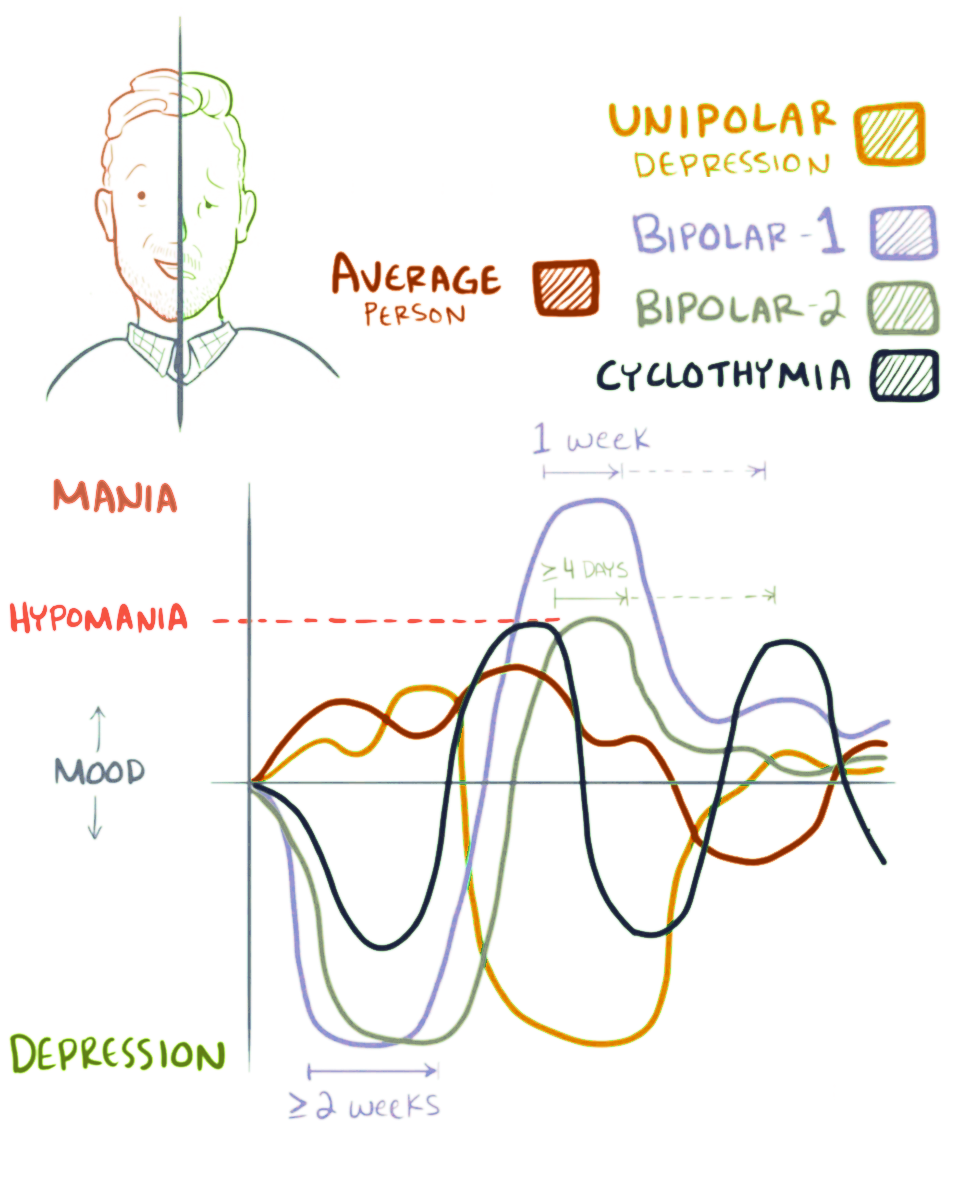
VU Research Portal.ISBN 978-94-93270-96-1."Mood dynamics are the patterns that characterize fluctuations in a person's mood 4 Mood dynamics are often operationalized by a combination of "mood variability" and "emotional inertia" 5,66 # Mood swings in cyclothymia: Mood swings occur episodically and aperiodic within 2 years or more at a moderate degree and frequently. Characterized by coexisting with anxiety, persistence, rapid shift, intense, impulsive, heightened by sensitivity and reactivity to external stimuli. # Mood swings in bipolar II: Episodic, hypomanic (severe degree) episodes occur continuously for 4 days, depression episodes for weeks, and sometimes erratic episodes at moderate degree in between episodes. # Mood swings in bipolar I: Episodic, manic episodes (severe degree) occur continuously for 7 days, depressive episodes for weeks,Last, C. G. (2009). When Someone You Love Is Bipolar: Help and Support for You and Your Partner. Ukraina: Guilford Publications."''Research indicates that bipolar II depressions persist for longer periods of time than bipolar I depressions, nearly twice as long (1 year versus 6 months)."'' and sometimes erratic episodes at moderate degree in between episodes. Alterations in bipolar I and II can be ''rapid cyclic'', which means changes of mood happen 4 times or more within a year. Symptoms of manic and hypomanic episodes are similar between bipolar I and bipolar II, just different in degree of intensity. # Mood swings in Premenstrual symptoms (PMS): Episodically at mild to severe degree in the menses period, occur gradually or rapidly, start 7 days before and decrease at the onset of menses. Characterized by angry outbursts, depression, anxiety, confusion, irritability or social withdrawal. # Mood swings in borderline personality disorder (BPD): Mood changes erratically with episodic mood swings. Mood swings fluctuate in rapid shifts for hours or days, not persistent, sensitive and heightened negative mood (e.g. irritability) by external stimuli. Mood appears in the form of high intensity of irritability, anxiety, and moderate degree depression (characterized by hostility, anger towards self, loneliness, isolation, related with relationships, emptiness or boredom). # Mood swings in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) : Mood changes erratically and mood swings occur episodically, sometimes several times a day in rapid shifts.FW, Reimherr & Marchant, Barrie & Olsen, John & C, Halls & Kondo, Douglas & ED, Lyon & Robison, Reid. (2010)
Emotional dysregulation as a core feature of adult ADHD: Its relationship with clinical variables and treatment response in two methylphenidate trials
Journal of ADHD and Related Disorders. 1. 53-64.
Graph
Characterized by a mild to moderate degree of irritability, related to the environment, impulsiveness (impatience to get rewards). In adult ADHD, high mood appears as excitement and low mood appears as boredom. # Mood swings in schizophrenia: Although schizophrenia has flat emotions, a study in 2021 based on ALS-SF measures, Margrethe Collier et al., found that the score pattern of schizophrenia is similar to bipolar I. The alteration being related to delusions or hallucinations, mood changes that occur internally may be difficult to express externally ( blunt affect), and heightened by external stimuli. # Mood swings in major depressive disorder (MDD): Various mood patterns, and mood changes erratically. Mood swings occur episodically and fluctuate in moderate high mood and severe low mood. Characterized by having high negative affect (bad mood) most of the time, particularly in melancholic subtype. And also positive diurnal variation mood (bad mood in the morning, good mood in the evening), sensitivity to negative stimulation and mixed symptoms in some people, etc. # Mood swings in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Mood changes erratically with episodic mood swings rising in the period of recovery process. Characterized by temporary fluctuations in negative affect (anxiety, irritability, shame, guilt) and self-esteem, reactive to environmental reminders, difficulty to control emotions, hyperarousal symptoms, etc.
Understanding mood swings
{{Mood disorders Borderline personality disorder Mood disorders Symptoms and signs of mental disorders
 A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of mood. Such changes can play a positive or a disruptive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as part of a mental illness, such as
A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of mood. Such changes can play a positive or a disruptive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as part of a mental illness, such as bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
, where erratic and disruptive mood swings are a defining feature.
To determine mental health problems, people usually use charting with papers, interviews, or smartphone to track their mood/affect/emotion. Furthermore, mood swings do not just fluctuate between mania and depression, but in some conditions, involve anxiety.
Terminology
Definitions of the terms mood swings, mood instability, affective lability, or emotional lability are commonly similar, which describe fluctuating or oscillating of mood and emotions. But each has unique characteristics that are used to describe specific phenomena or patterns of oscillation. Different from emotions or affect, mood is associated with emotional responses without knowing the reason (being unaware). The dynamics of mood, mood patterns for long times are commonly erratic, labile or instable, also known as euthymic. Although the term of mood swing is unspecific, it may be used to describe a pattern where mood goes down from positive to negative valency immediately (without delay in baseline) at specific periods. And also generally have aperiodic patterns. This is because mood dynamics are influenced by various factors which can magnify or lessen fluctuations, such as when expectations become reality or not. Other terms for describing patterns are episodic, periodic, cyclothymia, rapid cycling, mixed states, short episodes, soft spectrum, diurnal variation, etc., although the definition of each term may be unclear.Overview
Speed and extent
Mood swings can happen any time at any place, varying from the microscopic to the wild oscillations ofbipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
, so that a continuum can be traced from normal struggles around self-esteem, through cyclothymia, up to a depressive disease. However, most people's mood swings remain in the mild to moderate range of emotional ups and downs. The duration of bipolar mood swings also varies. They may last a few hours – ''ultrarapid'' – or extend over days – ''ultradian'': clinicians maintain that only when four continuous days of hypomania, or seven days of mania, occur, is a diagnosis of bipolar disorder justified. In such cases, mood swings can extend over several days, even weeks; these episodes may consist of rapid alternation between feelings of depression and euphoria.
Characteristics
* Changing mood up and down without knowing the reason or external stimuli, in various degrees, duration and frequent, from high mood ( happy, ''elevated'', irritated) to low mood ( sad, depressed). * Sometimes it's mixed, a combination between manic and depression symptoms or similar with bittersweet experiences that last for a day. * Mood swings in normal people appear like "climate changing" at mild to moderate degree. Thus, unless it happens at a moderate degree or more, some people need more high emotional intelligence to recognize their mood change. * Mood swings in mental illness simply can be described by generalized complexity based on ''mood dynamics'' (patterns that characterize the oscillation) like intensity (mild, moderate, severe), duration (days, weeks, years), average mood and other features, such as:van Genugten, Claire. (2022)Measurement innovation: studies on smartphone-based ecological momentary assessment in depression
VU Research Portal.ISBN 978-94-93270-96-1."Mood dynamics are the patterns that characterize fluctuations in a person's mood 4 Mood dynamics are often operationalized by a combination of "mood variability" and "emotional inertia" 5,66 # Mood swings in cyclothymia: Mood swings occur episodically and aperiodic within 2 years or more at a moderate degree and frequently. Characterized by coexisting with anxiety, persistence, rapid shift, intense, impulsive, heightened by sensitivity and reactivity to external stimuli. # Mood swings in bipolar II: Episodic, hypomanic (severe degree) episodes occur continuously for 4 days, depression episodes for weeks, and sometimes erratic episodes at moderate degree in between episodes. # Mood swings in bipolar I: Episodic, manic episodes (severe degree) occur continuously for 7 days, depressive episodes for weeks,Last, C. G. (2009). When Someone You Love Is Bipolar: Help and Support for You and Your Partner. Ukraina: Guilford Publications."''Research indicates that bipolar II depressions persist for longer periods of time than bipolar I depressions, nearly twice as long (1 year versus 6 months)."'' and sometimes erratic episodes at moderate degree in between episodes. Alterations in bipolar I and II can be ''rapid cyclic'', which means changes of mood happen 4 times or more within a year. Symptoms of manic and hypomanic episodes are similar between bipolar I and bipolar II, just different in degree of intensity. # Mood swings in Premenstrual symptoms (PMS): Episodically at mild to severe degree in the menses period, occur gradually or rapidly, start 7 days before and decrease at the onset of menses. Characterized by angry outbursts, depression, anxiety, confusion, irritability or social withdrawal. # Mood swings in borderline personality disorder (BPD): Mood changes erratically with episodic mood swings. Mood swings fluctuate in rapid shifts for hours or days, not persistent, sensitive and heightened negative mood (e.g. irritability) by external stimuli. Mood appears in the form of high intensity of irritability, anxiety, and moderate degree depression (characterized by hostility, anger towards self, loneliness, isolation, related with relationships, emptiness or boredom). # Mood swings in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) : Mood changes erratically and mood swings occur episodically, sometimes several times a day in rapid shifts.FW, Reimherr & Marchant, Barrie & Olsen, John & C, Halls & Kondo, Douglas & ED, Lyon & Robison, Reid. (2010)
Emotional dysregulation as a core feature of adult ADHD: Its relationship with clinical variables and treatment response in two methylphenidate trials
Journal of ADHD and Related Disorders. 1. 53-64.
Graph
Characterized by a mild to moderate degree of irritability, related to the environment, impulsiveness (impatience to get rewards). In adult ADHD, high mood appears as excitement and low mood appears as boredom. # Mood swings in schizophrenia: Although schizophrenia has flat emotions, a study in 2021 based on ALS-SF measures, Margrethe Collier et al., found that the score pattern of schizophrenia is similar to bipolar I. The alteration being related to delusions or hallucinations, mood changes that occur internally may be difficult to express externally ( blunt affect), and heightened by external stimuli. # Mood swings in major depressive disorder (MDD): Various mood patterns, and mood changes erratically. Mood swings occur episodically and fluctuate in moderate high mood and severe low mood. Characterized by having high negative affect (bad mood) most of the time, particularly in melancholic subtype. And also positive diurnal variation mood (bad mood in the morning, good mood in the evening), sensitivity to negative stimulation and mixed symptoms in some people, etc. # Mood swings in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Mood changes erratically with episodic mood swings rising in the period of recovery process. Characterized by temporary fluctuations in negative affect (anxiety, irritability, shame, guilt) and self-esteem, reactive to environmental reminders, difficulty to control emotions, hyperarousal symptoms, etc.
Causes
There can be many different causes for mood swings. Some mood swings can be classified as normal/healthy reactions, such as grief processing, adverse effects of substances/drugs, or a result of sleep deprivation. Mood swings can also be a sign of psychiatric illnesses in the absence of external triggers or stressors. Changes in a person's energy level, sleep patterns, self-esteem, sexual function, concentration, drug or alcohol use can be signs of an oncoming mood disorder. Other major causes of mood swings (besidesbipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
and major depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
) include diseases/disorders which interfere with nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
function. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple con ...
( ADHD), epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
, and autism spectrum
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
are three such examples.
The hyperactivity sometimes accompanied by inattentiveness, impulsiveness, and forgetfulness are cardinal symptoms associated with ADHD. As a result, ADHD is known to bring about usually short-lived (though sometimes dramatic) mood swings. The communication difficulties associated with autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
, and the associated changes in neurochemistry, are also known to cause autistic fits (autistic mood swings). The seizures associated with epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
involve changes in the brain's electrical firing, and thus may also bring about striking and dramatic mood swings. If the mood swing is not associated with a mood disorder, treatments are harder to assign. Most commonly, however, mood swings are the result of dealing with stressful and/or unexpected situations in daily life.
Degenerative diseases of the human central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
such as Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, and Huntington's disease may also produce mood swings. Celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
can also affect the nervous system and mood swings can appear.
Not eating on time can contribute, or eating too much sugar, can cause fluctuations in blood sugar, which can cause mood swings.
Brain chemistry
If a person has an abnormal level of one or several of certainneurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s (NTs) in their brain, it may result in having mood swings or a mood disorder. Serotonin is one such neurotransmitter that is involved with sleep, moods, and emotional states. A slight imbalance of this NT could result in depression. Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
is a neurotransmitter that is involved with learning, memory, and physical arousal. Like serotonin, an imbalance of norepinephrine may also result in depression.
List of conditions known to cause mood swings
*Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
or cyclothymia: Bipolar disorder is a mood disorder with characteristics of mood swings from hypomania or mania to depression. While cyclothymia is a lower degree of bipolar disorder. In 2022, ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group found that people with bipolar disorder have smaller subcortical volumes, lower cortical thickness and altered white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
integrity, which one of the functions is for emotion processing.
* Anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids, also known as anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS), are a class of drugs that are structurally related to testosterone, the main male sex hormone, and produce effects by binding to the androgen receptor (AR). Anabolism, Anaboli ...
abuse: Anabolic steroids are synthetic derivatives of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
. Used for treatment of male hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the human gonad, gonads—the testicles or the ovary, ovaries—that may result in diminished biosynthesis, production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred t ...
or delayed puberty, stimulating muscle growth, as well as treating impotence
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
, and AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
. Studies found that overusing anabolic-androgenic steroids can cause mood swings, impulsive, and aggressive behavior. This behavior is associated with decreased emotion regulation systems such as the frontal cortex, temporal, parietal, and occipital. Studies also found that using anabolic-androgenic steroids can cause neuronal changes and death in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, thus symptoms of sleep and mood disorder occur.
* Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): ADHD is known as a disorder with difficulty keeping control of attention, hyperactivity, frequently changing focus and losing interest and also hyperfocus
Hyperfocus is an intense form of mind, mental attention, concentration or creative visualization, visualization that focuses consciousness on a subject, topic, or task. In some individuals, various subjects or topics may also include daydreams, c ...
when doing something interesting or pleasurable tasks. Mood dysregulation may be caused by distraction when absorbed in pleasurable tasks. Another contribution to mood swings is lower brain activity in the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is the association cortex in the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, ...
(PFC), orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 1 ...
(OFC), increased size of the hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
and decreasing size of the amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is c ...
in some people. Abnormalities in these parts of the brain can cause disturbance in attention, motivation, mood, and behavioral inhibition.
* Autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
or other pervasive developmental disorder: Autism is a neurological and development disorder with symptoms such as lack of social skills, restricted repetitive behaviors, hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input, etc. Abnormal sensory processing is one of the reasons for mood swings in autism. Studies in 2015 found that in autism, the brain becomes overactivated in limbic areas, primary sensory cortices, and orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 1 ...
(OFC), which functions for emotional and sensory processing. Studies found too, that the brain in autism has decreased connectivity between the amygdala and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, increased amygdala reactivity, and reduced prefrontal response which contribute to emotion dysregulation.
* Borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive, long-term pattern of significant interpersonal relationship instability, an acute fear of Abandonment (emotional), abandonment, and intense emotiona ...
: It has been theorized that borderline personality disorder comes from lack of ability to endure, learn and overcome negative events. People with BPD commonly have difficulty in relationships, which is associated with a tendency to anger-outbursts, judgment or expecting how others behave. Emotion dysregulation may be as a result of lack of interpersonal skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called socia ...
such as knowledge about emotions and how to control them, especially with intense emotions. Mostly, people with BPD use maladaptive emotion regulations like self-criticism, thought suppression, avoidance, and alcohol, which may trigger more mood disruption.
* Dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, including Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
and Huntington's disease: Dementia is known as a decreasing brain function disease that affects older people. In Alzheimer's disease, mood dysregulation can be caused by decreasing function of emotional regulation, salience, cholinergic, GABAergic, and dopaminergic function. Parkinson's disease can generate mood swings and mood dysregulation such as depression, low self worth, shame and worry about the future caused by cognitive and physical problems. And in Huntington's disease, common mood swings occur as a result of psychosocial, cognitive deficits, neuropsychiatric and biological factors.
* Dopamine dysregulation syndrome: Dopamine dysregulation syndrome is an effect of abusing Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
drugs to decrease motor and non-motor syndromes, which result in mania, violent behavior, and depression when withdrawal. Mood dysregulation from dopamine dysregulation syndrome occurs as a result of changes in the neurotransmitter systems such as disturbance in the dopaminergic reward system.
* Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
: Epilepsy is an abnormal brain activity disease marked with seizures. Seizures occur because hypersynchronous and hyperexcitability of neurons, in other words, too much neural activity and excitability at the same time. Mood swings commonly appear before, during, after a seizure and during treatment. Studies found that seizures contribute to decreased function of emotions and mood processing as a consequence of abnormal neurogenesis and damaged neuron connections in the hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the ...
and amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is c ...
. Experiencing a seizure can cause mood swings caused by depression, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, or worry about life being threatened. Another source of mood change comes from anticonvulsant drugs for epilepsy, like phenobarbital for increasing brain inhibitors or antiglutamatergic for decreasing brain activity which generates depression, cognitive dysfunction, sedation or mood lability.
* Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism: Hypo- and hyperthyroidism is an endocrine disease caused by low or excessive production of thyroid hormone. Abnormal thyroid hormone can affect mood, although the correlation between thyroid hormone and mood disorder is still not known.
* Intermittent explosive disorder: Intermittent explosive disorder is frequent rage that occurs spontaneous, uncontrolled, unproportioned and not persistent. This short duration of alternate mood occurs in the form of aggression verbally or physically towards people or property, sometimes followed by regret, shame and guilt after an act which might generate depression symptoms. Impulsive behavior in IED can be associated with hyperactivity in brain regions for regulating and emotional expression, such as the amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is c ...
, insula, and orbitofrontal area.
* Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
: Menopause in women commonly happens at age 52. One factor that causes mood disturbance is fluctuation of milieu hormones including sex steroids, growth hormones, stress hormones, etc.
* Major depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
: Major depression is a disorder with symptoms such as feelings of sadness, loss of interest, emptiness and, for some people, mixed with irritability, ''mental overactivity,'' and ''behavioral overactivity''. Development of irritability or anger may result from personality traits like narcissistic or coping strategies to avoid looking sad, worthless, or frustrated.
* Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Obsessive compulsive disorder is marked with obsessions and compulsions about something that causes life distress and dysfunction. Alteration of mood and feeling discomfort such as shame, guilt or anxiety may occur caused by intrusive thoughts, fear, urge, and fantasy.
* Pathological demand avoidance
* Post traumatic stress disorder: Post-traumatic stress disorder is a disorder which is associated with frequently being disturbed by flashback memories and being haunted by feelings of fear and horror in the past. This contributes to the alteration of mood that occurs after a traumatic event happens, such as depression, outbursts of anger, self-destructive behaviors, and feelings of shame.
* Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
: Women commonly experience mood swings during the pregnancy and the postpartum period. Hormone changes, stress and worry may be the reasons for changes of mood.
* Premenstrual syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a disruptive set of emotional and physical symptoms that regularly occur in the one to two weeks before the start of each menstrual period. Symptoms resolve around the time menstrual bleeding begins. Symptoms v ...
: Women experience premenstrual syndrome like physical pains, mood swings, irritability or depression in a few days until 2 weeks of their period with different intensity. Furthermore, 4% to 14% of women experience severe PMS or premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), which can decrease life quality. Despite the reason mood dysregulation in PMS is still unclear, Studies found that mood dysregulation is related with drop in progesterone concentrations, disruption of serotonergic transmission, GABAergic, stress, body-mass index, and traumatic events.
* Schizoaffective disorder: Mood swings in schizoaffective disorder are caused by mixed symptoms between schizophrenia and mood disorder.
* Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
: Schizophrenia is a disorder with symptoms of delusions
A delusion is a fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some other m ...
, hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ...
s, mood dysregulation, etc. Mood changes may be generated from hallucinations and delusions which cause anger, paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety, suspicion, or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of co ...
, and shame.
* Seasonal affective disorder: Seasonal affective disorder is depression which occurs during some seasons (commonly in winter), then manic or hypomanic episodes in the other season and that happens every year. These fluctuating moods appear in the form of anger attacks with depression and occur from season to season, also known as ''seasonal mood swings''.
* XXYY syndrome: XXYY syndrome is a rare type of sex chromosome aneuploidies (SCAs). XXYY syndrome contributes to abnormal neurodevelopment and psychiatric diseases which can cause mood disorders.
Treatment
It's part of human nature's mood going up and down caused by various factors. Individual strength, coping skill or adaptation ability, social support or another recovery model might determine whether mood swings will create disruption in life or not.Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders.
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on challenging and chang ...
recommends using ''emotional dampeners'' to break the self-reinforcing tendencies of either manic or depressive mood swings. Exercise, treats, seeking out small (and easily attainable) triumphs, and using vicarious distractions like reading or watching TV, are among the techniques found to be regularly used by people in breaking depressive swings. Learning to bring oneself ''down'' from grandiose states of mind, or ''up'' from exaggerated shame states, is part of taking a proactive approach to managing one's own moods and varying sense of self-esteem.
Behavioral activation is a component of CBT that can break the cycle (depression leads to inactivity, inactivity leads to depression). This may rely on individual strengths to "cold start" the reward system.
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT): Another manifestation of mood swing is irritability, which can lead to elation, anger or aggression. DBT has a lot of coping skills that can be used for emotion dysregulation, such as mindfulness with the "wise mind" or emotion regulation with opposite action.
Emotion regulation therapy (ERT) has a package of mindful emotion regulation skills (e.g., attention regulation skills, metacognitive regulation skills, etc.) that can be handy to have when mood swings happen.
Interpersonal and social rhythm therapy can be used to regulate life rhythm when mood swings happen frequently and disrupt the rhythm of life. Episodes of mood disorder often liberate people from daily routines by making a mess of sleep schedules, social interaction, or work and causing irregular circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
s.
Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) has a function to increase psychological flexibility by learning to assess present experience or be mindful, accept everything internally or externally, commit action to move toward personal recovery, etc.
See also
References
Further reading
* Ronald R. Fieve, ''Moodswing'' (1989) * Susanne P. Schad-Somers, ''On mood swings'' (1990)External links
Understanding mood swings
{{Mood disorders Borderline personality disorder Mood disorders Symptoms and signs of mental disorders