|
Sensory Cortex
The sensory cortex can refer sometimes to the primary somatosensory cortex, or it can be used as a term for the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses (two cortices each, on left and right hemisphere): the visual cortex on the occipital lobes, the auditory cortex on the temporal lobes, the primary olfactory cortex on the uncus of the piriform region of the temporal lobes, the gustatory cortex on the insular lobe (also referred to as the insular cortex), and the primary somatosensory cortex on the anterior parietal lobes. Just posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex lies the somatosensory association cortex or area, which integrates sensory information from the primary somatosensory cortex (temperature, pressure, etc.) to construct an understanding of the object being felt. Inferior to the frontal lobes are found the olfactory bulbs, which receive sensory input from the olfactory nerves and route those signals throughout the brain. Not all olfactory infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
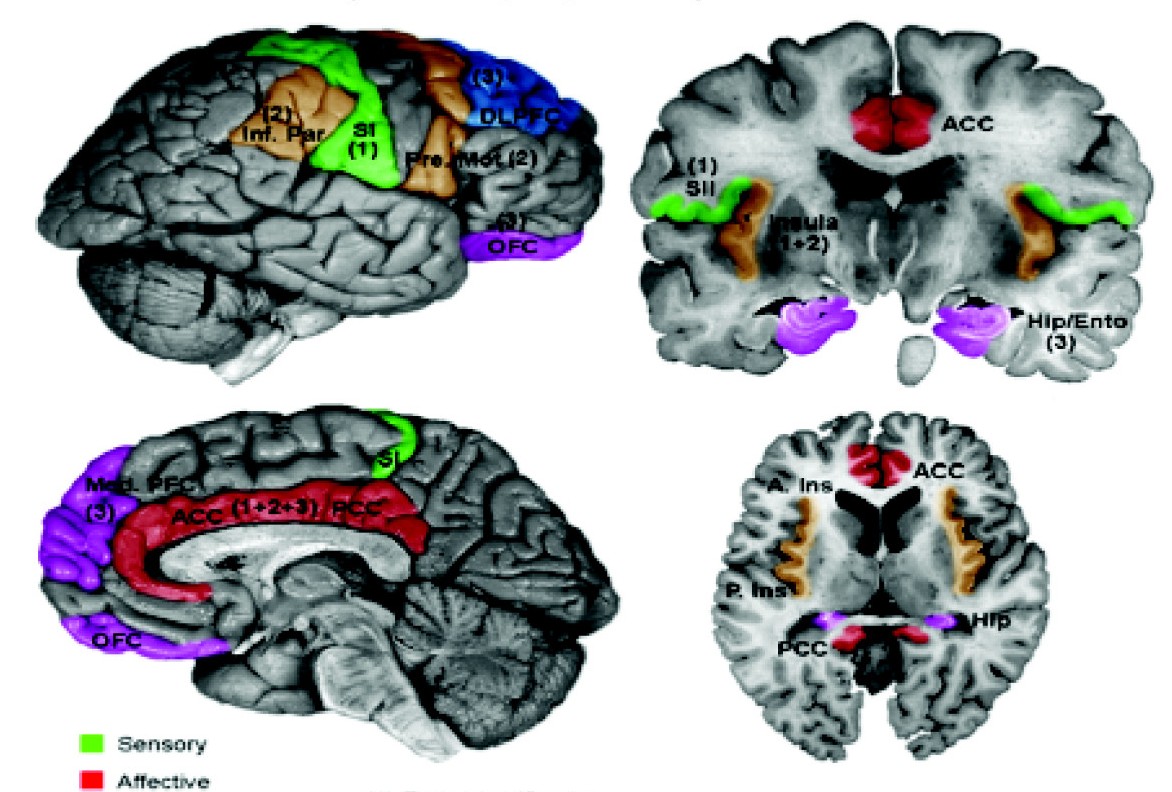 |
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
In neuroanatomy, the primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus of the brain's parietal lobe, and is part of the somatosensory system. It was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and parallel surface potential studies of Bard, Woolsey, and Marshall. Although initially defined to be roughly the same as Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2, more recent work by Kaas has suggested that for homogeny with other sensory fields only area 3 should be referred to as "primary somatosensory cortex", as it receives the bulk of the thalamocortical projections from the sensory input fields. At the primary somatosensory cortex, tactile representation is orderly arranged (in an inverted fashion) from the toe (at the top of the cerebral hemisphere) to mouth (at the bottom). However, some body parts may be controlled by partially overlapping regions of cortex. Each cerebral hemisphere of the primary somatosensory cortex only contains a tactile representatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Insular Cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere, hemisphere of the mammalian brain. The insulae are believed to be involved in consciousness and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to emotion or the regulation of the body's homeostasis. These functions include compassion, empathy, taste, perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning, interpersonal relationships, and awareness of homeostatic emotions such as Hunger (physiology), hunger, pain and fatigue. In relation to these, it is involved in psychopathology. The insular cortex is divided by the central sulcus of the insula, into two parts: the anterior insula and the posterior insula in which more than a dozen field areas have been identified. The cortical area overlying the insula toward the lateral su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Postcentral Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, the postcentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus in the lateral parietal lobe of the human brain. It is the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch. Like other sensory areas, there is a map of sensory space in this location, called the '' sensory homunculus''. The primary somatosensory cortex was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and parallel surface potential studies of Bard, Woolsey, and Marshall. Although initially defined to be roughly the same as Brodmann areas 3, 1, and 2, more recent work by Kaas has suggested that for homogeny with other sensory fields only area 3 should be referred to as "primary somatosensory cortex", as it receives the bulk of the thalamocortical projections from the sensory input fields. Structure The lateral postcentral gyrus is bounded by: * medial longitudinal fissure medially (to the middle) * central sulcus rostrally (in front) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Precentral Gyrus
The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4. Structure The precentral gyrus lies in front of the postcentral gyrus - mostly on the lateral (convex) side of each cerebral hemisphere - from which it is separated by the central sulcus. Its anterior border is represented by the precentral sulcus, while inferiorly it borders to the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). Medially, it is contiguous with the paracentral lobule. The internal pyramidal layer (layer V) of the precentral cortex contains giant (70-100 micrometers) pyramidal neurons called Betz cells, which send long axons to the contralateral motor nuclei of the cranial nerves and to the lower motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. These axons form the corticospinal tract. The Betz cells along with their long axons are referred to as upper motor n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Primary Motor Cortex
The primary motor cortex ( Brodmann area 4) is a brain region that in humans is located in the dorsal portion of the frontal lobe. It is the primary region of the motor system and works in association with other motor areas including premotor cortex, the supplementary motor area, posterior parietal cortex, and several subcortical brain regions, to plan and execute voluntary movements. Primary motor cortex is defined anatomically as the region of cortex that contains large neurons known as Betz cells, which, along with other cortical neurons, send long axons down the spinal cord to synapse onto the interneuron circuitry of the spinal cord and also directly onto the alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord which connect to the muscles. At the primary motor cortex, motor representation is orderly arranged (in an inverted fashion) from the toe (at the top of the cerebral hemisphere) to mouth (at the bottom) along a fold in the cortex called the central sulcus. However, some body p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Central Sulcus
In neuroanatomy, the central sulcus (also central fissure, fissure of Rolando, or Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando) is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal fissure. The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain, separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex. Evolution of the central sulcus The evolution of the central sulcus is theorized to have occurred in mammals when the complete dissociation of the original somatosensory cortex from its mirror duplicate developed in placental mammals such as primates, though the development did not stop there as time progressed the distinction between the two cortices grew. Evolution in primates The central sulcus is more prominent in apes as a result of fine-tuning of the motor system in apes. Hominins (bipedal apes) continued this trend through increased use of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Lateral Fissure
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to: Biology and healthcare * Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side" * Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx * Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure to release tight capsular structures Other uses * ''Lateral'', a digital journal and production of the Cultural Studies Association * ''Lateral'', a podcast by English YouTuber and web developer Tom Scott * Lateral canal, a canal built along the same right-of-way as an existing stream * Lateral consonant, a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue * Lateral mark, a sea mark used in maritime pilotage to indicate the edge of a channel * Lateral modes, an aspect of dynamic stability and control in the field of aircraft flight dynamics * Lateral pass, a non-advancing move in gridiron football * Lateral release (phonetics), the release of a plosive consonant into a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Limbic
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Psychology''.sec. 3.20 Its various components support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long-term memory, and olfaction. The limbic system is involved in lower order emotional processing of input from sensory systems and consists of the amygdala, mammillary bodies, stria medullaris, central gray and dorsal and ventral nuclei of Gudden. This processed information is often relayed to a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon, including the prefrontal cortex, cingulate gyrus, limbic thalamus, hippocampus including the parahippocampal gyrus and subiculum, nucleus accumbens (limbic striatum), anterior hypothalamus, ventral tegmental area, midbrain raphe nuclei, habenular commissure, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Parietal Lobes
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "little man") in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Gustatory Cortex
The primary gustatory cortex (GC) is a brain structure responsible for the perception of taste. It consists of two substructures: the anterior insula on the insular lobe and the frontal operculum on the inferior frontal gyrus of the frontal lobe. Because of its composition the primary gustatory cortex is sometimes referred to in literature as the AI/FO(Anterior Insula/Frontal Operculum). By using extracellular unit recording techniques, scientists have elucidated that neurons in the AI/FO respond to sweetness, saltiness, bitterness, and sourness, and they code the intensity of the taste stimulus. Role in the taste pathway Like the olfactory system, the taste system is defined by its specialized peripheral receptors and central pathways that relay and process taste information. Peripheral taste receptors are found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, pharynx, and the upper part of the esophagus. Taste cells synapse with primary sensory axons that run in the cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The six-layered neocortex makes up approximately 90% of the Cortex (anatomy), cortex, with the allocortex making up the remainder. The cortex is divided into left and right parts by the longitudinal fissure, which separates the two cerebral hemispheres that are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum and other commissural fibers. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the neurocranium, cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, gyrification, cortical folding is crucial for the Neural circuit, brain circuitry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |