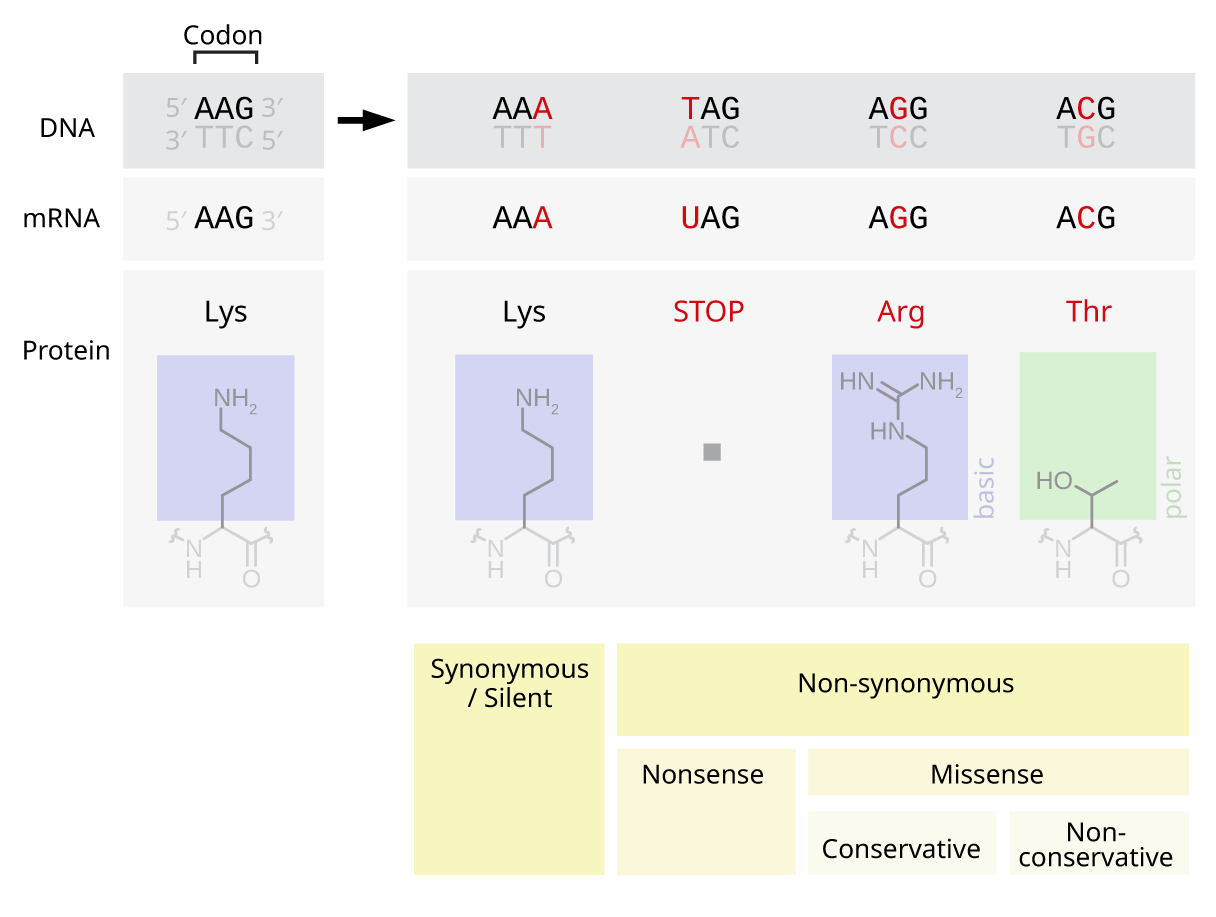
missense mutations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 
 Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, due to misfolding of the protein. These mutations are responsible for human diseases, such as Epidermolysis bullosa,
Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, due to misfolding of the protein. These mutations are responsible for human diseases, such as Epidermolysis bullosa,
 DNA polymerase replication errors during cell division may lead to spontaneous missense mutations if DNA polymerase's proofreading ability does not detect and repair an error it makes. Spontaneous DNA polymerase errors are estimated to occur at a frequency of 1/109 base pairs.
Although rarer, tautomerization of bases also creates spontaneous missense mutations. Tautomerization occurs when hydrogen atoms on DNA bases spontaneously change locations, impacting the structure of the base, and allowing it to pair with an incorrect base. If this strand of DNA is replicated, the incorrect base will be the template for a new strand, leading to a mutation, possibly changing the amino acid and therefore, the protein. For example, Wang et al., (2011) used X-ray cystallography to demonstrate that a de novo mutation was created when DNA repair mechanisms did not recognize a C-A base mismatch due to tautomerization allowing the base structures to be compatible.
DNA polymerase replication errors during cell division may lead to spontaneous missense mutations if DNA polymerase's proofreading ability does not detect and repair an error it makes. Spontaneous DNA polymerase errors are estimated to occur at a frequency of 1/109 base pairs.
Although rarer, tautomerization of bases also creates spontaneous missense mutations. Tautomerization occurs when hydrogen atoms on DNA bases spontaneously change locations, impacting the structure of the base, and allowing it to pair with an incorrect base. If this strand of DNA is replicated, the incorrect base will be the template for a new strand, leading to a mutation, possibly changing the amino acid and therefore, the protein. For example, Wang et al., (2011) used X-ray cystallography to demonstrate that a de novo mutation was created when DNA repair mechanisms did not recognize a C-A base mismatch due to tautomerization allowing the base structures to be compatible.

 If a missense mutation is not deleterious, it will not be selected against and can contribute to
If a missense mutation is not deleterious, it will not be selected against and can contribute to
genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, a missense mutation is a point mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences ...
in which a single nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
change results in a codon
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links prote ...
that codes for a different amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution. Missense mutations change amino acids, which in turn alter proteins and may alter a protein's function or structure. These mutations may arise spontaneously from mutagens like UV radiation, tobacco smoke, an error in DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
, and other factors. Screening for missense mutations can be done by sequencing the genome of an organism and comparing the sequence to a reference genome
A reference genome (also known as a reference assembly) is a digital nucleic acid sequence database, assembled by scientists as a representative example of the genome, set of genes in one idealized individual organism of a species. As they are a ...
to analyze for differences. Missense mutations can be repaired by the cell when there are errors in DNA replication by using mechanisms such as DNA proofreading and mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of nucleobase, bases that can arise during DNA replication and Genetic recombination, recombination, as well as DNA repair, ...
. They can also be repaired by using genetic engineering technologies or pharmaceuticals. Some notable examples of human diseases caused by missense mutations are Rett syndrome, cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
, and sickle-cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying ...
.
Impact on Protein Function
Missense mutation refers to a change in one amino acid in aprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
arising from a point mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences ...
in a single nucleotide. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Missense mutations are a type of nonsynonymous substitution in a DNA sequence. Two other types of nonsynonymous substitutions are nonsense mutations, in which a codon is changed to a premature stop codon
In molecular biology, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the additio ...
that results in the resulting protein being cut short, and nonstop mutations, in which a stop codon deletion results in a longer but nonfunctional protein. The latter two types are not considered to be missense mutations.
 Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, due to misfolding of the protein. These mutations are responsible for human diseases, such as Epidermolysis bullosa,
Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, due to misfolding of the protein. These mutations are responsible for human diseases, such as Epidermolysis bullosa, sickle-cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying ...
, SOD1 mediated ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and low ...
, and a substantial number of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s.
Not all missense mutations lead to appreciable protein changes. An amino acid may be replaced by a different amino acid of very similar chemical properties in which case the protein may still function normally; this is termed a conservative mutation. Alternatively, the amino acid substitution could occur in a region of the protein which does not significantly affect the protein secondary structure or function. Lastly, when more than one codon codes for the same amino acid (termed "degenerate coding"), the resulting mutation does not produce any change in translation and hence no change in protein is observed; degenerate coding would be classified as a synonymous substitution
A synonymous substitution (often called a ''silent'' substitution though they are not always silent) is the evolutionary substitution of one base for another in an exon of a gene coding for a protein, such that the produced amino acid sequence ...
, or a silent mutation, and not a missense mutation.
Origin
Missense mutations may be inherited or arise spontaneously, termed de novo mutations. Well studied diseases arising from inherited missense mutations include sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and early-onset Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. De novo mutations that increase or decrease the activity of synapses have been implicated in the development of neurological and developmental disorders, such a Autism Spectrum Disorder and intellectual delay.Agents of Spontaneous Missense Mutation
Environmental mutagens, such as tobacco smoke or UV radiation, may be a cause of spontaneous missense mutations. Tobacco smoke has been implicated in transversion mutations in the K-''ras'' gene, with a meta-analysis of lung carcinomas showing 25 tumours containing a G to T mutation causing an amino acid change from glycine to cysteine, and 11 tumours with a G to T mutation causing an amino acid change from glycine to valine. Similarly, numerous studies have shown ultraviolet light induces missense mutations in the p53 gene, which when unregulated, reduces the cell's ability to recognize DNA damage and engage inapoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, leading to cell proliferation and potential skin carcinogenesis.
 DNA polymerase replication errors during cell division may lead to spontaneous missense mutations if DNA polymerase's proofreading ability does not detect and repair an error it makes. Spontaneous DNA polymerase errors are estimated to occur at a frequency of 1/109 base pairs.
Although rarer, tautomerization of bases also creates spontaneous missense mutations. Tautomerization occurs when hydrogen atoms on DNA bases spontaneously change locations, impacting the structure of the base, and allowing it to pair with an incorrect base. If this strand of DNA is replicated, the incorrect base will be the template for a new strand, leading to a mutation, possibly changing the amino acid and therefore, the protein. For example, Wang et al., (2011) used X-ray cystallography to demonstrate that a de novo mutation was created when DNA repair mechanisms did not recognize a C-A base mismatch due to tautomerization allowing the base structures to be compatible.
DNA polymerase replication errors during cell division may lead to spontaneous missense mutations if DNA polymerase's proofreading ability does not detect and repair an error it makes. Spontaneous DNA polymerase errors are estimated to occur at a frequency of 1/109 base pairs.
Although rarer, tautomerization of bases also creates spontaneous missense mutations. Tautomerization occurs when hydrogen atoms on DNA bases spontaneously change locations, impacting the structure of the base, and allowing it to pair with an incorrect base. If this strand of DNA is replicated, the incorrect base will be the template for a new strand, leading to a mutation, possibly changing the amino acid and therefore, the protein. For example, Wang et al., (2011) used X-ray cystallography to demonstrate that a de novo mutation was created when DNA repair mechanisms did not recognize a C-A base mismatch due to tautomerization allowing the base structures to be compatible.
Screening
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) has changed the world of sequencing by decreasing the cost of sequencing and increasing the throughput. It does this by utilizing massively parallel sequencing to sequence the genome. This involves clonally amplifiedDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
fragments that can be spatially separated into second generation sequencing (SGS) or third generation sequencing (TGS) platforms. There is variation between these protocols, but the overall methods are similar. Using massively parallel sequencing allows the NGS platform to produce very large sequences in a single run. The DNA fragments are typically separated by length using gel electrophoresis.
NGS consists of four main steps, DNA isolation, target enrichment, sequencing, and data analysis. The DNA isolation step involves breaking the genomic DNA into many small fragments. There are many different mechanisms that can be used to accomplish this such as mechanical methods, enzymatic digestion, and more. This step also consists of adding adaptors to either end of the DNA fragments that are complementary to the flow cell oligos and include primer binding sites for the target DNA. The target enrichment step amplifies the region of interest. This includes creating a complementary strand to the DNA fragments through hybridization to a flow cell oligo. It then gets denatured and bridge amplification occurs before the reverse strand is finally washed and sequencing can occur. The sequencing step involves massive parallel sequencing of all DNA fragments simultaneously using a NGS sequencer. This information is saved and analyzed in the last step, data analysis, using bioinformatics software. This compares the sequences to a reference genome to align the fragments and show mutations in the targeted area of the sequence.
Newborn Screening (NBS)
Newborn screening
Newborn screening (NBS) is a public health program of screening (medicine), screening in infants shortly after birth for conditions that are treatable, but not clinically evident in the newborn period. The goal is to identify infants at risk for ...
(NBS) for missense mutations is increasingly incorporating genomic technologies in addition to traditional biochemical methods to improve the detection of genetic disorders early in life. Traditional NBS primarily relies on biochemical assays, such as tandem mass spectrometry
Tandem mass spectrometry, also known as MS/MS or MS2, is a technique in instrumental analysis where two or more stages of analysis using one or more mass analyzer are performed with an additional reaction step in between these analyses to increa ...
, to detect metabolic abnormalities indicative of conditions like phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also r ...
or congenital hypothyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth. If untreated for several months after birth, severe congenital hypothyroidism can lead to growth failure and permanent intellectual disability. Infants born with co ...
. However, these methods may miss genetic causes or produce ambiguous results. To address these deficiencies, next-generation sequencing
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation ...
(NGS) is being added to NBS programs. For instance, targeted gene panels and whole-exome sequencing (WES) are used to identify disease causing missense mutations in genes associated with treatable conditions, such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
. Studies like the BabyDetect project have demonstrated the utility of genomic screening in identifying disorders missed by conventional methods, with actionable results for conditions affecting more than 400 genes. In addition, genomic approaches allow for the detection of rare or recessive conditions that may not manifest biochemically at birth, significantly expanding the scope of diseases screened. These advancements align with the established principles of NBS, which emphasize early detection and intervention to prevent morbidity and mortality.
Prevention and Repair Mechanisms

Cellular mechanisms
DNA polymerases, used inDNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
, have a high specificity of 104 to 106-fold in base pairing. They have proofreading abilities to correct incorrect matches, allowing 90-99.9% of mismatches to be excised and repaired. The base mismatches that go unnoticed are repaired by the DNA mismatch repair pathway, also inherent in cells. The DNA mismatch repair pathway uses exonucleases
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolysis, hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the Directionality (molecular biolog ...
that move along the DNA strand and remove the incorrectly incorporated base in order for DNA polymerase to fill in the correct base. Exonuclease1 is involved in many DNA repair systems and moves 5' to 3' on the DNA strand.
Genetic engineering and drug-based interventions
More recently, research has explored the use ofgenetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of Genetic engineering techniques, technologies used to change the genet ...
and pharmaceuticals as potential treatments. tRNA therapies have emerged in research studies as a potential missense mutation treatment, following evidence supporting their use in nonsense mutation correction. Missense-correcting tRNAs are engineered to identify the mutated codon, but carry the correct charged amino acid which is inserted into the nascent protein.
Pharmaceuticals that target specific proteins affected by missense mutations have also shown therapeutic potential. Pharmaceutical studies have particularly focused on targeting the p53 mutant protein and Ca2+ channel abnormalities, both caused by gain of function missense mutations due to their high prevalence in a number of cancers and genetic diseases respectively. In cystic fibrosis, most commonly caused by missense mutations, drugs known as modulators target the defective Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) protein. For example, to reduce the defects caused by class III CFTR mutations, Ivacaftor, part of the modulator Kalydeco, forces the chloride channel to remain in an open position.
Future Technology and Research
Gene therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
The first attempt at modifying human DNA ...
is being explored as a treatment for missense mutations. This involves inserting the correct sequence of DNA into an incorrect gene. Artificial Intelligence programs, such as AlphaFold, are also being developed to predict the effect of missense mutations. Identifying potential deleterious mutations can assist with disease diagnosis and treatment.
Evolution
 If a missense mutation is not deleterious, it will not be selected against and can contribute to
If a missense mutation is not deleterious, it will not be selected against and can contribute to species divergence
Divergent evolution or divergent selection is the accumulation of differences between closely related populations within a species, sometimes leading to speciation. Divergent evolution is typically exhibited when two populations become separate ...
. Over time, mutations occur randomly in individuals and can become fixed
Fixed may refer to:
* ''Fixed'' (EP), EP by Nine Inch Nails
* ''Fixed'' (film), an upcoming animated film directed by Genndy Tartakovsky
* Fixed (typeface), a collection of monospace bitmap fonts that is distributed with the X Window System
* Fi ...
in populations if they are not selected against. Missense mutations are a type of mutation that are not neutral, and therefore can be acted on by selection. Selection cannot act on synonymous mutations (mutations that do not change anything phenotypically).
Tracking missense mutations, like nonsynonymous SNPs, in ancestral species populations allow genealogies and phylogenetic trees to be created and evolutionary connections to be made. Missense mutation analysis is often used in evolutionary genetics to create relationships between species, as amino acid changes leading to protein changes are needed for species to diverge from each other.
Notable Examples
LMNA
DNA: 5' - AAC AGC CTG CGT ACG GCT CTC - 3' 3' - TTG TCG GAC GCA TGC CGA GAG - 5' mRNA: 5' - AAC AGC CUG CGU ACG GCU CUC - 3' Protein: Asn Ser Leu Arg Thr Ala LeuLMNA
Prelamin-A/C, or lamin A/C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LMNA'' gene. Lamin A/C belongs to the lamin family of proteins.
Function
In the setting of ZMPSTE24 deficiency, the final step of lamin processing does not occur, r ...
missense mutation (c.1580G>T) introduced at LMNA gene – position 1580 (nt) in the DNA sequence (CGT) causing the guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
to be replaced with the thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
, yielding CTT in the DNA sequence. This results at the protein level in the replacement of the arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
by the leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-Car ...
at the position 527. This leads to destruction of salt bridge
In electrochemistry, a salt bridge or ion bridge is an essential laboratory device discovered over 100 years ago. It contains an electrolyte solution, typically an inert solution, used to connect the Redox, oxidation and reduction Half cell, ...
and structure destabilization. At phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
level this manifests with overlapping mandibuloacral dysplasia and progeria syndrome.
The resulting transcript and protein product is:
DNA: 5' - AAC AGC CTG CTT ACG GCT CTC - 3'
3' - TTG TCG GAC GAA TGC CGA GAG - 5'
mRNA: 5' - AAC AGC CUG CUU ACG GCU CUC - 3'
Protein: Asn Ser Leu Leu Thr Ala Leu
Rett Syndrome
Missense mutations in the MeCP2 protein can cause Rett syndrome, otherwise known as the RTT phenotype. This phenotype primarily effects females, as males do not live with this mutation past infancy. T158M, R306C and R133C are the most common missense mutations causing RTT. T158M is a mutation of anadenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
being substituted for a guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
causing the threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
at amino acid position 158 being substituted with a methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
. R133C is a mutation of a cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
at base position 417 in the gene encoding the MeCP2 protein being substituted for a thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
, causing an amino acid substitution at position 133 in the protein of arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
with cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
.Sickle Cell

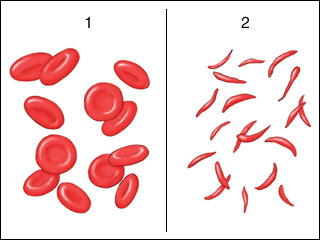
Sickle-cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying ...
changes the shape of red blood cells from round to sickle shaped. In the most common variant of sickle-cell disease, the 20th nucleotide of the gene for the beta chain of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
is altered from the codon
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links prote ...
GAG to GTG. Thus, the 6th amino acid, glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
, is substituted by valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deproton ...
—notated as an "E6V" or a "Glu6Val" mutation—which causes the protein to be sufficiently altered with a sickle-cell phenotype. The affected cells cause issues in the bloodstream as they can become sticky due to their improper ion transport leading to them being susceptible to water loss. This can cause a buildup of blood cells that obstructs blood flow to any organ in the body.
Other conditions that can be caused by missense mutations
*Alzheimers
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can incl ...
* X-linked intellectual disability
* Hypocholesterolemia
* Tangier disease
* Congenital nemaline myopathy
See also
* Ka/Ks ratio * Missense mRNAReferences
External links
{{Mutation Modification of genetic information Mutation