|
De Novo Mutation
A de novo mutation (DNM) is any mutation or alteration in the genome of an individual organism (human, animal, plant, microbe, etc.) that was not inherited from its parents. This type of mutation spontaneously occurs during the process of DNA replication during cell division. De novo mutations, by definition, are present in the affected individual but absent from both biological parents' genomes. A de novo mutation can arise in a sperm or egg cell and become a germline mutation, or after fertilization as a post-zygotic mutation that cannot be inherited by offspring. These mutations can occur in any cell of the offspring, but those in the germ line (eggs or sperm) can be passed on to the next generation. In most cases, such a mutation has little or no effect on the affected organism due to the redundancy and robustness of the genetic code. However, in rare cases, it can have notable and serious effects on overall health, physical appearance, and other traits. Disorders that most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a nucleic acid double helix, double helix of two Complementary DNA, complementary DNA strand, strands. DNA is often called double helix. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HBB Gene
Hemoglobin subunit beta (beta globin, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta) is a globin protein, coded for by the ''HBB'' gene, which along with alpha globin ( HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, hemoglobin A (HbA). It is 147 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of 15,867 Da. Normal adult human HbA is a heterotetramer consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. β-globin is encoded by the ''HBB'' gene on human chromosome 11. Mutations in the gene produce several variants of the proteins which are implicated with genetic disorders such as sickle-cell disease and beta thalassemia, as well as beneficial traits such as genetic resistance to malaria. At least 50 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Gene locus Beta-globin is produced by the gene ''HBB'' which is located in the multigene locus of β-globin locus on chromosome 11, specifically on the short arm position 15.4. Expression of beta globi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indel
Indel (insertion-deletion) is a molecular biology term for an insertion or deletion of bases in the genome of an organism. Indels ≥ 50 bases in length are classified as structural variants. In coding regions of the genome, unless the length of an indel is a multiple of 3, it will produce a frameshift mutation. For example, a common microindel which results in a frameshift causes Bloom syndrome in the Jewish or Japanese population. Indels can be contrasted with a point mutation. An indel inserts or deletes nucleotides from a sequence, while a point mutation is a form of substitution that ''replaces'' one of the nucleotides without changing the overall number in the DNA. Indels can also be contrasted with Tandem Base Mutations (TBM), which may result from fundamentally different mechanisms. A TBM is defined as a substitution at adjacent nucleotides (primarily substitutions at two adjacent nucleotides, but substitutions at three adjacent nucleotides have been observed). In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring, such as the chick (young bird), chicks hatched from one clutch (eggs), clutch of eggs, or to all offspring produced over time, as with the brood (honeybee), honeybee. Offspring can occur after mating, artificial insemination, or as a result of cloning. Human offspring (lineal descendant, descendants) are referred to as children; male children are sons and female children are daughters (see Kinship). Overview Offspring contains many parts and properties that are precise and accurate in what they consist of, and what they define. As the offspring of a new species, also known as a child or f1 generation, consist of genes of the father and the mother, which is also known as the parent generation. Each of these offspring contains numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermatozoon). Once fertilized, the ovum becomes a single diploid cell known as a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitosis, mitotic cell division, divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage (embryo), cleavage) and cellular differentiation, leading to development of a multicellular embryo after passing through an organizational checkpoint during mid-embryogenesis. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to the early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages. The main stages of animal embryonic development are as follows: * The zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions (called cleavage) to form a structure called a morula. * The morula develops into a structure called a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
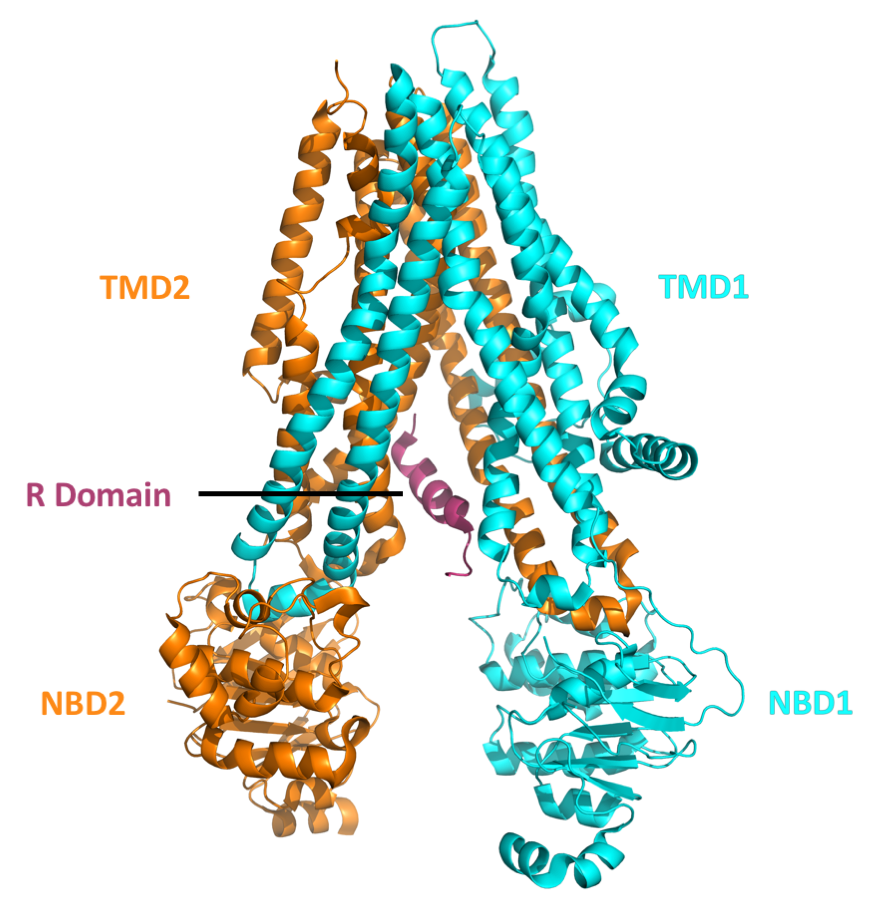
Delta F508
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a membrane protein and anion channel in vertebrates that is encoded by the ''CFTR'' gene. Geneticist Lap-Chee Tsui and his team identified the ''CFTR'' gene in 1989 as the gene linked with CF (cystic fibrosis). The ''CFTR'' gene codes for an ABC transporter-class ion channel protein that conducts chloride and bicarbonate ions across epithelial cell membranes. Mutations of the ''CFTR'' gene affecting anion channel function lead to dysregulation of epithelial lining fluid (mucus) transport in the lung, pancreas and other organs, resulting in cystic fibrosis. Complications include thickened mucus in the lungs with frequent respiratory infections, and pancreatic insufficiency giving rise to malnutrition and diabetes. These conditions lead to chronic disability and reduced life expectancy. In male patients, the progressive obstruction and destruction of the developing vas deferens (spermatic cord) and epididymis appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphylococcus aureus''. CF is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. The hallmark feature of CF is the accumulation of thick mucus in different organs. Long-term issues include Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent pneumonia, lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include Sinusitis, sinus infections, failure to thrive, poor growth, Steatorrhea, fatty stool, Nail clubbing, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies (alleles) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cftr (gene)
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a membrane protein and anion channel in vertebrates that is encoded by the ''CFTR'' gene. Geneticist Lap-Chee Tsui and his team identified the ''CFTR'' gene in 1989 as the gene linked with CF (cystic fibrosis). The ''CFTR'' gene codes for an ABC transporter-class ion channel protein that conducts chloride and bicarbonate ions across epithelial cell membranes. Mutations of the ''CFTR'' gene affecting anion channel function lead to dysregulation of epithelial lining fluid (mucus) transport in the lung, pancreas and other organs, resulting in cystic fibrosis. Complications include thickened mucus in the lungs with frequent respiratory infections, and pancreatic insufficiency giving rise to malnutrition and diabetes. These conditions lead to chronic disability and reduced life expectancy. In male patients, the progressive obstruction and destruction of the developing vas deferens (spermatic cord) and epididymis appear to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Synthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases: transcription and translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form (pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptional modifications to produce mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the cell nucleus via nuclear pores to the cytoplasm of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Stop Codon
In genetics, a nonsense mutation is a point mutation in a sequence of DNA that results in a ''nonsense codon'', or a premature stop codon in the transcribed mRNA, and leads to a truncated, incomplete, and possibly nonfunctional protein product. Nonsense mutations are not always harmful; the functional effect of a nonsense mutation depends on many aspects, such as the location of the stop codon within the coding DNA. For example, the effect of a nonsense mutation depends on the proximity of the nonsense mutation to the original stop codon, and the degree to which functional subdomains of the protein are affected. As nonsense mutations leads to premature termination of polypeptide chains; they are also called chain termination mutations. Missense mutations differ from nonsense mutations since they are point mutations that exhibit a single nucleotide change to cause substitution of a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation also differs from a nonstop mutation, which is a point muta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germline
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes ( eggs and sperm), which can come together to form a zygote. They differentiate in the gonads from primordial germ cells into gametogonia, which develop into gametocytes, which develop into the final gametes. This process is known as gametogenesis. Germ cells pass on genetic material through the process of sexual reproduction. This includes fertilization, recombination and meiosis. These processes help to increase genetic diversity in offspring. Certain organisms reproduce asexually via processes such as apomixis, parthenogenesis, autogamy, and cloning. Apomixis and Parthenogenesis both refer to the development of an embryo without fertilization. The former typically occurs in plants seeds, while the latter tends to be seen in nematodes, as well as certain species of reptiles, birds, and fish. Autogamy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |