Midline Shift on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Midline shift is a shift of the
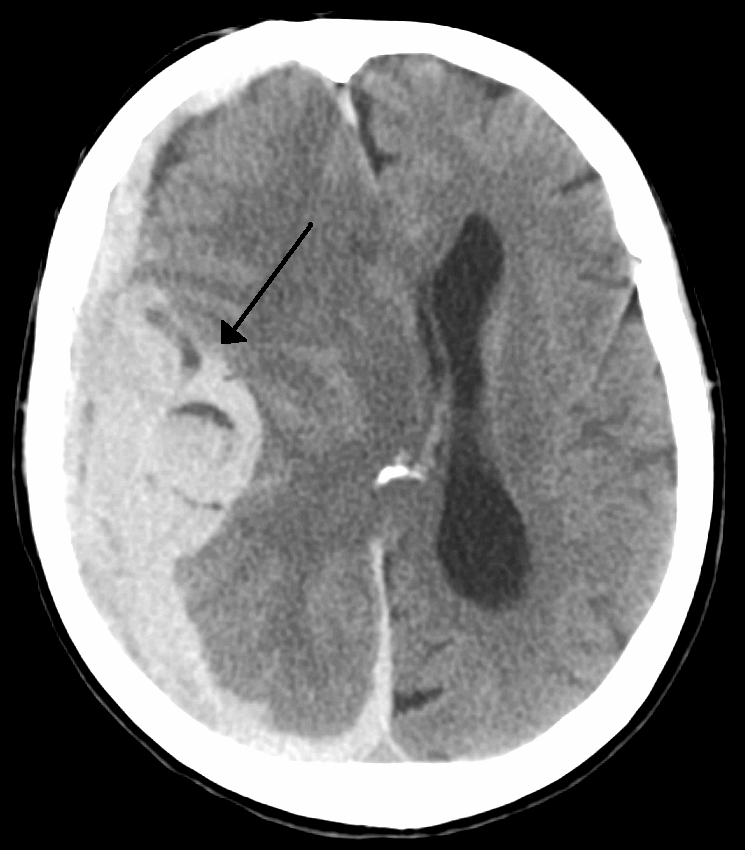 Doctors detect midline shift using a variety of methods. The most prominent measurement is done by a
Doctors detect midline shift using a variety of methods. The most prominent measurement is done by a
brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
past its center line. The sign may be evident on neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive ...
such as CT scanning
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
. The sign is considered ominous because it is commonly associated with a distortion of the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
that can cause serious dysfunction evidenced by abnormal posturing
Abnormal posturing is an involuntary flexion or extension of the arms and legs, indicating severe brain injury. It occurs when one set of muscles becomes incapacitated while the opposing set is not, and an external stimulus such as pain caus ...
and failure of the pupils to constrict in response to light. Midline shift is often associated with high intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
(ICP), which can be deadly. In fact, midline shift is a measure of ICP; presence of the former is an indication of the latter. Presence of midline shift is an indication for neurosurgeons to take measures to monitor and control ICP. Immediate surgery may be indicated when there is a midline shift of over 5 mm. The sign can be caused by conditions including traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
, or birth deformity that leads to a raised intracranial pressure.
Methods of detection
 Doctors detect midline shift using a variety of methods. The most prominent measurement is done by a
Doctors detect midline shift using a variety of methods. The most prominent measurement is done by a computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT) scan and the CT Gold Standard is the standardized operating procedure for detecting MLS. Since the midline shift is often easily visible with a CT scan, the high precision of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) is not necessary, but can be used with equally adequate results. Newer methods such as bedside sonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints ...
can be used with neurocritical patients who cannot undergo some scans due to their dependence on ventilators or other care apparatuses. Sonography has proven satisfactory in the measurement of MLS, but is not expected to replace CT or MRI. Automated measurement algorithms are used for exact recognition and precision in measurements from an initial CT scan. A major benefit to using the automated recognition tools includes being able to measure even the most deformed brains because the method doesn’t depend on normal brain symmetry. Also, it lessens the chance of human error
Human error is an action that has been done but that was "not intended by the actor; not desired by a set of rules or an external observer; or that led the task or system outside its acceptable limits".Senders, J.W. and Moray, N.P. (1991) Human Er ...
by detecting MLS from an entire image set compared to selecting the single most important slice, which allows the computer to do the work that was once manually done.
Structures of the midline
Three main structures are commonly investigated when measuring midline shift. The most important of these is theseptum pellucidum
The septum pellucidum (Latin for "translucent wall") is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the f ...
, which is a thin and linear layer of tissue located between the right and left ventricles. It is easily found on CT or MRI images due to its unique hypodensity. The other two important structures of the midline include the third ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected cerebral ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and lef ...
and the pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
, which are both centrally located and caudal to the septum pellucidum. Identifying the location of these structures on a damaged brain compared to an unaffected brain is another way of categorizing the severity of the midline shift. The terms mild, moderate, and severe are associated with the extent of increasing damage.
Midline shift in diagnoses
Midline shift measurements and imaging has multiple applications. The severity of brain damage is determined by the magnitude of the change in symmetry. Another use is secondary screening to determine deviations in brain trauma at different times after a traumatic injury as well as initial shifts immediately after. The severity of shift is directly proportional to the likeliness of surgery having to be performed. The degree of MLS can also be used to diagnose thepathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
that caused it. The MLS measurement can be used to successfully distinguish between a variety of intracranial conditions including acute subdural hematoma, malignant middle cerebral artery infarction, epidural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
, chronic subdural hematoma, infarction
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to Ischemia, inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by Thrombosis, artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as a ...
, intraventrical hemorrhage, a combination of these symptoms, or the absence of pertinent damage altogether.
See also
*Mass effect (medicine)
In medicine, a mass effect is the effect of a growing mass that results in secondary pathological effects by pushing on or displacing surrounding tissue.
In oncology, the mass typically refers to a tumor.
For example, cancer of the thyroid gla ...
References
{{reflist Neurotrauma Neuroimaging Neurology