Middle East Campaign on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mediterranean and Middle East theatre was a major
 At the
At the
 On 10 June 1940, Italy declared war on France and the United Kingdom and next day the British Commonwealth declared war on Italy. The fleets of Italy, France and the United Kingdom began the hostilities of the
On 10 June 1940, Italy declared war on France and the United Kingdom and next day the British Commonwealth declared war on Italy. The fleets of Italy, France and the United Kingdom began the hostilities of the

 In the Balkans, the Greeks had been reluctant to allow
In the Balkans, the Greeks had been reluctant to allow
 On 1 April, Rashid Ali, along with four senior Army and Air Force officers known as the "
On 1 April, Rashid Ali, along with four senior Army and Air Force officers known as the "
 In Operation Exporter, Australian,
In Operation Exporter, Australian,
 Gibraltar commanded the entrance to the Mediterranean and had been a British fortress since the early 18th century. The territory provided a strongly defended harbour, from which ships could operate in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean.
Gibraltar commanded the entrance to the Mediterranean and had been a British fortress since the early 18th century. The territory provided a strongly defended harbour, from which ships could operate in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean.
 During 1941, the British launched several offensives to push back the Axis forces in North Africa.
During 1941, the British launched several offensives to push back the Axis forces in North Africa.
 Following the Japanese
Following the Japanese
 On 15 August 1944, in an effort to aid their operations in
On 15 August 1944, in an effort to aid their operations in
Mediterranean sources and US Official accounts
* ttp://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/UN/UK/UK-Med-II/index.html The Mediterranean and Middle East Volume II The Germans come to the Help of their Ally (1941). 1956 {{DEFAULTSORT:Mediterranean, Middle East And African Theatres Of World War Ii African theatres of World War II
theatre of operations
In warfare, a theater or theatre is an area in which important military events occur or are in progress. A theater can include the entirety of the airspace, land, and sea area that is—or that may potentially become—involved in war operation ...
during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The vast size of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
theatre saw interconnected land, naval, and air campaigns fought for control of the Mediterranean, North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
. The fighting started with Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
's declaration of war against the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, until 2 May 1945 when all Axis forces
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
in Italy surrendered. However, fighting would continue in Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
– where British troops
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Gurkhas, 25,742 volunteer reserve personnel and 4,697 "other personnel", for a total of 108,4 ...
had been dispatched to aid the Greek government
The Government of Greece (Greek language, Greek: Κυβέρνηση της Ελλάδας), officially the Government of the Hellenic Republic (Κυβέρνηση της Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας) is the collective body of the Gre ...
– during the early stages of the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
.
The British referred to this theatre as the Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre (so called due to the location of the fighting and the name of Middle East Command
Middle East Command, later Middle East Land Forces, was a British Army Command established prior to the Second World War in Egypt. Its primary role was to command British land forces and co-ordinate with the relevant naval and air commands to ...
), the Americans called it the Mediterranean Theater of War and the German informal official history of the fighting is the Mediterranean, South-East Europe, and North Africa 1939–1941. Despite the large size of the theatre, the various campaigns were not seen as neatly separated areas of operations but part of a vast, contiguous theatre of war.
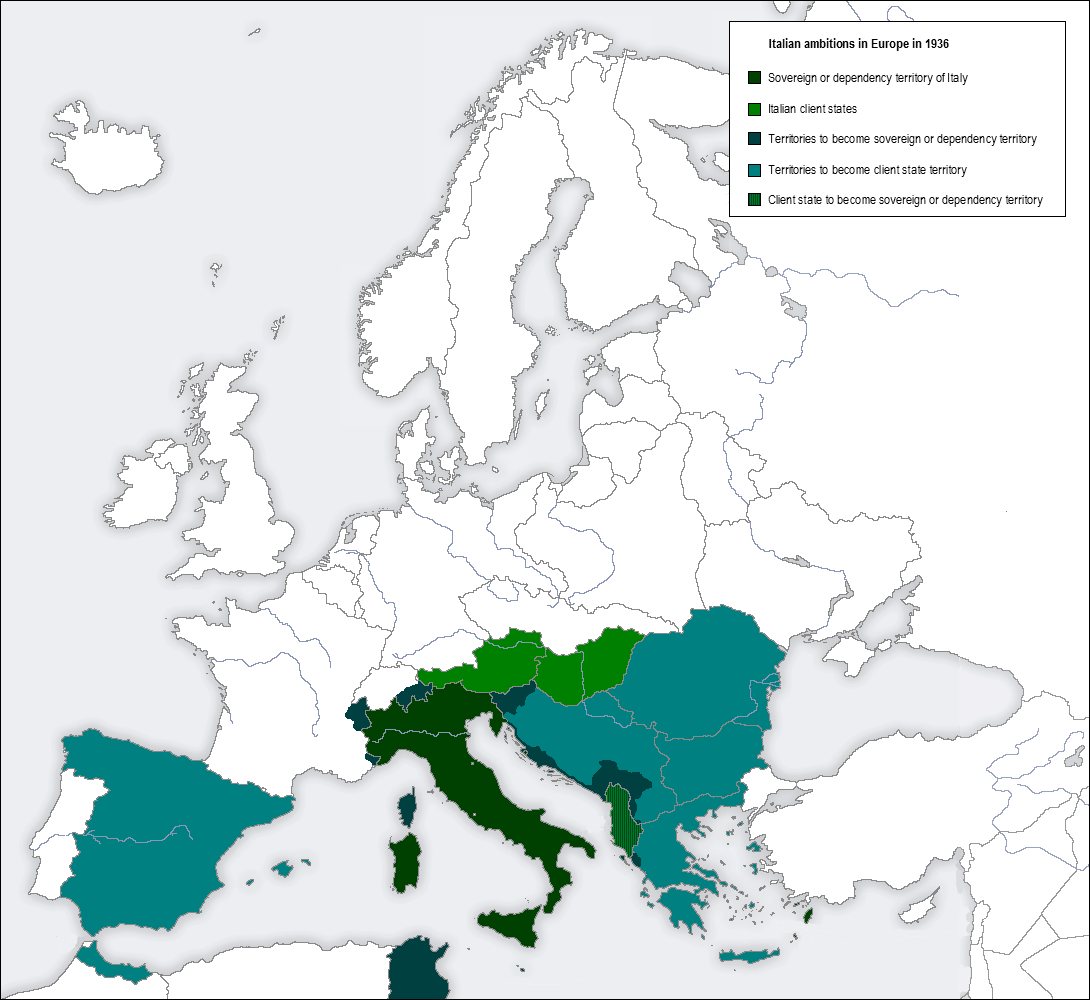
Italy aimed to carve out a new Roman Empire, while the Allies aimed to retain the status quo. Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940, and immediately invaded France and bombed Malta, which would remain under siege for over two years. Italian forces then invaded Greece, but it was not until the intervention of German forces that got it occupied. Yugoslavia was then invaded
An invasion is a military offensive of combatants of one geopolitical entity, usually in large numbers, entering territory controlled by another similar entity, often involving acts of aggression.
Generally, invasions have objectives of co ...
by Axis forces. Allied and Axis forces fought back and forth across North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, while Axis interference in the Middle East caused fighting to spread as far as Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
and Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
. With confidence high from early gains, German forces planned to capture the Middle East with a view to possibly attacking the southern border of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. Devastating losses in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, and Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
stopped the Axis threat in North Africa by May 1943. The Allies then invaded Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, resulting in an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from t ...
authorized by the royal government, causing a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. A prolonged battle for Italy was commenced between Allied and Axis forces, supported by the Allied-aligned Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
in the south and Axis-aligned Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic (, ; RSI; , ), known prior to December 1943 as the National Republican State of Italy (; SNRI), but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò (, ), was a List of World War II puppet states#Germany, German puppe ...
in the north, lasting until 2 May 1945 with the Surrender at Caserta
The Surrender at Caserta (, ) of 29 April 1945 was the written agreement that formalized the surrender of German and Italian Fascist forces in Italy, ending the Italian Campaign of World War II.
Background
Since March 1945, SS ''Obergruppen ...
.
The Mediterranean and Middle East theatre had the longest duration of the World War II, resulted in the destruction of the Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire (), also known as the Italian Empire (''Impero italiano'') between 1936 and 1941, was founded in Africa in the 19th century. It comprised the colonies, protectorates, concession (territory), concessions and depende ...
, and severely undermined the strategic position of Germany, resulting in German divisions being deployed to Africa and Italy and total German losses (including those captured upon final surrender) being over two million. Italian losses amounted to around 177,000 men with a further several hundred thousand captured during the process of the various campaigns. British losses amount to over 300,000 men killed, wounded, or captured, and total American losses in the region amounted to 130,000.
Background

Italy
During the late 1920s,Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
claimed that Italy needed an outlet for its " surplus population" and that it would be in other countries' best interests to aid in this expansion. The regime wanted "hegemony in the Mediterranean–Danubian–Balkan region" and the gaining of world power by the conquest "of an empire stretching from the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
to the Strait of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz ( ''Tangeh-ye Hormoz'' , ''Maḍīq Hurmuz'') is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world's most strategica ...
". The Fascists had designs on Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, large parts of Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
, Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
and Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
and harked back to the Roman Empire. The regime also sought to establish protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
s with Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
. Covert motives were for Italy to become the dominant power in the Mediterranean, capable of challenging France or Britain and gaining access to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
and Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
s.
On 30 November 1938, Mussolini addressed the Fascist Grand Council
The Grand Council of Fascism (, also translated "Fascist Grand Council") was the main body of Mussolini's Fascist regime in Italy, which held and applied great power to control the institutions of government. It was created as a body of the N ...
on the goal of capturing Albania, Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
, the Ticino
Ticino ( ), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts ...
canton of Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
and "French territory east of the River Var (to include Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionSavoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
)". Mussolini alleged that Italy required uncontested access to the oceans and shipping lanes to ensure its national sovereignty. Italy was a "prisoner in the Mediterranean" and had to break the chains of British and French control. Corsica, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
, Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, Suez
Suez (, , , ) is a Port#Seaport, seaport city with a population of about 800,000 in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez on the Red Sea, near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal. It is the capital and largest c ...
and Tunisia would need to be taken and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, France, Greece, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and the United Kingdom had to be challenged. Through armed conquest, the north and east African colonies would be linked and this 'prison' destroyed. Italy would be able to march "either to the Indian Ocean through the Sudan and Abyssinia, or to the Atlantic by way of French North Africa". On 2 October 1935, the Second Italo–Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression waged by Italy against Ethiopia, which lasted from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethiopia it is often referred to simply as the Ital ...
began when Italian forces invaded Abyssinia.
Mussolini lauded the conquest as a new source of raw materials and location for emigration and speculated that a native army could be raised there to "help conquer the Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
. "Almost as soon as the Abyssinian campaign ended, Italian intervention in the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War () was a military conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republicans and the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the Left-wing p ...
" began. On 7 April 1939, Mussolini began the Italian invasion of Albania
The Italian invasion of Albania was a brief military campaign which was launched by Fascist Italy, Italy against Albanian Kingdom (1928–1939), Albania in 1939. The conflict was a result of the imperialistic policies of the Italian prime m ...
and within two days had occupied the country. In May 1939, Italy formally allied to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
in the Pact of Steel
The Pact of Steel (, ), formally known as the Pact of Friendship and Alliance between Germany and Italy (, ), was a military and political alliance between Germany and Italy, signed in 1939.
The pact was initially drafted as a tripartite milita ...
.
Italian foreign policy went through two stages during the Fascist regime. Until 1934–35, Mussolini followed a "modest ... and responsible" course and following that date there was "ceaseless activity and aggression". "Prior to the Italian invasion of Ethiopia, Mussolini had made military agreements with the French and formed a coalition with the British and French to prevent German aggression in Europe." The Ethiopian War "exposed vulnerabilities and created opportunities that Mussolini seized to realise his imperial vision"
Britain
 At the
At the Nyon Conference
The Nyon Conference was a diplomatic conference held in Nyon, Switzerland, in September 1937 to address attacks on international shipping in the Mediterranean Sea during the Spanish Civil War. The conference was convened in part because Italy h ...
of 1937, Italy and the United Kingdom "disclaimed any desire to modify or see modified the national sovereignty of any country in the Mediterranean area, and agreed to discourage any activities liable to impair mutual relations." Italian diplomatic and military moves did not reflect this agreement. In the aftermath of the Italian invasion of Abyssinia, British and Italian forces in North Africa were reinforced. Due to various Italian moves, in July 1937, the British decided "that Italy could not now be regarded as a reliable friend" and preparations began to bring "the defences of the Mediterranean and the Red Sea ports up-to-date". In 1938, a weak armoured division was established in Egypt and further army and air force reinforcements were dispatched from Britain.
With rising tension in Europe, in June 1939, the United Kingdom established Middle East Command
Middle East Command, later Middle East Land Forces, was a British Army Command established prior to the Second World War in Egypt. Its primary role was to command British land forces and co-ordinate with the relevant naval and air commands to ...
(MEC) in Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
to provide centralised command for British army units in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre. All three branches of the British military were made equally responsible for the defence of the area. The authority of MEC included Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
, British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
, Cyprus, Egypt, Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
, Ethiopia, Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Greece, Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
, Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, Sudan, Tanganyika, Transjordan Transjordan may refer to:
* Transjordan (region), an area to the east of the Jordan River
* Oultrejordain, a Crusader lordship (1118–1187), also called Transjordan
* Emirate of Transjordan, British protectorate (1921–1946)
* Hashemite Kingdom o ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
and the shores of the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
. If necessary, command would be exerted as far away as the Caucasus and the Indian Ocean. The purpose of the command was to be "the western bastion of defence of India", keep British supply lines open to India and the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
, and keep the Middle Eastern oilfields out of Axis hands.
Upon the establishment of MEC, it was ordered to co-ordinate with the French military in the Middle East and Africa as well as liaise with the Turkish General Staff
The General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Türk Silahlı Kuvvetleri Genelkurmay Başkanlığı'', ''abbreviation: TSK Gnkur. Bşk.lığı'') is the highest staff organization in the Turkish Armed Forces.
Chief ...
and possibly the Greek General Staff. On 19 October 1939, the ''Treaty of Mutual Assistance'' was signed between the United Kingdom, France and Turkey and British military forces were authorised to begin discussions with the Turkish general staff; a further conference was held during March 1940. Within a week of the Italian occupation of Albania, France and the United Kingdom "announced they had promised to give all the help in their power if Greek and Romanian independence were threatened and if the Greek Government
The Government of Greece (Greek language, Greek: Κυβέρνηση της Ελλάδας), officially the Government of the Hellenic Republic (Κυβέρνηση της Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας) is the collective body of the Gre ...
or Romanian Government
The Government of Romania () forms one half of the executive branch of the government of Romania (the other half being the office of the President of Romania). It is headed by the Prime Minister of Romania, and consists of the ministries, variou ...
considered it vital to resist."
British forces in the Middle East were ordered to avoid provocation. Following the defeat of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, the threat of an Axis attack from the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
against British positions in the Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean region increased. In late 1939, with the assumption that Britain would soon be at war with Italy, planning began for attacks to capture Bardia
Bardia, also El Burdi or Bardiyah ( or ) is a Mediterranean seaport in the Butnan District of eastern Libya, located near the border with Egypt. It is also occasionally called ''Bórdi Slemán''.
The name Bardia is deeply rooted in the ancient ...
and Jaghbub
Jaghbub () () is a remote desert village in the Al Jaghbub Oasis in the eastern Libyan Desert. It is actually closer to the Egyptian town of Siwa than to any Libyan town of note. The oasis is located in Butnan District and was the administrati ...
(Giarabub) in Libya and arrangements began in Egypt, to accommodate a much larger force. Preparations to reinforce the Iraqi army were made and Palestinian security forces were to be reduced to the minimum. British forces in East Africa were to study operations to destroy the Italian forces and support local risings, all in support of the main Allied offensive, which was planned to be launched from French Somaliland
French Somaliland (; ; ) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which became the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas. The Republic of Djibouti is its legal successor state.
History
French Somalil ...
. Troops in Sudan were also asked to consider launching operations against Kufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of the 19th century, Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
in southern Libya.
Initial military operations
Battle of the Mediterranean
The Battle of the Mediterranean was the name given to the naval campaign fought in the Mediterranean Sea during World War II, from 10 June 1940 to 2 May 1945.
For the most part, the campaign was fought between the Kingdom of Italy, Italian Reg ...
. The siege of Malta soon began, with the first Italian air attack on 11 June. In the Western Desert
In Egypt, the Western Desert is an area of the Sahara that lies west of the river Nile, up to the Libyan border, and south from the Mediterranean Sea to the border with Sudan. It is named in contrast to the Eastern Desert which extends east fro ...
, Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
(RAF) aircraft attacked Italian positions inside Libya. On 11 June, the Western Desert Campaign
The Western Desert campaign (Desert War) took place in the Sahara Desert, deserts of Egypt and Libya and was the main Theater (warfare), theatre in the North African campaign of the Second World War. Military operations began in June 1940 with ...
began, as the British launched minor raids and conducted patrols along the Libyan–Egyptian border and on 17 June, Fort Capuzzo
Fort Capuzzo () was a fort in the colony of Italian Libya, near the Libya–Egypt border, next to the Italian Frontier Wire. The () ran south from Bardia to Fort Capuzzo, inland, west of Sollum, then east across the Egyptian frontier to the ...
was captured. On 20 June, Mussolini began the Italian invasion of France
The Italian invasion of France (10–25 June 1940), also called the Battle of the Alps, was the first major Fascist Italy, Italian engagement of World War II and the last major engagement of the Battle of France.
The Italian entry into the war ...
, just before the end of the Battle of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembour ...
. During June, the East African Campaign began with Italian attacks in East Africa, although ground combat did not start until July.
On 22 June, France signed an armistice at Compiegne with Germany and on 24 June, the Franco-Italian Armistice
The Franco-Italian Armistice, or Armistice of Villa Incisa, signed on 24 June 1940, in effect from 25 June, ended the brief Italian invasion of France during the Second World War.
On 10 June 1940, Italy declared war on France while the latter wa ...
was signed. Italy gained a demilitarised zone inside France (as well as similar zones where Italian and French colonies met). Italian occupation forces took over an area of France, which included 28,500 people and the town of Menton
Menton (; in classical norm or in Mistralian norm, , ; ; or depending on the orthography) is a Commune in France, commune in the Alpes-Maritimes department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region on the French Riviera, close to the Italia ...
. The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
attacked the French fleet in the North African port of Mers-el-Kébir on 3 July 1940, after it refused to sail to Britain or the French West Indies and demobilise, as part of a larger plan to stop the French fleet from falling into German or Italian hands.
When Italy entered the war, there were no plans for an invasion of Egypt while France was still able to resist. When France surrendered, Mussolini gave instructions for his generals to prepare an offensive. On 10 August, he instructed his forces to be prepared to attack in conjunction with the German invasion of the United Kingdom. While his generals did not believe they were prepared, they were ordered to push forward without any solid objectives.
On 9 September, Italian aircraft start preparation bombardments for the invasion of Egypt. Four days later, Italian forces invaded Egypt as far as Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani ( ) is a town in Egypt, near the Mediterranean Sea, about east of the Egypt–Libya border, and around from Tobruk, Libya.
Named after Sidi es-Saadi el Barrani, a Senussi sheikh who was a head of its Zawiya, the village ...
before digging in, west of the main British position at Mersa Matruh
Mersa Matruh (), also transliterated as Marsa Matruh ( Standard Arabic ''Marsā Maṭrūḥ'', ), is a port in Egypt and the capital of Matrouh Governorate. It is located west of Alexandria and east of Sallum on the main highway from the Nile ...
. In East Africa, after some initial offensive actions, the Italian conquest of British Somaliland
The Italian invasion of British Somaliland (3–19 August 1940) was part of the East African campaign (1940–1941) in which Italian, Eritrean and Somali forces entered the Somaliland Protectorate and defeated its garrison of British, Common ...
began in August and annexed the colony. After crossing the Albanian border, Italian forces began the Greco-Italian War
The Greco-Italian War (), also called the Italo-Greek War, Italian campaign in Greece, Italian invasion of Greece, and War of '40 in Greece, took place between Italy and Greece from 28 October 1940 to 23 April 1941. This conflict began the Balk ...
by invading Greece on 28 October. The Greek army repulsed the Italian attack and commenced a counter-offensive on 14 November, which pushed Italian forces back into Albania.
The British and Italian fleets began a series of engagements on the Mediterranean, such as the Battle of Calabria
The Battle of Calabria (9 July 1940) known to the Italian Navy as the Battle of Punta Stilo, was a naval battle during the Battle of the Mediterranean in the Second World War. Ships of the were opposed by vessels of the Mediterranean Fleet. ...
, Espero Convoy, Cape Spada
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment of any length that hangs loosely and connects either at the neck or shoulders. They usually cover the back, shoulders, and arms. They come in a variety of styles and have been used thr ...
, and Cape Spartivento
Domus de Maria is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of South Sardinia in the Italian region Sardinia, located about southwest of Cagliari.
Domus de Maria borders the following municipalities: Pula, Santadi, and Teulada.
See also
* ...
.
The Royal Navy inflicted a major setback upon the Italian Royal Navy during the Battle of Taranto
The Battle of Taranto took place on the night of 11/12 November 1940 during the Second World War between British naval forces (Admiral Andrew Cunningham) and Italian naval forces (Admiral Inigo Campioni). The Royal Navy launched the first all ...
on the night of 12/13 November. After assembling enough forces the British launched a counter-attack upon the Italians in Egypt. Operation Compass
Operation Compass (also ) was the first large British military operation of the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) during the Second World War. British metropolitan, Imperial and Commonwealth forces attacked the Italian and Libyan forces of ...
drove the Italians out of Egypt and resulted in the destruction of the Italian 10th Army in February 1941. Following this success, British forces adopted a defensive position in North Africa and redeployed most troops to Greece in Operation Lustre
Operation Lustre was an action during the Second World War: the movement of British and other Allied troops (Australian, Indian, South African, New Zealand, Czech and Polish) from Egypt to Greece in March and April 1941, in response to the fai ...
, leaving a weak force garrisoning the gains made from Operation Compass. In March, the Battle of Kufra ended with the Italians losing the desert oasis of Kufra—a vital link between Italian east and north Africa—which was located in south-eastern Libya.
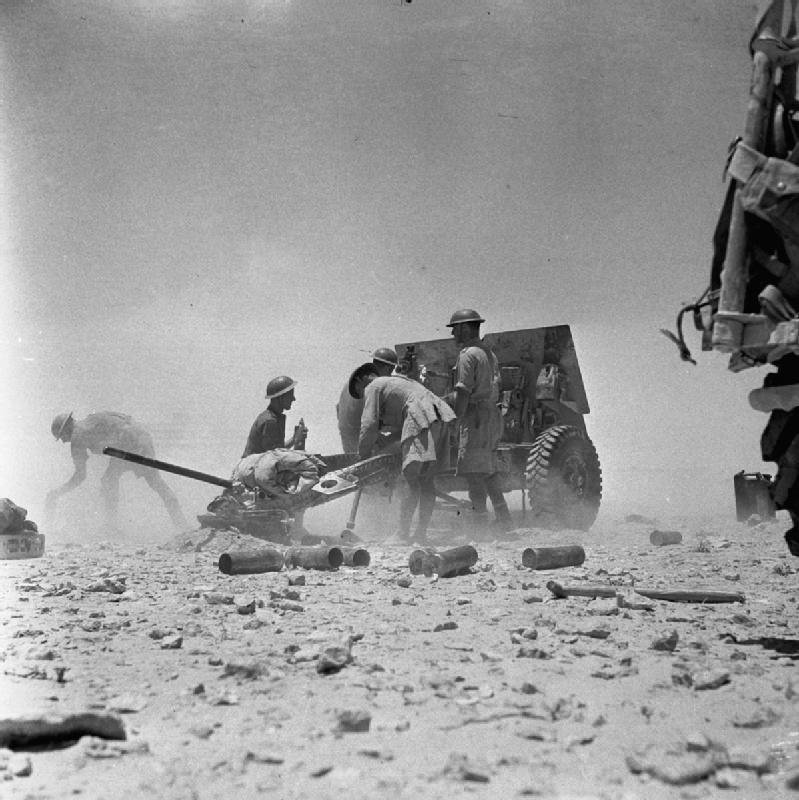
Axis success
North Africa
In North Africa, the Italians responded to the defeat of their Tenth Army by dispatching armour and motorised divisions. Germany dispatched the ''Afrika Korps
The German Africa Corps (, ; DAK), commonly known as Afrika Korps, was the German expeditionary force in Africa during the North African campaign of World War II. First sent as a holding force to shore up the Italian defense of its Africa ...
'' in Operation Sonnenblume
Operation Sonnenblume (, "Operation Sunflower") was the name given to the dispatch of German and Italian troops to North African campaign, North Africa in February 1941, during the Second World War. The Italian Tenth Army (Italy), 10th Army () ha ...
, to bolster the Italians with a mission to block further Allied attempts to drive the Italians out of the region. Its commander was General Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel (; 15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944), popularly known as The Desert Fox (, ), was a German '' Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal) during World War II. He served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of ...
and Rommel himself was subordinated to the Italian command. But Rommel seized on the weakness of his opponents and without waiting for his forces to fully assemble, rapidly went on the offensive. In March–April 1941, the German and Italian forces defeated the British forces and forced the British and Commonwealth forces into retreat.
The Australian 9th Infantry Division fell back to the fortress port of Tobruk
Tobruk ( ; ; ) is a port city on Libya's eastern Mediterranean coast, near the border with Egypt. It is the capital of the Butnan District (formerly Tobruk District) and has a population of 120,000 (2011 est.)."Tobruk" (history), ''Encyclop� ...
and the remaining British and Commonwealth forces withdrew a further east to Sollum
Sallum ( various transliterations include ''El Salloum'', ''As Sallum'' or ''Sollum'') is a harbourside village or town in Egypt. It is along the Egypt/Libyan short north–south aligned coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the far northwest corner o ...
on the Libyan–Egyptian border. The main Axis force began the Siege of Tobruk
The siege of Tobruk () took place between 10 April and 27 November 1941, during the Western Desert campaign (1940–1943) of the World War II, Second World War. An Allies of World War II, Allied force, consisting mostly of the 9th Division ...
, and a small German force pressed eastwards, retaking all territory lost to Operation Compass, and advanced into Egypt. By the end of April, Sollum had fallen and the important Halfaya Pass captured.
East Africa
InEast Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
, the British launched a counter-attack against the Italians from Kenya Colony
The Colony and Protectorate of Kenya, commonly known as British Kenya or British East Africa, was part of the British Empire in Africa from 1920 until 1963. It was established when the former East Africa Protectorate was transformed into a Brit ...
and Sudan through Somaliland, Eritrea and Ethiopia in 1940 and early 1941. Landings were subsequently conducted in British Somaliland and Italian Ethiopia
Italian East Africa (, A.O.I.) was a short-lived colonial possession of Fascist Italy from 1936 to 1941 in the Horn of Africa. It was established following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, which led to the military occupation of the Ethiopian Em ...
, while an expedition from the Sudan moved on Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; ,) is the capital city of Ethiopia, as well as the regional state of Oromia. With an estimated population of 2,739,551 inhabitants as of the 2007 census, it is the largest city in the country and the List of cities in Africa b ...
. The Italian Viceroy, Duke Amedeo d'Aosta, was forced to surrender by 18 May which effectively ended the campaign, allowing the Empire of Ethiopia to be re-established under Haile Selassie
Haile Selassie I (born Tafari Makonnen or ''Ethiopian aristocratic and court titles#Lij, Lij'' Tafari; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as the Ethiopian aristocratic and court titles, Rege ...
. A number of Italian garrisons continued to hold out, but the last of these, at Gondar
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on ...
, surrendered in November. Small groups of Italian troops carried out the Italian guerrilla war in Ethiopia
The Italian guerrilla war in Ethiopia was a conflict fought from the summer of 1941 to the autumn of 1943 by remnants of Italian troops in Ethiopia and Somalia, in a short-lived attempt to re-establish Italian East Africa. The guerrilla campai ...
until October 1943.
Balkans
 In the Balkans, the Greeks had been reluctant to allow
In the Balkans, the Greeks had been reluctant to allow British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
troops into the country, because Britain could not spare enough forces to guarantee victory. They had, however, accepted aid from the RAF in their war with the Italians in Albania. As it became likely Germany would attack Greece, four British divisions were switched from North Africa to reinforce Greek Army. The advanced guards of these troops began arriving in March 1941, triggering the entry of German forces into Bulgaria, which made clear the German intent to invade Greece.
In April 1941, the Axis forces invaded Yugoslavia. They captured Yugoslavia in 11 days and partitioned it among themselves and newly formed client states: The Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia (, NDH) was a World War II–era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Fascist Italy. It was established in parts of Axis occupation of Yugoslavia, occupied Yugoslavia on 10 April 1941, ...
and Nedić's Serbia
The Government of National Salvation (; , VNS), also referred to as Nedić's government or Nedić's regime, was the colloquial name of the second Serbian collaborationist puppet government established after the Commissioner Government in the ...
. In spring 1941, Italy created a Montenegrin client state and annexed most of the Dalmatian coast as the Governorship of Dalmatia
The Governorate of Dalmatia (; ) was an administrative division of the Kingdom of Italy that existed during two periods, first from 1918 to 1920 and then from 1941 to 1943. The first Governorate of Dalmatia was established following the end of Wo ...
(''Governatorato di Dalmazia''). A complex guerrilla uprising of communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
-led Partisans
Partisan(s) or The Partisan(s) may refer to:
Military
* Partisan (military), paramilitary forces engaged behind the front line
** Francs-tireurs et partisans, communist-led French anti-fascist resistance against Nazi Germany during WWII
** Itali ...
, commanded by Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
, soon broke out. A more ambivalent, predominantly Serb paramilitary movement of royalist Chetniks both fought the occupying forces and collaborated with them against the communists. The Yugoslav partisans eventually gained recognition from the Allies as the sole resistance movement. With help from both the Soviets and the Western Allies, they turned into a formidable fighting force and successfully liberated the country.
Following the Italian invasion on 28 October 1940, which is usually known as the Greco-Italian War
The Greco-Italian War (), also called the Italo-Greek War, Italian campaign in Greece, Italian invasion of Greece, and War of '40 in Greece, took place between Italy and Greece from 28 October 1940 to 23 April 1941. This conflict began the Balk ...
, the Greek forces, with British air and material support, repelled the initial Italian attack and a counter-offensive in March 1941. When the German invasion, known as Operation Marita
The German invasion of Greece or Operation Marita (), were the attacks on Greece by Italy and Germany during World War II. The Italian invasion in October 1940, which is usually known as the Greco-Italian War, was followed by the German invasio ...
, began on 6 April, the bulk of the Greek Army
The Hellenic Army (, sometimes abbreviated as ΕΣ), formed in 1828, is the land force of Greece. The term '' Hellenic'' is the endogenous synonym for ''Greek''. The Hellenic Army is the largest of the three branches of the Hellenic Armed F ...
was on Albania fighting against the Italian forces and only six Greek divisions were only deployed to defend the Metaxas Line
The Metaxas Line (, ''Grammi Metaxa'') was a chain of fortifications constructed along the line of the Greco-Bulgarian border, designed to protect Greece in case of a Bulgarian invasion after the rearmament of Bulgaria. It was named after Ioa ...
in case of a looming German invasion.
German troops invaded Greece from Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, creating a second front. Greece received a small reinforcement from British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
n and New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
forces in anticipation of the German attack. While the Italians had launched a second spring offensive in Albania forcing the Greeks to retreat back to mainland Greece. The Greek army found itself outnumbered in its effort to defend against both German and Italian forces. As a result, the Metaxas defensive line did not receive adequate troop reinforcements and was quickly overrun by the Germans, who then outflanked the Greek forces at the Albanian border, forcing their surrender. British, Australian and New Zealand forces were overwhelmed and forced to retreat, with the ultimate goal of evacuation.
After moving through south-eastern Yugoslavia, the Germans had been able to turn the Allied flank, cutting off Greek units in the east of the country. Greek forces in central Macedonia were isolated from the Commonwealth forces moving up in an attempt stabilise the front, with the Germans then falling on the rear of the main Greek army facing the Italians in Macedonia. The German advance into Greece was made easier because the bulk of the Greek Army was engaged fighting the Italians on the Albanian front in the north of the country.
The Greeks were forced to capitulate, ending resistance on the mainland by the end of the month. Abandoning most of its equipment, the Commonwealth force retreated to the island of Crete. From 20 May, the Germans attacked the island by using paratroops
A paratrooper or military parachutist is a soldier trained to conduct military operations by parachuting directly into an area of operations, usually as part of a large airborne forces unit. Traditionally paratroopers fight only as light infa ...
to secure an air bridgehead despite suffering heavy casualties. They then flew in more troops and were able to capture the rest of the island by 1 June. With their victory in the Battle of Crete
The Battle of Crete (, ), codenamed Operation Mercury (), was a major Axis Powers, Axis Airborne forces, airborne and amphibious assault, amphibious operation during World War II to capture the island of Crete. It began on the morning of 20 May ...
the Germans had secured their southern flank and turned their attention towards the Soviet Union.
Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
later blamed the failure of his invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along a ...
on Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his overthrow in 194 ...
's failed conquest of Greece. Andreas Hillgruber
Andreas Fritz Hillgruber (18 January 1925 – 8 May 1989) was a Conservatism, conservative German historian who was influential as a military and diplomatic historian who played a leading role in the ''Historikerstreit'' of the 1980s. In his contr ...
has accused Hitler of trying to deflect blame for his country's defeat from himself to his ally, Italy. It nevertheless had serious consequences for the Axis war effort in the North African theatre. Enno von Rintelen, who was the military attaché in Rome, emphasises, from the German point of view, the strategic mistake of not taking Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
.
Middle East operations
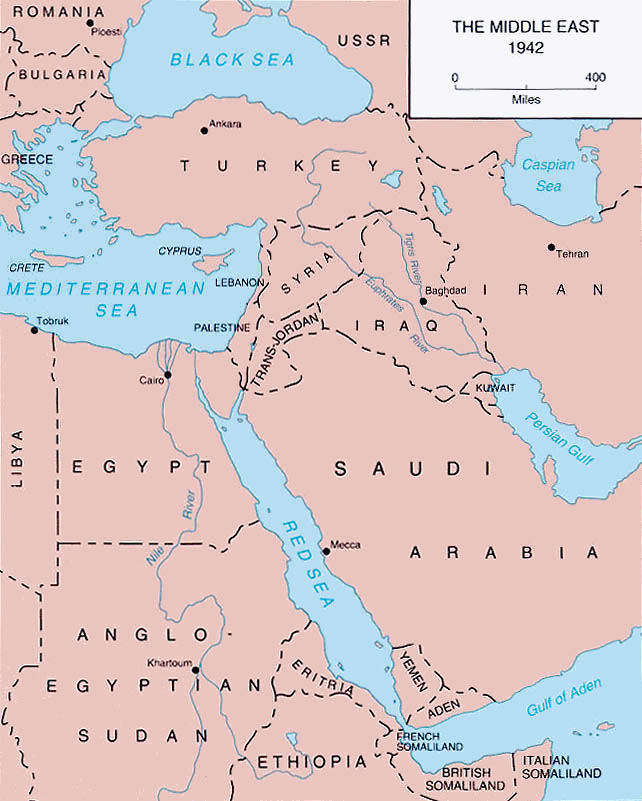
Iraq
When Italy entered the war, the Iraqi government did not break off diplomatic relations, as they had done with Germany. The Italian Legation in Baghdad became the centre for Axis propaganda and for fomenting anti-British feeling. In this they were aided byMohammad Amin al-Husayni
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, ...
, the British appointee as the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem
The Grand Mufti of Jerusalem is the Sunni Muslim cleric in charge of Jerusalem's Islamic holy places, including Al-Aqsa. The position was created by the British military government led by Ronald Storrs in 1918.See Islamic Leadership in Jerusa ...
, who had fled from the British Mandate of Palestine shortly before the outbreak of war and later received asylum in Baghdad. In January 1941, there was a political crisis within Iraq as Rashid Ali resigned as Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
of Iraq and was replaced by Taha al-Hashimi; civil war loomed. On 31 March, the Regent
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
of Iraq, Prince 'Abd al-Ilah
Abd al-Ilah of Hejaz () (; also written Abdul Ilah or Abdullah; 14 November 1913 – 14 July 1958) was a cousin and brother-in-law of Ghazi of Iraq, King Ghazi of the Kingdom of Iraq, Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq and was regent for his nephew Fai ...
, learnt of a plot to arrest him and fled Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
for RAF Habbaniya
Royal Air Force Habbaniya, more commonly known as RAF Habbaniya (), (originally RAF Dhibban), was a Royal Air Force station at Habbaniyah, about west of Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, on the banks of the Euphrates near Lake Habbaniyah. It was dev ...
, from whence he was flown to Basra and given refuge on the .
 On 1 April, Rashid Ali, along with four senior Army and Air Force officers known as the "
On 1 April, Rashid Ali, along with four senior Army and Air Force officers known as the "Golden Square
Golden Square, in Soho, the City of Westminster, London, is a mainly hardscaped garden square planted with a few mature trees and raised borders in Central London flanked by classical office buildings. Its four approach ways are north and so ...
", seized power via a ''coup d'état
A coup d'état (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
'' and Rashid Ali proclaimed himself Chief of the "National Defence Government." The Golden Square deposed al-Hashimi and restored Rashid Ali. Ali did not overthrow the monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
and named a new Regent to King
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
Faisal II
Faisal II (; 2 May 1935 – 14 July 1958) was the last King of Iraq. He reigned from 4 April 1939 until July 1958, when he was killed during the 14 July Revolution. This regicide marked the end of the thirty-seven-year-old Hashemite monarchy ...
, Sherif Sharaf. The leaders of the "National Defence Government" proceeded to arrest many pro-British citizens and politicians but many escaped through Amman
Amman ( , ; , ) is the capital and the largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of four million as of 2021, Amman is Jordan's primate city and is the largest city in the Levant ...
in Transjordan. The new regime planned to refuse further concessions to the United Kingdom, to retain diplomatic links with Fascist Italy and to expel the most prominent pro-British politicians. The plotters considered the United Kingdom to be weak and believed that its government would negotiate with their new government regardless of its legality. On 17 April, Rashid Ali, on behalf of the "National Defence Government" asked Germany for military assistance in the event of war with the British. Ali attempted to restrict British rights guaranteed under Article 5 of the 1930 Anglo-Iraqi Treaty, when he insisted that newly arrived British troops quickly be transported through Iraq and to Palestine.
Before the coup, Rashid Ali's supporters had been informed that Germany would recognise the independence of Iraq from the British Empire. There had also been discussions on war material being sent to support the Iraqis and other Arab factions in fighting the British. On 3 May, German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich-Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German Nazi politician and diplomat who served as Minister for Foreign Affairs (Germany), Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945. ...
persuaded Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
to secretly return Dr. Fritz Grobba
Fritz Konrad Ferdinand Grobba (18 July 1886 – 2 September 1973) was a German diplomat during the interwar period and World War II. Early life
He was born in Gartz on the Oder in the Province of Brandenburg, Germany. His parents were Rudolf Grob ...
to Iraq to lead a diplomatic mission to channel support to the Rashid Ali regime but the British quickly learned of the German arrangements through intercepted Italian diplomatic transmissions. On 6 May, in accordance with the Paris Protocols
The Paris Protocols were an agreement between Nazi Germany and Vichy France negotiated in May 1941. Although not ratified, the protocols were implemented. Admiral François Darlan represented the French and the German ambassador to France, Otto ...
, Germany concluded a deal with the Vichy French
Vichy France (; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was a French rump state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II, established as a result of the French capitulation after the defeat against G ...
government to release war materials, including aircraft, from sealed stockpiles in the French Mandate of Syria
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (; , also referred to as the Levant States; 1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate founded in the aftermath of the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, concerning the territories ...
and transport them to Iraq. The French also agreed to allow passage of other weapons and material and loaned several airbases in northern Syria to Germany, for the transport of German aircraft to Iraq. Between 9 May and the end of the month, about 100 German and about 20 Italian aircraft landed on Syrian airfields.
On 30 April, the Iraqi Army surrounded and besieged RAF Habbaniya; the base had no operational aircraft but the RAF converted trainers to carry weapons and a battalion of infantry reinforcements was flown in. German and Italian aircraft supported the Iraqi army and British reinforcements were dispatched to Iraq from Transjordan and India. The larger but poorly trained Iraqi force was defeated and Baghdad and Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ...
were captured. Ali and his supporters fled the country and an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from t ...
was signed, restoring the monarchy of Faisal II, the Kingdom of Iraq
The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq was the Iraqi state located in the Middle East from 1932 to 1958. It was founded on 23 August 1921 as the Kingdom of Iraq, following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in the Mesopotamian campaign of the First World W ...
and a pro-British government. The defeat of the rebellion saw the defeat of the German-Italian attempt to entrench an Axis state in Iraq and worsened relations between the UK and Vichy France, culminating in the Syria-Lebanon Campaign.
Operation Exporter
 In Operation Exporter, Australian,
In Operation Exporter, Australian, Free French
Free France () was a resistance government
claiming to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third French Republic, Third Republic during World War II. Led by General , Free France was established as a gover ...
, British and Indian units invaded Syria and Lebanon from Palestine in the south on 8 June 1941. Vigorous resistance was met from the Vichy French but superior Allied infantry equipment and numbers overwhelmed the defenders. More attacks were launched at the end of June and early July from Iraq into northern and central Syria, by Iraqforce
Iraqforce was a British and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth formation that came together in the Kingdom of Iraq. The formation fought in the Middle East during World War II.
Background
During World War I, the British Army defeated the Otto ...
. By 8 July, north-east Syria had been captured and elements of Iraqforce had advanced up the river Euphrates towards Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
, the rear of the Vichy forces defending Beirut from the advance from the south. Negotiations for an armistice were started on 11 July and surrender terms signed on 14 July.
Iran
Supplies to theSoviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
had been sent via the North Cape to Murmansk
Murmansk () is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far Far North (Russia), northwest part of Russia. It is the world's largest city north of the Arctic Circle and sits on both slopes and banks of a modest fjord, Ko ...
and Archangel
Archangels () are the second lowest rank of angel in the Catholic hierarchy of angels, based on and put forward by Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite in the 5th or 6th century in his book ''De Coelesti Hierarchia'' (''On the Celestial Hierarchy'') ...
soon after the German invasion but the number of ships available was limited and convoys were vulnerable to German air and submarine attack. Supplies were also sent from American pacific ports to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
in Soviet-flagged ships but Allied planners wished to open another supply route through Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. Though officially neutral, the Shah
Shāh (; ) is a royal title meaning "king" in the Persian language.Yarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII, no. 1 (1989) Though chiefly associated with the monarchs of Iran, it was also used to refer to the leaders of numerous Per ...
was widely viewed as pro-German by the allies. Following the Shah's refusal to open Iran up as a supply route for war materiel to the USSR; the allies invaded and occupied Iran in August 1941. The Shah, who urged his military not to resist the invasion, was deposed and his young son placed on the throne as titular head of an allied controlled puppet government
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its ord ...
. Iranian oil fields were secured and the line of supply to Russia established and maintained for the remainder of the war.
Mandatory Palestine
Operation Atlas was carried out by a special commando unit of theWaffen SS
The (; ) was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's paramilitary ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with volunteers and conscripts from both German-occupied Europe and unoccupied lands. ...
and took place in October 1944. It involved five soldiers: three who were previously members of the Templer religious sect in Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine was a British Empire, British geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine, and after 1922, under the terms of the League of Nations's Mandate for Palestine.
After ...
, and two Palestinian Arabs
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
who were close collaborators of the mufti of Jerusalem
The Grand Mufti of Jerusalem is the Sunni Muslim cleric in charge of Jerusalem's Islamic holy places, including Al-Aqsa. The position was created by the British military government led by Ronald Storrs in 1918.See Islamic Leadership in Jerusal ...
, Amin al-Husseini
Mohammed Amin al-Husseini (; 4 July 1974) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist and Muslim leader in Mandatory Palestine. was the scion of the family of Jerusalemite Arab nobles, who trace their origins to the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Hussein ...
. Atlas aimed at establishing an intelligence-gathering base in Mandatory Palestine, radioing information back to Germany, and recruiting and arming anti-British Palestinians by buying their support with gold. The plan failed utterly, and no meaningful action could be undertaken by the commandos. Three of the participants were arrested by the Transjordan Frontier Force
The Trans-Jordan Frontier Force was formed on 1 April 1926, to replace the disbanded British Gendarmerie. It was a creation of the British High Commissioner for Palestine whose intention was that the Force should defend Trans-Jordan's northe ...
a few days after their landing. The German commander was captured in 1946 and the fifth, Hasan Salama
Hasan Salama (also spelled Hassan Salameh; , ; 1913 – 2 June 1948) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist guerrilla leader and commander who led the Palestinian Holy War Army (''Jaysh al-Jihad al-Muqaddas'', Arabic: ) in the 1948 Palestine War ...
, succeeded in escaping.
Operation Mammoth
In 1943 a small team of German agents parachuted intoIraqi Kurdistan
Iraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan () refers to the Kurds, Kurdish-populated part of northern Iraq. It is considered one of the four parts of Greater Kurdistan in West Asia, which also includes parts of southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdist ...
with the goal of covertly sabotaging Kirkuk oil fields and create a Kurdish uprising against the British with assistance from local Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
who were seeking to create an independent Kurdistan
Kurdistan (, ; ), or Greater Kurdistan, is a roughly defined geo- cultural region in West Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity have historically been based. G ...
. Further reinforcements of Nazis with weapons was supposed to be sent but the mission failed within days as the Nazi commandos landed 300 km away from their target destination and lost their weapons. They were soon arrested by the British and faced execution as spies, however they were released several years after World War II ended. Gottfried Müller, one of the Nazi parachuters, would later write and publish a book describing his experiences in Kurdistan named “Im brennenden Orient” ('The Burning Orient'), which was published in Germany in 1959.
Gibraltar and Malta
 Gibraltar commanded the entrance to the Mediterranean and had been a British fortress since the early 18th century. The territory provided a strongly defended harbour, from which ships could operate in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean.
Gibraltar commanded the entrance to the Mediterranean and had been a British fortress since the early 18th century. The territory provided a strongly defended harbour, from which ships could operate in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean. Force H
Force H was a British naval formation during the Second World War. It was formed in late-June 1940, to replace French naval power in the western Mediterranean removed by the French armistice with Nazi Germany. The force occupied an odd place ...
(Vice-Admiral
Vice admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, usually equivalent to lieutenant general and air marshal. A vice admiral is typically senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral.
Australia
In the Royal Australian Navy, the rank of vic ...
James Somerville
Admiral of the Fleet Sir James Fownes Somerville (17 July 1882 – 19 March 1949) was a Royal Navy admiral of the fleet. He served in the First World War as fleet wireless officer for the Mediterranean Fleet where he was involved in providing ...
) was based in Gibraltar and had the task of maintaining naval superiority and providing a strong escort for convoys to and from the Malta. Malta was from Sicily and one of the first targets of the Italian army and the ''Regia Aeronautica
The Royal Italian Air Force (''Regia Aeronautica Italiana'') (RAI) was the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Regio Esercito, Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946. In 1946, the monarchy was ...
''; the air defence of Malta comprised six obsolescent Gloster Gladiator
The Gloster Gladiator is a British biplane fighter. It was used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) (as the Sea Gladiator variant) and was exported to a number of other air forces during the late 1930s.
Developed privat ...
biplanes. After the first Italian air attacks it became clear that Malta could be defended and in early July, the Gladiators were reinforced by twelve Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by ...
fighters.
The ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official military branch, branche ...
'' began operations in the Mediterranean with establishment of the 23rd U-boat Flotilla
''23rd U-boat Flotilla'' ("23. Unterseebootsflottille") was a unit of Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine'' during World War II.
The flotilla was first formed in Salamis, Greece, on 11 September 1941 under the command of '' Kapitänleutnant'' Fritz Fr ...
at a base on Salamis Island
Salamis ( ; ) or Salamina () is the largest Greece, Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about from the coast of Athens' port of Piraeus and about west of Athens center.
The chief city, Salamina (city), Salamina, lies in the west-facing core of ...
in Greece in September 1941. The flotilla was to operate against British supply convoys to Allied forces on Malta and in Tobruk. On 7 December, control of the 23rd Flotilla was transferred from Kernével to Field Marshal Albert Kesselring
Albert Kesselring (30 November 1885 – 16 July 1960) was a German military officer and convicted war crime, war criminal who served in the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. In a career which spanned both world wars, Kesselring reached the ra ...
, Commander in Chief South (''OB Süd
The Ob (; ) is a major river in Russia. It is in western Siberia, and with its tributary the Irtysh forms the world's seventh-longest river system, at . The Ob forms at the confluence of the Biya and Katun which have their origins in the Alta ...
'') in Italy. Additional bases were established in Pola and La Spezia
La Spezia (, or ; ; , in the local ) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second-largest city in the Liguria ...
in northern Italy, as more U-boats were sent to the Mediterranean.
Bombing and the naval blockade led to food and commodity shortages and rationing was imposed on the inhabitants. The ''Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
'' and the ''Regia Aeronautica
The Royal Italian Air Force (''Regia Aeronautica Italiana'') (RAI) was the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Regio Esercito, Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946. In 1946, the monarchy was ...
'' reinforcements in the Mediterranean joined in the bombing but during a lull in early 1942, 61 Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft that was used by the Royal Air Force and other Allies of World War II, Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. It was the only British fighter produced conti ...
s were delivered, which very much improved the defensive situation, although food, ammunition, and fuel were still short. Supply runs during lulls in the bombing kept Malta in being but many ships like were damaged too severely to leave. The defence of the island ensured that the Allies had an advantage in the fight to control the Mediterranean and as the garrison recovered from periods of intense bombing, aircraft, submarines and light surface ships resumed attacks on Axis supply ships, leading to fuel and supply shortages for the Axis forces in Libya.
Allied reply
Western Desert
 During 1941, the British launched several offensives to push back the Axis forces in North Africa.
During 1941, the British launched several offensives to push back the Axis forces in North Africa. Operation Brevity
Operation Brevity was a limited offensive conducted in mid-May 1941, during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global c ...
failed as did Operation Battleaxe
Operation Battleaxe (15–17 June 1941) was a British Army offensive during the Second World War to raise the Siege of Tobruk and re-capture eastern Cyrenaica from German and Italian forces. It was the first time during the war that a signific ...
but Operation Crusader
Operation Crusader (18 November – 30 December 1941) was a military operation of the Western Desert campaign during World War II by the British Eighth Army (with Commonwealth, Indian and Allied contingents) against the Axis forces (German and ...
, the third and larger offensive was launched at the end of the year. Over December 1941 into early 1942, Allied forces pushed the Italian-German forces back through Libya to roughly the limit of the previous Operation Compass advance. Taking advantage of the Allied position, German and Italian forces counter-attacked and pushed back the Allies to Gazala, west of Tobruk. As both sides prepared offensives, the Axis forces struck first and inflicted a big defeat upon the Allied forces during the Battle of Gazala
The Battle of Gazala, also the Gazala Offensive (Italian language, Italian: ''Battaglia di Ain el-Gazala'') was fought near the village of Gazala during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War, west of the port of Tobruk in Libya, f ...
. The routed Allied forces retreated to Egypt where they made a stand at El Alamein.
Following the First Battle of El Alamein
The First Battle of El Alamein (1–27 July 1942) was a battle of the Western Desert campaign of World War II, fought in Egypt between Axis (German and Italian) forces of the Panzer Army Africa—which included the under Field Marshal Erwin ...
, which had stalled the Axis advance into Egypt, British forces went onto the offensive in October. The Second Battle of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian Railway station, railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa ...
marked a watershed in the Western Desert Campaign and turned the tide in the North African Campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
. It ended the Axis threat to Egypt, the Suez Canal and of gaining access to the Middle Eastern and Persian oil fields via North Africa. As the Eighth Army pushed west across the desert, capturing Libya, German and Italian forces occupied southern France and landed in Tunisia. On 8 November, Allied forces launched Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8–16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa whil ...
landing in various places across French North Africa. In December 1942, after a 101-day British blockade, French Somaliland
French Somaliland (; ; ) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which became the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas. The Republic of Djibouti is its legal successor state.
History
French Somalil ...
fell to the Allies.
Tunisia
 Following the Japanese
Following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
on 7 December 1941, the United States joined the war. On 8 November 1942, American forces entered combat in North Africa with Operation Torch, which "transformed the Mediterranean from a British to an Allied theater of war", "succeeding operations in the Mediterranean area proved far more extensive than intended. One undertaking was to lead to the next".
After liberating French North Africa and clearing the enemy from the Italian colonies, the Allies sought to bring the entire French empire effectively into the war against the Axis powers. They reopened the Mediterranean route to the Middle East. They went on from Africa to liberate Sicily, Sardinia, and Corsica. They caused Mussolini to topple from power, and they brought his successors to surrender. They drew more and more German military resources into a stubborn defence of the Italian peninsula, and helped the Yugoslavs to pin down within their spirited country thousands of Axis troops. Eventually, the Allies delivered a solid blow from southern France against the German forces which were opposing the Allied drive from the beaches of Normandy! They made Marseilles available for Allied use and they occupied northern Italy and Greece." Howe further notes that "Hitler had always accepted the principle that the Mediterranean was an area of paramount Italian interest just as, farther north, German interests were exclusive.Allied forces were placed under the command of a Supreme Allied Commander AFHQ Mediterranean, General
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
. Axis forces were caught between the Allied armies during the Tunisia Campaign
The Tunisian campaign (also known as the battle of Tunisia) was a series of battles that took place in Tunisia during the North African campaign of the Second World War, between Axis and Allied forces from 17 November 1942 to 13 May 1943. The ...
but managed to delay the Allied advance by defensive operations, most notably with the Battle of the Kasserine Pass
The Battle of Kasserine Pass took place from 19-24 February 1943 at Kasserine Pass, a gap in the Grand Dorsal chain of the Atlas Mountains in west central Tunisia. It was a part of the Tunisian campaign of World War II.
The Axis forces, led ...
and a temporary defensive success at the Battle of the Mareth Line
The Battle of the Mareth Line or the Battle of Mareth was an attack in the Second World War by the British Eighth Army (General Bernard Montgomery) in Tunisia, against the Mareth Line held by the Italo–German 1st Army (General Giovanni Mess ...
. After shattering the Axis defence on the Mareth Line, the Allies squeezed Axis forces into a pocket around Tunis. Axis resistance in Africa ended on 13 May 1943, with the unconditional surrender of nearly 240,000 men, who became prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
.
Southern Europe
Italian campaign and Italian Civil War
Following their victory in North Africa, the Allies turned their attention to knocking out Italy from the war and forcing Germany to disperse its forces, the Allies invaded Sicily in Operation Husky on 10 July 1943, withamphibious
Amphibious means able to use either land or water. In particular it may refer to:
Animals
* Amphibian, a vertebrate animal of the class Amphibia (many of which live on land and breed in water)
* Amphibious caterpillar
* Amphibious fish, a fish ...
and airborne landings. The German and Italian forces were unable to prevent the Allied capture of the island but evacuated most of their troops and equipment to the mainland before the Allies entered Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
on 17 August. On 25 July, the Italian government
The government of Italy is that of a democratic republic, established by the Italian constitution in 1948. It consists of Legislature, legislative, Executive (government), executive, and Judiciary, judicial subdivisions, as well as of a head of ...
deposed Mussolini, the Italian leader, who was subsequently arrested. The new government announced that it would continue the war but secretly commenced negotiations with the Allies.
The Allied invasion of Italy
The Allied invasion of Italy was the Allies of World War II, Allied Amphibious warfare, amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place from 3 September 1943, during the Italian campaign (World War II), Italian campaign of World War II. T ...
started when the British Eighth Army
The Eighth Army was a field army of the British Army during the Second World War. It was formed as the Western Army on 10 September 1941, in Egypt, before being renamed the Army of the Nile and then the Eighth Army on 26 September. It was cr ...
landed in the toe of Italy on 3 September 1943, in Operation Baytown
Operation Baytown was an Allied amphibious landing on the mainland of Italy that took place on 3 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy, itself part of the Italian Campaign, during the Second World War.
Planning
The attack wa ...
. The Italian government signed the surrender the same day, believing they would be given time to make preparations against the anticipated German intervention. The Allies announced the Armistice of Cassibile
The Armistice of Cassibile ( Italian: ''Armistizio di Cassibile'') was an armistice that was signed on 3 September 1943 by Italy and the Allies, marking the end of hostilities between Italy and the Allies during World War II. It was made public ...
on 8 September and German forces implemented plans to occupy the Italian peninsula. On 9 September, American and British forces of the US Fifth Army
The United States Army North (ARNORTH) is a formation of the United States Army. An Army Service Component Command (ASCC) subordinate to United States Northern Command (NORTHCOM), ARNORTH is the joint force land component of NORTHCOM.
landed at Salerno in Operation Avalanche and more British airborne troops landed at Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
in Operation Slapstick
Operation Slapstick was the code name for a British landing from the sea at the Italian port of Taranto during the Second World War. The operation, one of three landings during the Allied invasion of Italy in September 1943, was undertaken by ai ...
. German forces which had escaped from Sicily were concentrated against Avalanche, while additional forces were brought in to occupy Rome and disarm the Italian Army
The Italian Army ( []) is the Army, land force branch of the Italian Armed Forces. The army's history dates back to the Italian unification in the 1850s and 1860s. The army fought in colonial engagements in China and Italo-Turkish War, Libya. It ...
in central and northern Italy.
The Germans were unable to prevent the Italian fleet sailing to Malta, although the battleship ''Roma'' was sunk by the Luftwaffe on 9 September. In the occupied areas of southern Europe and the Mediterranean, German forces rapidly disarmed and captured Italian troops, putting down any resistance they offered in Yugoslavia, southern France and Greece. Meanwhile, on 16 September, a German airborne force led by Otto Skorzeny
Otto Johann Anton Skorzeny (12 June 1908 – 5 July 1975) was an Austrian-born German SS-''Standartenführer'' in the ''Waffen-SS'' during World War II. During the war, he was involved in a number of operations, including the removal from power ...
rescued Mussolini from the mountain resort in the Gran Sasso
Gran Sasso d'Italia (; ) is a massif in the Apennine Mountains of Italy. Its highest peak, Corno Grande , is the highest mountain in the Apennines, and the second-highest mountain in Italy outside the Alps. The mountain lies within Gran Sasso ...
where he was being held. A puppet government, the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic (, ; RSI; , ), known prior to December 1943 as the National Republican State of Italy (; SNRI), but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò (, ), was a List of World War II puppet states#Germany, German puppe ...
was established with Mussolini as head of state was set up in northern Italy as the successor state to the former fascist government.
The Italian Co-Belligerent Army
The Italian Co-belligerent Army (Italian: ''Esercito Cobelligerante Italiano''), or Army of the South (''Esercito del Sud''), were names applied to various of the now former Royal Italian Army during the period when it fought alongside the Alli ...
was created to fight against the puppet government headed by Mussolini and its German allies, alongside the large Italian resistance movement
The Italian Resistance ( ), or simply ''La'' , consisted of all the Italian resistance groups who fought the occupying forces of Nazi Germany and the fascist collaborationists of the Italian Social Republic during the Second World War in Italy ...
, while other Italian troops continued to fight alongside the Germans in the National Republican Army
The National Republican Army (; abbreviated ENR), colloquially known as the Army of the North ( Italian: ''Esercito del Nord'') was the army of the Italian Social Republic (, or RSI) from 1943 to 1945, fighting on the side of Nazi Germany durin ...
; this period is known as the Italian Civil War
The Italian Civil War (, ) was a civil war in the Kingdom of Italy fought during the Liberation of Italy, Italian campaign of World War II between Italian fascists and Italian resistance movement, Italian partisans (mostly politically organized ...
. Although other European countries such as Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
also had partisan movements and collaborationist
Wartime collaboration is cooperation with the enemy against one's country of citizenship in wartime. As historian Gerhard Hirschfeld says, it "is as old as war and the occupation of foreign territory".
The term ''collaborator'' dates to the 19th ...
governments with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, armed confrontation between compatriots was most intense in Italy, making the Italian case unique. In 1965, the definition of "civil war" was used for the first time by fascist politician and historian Giorgio Pisanò in his books, while Claudio Pavone
Claudio Pavone (30 November 1920 – 29 November 2016) was an Italian historian and archivist.
Pavone was the president of the Historic Institute of the Liberation movement in Italy, the president of the Italian Society of Contemporary History ...
's book ''Una guerra civile. Saggio storico sulla moralità della Resistenza'' (''A Civil War. Historical Essay On the Morality Of the Resistance''), published in 1991, led to the term "Italian Civil War" being used more frequently by Italian and international historiography.
As the campaign in Italy continued, the rough terrain prevented fast movement and proved ideal for defence, the Allies continued to push the Axis forces northwards through the rest of the year. The Germans prepared a defensive line called the Winter Line
The Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section ...
(parts of which were called the Gustav Line) proved a major obstacle to the Allies at the end of 1943, halting the advance. Operation Shingle
The Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Campaign of World War II that commenced January 22, 1944. The battle began with the Allies of World War II, Allied amphibious landing known as Operation Shingle, an ...
, an amphibious assault at Anzio behind the line was intended to break it, but did not have the desired effect and was heavily opposed by German and RSI forces.Margaritis, 2019, p.103 The line was eventually broken by frontal assault at the Fourth Battle of Monte Cassino in the spring of 1944 and Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
was captured in June.
Following the liberation of Rome, the Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during the Second World War. Codenamed Operation Neptune and ...
(6 June 1944) that began Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The ope ...
and the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
victories on the Eastern Front, the Italian campaign became of secondary importance to both sides. The Gothic Line
The Gothic Line (; ) was a German and Italian defensive line of the Italian Campaign of World War II. It formed Field Marshal Albert Kesselring's last major line of defence along the summits of the northern part of the Apennine Mountains du ...
north of Rome was not broken until the Spring offensive of 1945. From 1944 to the end of war, the Italian Front was made up of a multi-national Allied force of Americans (including segregated African and Japanese-Americans
are Americans of Japanese ancestry. Japanese Americans were among the three largest Asian American ethnic communities during the 20th century; but, according to the 2000 census, they have declined in ranking to constitute the sixth largest Asi ...
), British, Canadians
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
, French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
, Brazilians
Brazilians (, ) are the citizens of Brazil. A Brazilian can also be a person born abroad to a Brazilian parent or legal guardian as well as a person who acquired Brazilian nationality law, Brazilian citizenship. Brazil is a multiethnic society, ...
, Greeks, Italian co-belligerent forces, Italian partisans, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, the 2nd New Zealand Division
The 2nd New Zealand Division, initially the New Zealand Division, was an infantry division of the New Zealand Military Forces (New Zealand's army) during the Second World War. The division was commanded for most of its existence by Lieutenant-G ...
, and the South Africans and Rhodesians as well as members of the British Commonwealth and French colonial forces, including the 3rd Algerian Infantry Division
The 3rd Algerian Infantry Division () was an infantry division of the Army of Africa which participated in World War II.
Following the liberation of French North Africa, the division fought in Tunisia, Italy, metropolitan France and in Germany. ...
, Moroccans
Moroccans () are the Moroccan nationality law, citizens and nationals of the Morocco, Kingdom of Morocco. The country's population is predominantly composed of Arabs and Berbers (Amazigh). The term also applies more broadly to any people who ...
, Gurkha Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
, and forces raised in Mandatory Palestine.
On April 25, the National Liberation Committee
The National Liberation Committee (, CLN) was a political umbrella organization and the main representative of the Italian resistance movement fighting against the occupying forces of Nazi Germany and the fascist collaborationist forces of the ...
in northern Italy had launched a general insurrection, at the same time, the remaining German and RSI forces are defeated by the Allied forces in the spring offensive. On April 28, two days before the death of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler, chancellor and dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, committed suicide via a gunshot to the head on 30 April 1945 in the in Berlin after it became clear that Germany would lose the Battle of Berlin, which led to the e ...
. Mussolini attempted to escape to Switzerland, but was captured and later executed
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender b ...
by Italian partisans along with the high-ranking Fascist officials of the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic (, ; RSI; , ), known prior to December 1943 as the National Republican State of Italy (; SNRI), but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò (, ), was a List of World War II puppet states#Germany, German puppe ...
. On May 1, after signing the Surrender at Caserta
The Surrender at Caserta (, ) of 29 April 1945 was the written agreement that formalized the surrender of German and Italian Fascist forces in Italy, ending the Italian Campaign of World War II.
Background
Since March 1945, SS ''Obergruppen ...
. Marshal Rodolfo Graziani
Rodolfo Graziani, 1st Marquis of Neghelli ( , ; 11 August 1882 – 11 January 1955), was an Italian military officer in the Kingdom of Italy's Royal Italian Army, Royal Army, primarily noted for his campaigns in Africa before and during World Wa ...
, the Minister of Defence of the Italian Social Republic, surrendered to the Allies along with the National Republican Army
The National Republican Army (; abbreviated ENR), colloquially known as the Army of the North ( Italian: ''Esercito del Nord'') was the army of the Italian Social Republic (, or RSI) from 1943 to 1945, fighting on the side of Nazi Germany durin ...
.
On 2 May, SS General Karl Wolff
Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff (13 May 1900 – 16 July 1984) was a senior German ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) officer who served as Chief of Personal Staff Reichsführer-SS (Heinrich Himmler) and an SS liaison to Adolf Hitler during World War II. He ende ...
and the Commander-in-Chief of the German 10th Army, General Heinrich von Vietinghoff
Heinrich Gottfried Otto Richard von Vietinghoff genannt Scheel (6 December 1887 – 23 February 1952) was a German general (''Generaloberst'') of the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with O ...
, after Operation Sunrise (secret negotiations
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more parties to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or Collective bargaining, collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. The parties aspire to agree on m ...
with the Allies), ordered German forces in Italy to make an unconditional surrender to the Allies.
Dodecanese Campaign
The brief campaign in the Italian-heldDodecanese Islands
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally defines ...
resulted as both Germany and the Allies scrambled to occupy them after the surrender of Italy in early September 1943. The main island of Rhodes was swiftly secured by German forces, but British garrisons were established on most islands by mid-September. German air superiority, tactical prowess, and the absence of Allied reinforcements doomed the Allied effort, however. German forces, including paratroopers
A paratrooper or military parachutist is a soldier trained to conduct military operations by parachuting directly into an area of operations, usually as part of a large airborne forces unit. Traditionally paratroopers fight only as light inf ...
and Brandenburger
The Brandenburger is a German horse breed, breed of warmblood sport horse from the states of Germany, state of Brandenburg in north-eastern Germany. From the 1960s – when Brandenburg was in East Germany – it was included in the stud-book ...
commandos, launched a counter-offensive, capturing the island of Kos
Kos or Cos (; ) is a Greek island, which is part of the Dodecanese island chain in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Kos is the third largest island of the Dodecanese, after Rhodes and Karpathos; it has a population of 37,089 (2021 census), making ...
within two days in early October. A massive 50-day-long aerial campaign was launched against the island of Leros
Leros (), also called Lero (from the Italian language), is a Greek island and municipality in the Dodecanese in the southern Aegean Sea. It lies from Athens's port of Piraeus, from which it can be reached by a nine-hour ferry ride or by a 45-min ...
defended by Italian troops commanded by Admiral Mascherpa, who resisted the German air offensive before the landing of British support troops, which was invaded by the Germans who landed by sea and air on 12 November and surrendered four days later. The remaining British garrisons were then evacuated to the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
.
Invasion of southern France
 On 15 August 1944, in an effort to aid their operations in
On 15 August 1944, in an effort to aid their operations in Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, the Allies launched Operation Dragoon
Operation Dragoon (initially Operation Anvil), known as Débarquement de Provence in French ("Provence Landing"), was the code name for the landing operation of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Provence (Southern France) on 15Augu ...
– the invasion of Southern France between Toulon
Toulon (, , ; , , ) is a city in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the French Riviera and the historical Provence, it is the prefecture of the Var (department), Var department.
The Commune of Toulon h ...
and Cannes
Cannes (, ; , ; ) is a city located on the French Riviera. It is a communes of France, commune located in the Alpes-Maritimes departments of France, department, and host city of the annual Cannes Film Festival, Midem, and Cannes Lions Internatio ...
. The Allies rapidly broke out of their beachheads and fanned out north and east to join up with the American 12th Army Group
The Twelfth United States Army group, Army Group was the largest and most powerful United States Army formation ever to take to the field, commanding four Field army, field armies at its peak in 1945: First United States Army, United States Army C ...
which was breaking out of the Normandy beachhead. In early September supreme command of the 6th Army Group
The 6th United States Army Group (also referred to as the Southern Group of Armies) was an Allied army group that fought in the European Theater of Operations
The European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA) was a Theater ( ...
moved from AFHQ to SHAEF
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF; ) was the headquarters of the Commander of Allies of World War II, Allied forces in northwest Europe, from late 1943 until the end of World War II. US General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the ...
and the 6th Army Group moved out of the Mediterranean Theatre and into the European Theatre
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II, taking place from September 1939 to May 1945. The Allied powers (including the United Kingdom, the United States, the Soviet Union and Franc ...
fighting as one of three Allied army groups on the Western Front.
Post-war conflicts
Trieste
At the end of the war in Europe, on 1 May 1945, troops of the 4th Army of theYugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
and the Slovene 9th Corpus NLA occupied the town of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
. The Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
surrendered to the Allies which entered the town the following day. The Yugoslavs had to leave the town some days after.
Greece
Allied forces which had been sent to Greece in October 1944 after the German withdrawal, were attacked by the leftist EAM-ELAS
The Greek People's Liberation Army (, ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós''; ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberation Front (EAM) during the period of the Greek resistance until February 1945, when, followi ...
Resistance movement, resulting in clashes in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
during December of that year, which began the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
.
Syria
In Syria, nationalist protests were on the rise at the continued occupation of theLevant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
by France in May 1945. French forces then tried to quell the protests but concern with heavy Syrian casualties forced Winston Churchill to oppose French action there. After being rebuffed by Charles De Gaulle he ordered British forces under general Bernard Paget
General Sir Bernard Charles Tolver Paget, (15 September 1887 – 16 February 1961) was a British Army officer who served with distinction in the First World War, and then later during the Second World War, when he commanded the 21st Army Group f ...
into Syria from Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
with orders to fire on the French if necessary. A crisis began as British armoured cars and troops then reached the Syrian capital Damascus following which the French were escorted and confined to their barracks. With political pressure added the French ordered a ceasefire; following which the French withdrew from Syria the following year.
Palestine
Prior to the war, the British Mandate of Palestine was faced with inter-ethnic violence between Arabs and Jews. Following the end of World War II and theUN Partition Plan
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations to partition Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. Drafted by the U.N. Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) on 3 September 1947, the Pl ...
, a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
between Palestinian Arabs and Jews broke out and lasted until the British withdrawal of the territory in May 1948, which later drew in neighbouring nations into the conflict, causing the start of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
.
See also
* List of World War II battles *Mediterranean U-boat Campaign (World War II)
The Mediterranean U-boat Campaign lasted from about 21 September 1941 to 19 September 1944 during the Second World War. Malta was an active British base strategically located near supply routes from Europe to North Africa. Axis supply convoys acr ...
* Military history of Gibraltar during World War II
The military history of Gibraltar during World War II exemplifies Gibraltar's position as a British fortress from the early-18th century onwards and as a vital factor in British military strategy, both as a foothold on the continent of Eur ...
* Timeline of the North African campaign
This is a timeline of the North African campaign of World War II.
1940
* May 1940 — Army of Africa (France) — 14 regiments of zouaves, 42 regiments of Algerian, Tunisian and Moroccan tirailleurs, 12 regiments and demi-brigades of the Forei ...
* European Theater of World War II
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main Theater (warfare), theatres of combat during World War II, taking place from September 1939 to May 1945. The Allies of World War II, Allied powers (including the United Kingdom, the ...
* Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War or the Pacific Theatre, was the Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II fought between the Empire of Japan and the Allies of World War II, Allies in East Asia, East and Southeast As ...
Notes
Citations
References
Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Journals
* *Websites
*Further reading
* *External links
Mediterranean sources and US Official accounts
* ttp://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/UN/UK/UK-Med-II/index.html The Mediterranean and Middle East Volume II The Germans come to the Help of their Ally (1941). 1956 {{DEFAULTSORT:Mediterranean, Middle East And African Theatres Of World War Ii African theatres of World War II
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Theaters of World War II