|
Afrika Korps
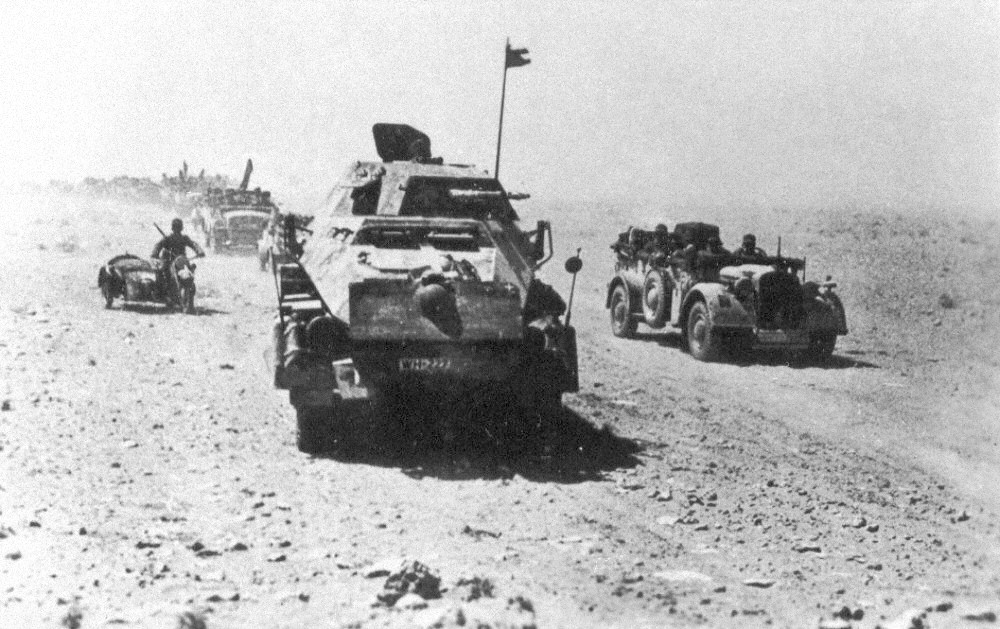
The German Africa Corps (, ; DAK), commonly known as Afrika Korps, was the German expeditionary force in Africa during the North African campaign of World War II. First sent as a holding force to shore up the Italian defense of its African colonies, the formation fought on in Africa, under various appellations, from March 1941 until its surrender in May 1943. The unit's best known commander was Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, whose reputation as one of the ablest tank commanders of the war earned him the nickname ''der Wüstenfuchs'', "the Desert Fox". History Organization The Afrika Korps formed on 11 January 1941 and one of Adolf Hitler's favourite generals, Erwin Rommel, was designated as commander on 11 February. Originally Hans von Funck was to have commanded it, but Hitler loathed von Funck, as he had been a personal staff officer of Werner von Fritsch until von Fritsch was dismissed in 1938. The German Armed Forces High Command (', OKW) had decided to send a "blocki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Battleaxe
Operation Battleaxe (15–17 June 1941) was a British Army offensive during the Second World War to raise the Siege of Tobruk and re-capture eastern Cyrenaica from German and Italian forces. It was the first time during the war that a significant German force fought on the defensive. The British lost over half of their tanks on the first day and only one of three attacks succeeded. The British achieved mixed results on the second day, being pushed back on their western flank and repulsing a big German counter-attack in the centre. On the third day, the British narrowly avoided disaster by withdrawing just ahead of a German encircling movement. The failure of Battleaxe led to the replacement of British General Sir Archibald Wavell, Commander-in-Chief Middle East, by Claude Auchinleck; Wavell took Auchinleck's position as Commander-in-Chief, India. Background /Operation Sunflower In late March 1941, soon after the arrival of the in Tripoli, Libya to reinforce the Italians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
90th Light Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 90th Light Infantry Division was a light infantry Division (military), division of the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army during World War II that served in North African Campaign, North Africa as well as Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, Sardinia and Italy. The division played a major role in most of the actions against the Eighth Army (United Kingdom), British Eighth Army in the Western Desert Campaign and eventually surrendered to the Allies of World War II, Allies in the final stages of the Tunisia Campaign in May 1943. It was re-constituted later in 1943 and deployed to Sardinia and when the expected Operation Mincemeat, Allied invasion of Sardinia failed to materialise, the division was moved to Italy. It was engaged in actions against the Allies in Italy from 1943 to April 1945 when the division was listed as "destroyed" in the Po (river), Po River valley. Formation On 26 June 1941, the Oberkommando des Heeres, OKH ordered the creation of a Div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
102nd Motorised Division Trento
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st Panzer Division (Wehrmacht)
The 21st Panzer Division was a German armoured warfare, armoured division best known for its role in the battles of the North African Campaign from 1941 to 1943 during World War II when it was one of the two armoured divisions making up the Afrika Korps, Deutsches Afrikakorps (DAK). It was first formed as the 5th Light Division in early 1941. 1941–1942 The Italian army group in North Africa was routed by the British Commonwealth Western Desert Force in Operation Compass 9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941 under Archibald Wavell, 1st Earl Wavell, General Wavell. The German Armed Forces High Command () decided to send a "blocking force" to Libya to support the Italian army, commanded by the future Field Marshal Erwin Rommel. The German blocking force at first was based only on Panzer Regiment 5, which was put together from the second regiment of the 3rd Panzer Division (Wehrmacht), 3rd Panzer Division. These elements were organized into the 5th Light Division when they arrived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th Panzer Division
The 15th Panzer Division () was an armoured division in the German Army, the Wehrmacht, during World War II, established in 1940. The division, formed from the 33rd Infantry Division, fought exclusively in North Africa from 1941 to 1943, eventually ceasing to exist after surrendering in Tunisia in May 1943. History The 33rd Infantry Division, forerunner of the 15th Panzer Division, was formed in April 1936 and part of the German defences in the Saarland during the early month of the war. It participated in the invasion of France and remained there after the French surrender as an occupation force. It returned to Germany in September 1940 to be converted to a tank division. The division was transported to Libya in April 1941, joining General Erwin Rommel's '' Deutsches Afrikakorps'' (DAK) as one of two German tank divisions in North Africa at the time, the other having been the 21st Panzer Division. However, the Royal Navy intercepted and sank the ships carrying the division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia Campaign
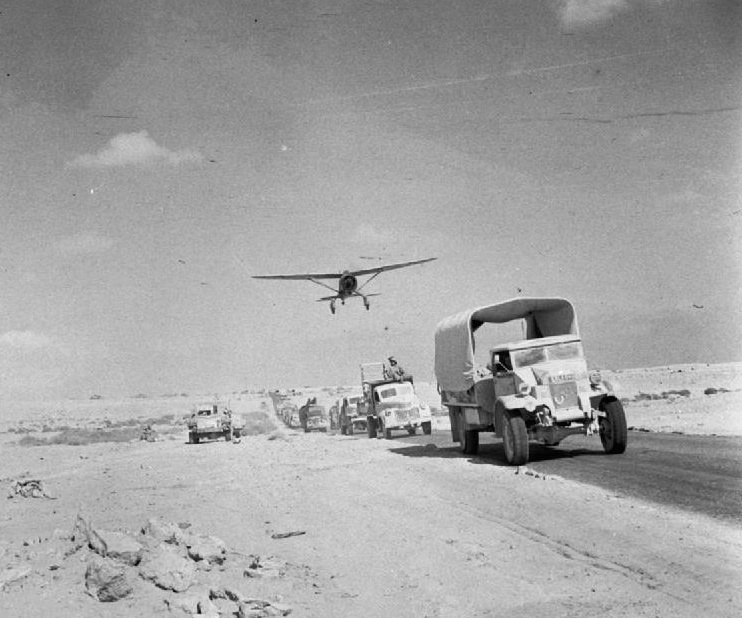
The Tunisian campaign (also known as the battle of Tunisia) was a series of battles that took place in Tunisia during the North African campaign of the Second World War, between Axis and Allied forces from 17 November 1942 to 13 May 1943. The Allies consisted of British Imperial Forces, including a Greek contingent, with American and French corps. Despite initial successes by the German and Italian forces brought from the mainland and which had withdrawn into and occupied Tunisia after their defeat in the Western Desert and the success of Operation Torch, massive supply interdiction efforts and Allied assaults from east and west led to the decisive defeat of the Axis. Over 260,000 German and Italian troops were taken as prisoners of war, including most of the Afrika Korps. Background Western Desert The first two years of the war in North Africa were characterized by chronic supply shortages and transport problems. The North African coast has few natural harbors and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
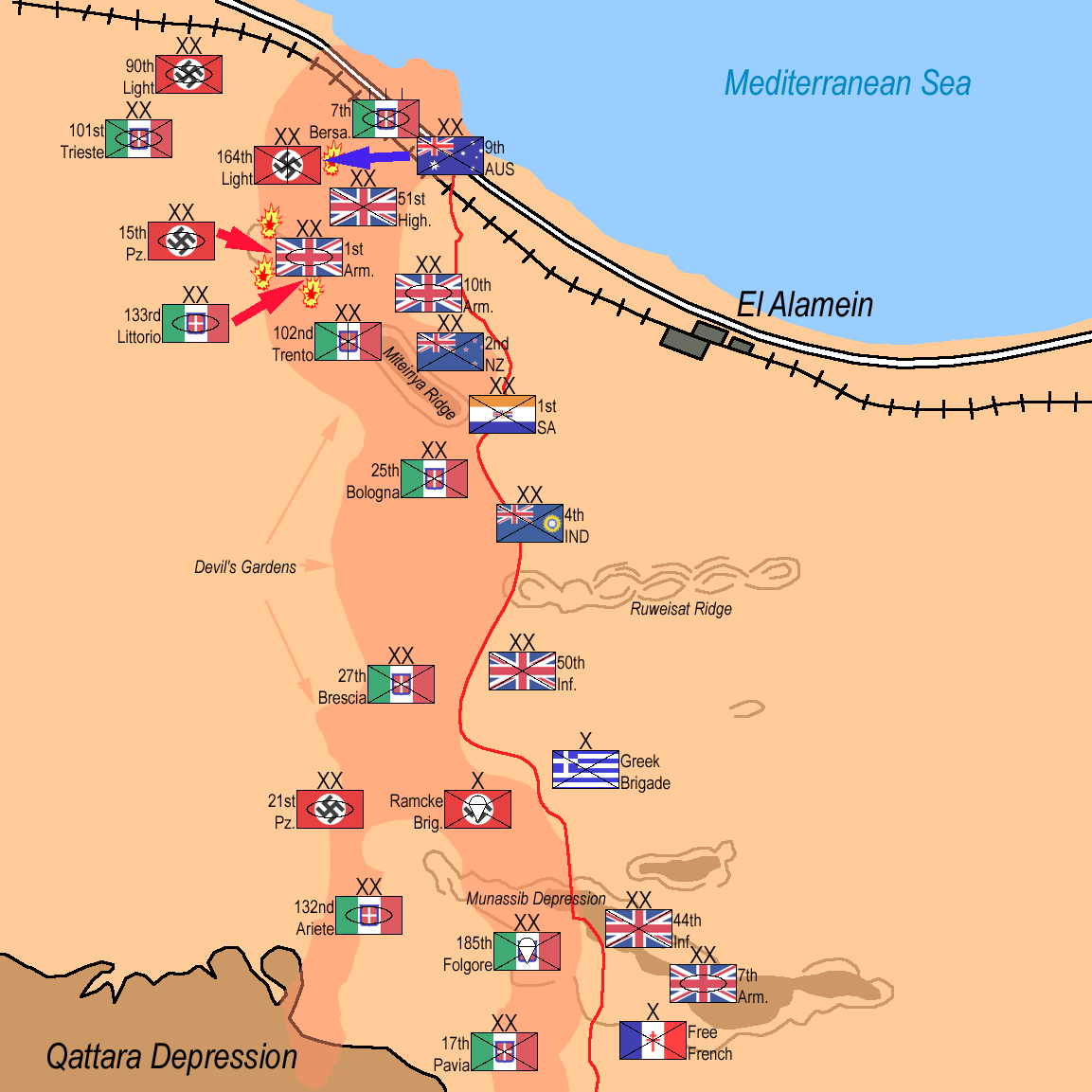
Second Battle Of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian Railway station, railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented the Axis powers, Axis from advancing further into Egypt. In October 1942 Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery, commander of Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army, opened his offensive against the Axis forces. In a 13-day battle the Axis ''Panzerarmee Afrika'' was crushed and forced to retreat from Egypt and Libya to the borders of Tunisia. The Allied victory at El Alamein was the beginning of the end of the Western Desert Campaign. The battle ended the Axis threat to the Middle East and Iran and revived the morale of the western Allies, being their first big success against the Axis since Operation Crusader in late 1941. The end of the battle coincided with the Allied invasion of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Alam El Halfa
The Battle of Alam el Halfa took place between 30 August and 5 September 1942 south of El Alamein during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. '' Panzerarmee Afrika'' (''Generalfeldmarschall'' Erwin Rommel), attempted an envelopment of the British Eighth Army (Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery). In (Operation Surf), the last big Axis offensive of the Western Desert Campaign, Rommel intended to defeat the Eighth Army before Allied reinforcements arrived. Montgomery knew of Axis intentions through Ultra signals intercepts and left a gap in the southern sector of the front, knowing that Rommel planned to attack there and deployed the bulk of his armour and artillery around Alam el Halfa Ridge, behind the front. Unlike in previous engagements, Montgomery ordered that the tanks were to be used as anti-tank guns, remaining in their defensive positions on the ridge. When Axis attacks on the ridge failed and short on supplies, Rommel ordered a withdrawal. The 2n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of El Alamein
The First Battle of El Alamein (1–27 July 1942) was a battle of the Western Desert campaign of World War II, fought in Egypt between Axis (German and Italian) forces of the Panzer Army Africa—which included the under Field Marshal Erwin Rommel—and Allied (British Empire and Commonwealth) forces of the Eighth Army under General Claude Auchinleck. In this battle the British halted a second advance by the Axis forces into Egypt. Axis positions near El Alamein, only from Alexandria, were dangerously close to the ports and cities of Egypt, the base facilities of the Commonwealth forces and the Suez Canal. However, the Axis forces were too far from their base at Tripoli in Libya to remain at El Alamein indefinitely, which led both sides to accumulate supplies for more offensives, against the constraints of time and distance. Background Retreat from Gazala After their defeat at the Battle of Gazala in Eastern Libya in June 1942, the British Eighth Army, commanded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mersa Matruh
The Battle of Mersa Matruh was fought from 26 to 29 June 1942, following the defeat of the Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army (General Sir Claude Auchinleck) at the Battle of Gazala and was part of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. The battle was fought with the Axis Powers, German–Italian Panzer Army Afrika ( ( Erwin Rommel). The Eighth Army comprised X Corps (United Kingdom), X Corps and XIII Corps (United Kingdom), XIII Corps. The battle was fought during the pursuit of the Eighth Army as it retreated into Egypt. Rommel intended to defeat in detail (one after the other) the British infantry formations, before they had a chance to regroup. The fortress port of Mersa Matruh and 6,000 prisoners were captured, along with a great deal of supplies and equipment. The Axis cut off the line of retreat of X Corps and XIII Corps but was too weak to stop the British from breaking out. Background After the defeat of the Eighth Army at the Battle of Gazala, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
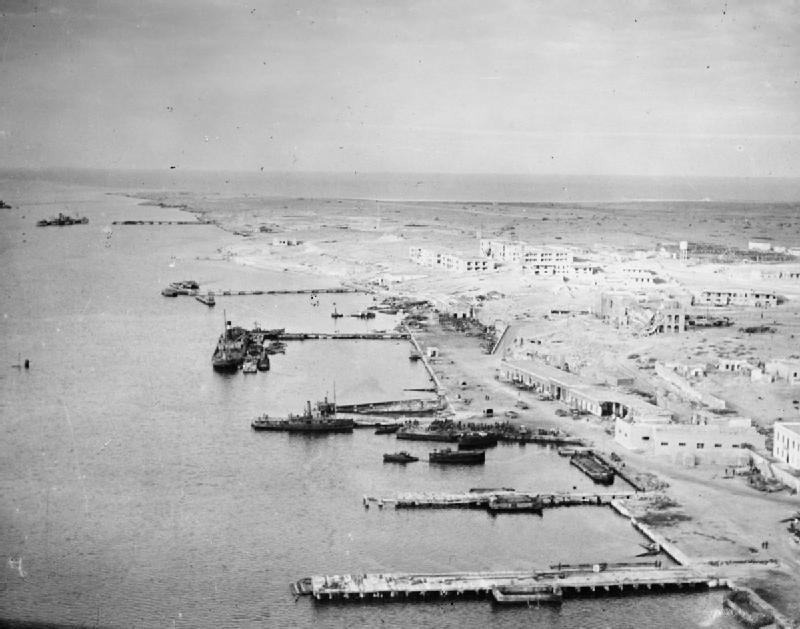
Axis Capture Of Tobruk
The Axis capture of Tobruk, also known as the Fall of Tobruk and the Second Battle of Tobruk (17–21 June 1942) was part of the Western Desert campaign in Libya during the Second World War. The battle was fought by the ( in Italian), a German–Italian military force in North Africa which included the ( Erwin Rommel), against the British Eighth Army (General Neil Ritchie) which comprised contingents from Britain, India, South Africa and other Allied nations. Axis forces had conducted the Siege of Tobruk for eight months in 1941 before its defenders, who had become an emblem of resistance, were relieved in December. Claude Auchinleck, the commander-in-chief Middle East Command, had decided not to defend Tobruk for a second time, due to the cost of bringing supplies in by sea; its minefields and barbed wire had been stripped for use in the Gazala Line to the west. By mid-1942 the Desert Air Force had been forced to move to airfields in Egypt, taking most of them beyond the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |